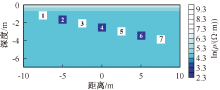
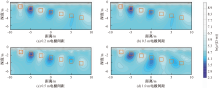
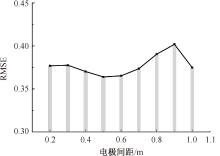
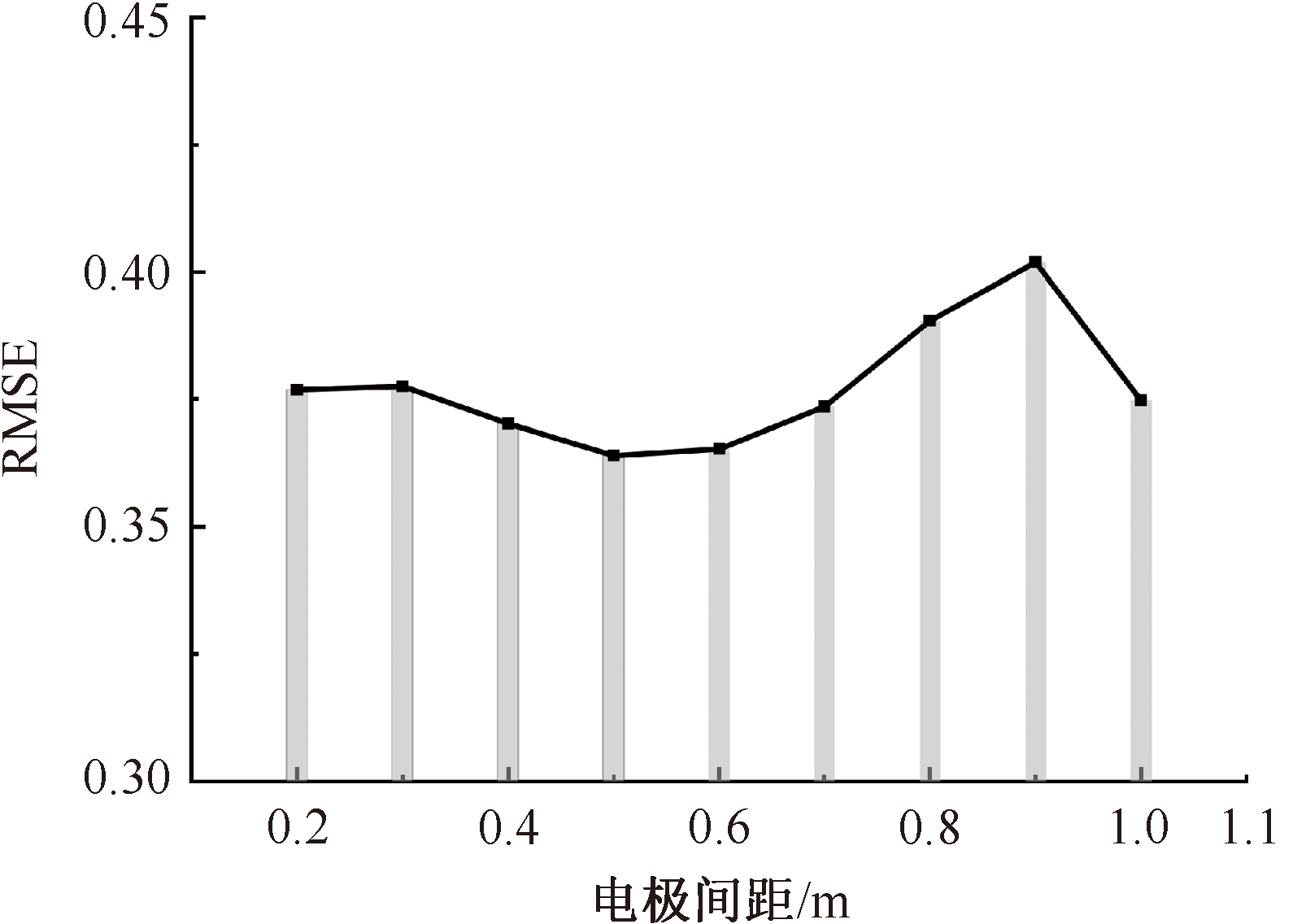
| [1] |
李泽霖. 城市道路路基缺陷雷达无损检测智能判识与评估方法[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2023.
|
|
LI Zelin. Intelligent identification and evaluation method for radar non destructive testing of urban road subgrade defects[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2023.
|
| [2] |
中规协地下管线专业委员会. 全国地下管线事故统计分析报告[R/OL].(2020-12-04). https://www.lingpiankeji.com/newsitem/278381568.
|
| [3] |
王巍, 徐成龙, 曹兵, 等. 城市道路地下病害体多种检测方法综合应用探究[J]. 城市勘测, 2023(增1):110-114.
|
|
WANG Wei, XU Chenglong, CAO Bing, et al. Comprehensive application of multiple detection methods for underground diseases on urban roads[J]. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2023(S1):110-114.
|
| [4] |
黄斌. 高密度电法在某公路岩溶路基勘察中的应用[J]. 中国新技术新产品, 2021(9):96-98.
