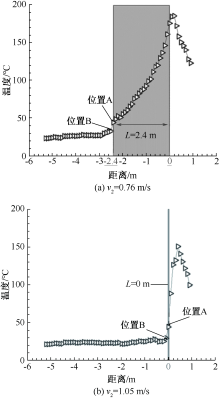
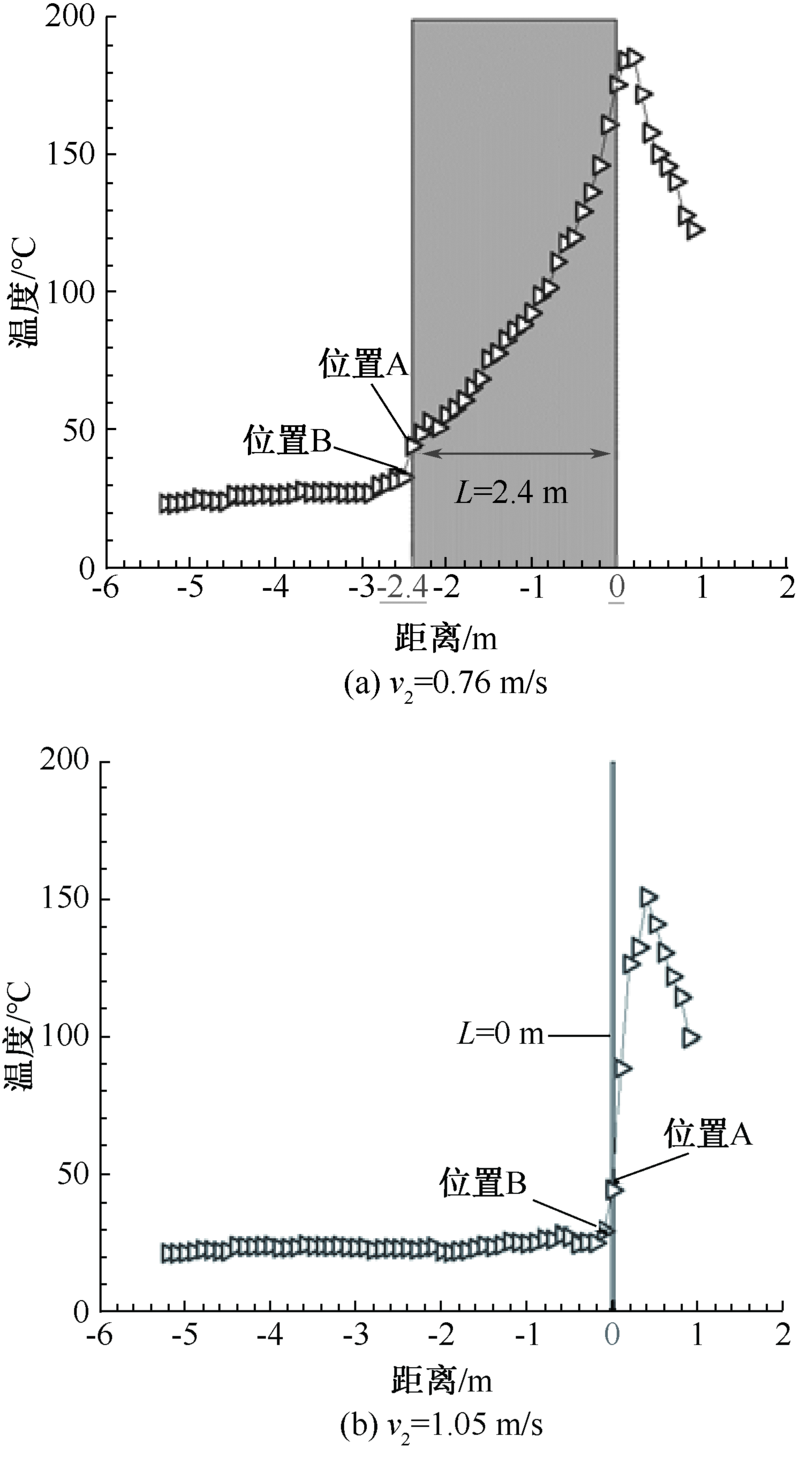
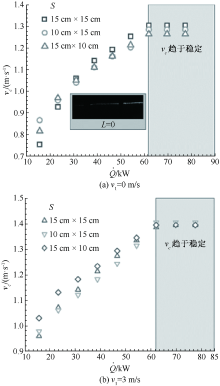
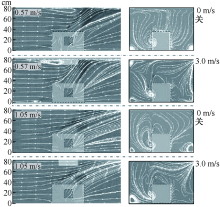
| [1] |
李涛, 谢玮, 张玉春, 等. 水雾强化隧道火灾火焰现象试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27 (3): 37-41.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.03.007
|
|
LI Tao, XIE Wei, ZHANG Yuchun, et al. Experimental study on flame strengthening with water mist in tunnel fires[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27 (3): 37-41.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.03.007
|
| [2] |
徐童, 唐飞, 何清. 隧道内贴壁火顶棚射流温度及火焰特性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(7):93-97.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.07.2080
|
|
XU Tong, TANG Fei, HE Qing. Study on temperature and fame characteristics of ceiling jet induced by wall-attached fire in a tunnel[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(7): 93-97.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.07.2080
|
| [3] |
THOMAS P H. The movement of smoke in horizontal passages against an air flow[J]. Fire Research Technical Paper, 1968, 7(1):1-8.
