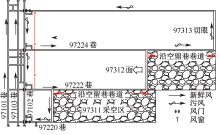
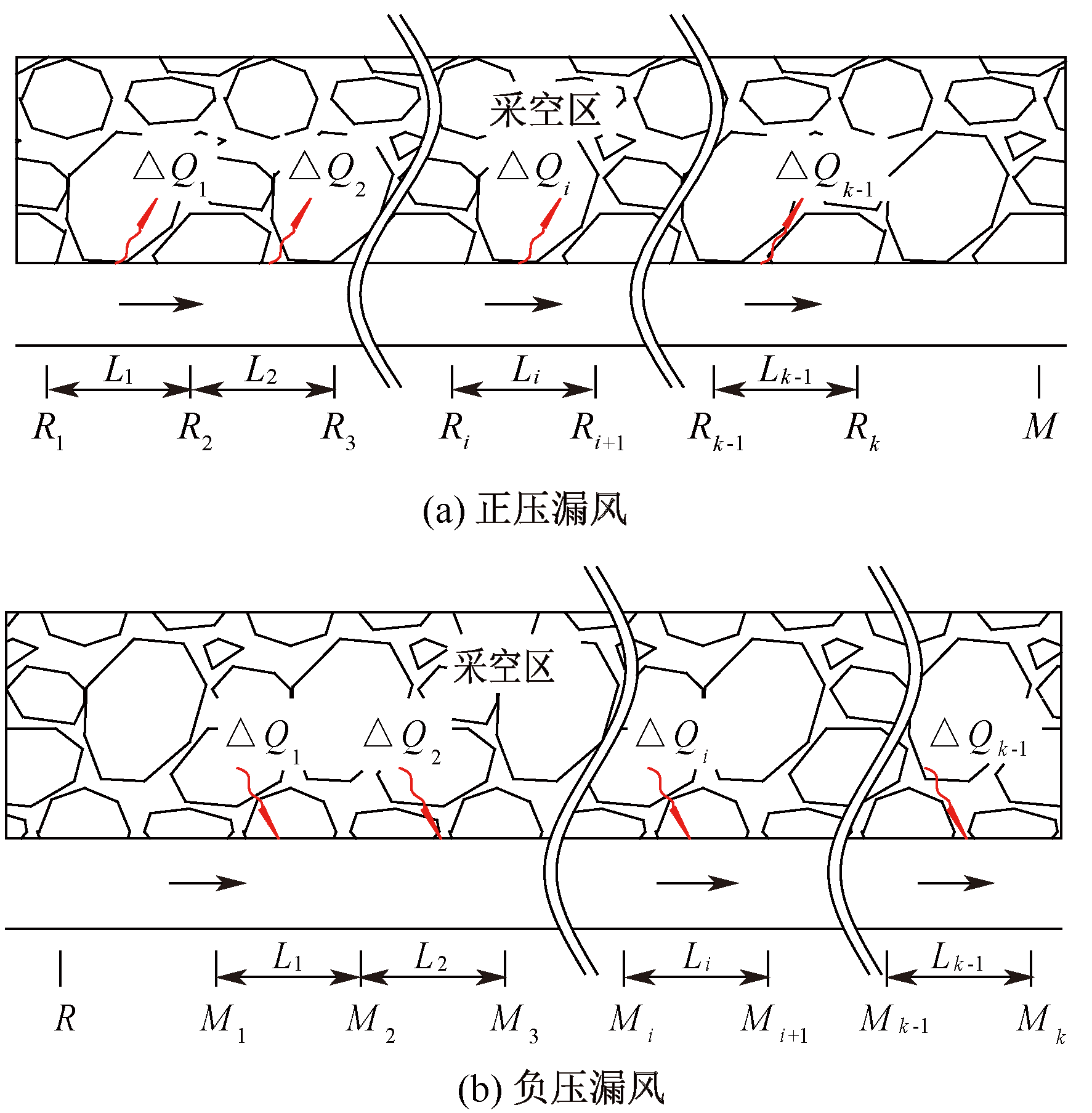
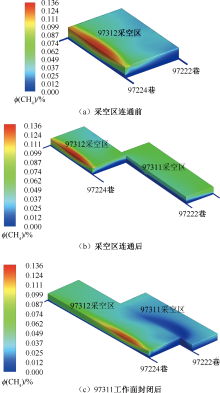
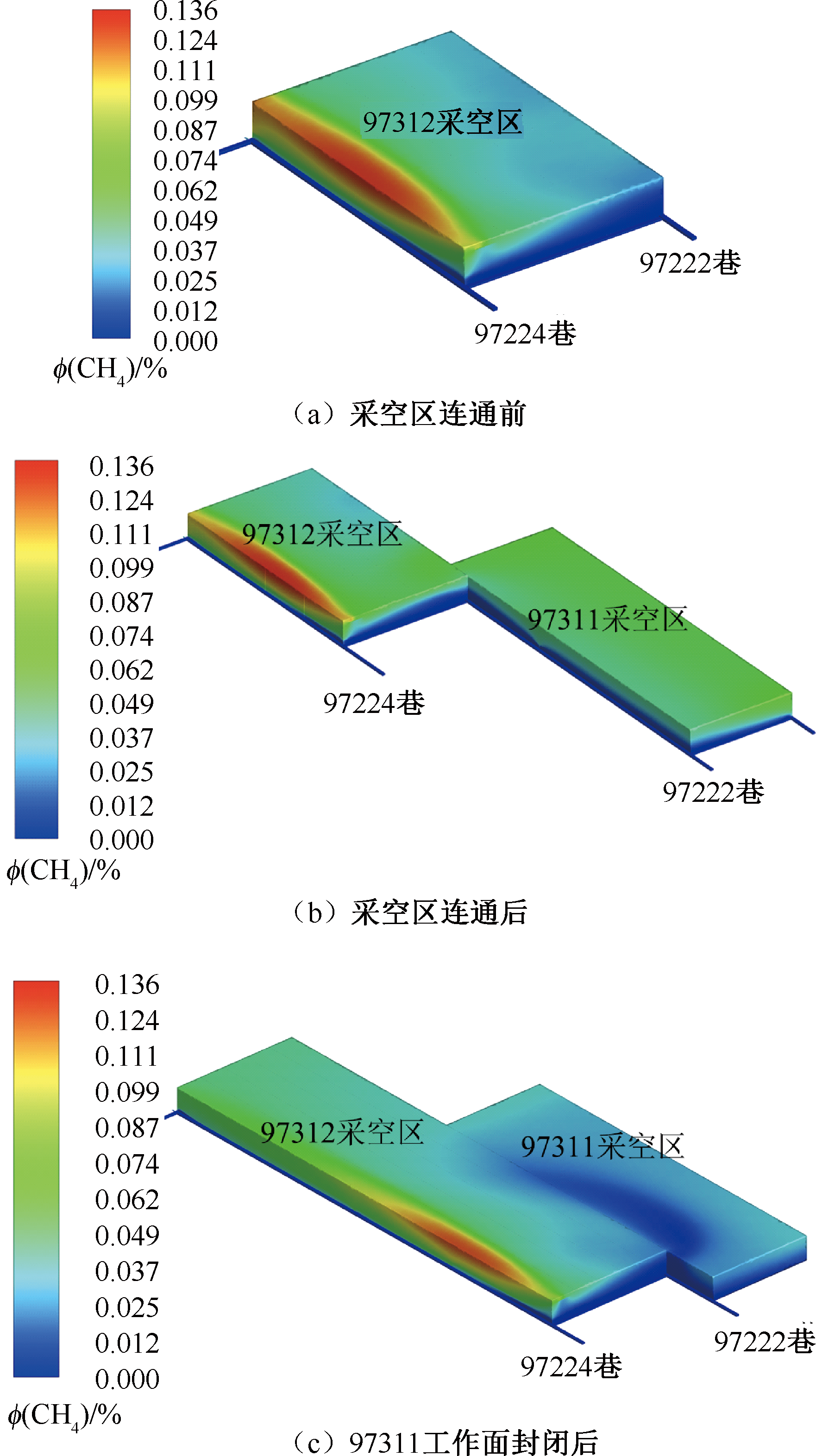
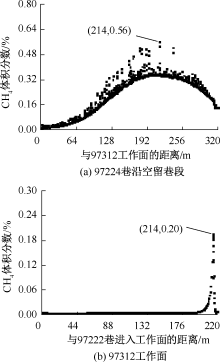
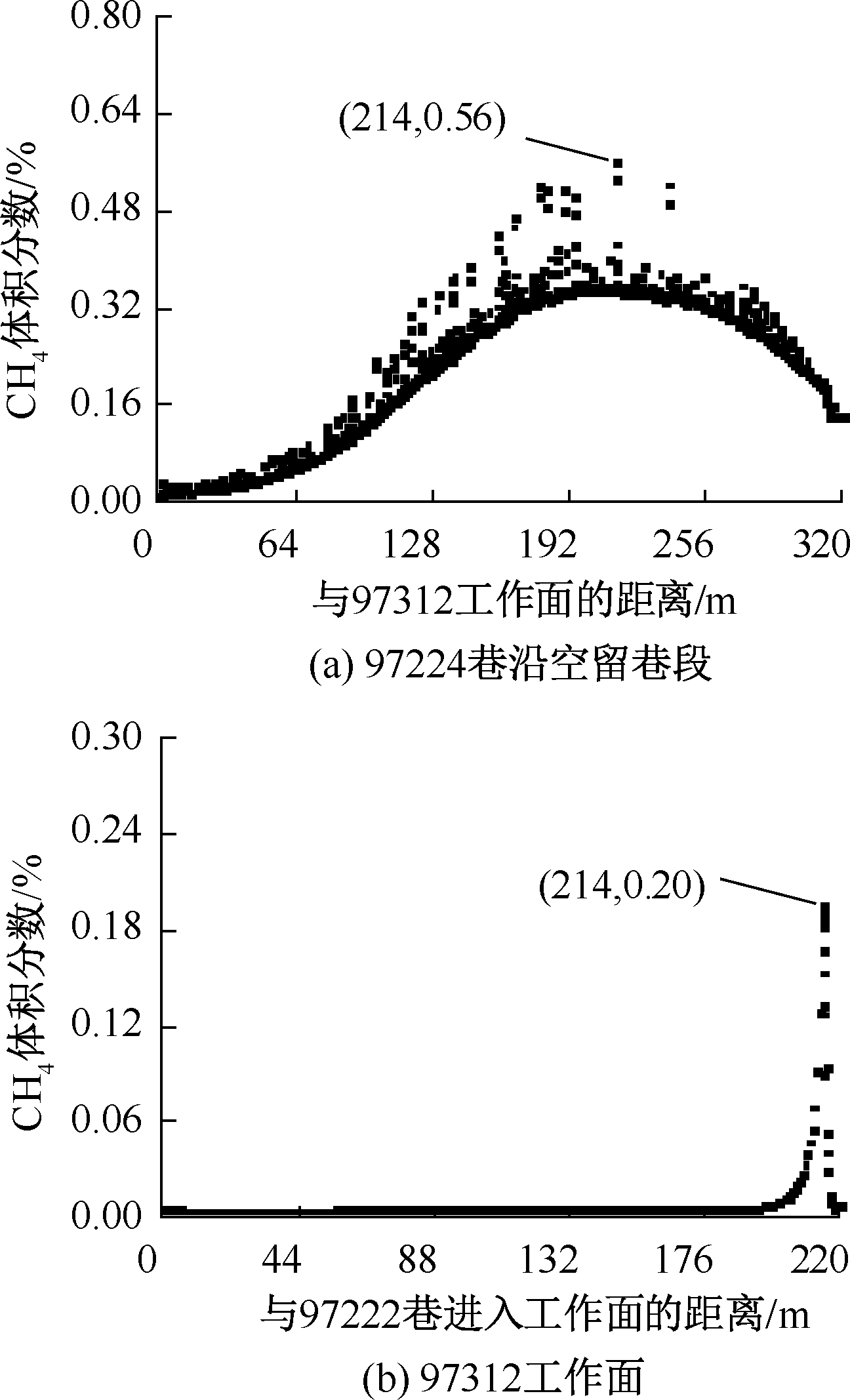
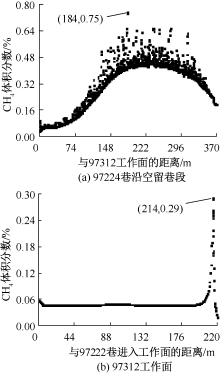
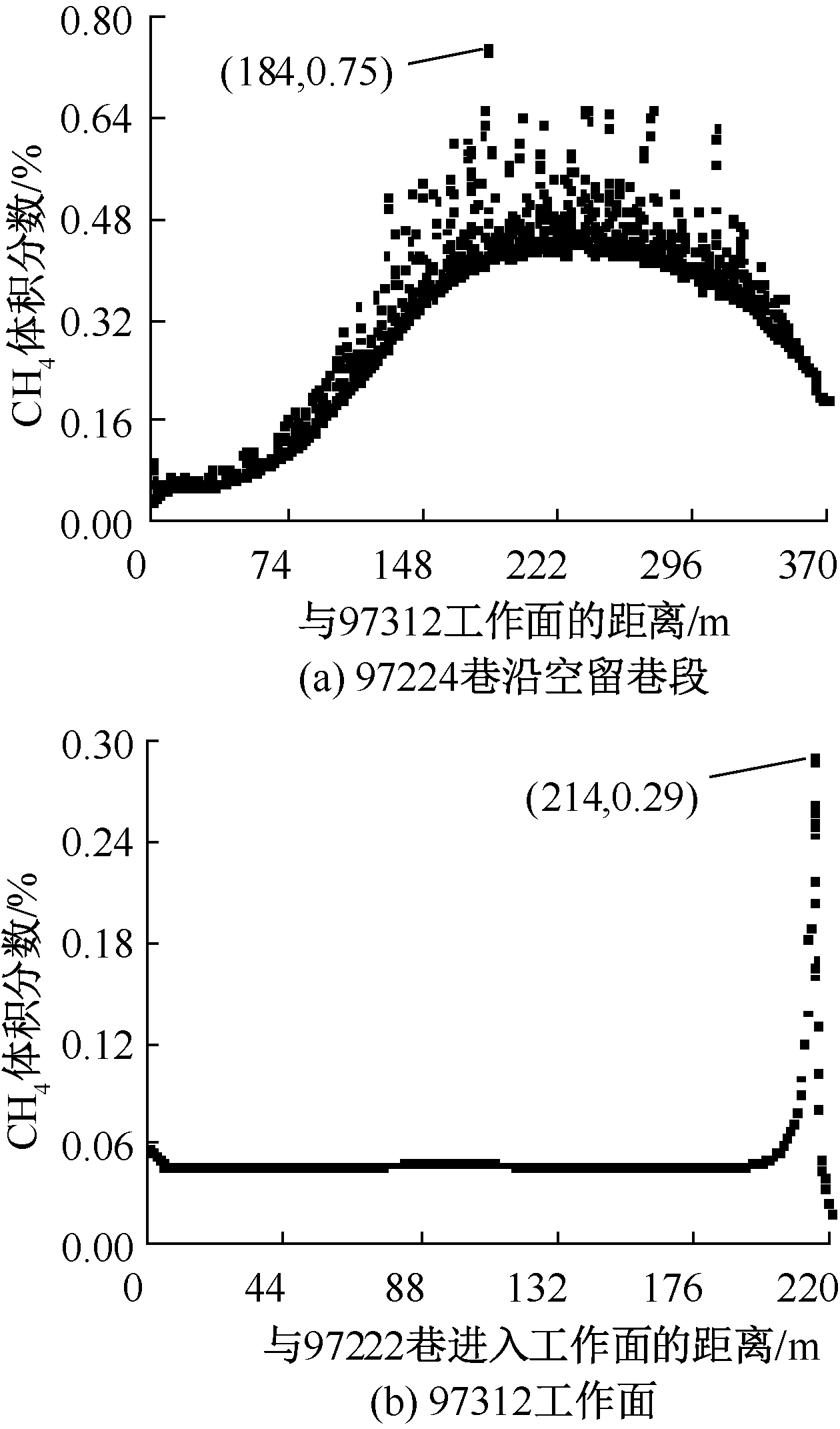
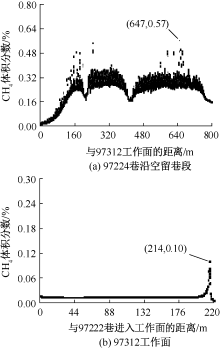
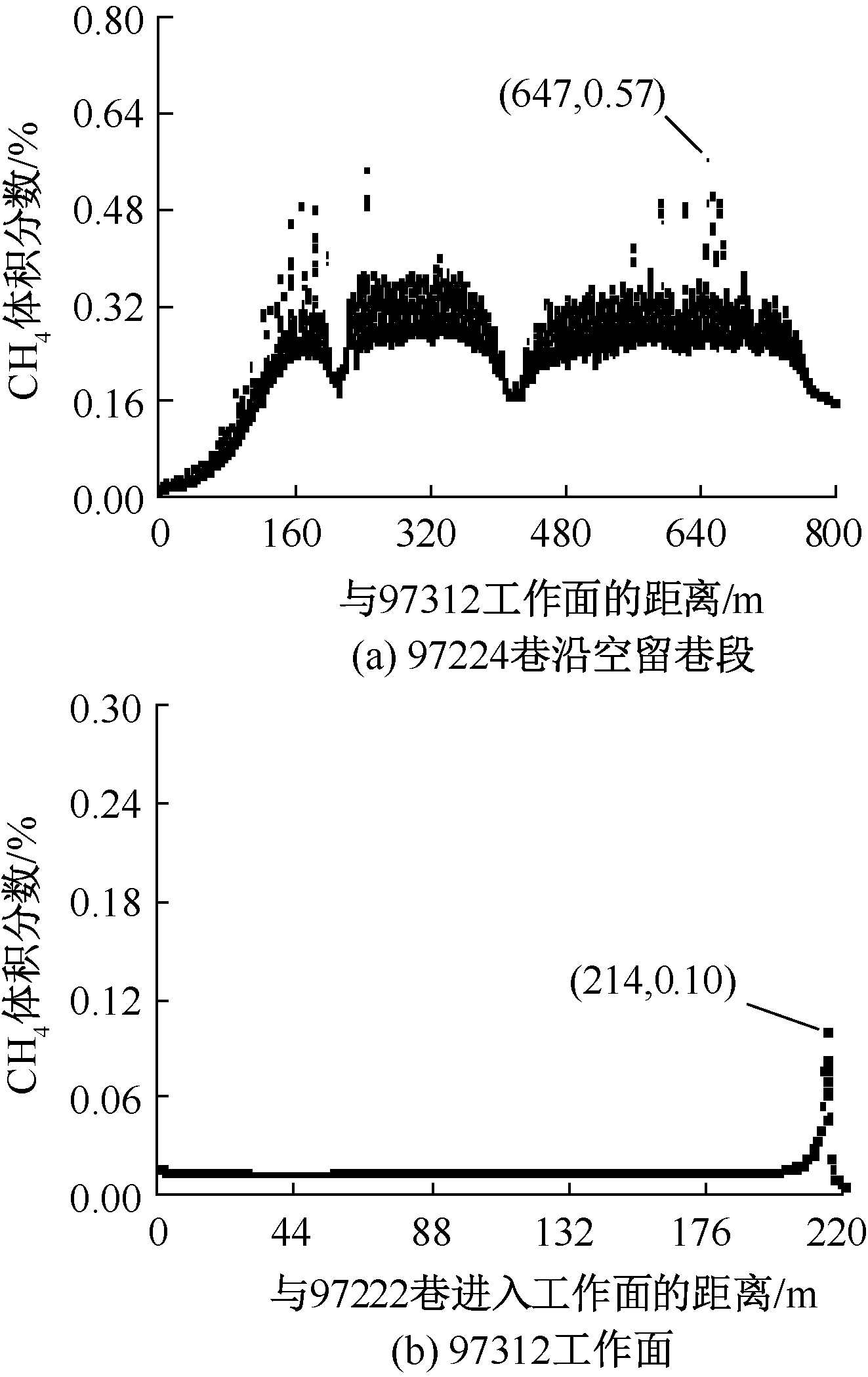
| [1] |
何满潮, 马新根, 牛福龙, 等. 中厚煤层复合顶板快速无煤柱自成巷适应性研究与应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(12): 2 641-2 654.
