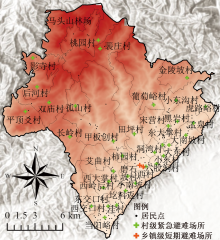
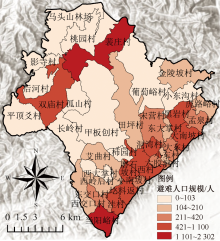
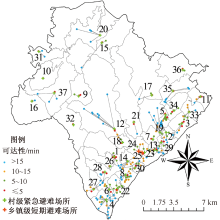
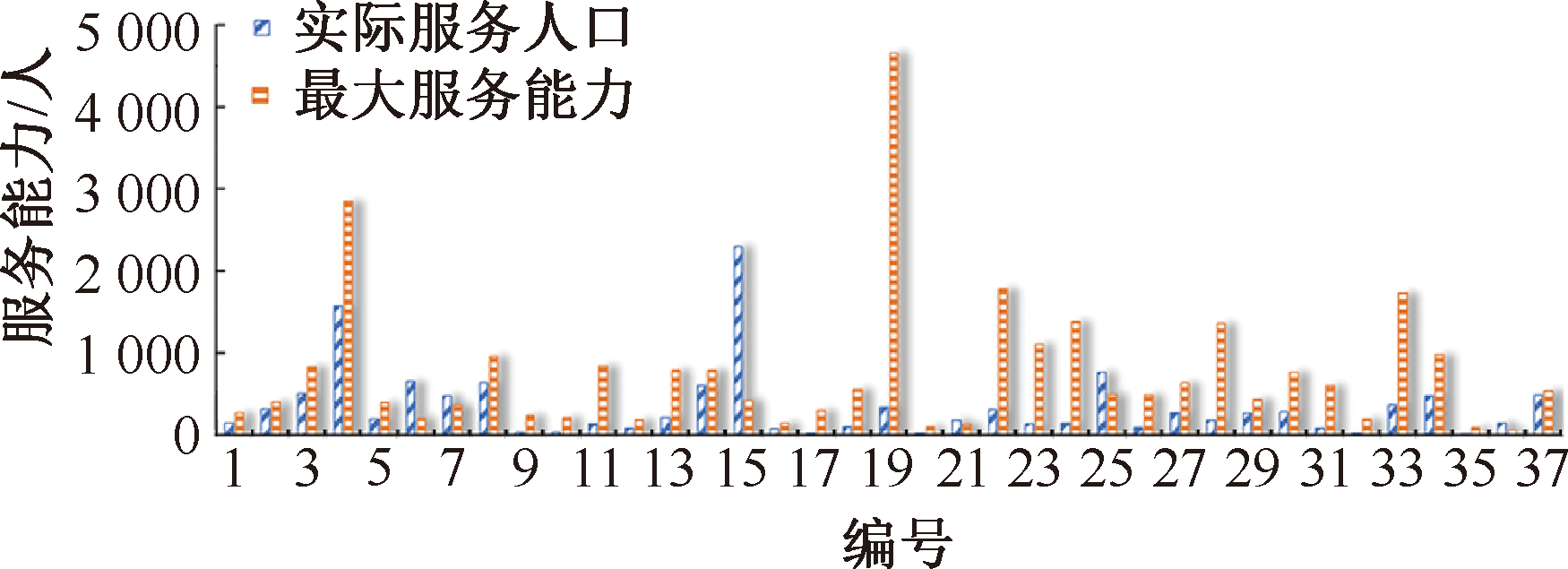
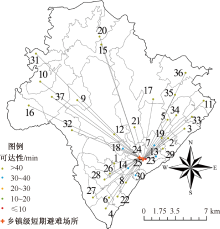
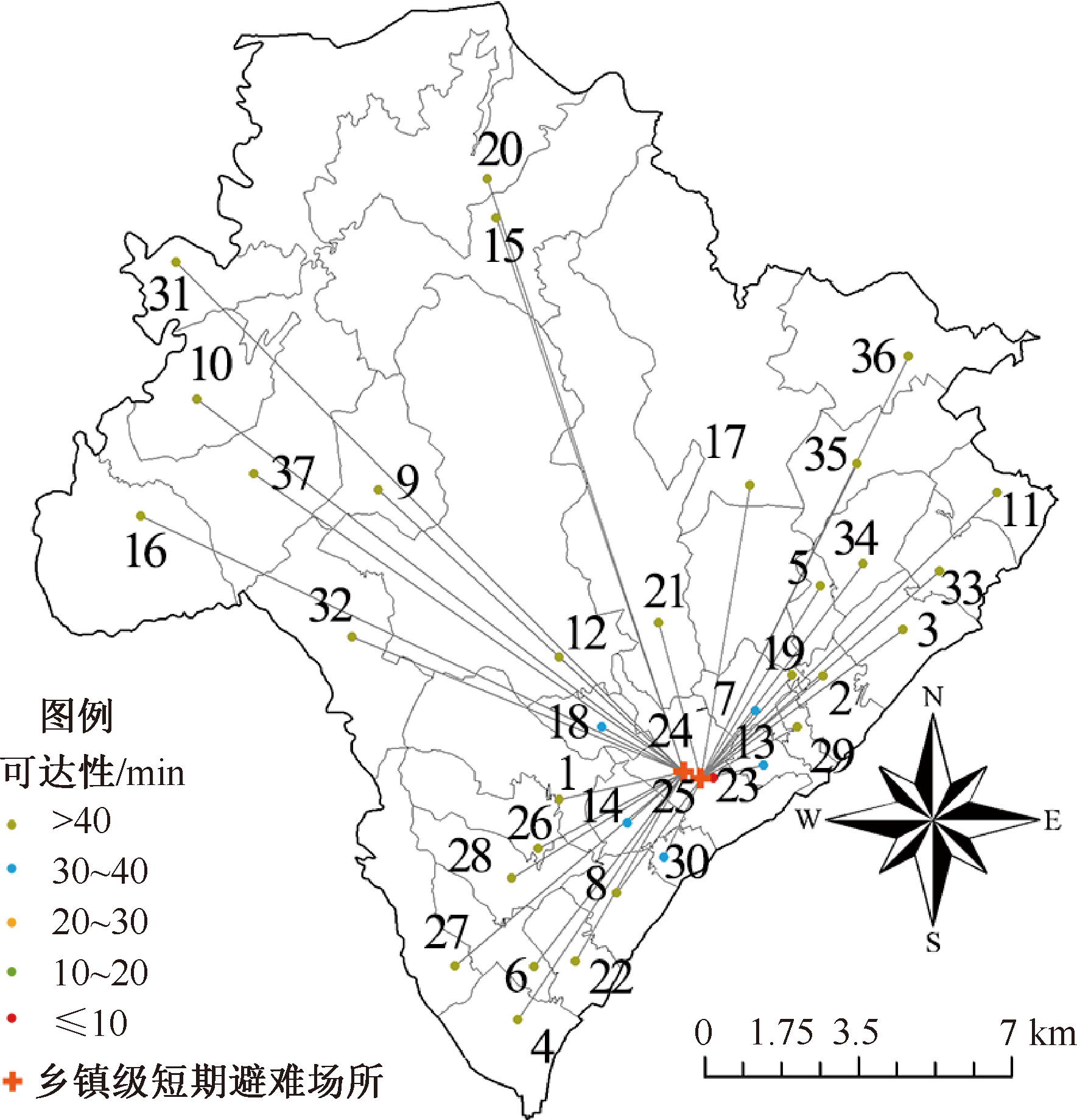
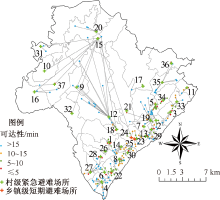
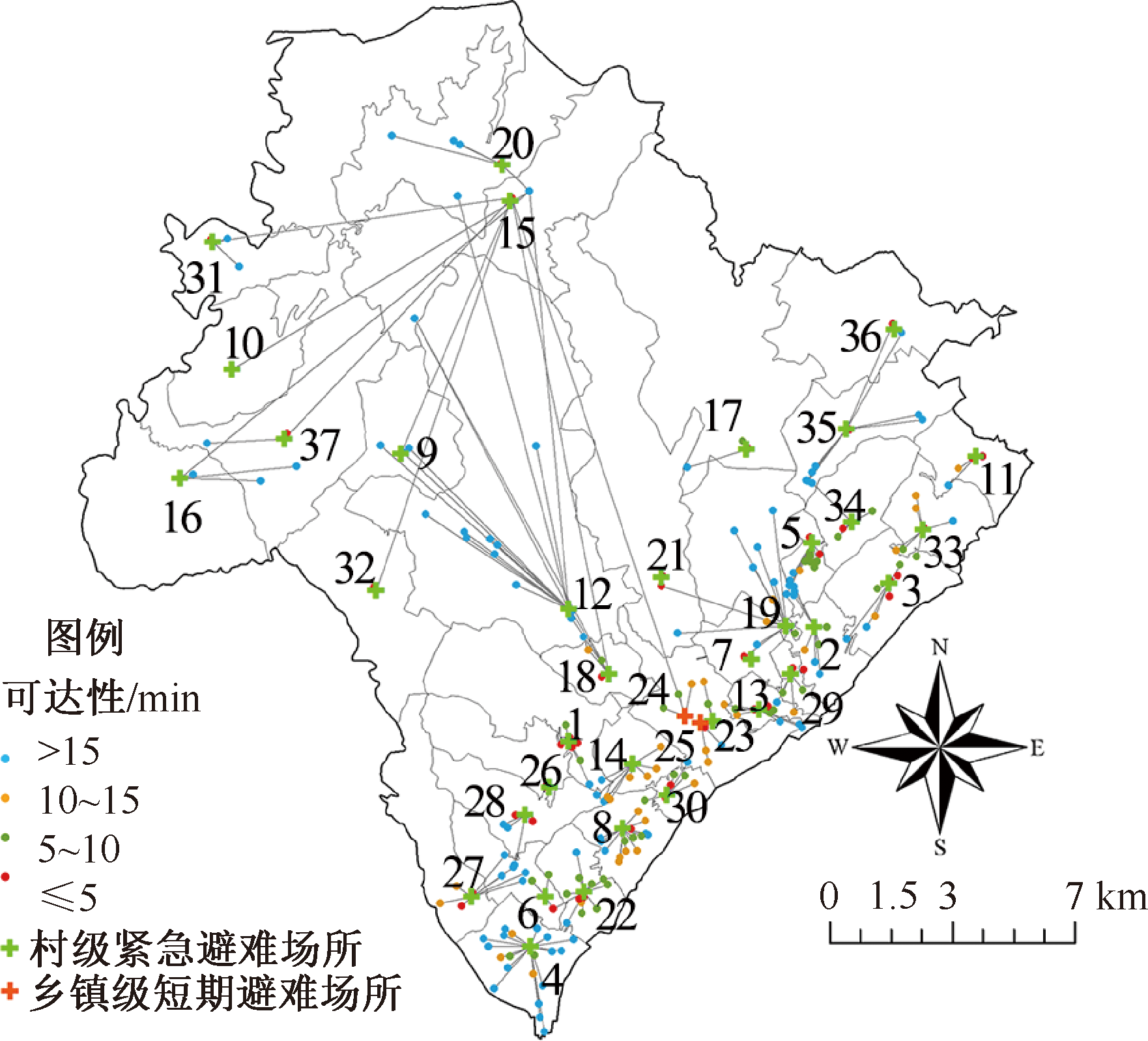
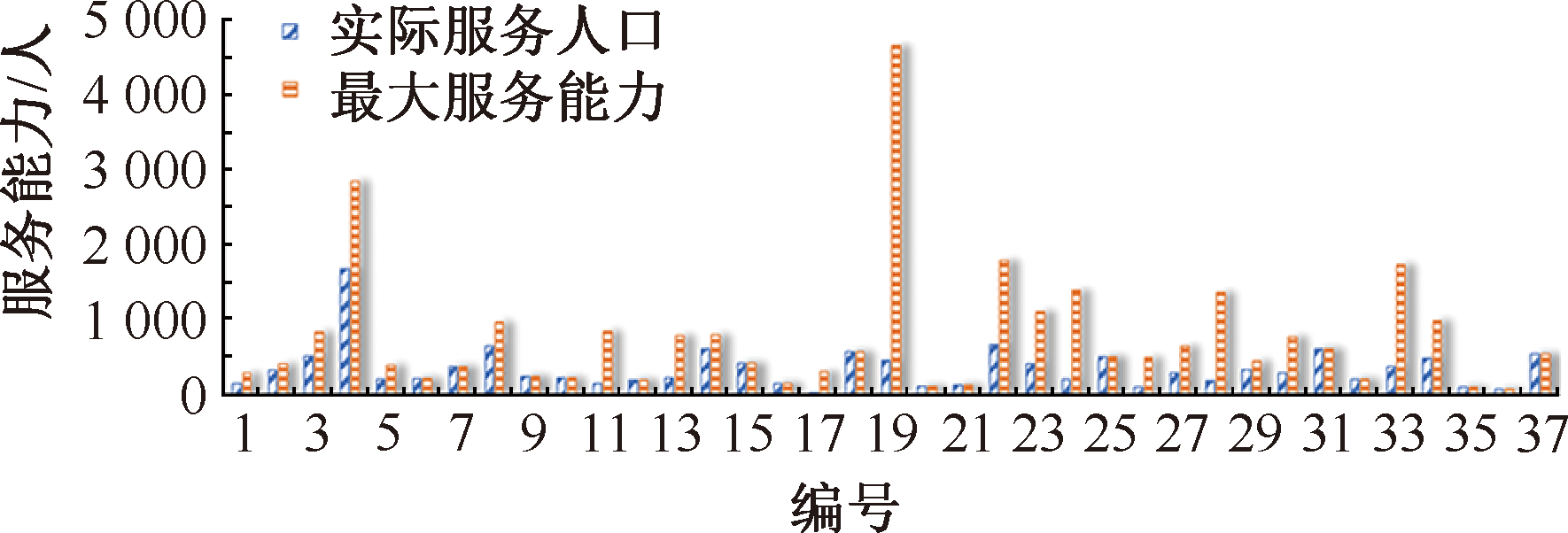
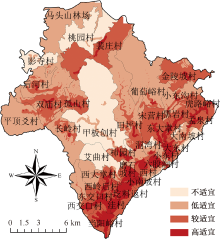
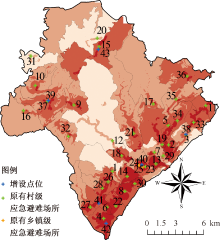
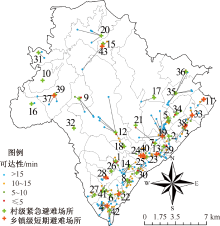
| [1] |
蔡梓涵. 以新质生产力助推应急管理体系和能力现代化建设[J]. 人民论坛, 2024(14): 73-75.
|
| [2] |
中华人民共和国应急管理部应急管理部. 发布2024年上半年全国自然灾害情况[EB/OL].(2024-07-12). https://www.mem.gov.cn/xw/yjglbgzdt/202407/t20240712_494600.shtml.
|
| [3] |
刘强, 阮雪景, 付碧宏. 特大地震灾害应急避难场所选址原则与模型研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 40(8): 129-135.
