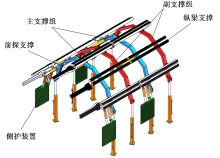
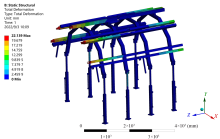
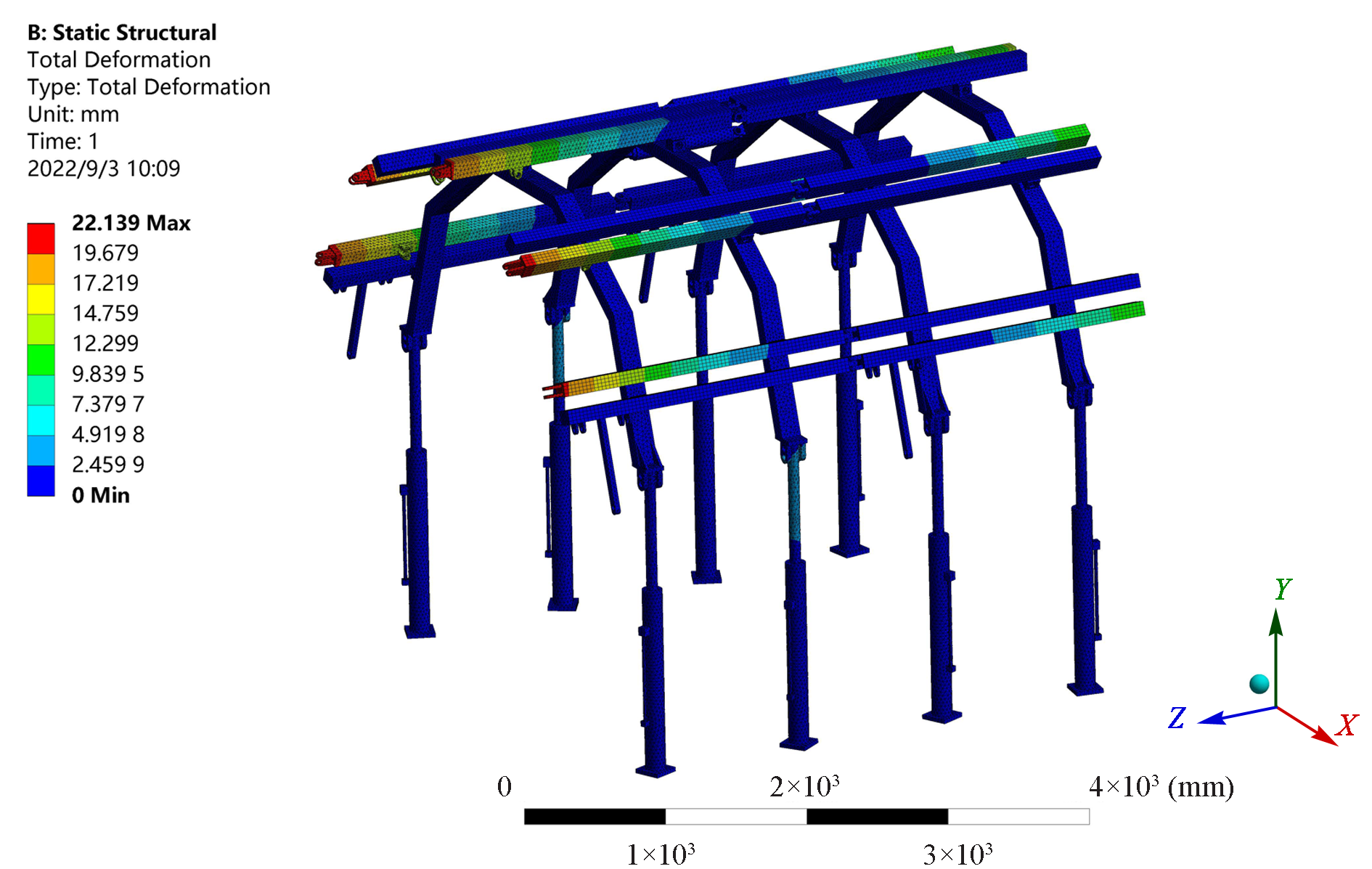
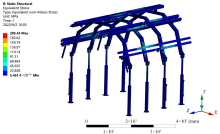
