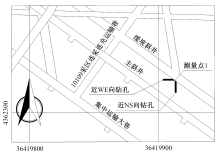
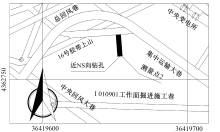
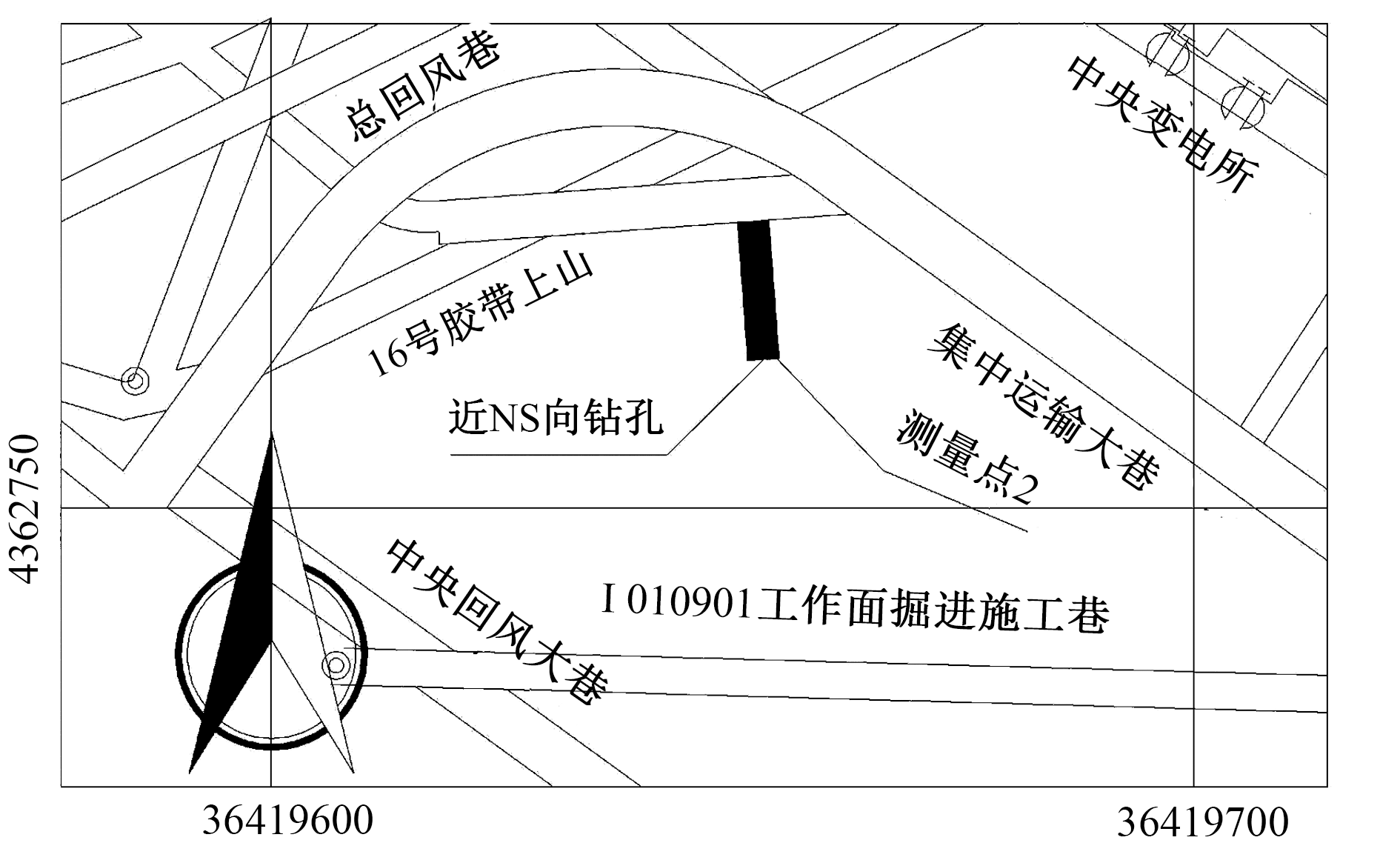
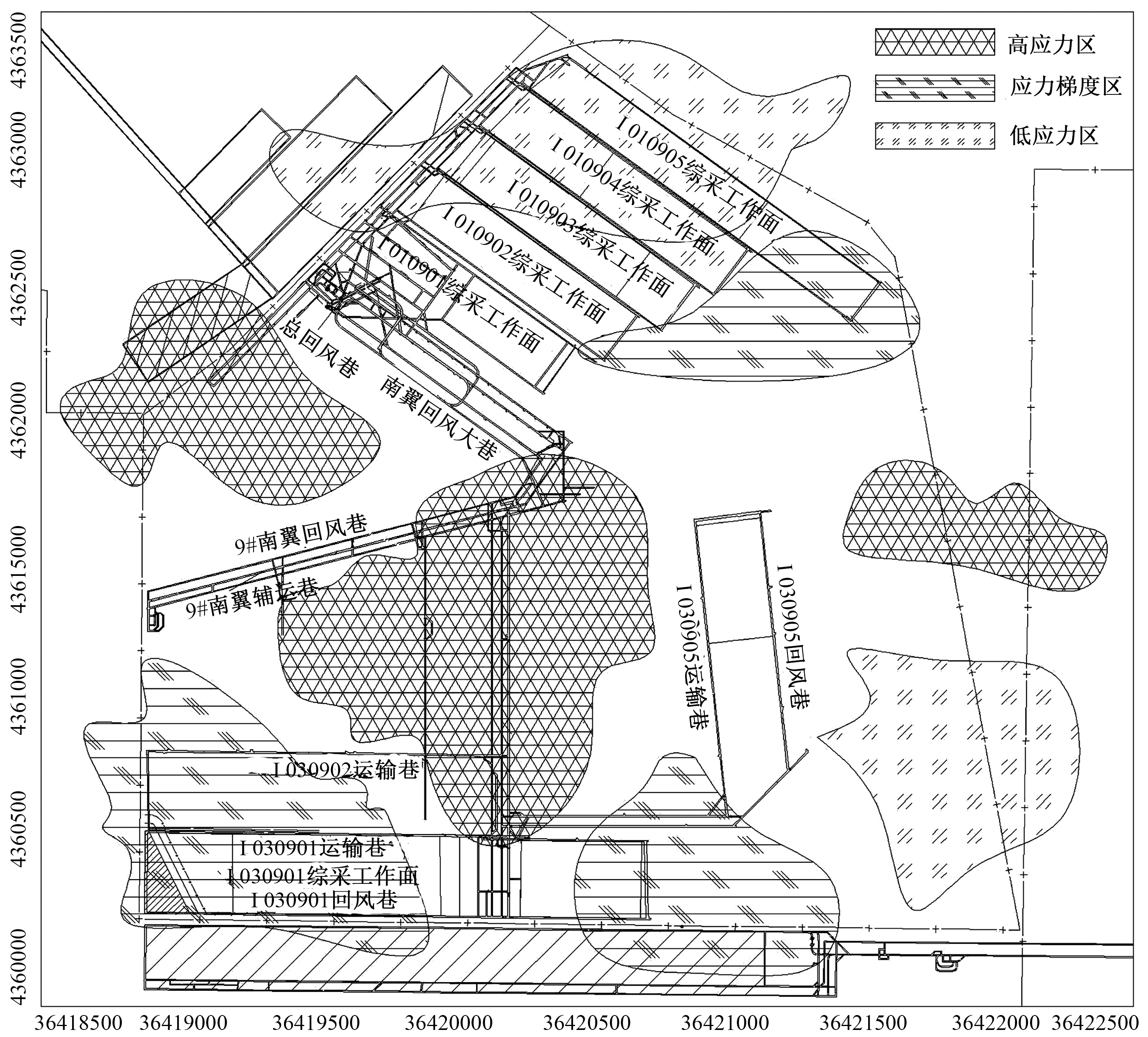
| [1] |
袁亮. 深部采动响应与灾害防控研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(3):716-725.
|
|
YUAN Liang. Research progress of mining response and disaster prevention and control in deep coal mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(3):716-725.
|
| [2] |
彭文庆, 朱豪, 汪琦. 破碎岩体巷道围岩承载结构应力分布规律[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2023, 54(6):2447-2 458.
|
|
PENG Wenqing, ZHU Hao, WANG Qi. Stress distribution law of surrounding rock bearing structure of broken surrounding rock roadway[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2023, 54(6):2447-2 458.
|
| [3] |
张岳桥, 施炜, 廖昌珍, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地周边断裂运动学分析与晚中生代构造应力体制转换[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(5):639-647.
|
|
ZHANG Yueqiao, SHI Wei, LIAO Changzhen, et al. Fault kinematic analysis and change in late mesozoic tectonic stress regimes in the peripheral zones of the Ordos basin, North China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 80(5):639-647.
|
| [4] |
张传庆, 黄书岭, 周辉, 等. 基于地应力水平评价的围岩潜在破坏模式研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(1):3187-3 195.
|
|
ZHANG Chuanqing, HUANG Shuling, ZHOU Hui, et al. Study on potential failure modes of surrounding rock mass based on evaluation of geostress level[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(1):3187-3 195.
|
| [5] |
康红普, 林健, 张晓. 深部矿井地应力测量方法研究与应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(5):929-933.
|
|
KANG Hongpu, LIN Jian, ZHANG Xiao. Research and application of in-situ stress measurement method in deep mines[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(5):929-933.
|
| [6] |
蔡美峰, 刘卫东, 李远. 玲珑金矿深部地应力测量及矿区地应力场分布规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(2):227-233.