|
| [4] |
OKA Y, ATKINSON G T. Control of smoke flow in tunnel fires[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 1995, 25(4): 305-322.
doi: 10.1016/0379-7112(96)00007-0
|
| [5] |
LI Yingzhen, LEI Bo, INGASON H. Study of critical velocity and back-layering length in longitudinally ventilated tunnel fires[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2011, 45(6/7/8): 361-370.
doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2010.07.003
|
| [6] |
WU Yang, BAKAR M Z A. Control of smoke flow in tunnel fires using longitudinal ventilation systems:a study of the critical velocity[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2000, 35(4): 363-390.
doi: 10.1016/S0379-7112(00)00031-X
|
| [7] |
MENG Na, HU Xiangming, TIAN Mengya. Effect of blockage on critical ventilation velocity in longitudinally ventilated tunnel fires[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2020:DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103580.
|
| [8] |
姜学鹏, 谢智云, 于思维, 等. 水下V形坡隧道烟气温度纵向衰减研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(9): 74-80.
|
|
JIANG Xuepeng, XIE Zhiyun, YU Siwei, et al. Study on longitudinal decay of flue gas temperature in underwater V-shaped slope tunnels[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(9): 74-80.
|
| [9] |
郭庆华, 朱合华, 闫治国. 顶部开口自然通风隧道火灾竖井排烟效率研究[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2021, 40(5): 661-664.
|
|
GUO Qinghua, ZHU Hehua, YAN Zhiguo. Studies on the smoke exhaust efficiency of the vertical shaft in naturally ventilated tunnel fires[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 661-664.
|
| [10] |
INGASON H, LI Yingzhen, LÖNNERMARK A. Tunnel fire dynamics[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2014:349-352.
|
| [11] |
钟委, 孙超鹏, 马文辉, 等. 隧道内顶棚和侧向机械排烟效果对比[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2021, 40(5): 639-643.
|
|
ZHONG Wei, SUN Chaopeng, MA Wenhui, et al. Comparison of smoke exhaust effect between ceiling and lateral mechanical smoke exhaust in tunnel[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 639-643.
|
| [12] |
ZHU Yuantao, TANG Fei, HUANG Yajun. Experimental study on the smoke plug-holing phenomenon and criteria in a tunnel under the lateral smoke extraction[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2022:DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2021.104330.
doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2021.104330
|
| [13] |
QUINTIERE J G. Scaling applications in fire research[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 1989, 15(1): 3-29.
doi: 10.1016/0379-7112(89)90045-3
|
| [14] |
TANG Fei, HU Peng, HE Qing, et al. Effect of sidewall on the flame extension characteristics beneath a ceiling induced by carriage fire in a channel[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2021, 223: 202-215.
doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2020.09.020
|
| [15] |
MCGRATTAN K, MCDERMOTT R, HOSTIKKA S, et al. Fire dynamics simulator version 5[M]. Washington: National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication, 2010: 222.
|
| [16] |
COANDA H. Device for deflecting a stream of elastic fluid projected into an elastic fluid:US Patent, No. 2052869[P]. 1936.
|