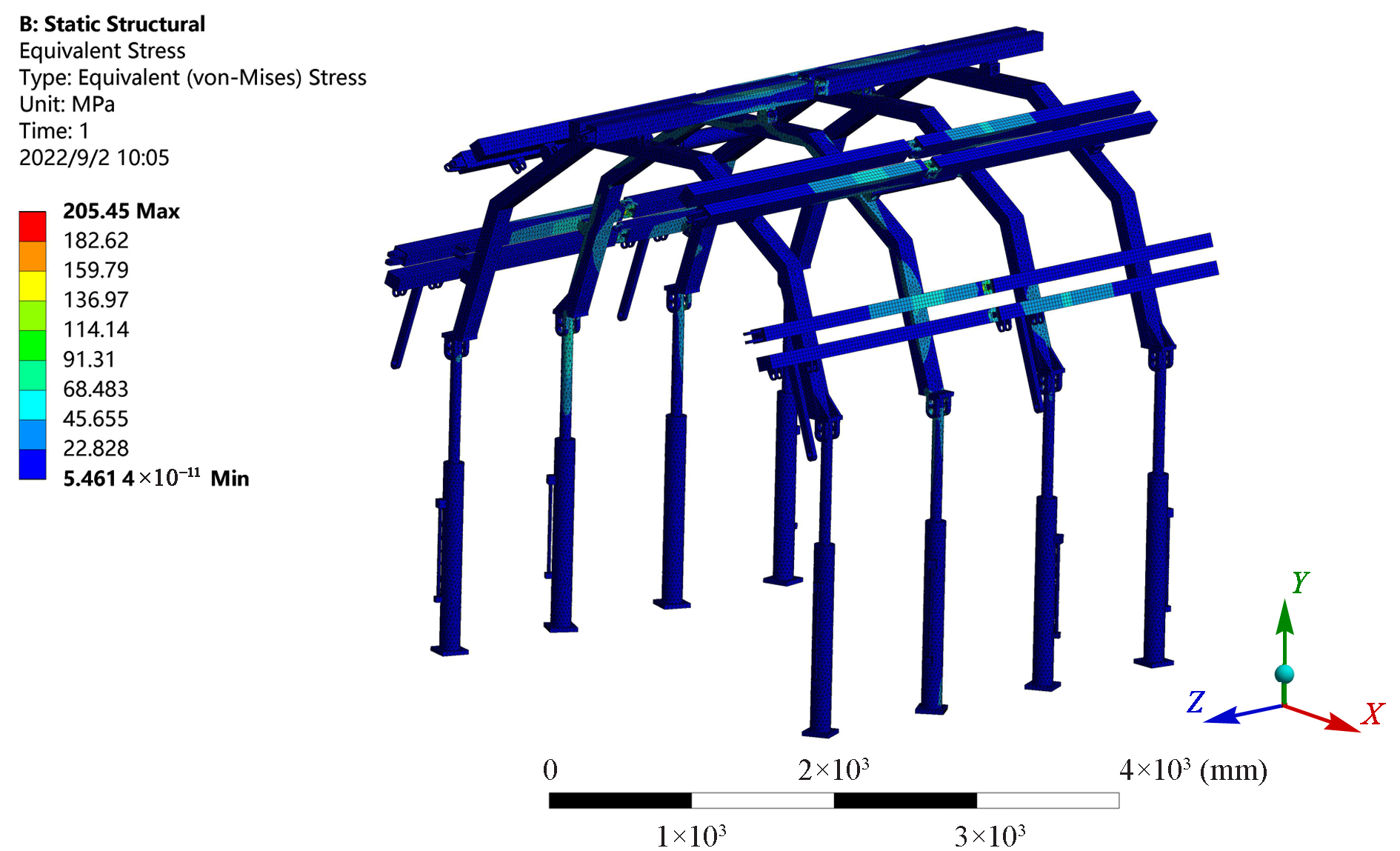