|
|
LIU Qiang, RUAN Xuejing, FU Bihong. A study of principles on emergency shelter site selection and modeling under disastrous earthquake[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2010, 40(8): 129-135.
|
| [4] |
张威涛, 任利剑, 运迎霞. 滨海城市竖向避难场所选址可靠性评价与若干问题探讨:以天津滨海新区临港城区为例[J]. 地理科学, 2020, 40(11): 1899-1908.
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.11.015
|
|
ZHANG Weitao, REN Lijian, YUN Yingxia. Siting reliability evaluation and discussion of vertical shelter in coastal cities: a case of port-urban area in Binhai NewDistrict, Tianjin[J]. Scientia Geographical Sinica, 2020, 40(11):1899-1908.
|
| [5] |
DE ALBUQUERQUE N L B, DA SILVA L B L, ALENCAR M H, et al. A multicriteria decision model to improve emergency preparedness: locating-allocating urban shelters against floods[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2024, 111: DOI: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2024.104695. |
| [6] |
GU Ziyuan, LIU Zhiyuan, SHIWAKOTI N, et al. Video-based analysis of school students' emergency evacuation behavior in earthquakes[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2016, 18: 1-11.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2016.05.008
|
| [7] |
陈伟, 汤一鸣, 赵军, 等. 基于手机信令数据的城市尺度地震避难疏散模拟[J]. 地震研究, 2023, 46(4): 611-621.
|
|
CHEN Wei, TANG Yiming, ZHAO Jun, et al. Urban-scale earthquake evacuation simulation based on mobile phone signaling data[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 2023, 46(4): 611-621.
|
| [8] |
XU Jinghai, WANG Chao, LI Shanshan, et al. Emergency evacuation shelter management and online drill method driven by real scene 3D model[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2023, 97: DOI: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2023.104057.
|
| [9] |
陈明洁, 吕飞. 基于社会网络分析的苏州古城区应急避难场所布局优化研究[J]. 城市发展研究, 2022, 29(4): 1-8,15.
|
|
CHEN Mingjie, LYU Fei. Research on layout optimization of emergency evacuation sites in ancient Suzhou city based on social network analysis[J]. Urban Development Studies, 2022, 29(4):1-8,15.
|
| [10] |
那麦提·艾合麦提, 曾坚, 蒋飞阳. 基于综合灾害风险的应急避难服务供需评估与规划干预:以天津市为例[J]. 灾害学, 2022, 37(4): 92-100.
|
|
AIHEMAITI Namaiti, ZENG Jian, JIANG Feiyang. Supply-Demand analysis and planning intervention of emergency shelter services based on comprehensive disaster risk: a case study in Tianjin[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2022, 37(4): 92-100.