|
|
CAI Meifeng, LIU Weidong, LI Yuan. In-situ stress measurement at deep position of Linglong gold mine and distribution law of in-situ stress field in mine area[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(2):227-233.
|
| [7] |
LI Peng, CAI Meifeng, GUO Qifeng, et al. In situ stress state of the northwest region of the Jiaodong Peninsula,China from overcoring stress measurements in three gold mines[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019,52:4 497-4 507.
|
| [8] |
YIN Shuai, XIE Runchen, WU Zhonghu, et al. In situ stress heterogeneity in a highly developed strike-slip fault zone and its effect on the distribution of tight gases:a 3D finite element simulation study[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 99(1):75-91.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.10.007
|
| [9] |
ZHAO Haijun, MA Fengshan, XU Jiamo, et al. In situ stress field inversion and its application in mining-induced rock mass movement[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2012,53:120-128.
|
| [10] |
GUO Peng, YAO Leihua. Simulation of three-dimensional tectonic stress fields and quantitative prediction of tectonic fracture within the damintun depression,Liaohe basin,northeast China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2016, 86(5):211-223.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2016.03.007
|
| [11] |
FENG Jianwei, SHANG Ling, LI Xize, et al. 3D numerical simulation of heterogeneous in situ stress field in low-permeability reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Science, 2019, 16(5):939-955.
doi: 10.1007/s12182-019-00360-w
|
| [12] |
陈立军, 刘伟, 王海萍, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地吴定区域侏罗系储层特征及其主控因素[J]. 甘肃科学学报, 2023, 35(6):31-37,43.
|
|
CHEN Lijun, LIU Wei, WANG Haiping, et al. Characteristics and main control factors of Jurassic reservoir in the Wuqi-Anding Area,Ordos basin[J]. Journal of Gansu Sciences, 2023, 35(6):31-37,43.
|
| [13] |
阴钰毅, 姚志纯, 郭小波, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘二叠系隐伏构造特征及勘探意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(4):79-88.
|
|
YIN Yuyi, YAO Zhichun, GUO Xiaobo, et al. Characteristics of Permian concealed structures in western margin of Ordos basin and its significance for oil and gas exploration[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2022, 34(4):79-88.
|
| [14] |
何登发, 包洪平, 开百泽, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地及其邻区关键构造变革期次及其特征[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(10):1255-1 269.
|
|
HE Dengfa, BAO Hongping, KAI Baize, et al. Critical tectonic modification periods and its geologic features of Ordos basin and adjacent area[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(10):1255-1 269.
|
| [15] |
欧阳征健, 冯娟萍, 龚慧山, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘横山堡地区构造特征与油气勘探目标优选[J]. 地质科学, 2021, 56(1):19-27.
|
|
OUYANG Zhengjian, FENG Juanping, GONG Huishan, et al. Structural characteristics and optimization of oil and gas exploration targets in Hengshanpu area, western margin of Ordos basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2021, 56(1):19-27.
|
| [16] |
开百泽, 何登发, 马静辉, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地构造沉降特征及对盆地成因的启示[J]. 地质科学, 2020, 55(3):657-671.
|
|
KAI Baize, HE Dengfa, MA Jinghui, et al. The characteristics of tectonic subsidence in Ordos basin and its enlightenment to basin genesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2020, 55(3):657-671.
|
| [17] |
郄晨龙, 卞正富, 杨德军, 等. 鄂尔多斯煤田高强度井工煤矿开采对土壤物理性质的扰动[J]. 煤炭学报, 2015, 40(6):1448-1 456.
|
|
QIE Chenlong, BIAN Zhengfu, YANG Dejun, et al. Effect of high-intensity underground coal mining disturbance on soil physical properties[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(6):1448-1 456.
|
| [18] |
高立新, 韩晓明, 戴勇, 等. 鄂尔多斯地块的运动特性与现今地震活动性[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2017, 37(4):349-354.
|
|
GAO Lixin, HAN Xiaoming, DAI Yong, et al. Movement characteristics and the present seismic behavior of the Ordos block[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2017, 37(4):349-354.
|
| [19] |
崔笃信, 郝明, 李煜航, 等. 鄂尔多斯块体周缘地区现今地壳水平运动与应变[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(10):3646-3 661.
|
|
CUI Duxin, HAO Ming, LI Yuhang, et al. Present-day crustal movement and strain of the surrounding area of Ordos block derived from repeated GPS observations[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(10):3646-3 661.
|
| [20] |
白相东, 迟宝明, 关成尧, 等. 鄂尔多斯南缘构造带现今地块运动模式[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2015, 45(3):674-682.
|
|
BAI Xiangdong, CHI Baoming, GUAN Chengyao, et al. Ordos block modern movement patterns in southern Ordos margin tectonic belt[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2015, 45(3):674-682.
|