|
|
HUANG Bin. Application of high-density electrical method in the investigation of karst roadbed on a certain highway[J]. New Technologies and New Products of China, 2021(9):96-98.
|
| [5] |
何胜, 董高峰, 张永兴, 等. 基于地质雷达技术的西宁市湿陷性黄土道路塌陷检测研究[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2024, 46(4):473-480.
|
|
HE Sheng, DONG Gaofeng, ZHANG Yongxing, et al. Research on collapse detection of collapsible loess road in Xining city based on GPR technology[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 46 (4):473-480.
|
| [6] |
师学明, 黄崇钰, 王瑞, 等. 基于深度学习SSD算法的高密度电法智能解译方法技术研究[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2024, 21(1):1-11.
|
|
SHI Xueming, HUANG Chongyu, WANG Rui, et al. High density electrical apparent resistivity anomaly intelligent inter pretation method based on SSD target detection algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2024, 21(1):1-11.
|
| [7] |
GANIYU S A, OLADUNJOVE M A, OLOBADOLA M O, et al. Investigation of incessant road failure in parts of Abeokuta, Southwestern Nigeria using integrated geoelectric methods and soil analysis[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2021, 80:DOI: 10.1007/s12665-021-09446-4.
|
| [8] |
XIE Jia, LIU Yang, LU Yulong, et al. Application of the high-density resistivity method in detecting a mined-out area of a quarry in Xiangtan city, Hunan province[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2022, 10:DOI: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.1068956.
|
| [9] |
YIN Chunhung, HO Shuchou, CHIH Pinglin. Appraisal of the spatial resolution of 2D electrical resistivity tomography for geotechnical investigation[J]. Applied Sciences. 2020, 10:DOI: 10.3390/app10124394.
|
| [10] |
方易小锁, 孟永东, 田斌, 等. 高密度电阻率法对不同电极排列的分辨率响应研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(6):2421-2428.
|
|
FANG Yixiaosuo, MENG Yongdong, TIAN Bin, et al. Study on resolution response of different electrode arrangements by high density resistivity method[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(6):2421-2428.
|
| [11] |
蒋亮, 邓居智, 陈辉, 等. 基于有限差分的2.5维直流电阻率法的改进[J]. 东华理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 36(增1):68-72.
|
|
JIANG Liang, DENG Juzhi, CHEN Hui, et al. Improvement of 2.5D dc resistivity based on the finite difference method[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology:Natural Science, 2016, 36(S1):68-72.
|
| [12] |
COCKETT R, KANG S, HEAGY L J, et al. SimPEG: an open source framework for simulation and gradient based parameter estimation in geophysical applications[J]. Computers & Geosciences. 2015, 85:142-154.
doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2015.09.015
|
| [13] |
LINDSEY J H, ROWAN C, SEOGI K, et al. A framework for simulation and inversion in electromagnetics[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2017, 107:1-19.
doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2017.06.018
|
| [14] |
赵丽媛. 地下管线渗漏引发城市道路塌陷形成机理研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2023.
|
|
ZHAO Liyuan. Study on the formation mechanism of urban roads collapse caused by underground pipeline leakage[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2023.
|
| [15] |
赵荣春, 吕玉增, 张智, 等. 基于2.5D有限元的高密度电法不同装置勘探效果研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2024, 52 (4):128-136.
|
|
ZHAO Rongchun, LYU Yuzeng, ZHANG Zhi, et al. Exploring the detection performance of different array configurations for Multi-electrode resistivity method tomography using a 2.5D finite element method[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2024, 52 (4):128-136.
|
| [16] |
YONATAN G D, PING Yuchang, JORDI M P. Uncertainty of the 2D resistivity survey on the subsurface cavities[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(7):DOI: 10.3390/app11073143.
|
| [17] |
曾雄鹰, 王佳龙, 梁晓东, 等. 基于双频高动态探地雷达技术的道路地下病害检测研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2022, 37(5):2225-2232.
|
|
ZENG Xiongying, WANG Jialong, LIANG Xiaodong, et al. Research on road underground disease detection by dual-frequency GPR based on high-dynamic range technology[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37(5):2225-2232.
|
| [18] |
戴自立, 彭凌豪, 包扬娟. 地下水力管线外渗引起的道路塌陷机理模型试验[J]. 中国公路学报, 2024, 37(10):49-60.
doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2024.10.005
|
|
DAI Zili, PENG Linghao, BAO Yangjuan. Model test investigation on the mechanism of ground collapse induced byunderground hydraulic pipe leakage[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2024, 37(10):49-60.
doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2024.10.005
|
| [19] |
余浩, 高镱滈, 潘险险, 等. 基于改进高斯混合模型的变电站负荷聚类算法[J]. 全球能源互联网, 2024, 7(5):591-601.
|
|
YU Hao, GAO Yixing, PAN Xianxian, et al. Substation load clustering algorithm based on improved Gaussian mixture model[J]. Journal of Global Energy Interconnection, 2024, 7(5):591-601.
|