|
| [11] |
ALAM M J, HABIB M A, POTHIER E. Shelter locations in evacuation: a multiple criteria evaluation combined with flood risk and traffic microsimulation modeling[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2021, 53: DOI: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2020.102016.
|
| [12] |
朱安峰, 范秀芳, 杜温瑞, 等. 韧性视角下应急避难场所防灾减灾能力综合评价:以温州市瓯海区为例[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(5): 223-230.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.05.1763
|
|
ZHU Anfeng, FAN Xiufang, DU Wenrui, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of disaster prevention and mitigation capacity of emergency shelters based on resilience perspective; a case study of Ouhai district in Wenzhou[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(5):223-230.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.05.1763
|
| [13] |
唐彦东, 曹帅, 于汐, 等. 河北省应急避难场所空间分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2024, 33(2): 29-36.
|
|
TANG Yandong, CAO Shuai, YU Xi, et al. Analysis of spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of emergency shelters in Hebei province[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2024, 33(2): 29-36.
|
| [14] |
HU Fuyu, YANG Saini, HU Xiaobing, et al. Integrated optimization for shelter service area demarcation and evacuation route planning by a ripple-spreading algorithm[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2017, 24: 539-548.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2017.06.006
|
| [15] |
吴超, 王其东, 李珊. 基于可达性分析的应急避难场所空间布局研究:以广州市为例[J]. 城市规划, 2018, 42(4): 107-112, 124.
|
|
WU Chao, WANG Qidong, LI Shan. Spatial distribution of emergency shelters based on accessibility: a case of Guangzhou[J]. City Planning Review, 2018, 42(4): 107-112, 124.
|
| [16] |
AMINI H K, ASADZADEH T S, MIRHAKIMI S A. A new index-based model for site selection of emergency shelters after an earthquake for Iran[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2022, 77: DOI: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2022.103110.
|
| [17] |
ZHOU Jie, NIE Gaozhong, LIU Yaohui. Multi-criteria comparison analysis of spatial equity for emergency shelters in old and new urban districts: a case study in Wuhua district and Chenggong district of Kunming city, China[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2024, 108: DOI: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2024.104547.
|
| [18] |
中华人民共和国应急管理部. 《应急避难场所术语》《应急避难场所分级及分类》《应急避难场所标志》国家标准发布[EB/OL].(2024-05-10). https://www.mem.gov.cn/xw/yjglbgzdt/202405/t20240510_487805.shtml.
|
| [19] |
翟石艳, 何新新, 孔云峰, 等. 基于最优供需分配的公共设施空间可达性分析[J]. 地理学报, 2022, 77(4): 1028-1038.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb202204017
|
|
ZHAI Shiyan, HE Xinxin, KONG Yunfeng, et al. Measuring the spatial accessibility of public services by optimal supply-demand allocation[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2022, 77(4): 1028-1038.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb202204017
|
| [20] |
GB/T 44013—2024,应急避难场所分级及分类[S].
|
|
GB/T 44013-2024, Emergency shelter-grading and classification[S].
|
| [21] |
SONG Genxin, HE Xinxin, KONG Yunfeng, et al. Improving the spatial accessibility of community-level healthcare service toward the "15-Minute City" goal in China[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2022, 11(8): DOI: 10.3390/ijgi11080436.
|
| [22] |
湛东升, 张文忠, 谌丽, 等. 城市公共服务设施配置研究进展及趋向[J]. 地理科学进展, 2019, 38(4): 506-519.
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.04.004
|
|
ZHAN Dongsheng, ZHANG Wenzhong, CHEN Li, et al. Research progress and its enlightenment of urban public service facilities allocation[J]. Progress in Geography, 2019, 38(4): 506-519.
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.04.004
|
| [23] |
宋英华, 高晓茜, 霍非舟, 等. 考虑洪涝灾害风险的城市应急避难场所选址研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2022, 18(6): 31-37.
|
|
SONG Yinghua, GAO Xiaoxi, HUO Feizhou, et al. Study on site selection of urban emergency shelters consider risk of flood disaster[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2022, 18(6): 31-37.
|
| [24] |
吕伟, 韩业凡, 周雯楠, 等. 避难场所适宜性评价及服务范围空间相关性分析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2023, 23(3): 694-703.
|
|
LYU Wei, HAN Yefan, ZHOU Wennan, et al. Study on the spatial correlation between the suitability evaluation of emergency shelters and the service scope[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2023, 23(3): 694-703.
|
| [25] |
GB/T 45290—2025,乡村应急避难场所设计规范[S].
|
|
GB/T 45290-2025,Specification for design of rural emergency shelter[S].
|