|
|
HE Manchao, MA Xin'gen, NIU Fulong, et al. Adaptability research and application of rapid gob-side entry retaining formed by roof cutting and pressure releasing with composite roof and medium thick coal seam[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(12): 2 641-2 654.
|
| [2] |
杨红运, 刘延保, 李勇, 等. 近距离煤层群切顶留巷覆岩应力及变形响应研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保, 2022, 49(1): 8-13, 19.
|
|
YANG Hongyun, LIU Yanbao, LI Yong, et al. Study on strata stress and deformation response of contiguous seams under cutting roof for entry retaining[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2022, 49(1): 8-13, 19.
|
| [3] |
闫肃. 深部厚硬顶板厚煤层切顶成巷综采工作面采空区漏风规律研究[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2021.
|
|
YAN Su. Research on the law of air leakage in the goaf of fully mechanized coal mining face in deep thick hard roof thick coal seam[D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2021.
|
| [4] |
王琰, 周建, 王元. 高地温综放工作面采空区漏风规律研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(增2): 155-158.
|
|
WANG Yan, ZHOU Jian, WANG Yuan. Study on air leakage law of goaf in fully mechanized top coal caving face with high ground temperature[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(S2): 155-158.
|
| [5] |
赵文彬, 刘方顺, 石新岩, 等. 放顶煤工作面立体自燃带动态变化特性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(3): 65-74.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.03.009
|
|
ZHAO Wenbin, LIU Fangshun, SHI Xinyan, et al. Research on dynamic change characteristics of three-dimensional spontaneous combustion zone in caving coal face[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(3): 65-74.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.03.009
|
| [6] |
王炯, 刘鹏, 姜健, 等. 切顶卸压沿空留巷回采工作面Y型通风漏风规律研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2021, 38(3): 625-633.
|
|
WANG Jiong, LIU Peng, JIANG Jian, et al. Y-shaped ventilation air leakage law of working face of gob-side entry retaining by cutting roof to release pressure[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2021, 38(3): 625-633.
|
| [7] |
杜云飞. 切顶卸压留巷Y型通风模式下采空区漏风特性研究[D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学, 2018.
|
|
DU Yunfei. Study on the characteristics of air leakage in the goal under a Y type ventilation system using cutting roof and release pressure method mining[D]. Jiaozuo: Henan Polytechnic University, 2018.
|
| [8] |
LI Tengteng, WU Bing, LEI Baiwei, et al. Study on air leakage and gas distribution in goaf of Y-type ventilation system[J]. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Utilization and Environmental Effects, 2020, 46(1):8632-8 645.
|
| [9] |
李艳昌, 靖泽浩, 贾进章. 切顶卸压沿空留巷“Y”型通风模式下采空区漏风规律研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2022, 31(3): 184-189.
|
|
LI Yanchang, JING Zehao, JIA Jinzhang. Study on the air leakage law of goaf under the "Y" ventilation mode of gob-side entry retaining with roof cutting and pressure relief[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2022, 31(3): 184-189.
|
| [10] |
ZHOU Xihua, JING Zehao, LI Yanchao. Research on controlling gas overrun in a working face based on gob-side entry retaining by utilizing ventilation type "Y"[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1):DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-36464-y.
|
| [11] |
MT/T 845—1999, 煤矿巷道用SF6示踪气体检测漏风技术规范[S].
|
|
MT/T 845-1999, Technical specification of leakage detection with SF6 tracer gas in roadways of coal mines[S].
|
| [12] |
杨明, 高建良, 冯普金. U型和Y型通风采空区瓦斯分布数值模拟[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2012, 12(5): 227-230.
|
|
YANG Ming, GAO Jianliang, FENG Pujin. Numerical simulation of gas distribution in goaf with U-type and Y-type ventilation[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2012, 12(5): 227-230.
|
| [13] |
陶远, 秦汝祥, 庞文华. U型综采工作面采空区流场数值模拟[J]. 煤矿安全, 2014, 45(1): 186-188,191.
|
|
TAO Yuan, QIN Ruxiang, PANG Wenhua. Numerical simulation of goaf flow field for U-type fully mechanized working face[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2014, 45(1): 186-188,191.
|
| [14] |
陈向军, 刘金钊, 司朝霞, 等. 切顶卸压留巷开采模式下工作面及采空区内风流运移特性[J]. 河南理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 39(6): 1-9.
|
|
CHEN Xiangjun, LIU Jinzhao, SI Zhaoxia, et al. Characteristics of air flow in working face and goaf under the mining mode of pressure relief by roof cutting of retaining gateway[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University :Natural Science, 2020, 39(6): 1-9.
|
| [15] |
王春霞, 艾德春, 杨付领, 等. 风帘对采空区漏风及工作面瓦斯分布的影响[J]. 煤炭技术, 2019, 38(6): 101-102.
|
|
WANG Chunxia, AI Dechun, YANG Fuling, et al. Influence of wind curtain on distribution of air leakage in gob and gas in working face[J]. Coal Technology, 2019, 38(6): 101-102.
|
| [16] |
杨永亮. 110工法工作面采空区漏风及煤自燃与瓦斯复合灾害研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2023.
|
|
YANG Yongliang. Study on air leakage and coal spontaneous combustion and gas compound disaster in the mining area of 110 working face[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Technology, 2023.
|
| [17] |
刘宇. 采空区瓦斯与自燃灾害关联3D数值模拟研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2014.
|
|
LIU Yu. Three-dimensional numerical simulation research on correlation of gas and spontaneous combustion disaster in goaf[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University, 2014.
|
| [18] |
CARMAN P C. Permeability of saturated sands, soils and clays[J]. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 1939, 29(2): 263-273.
|
| [19] |
高光超, 李宗翔, 张春, 等. 基于三维“O”型圈的采空区多场分布特征数值模[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2017, 17(3): 931-936.
|
|
GAO Guangchao, LI Zongxiang, ZHANG Chun. Numerical simulation for multi-field distribution characteristic features of the goaf based on 3D "O" type circle[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2017, 17(3): 931-936.
|
| [20] |
国家安全监管总局, 国家煤炭安监局, 国家能源局, 等. 建筑物、水体、铁路及主要井巷煤柱留设与压煤开采规范[L]. 2017-05-17.
|