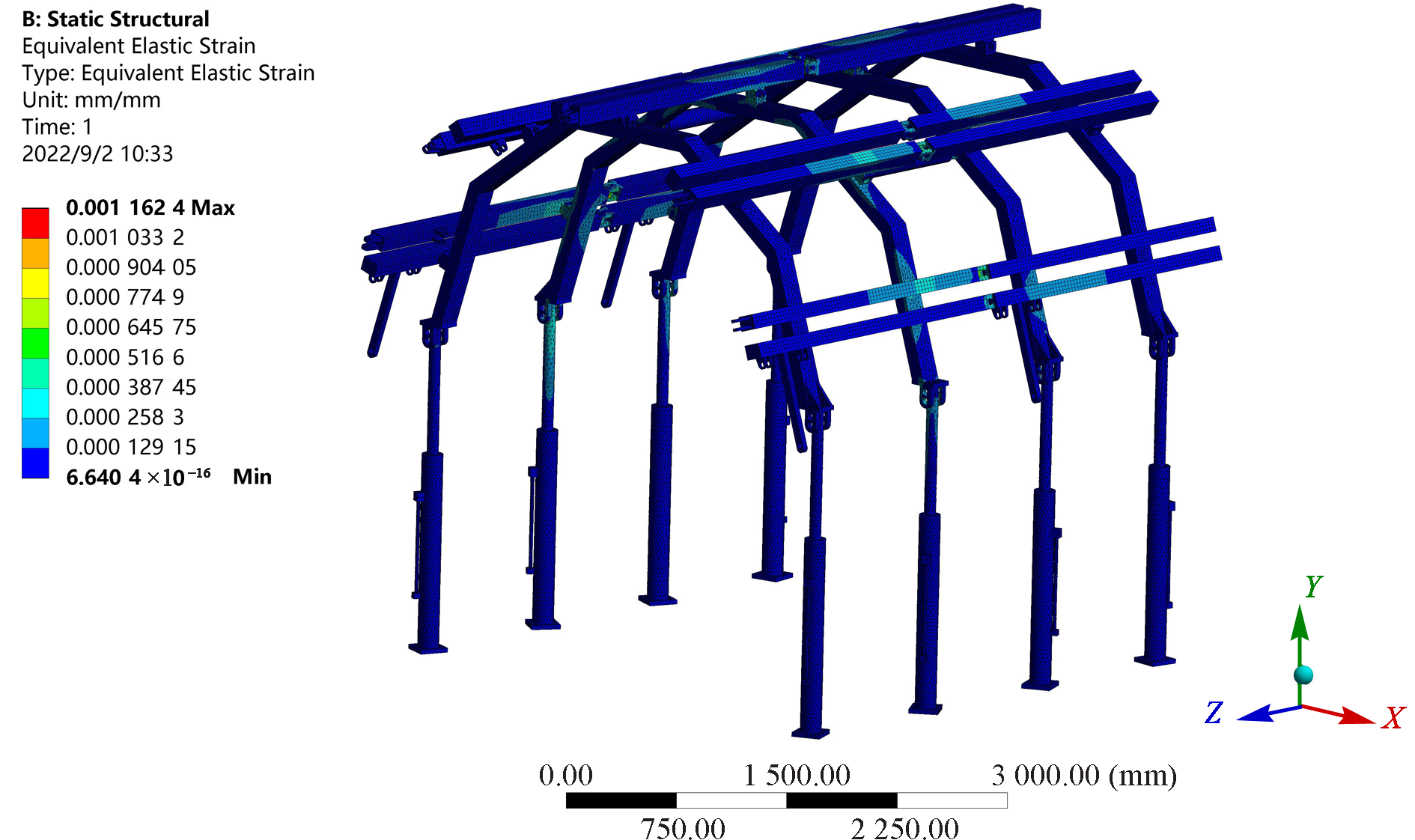
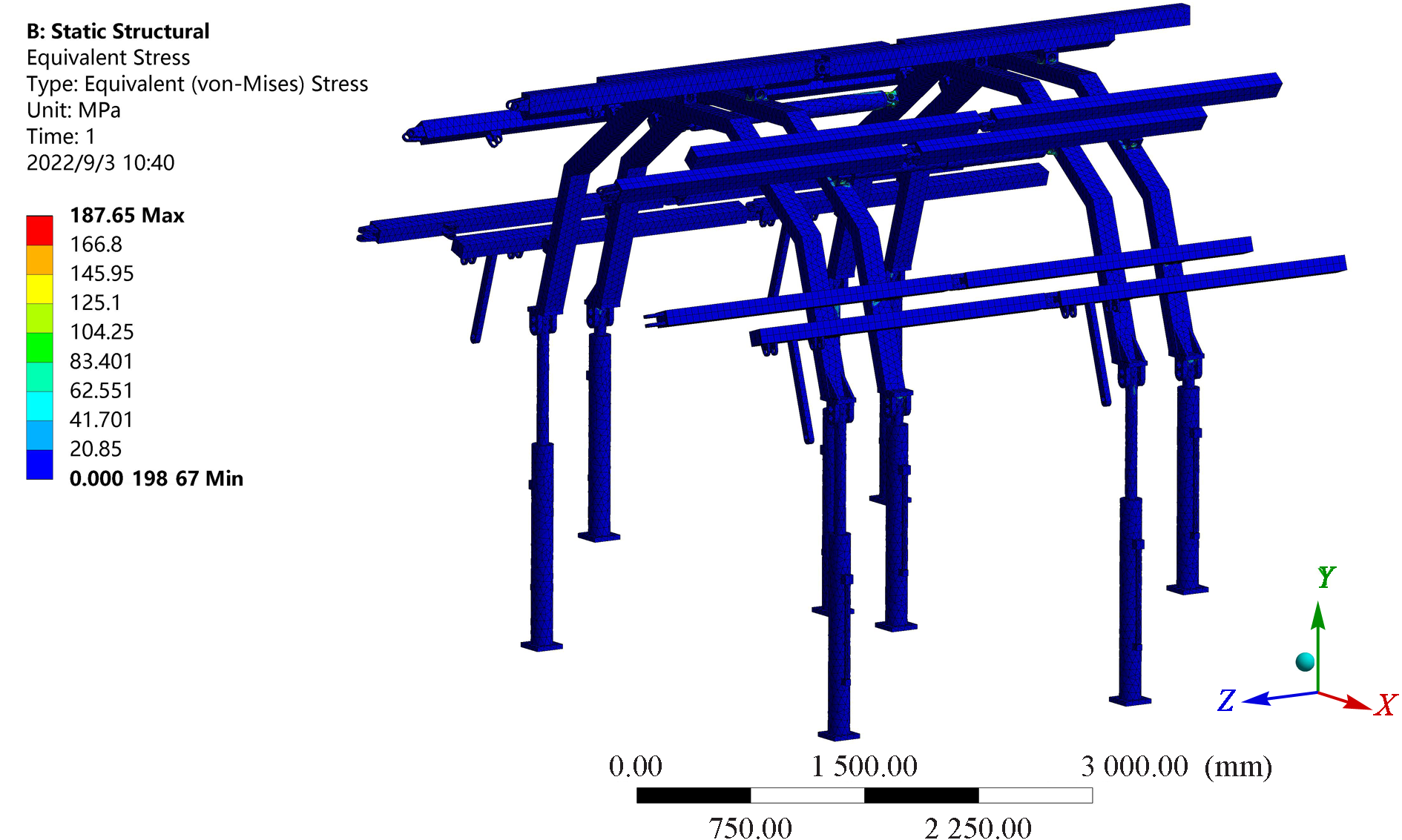
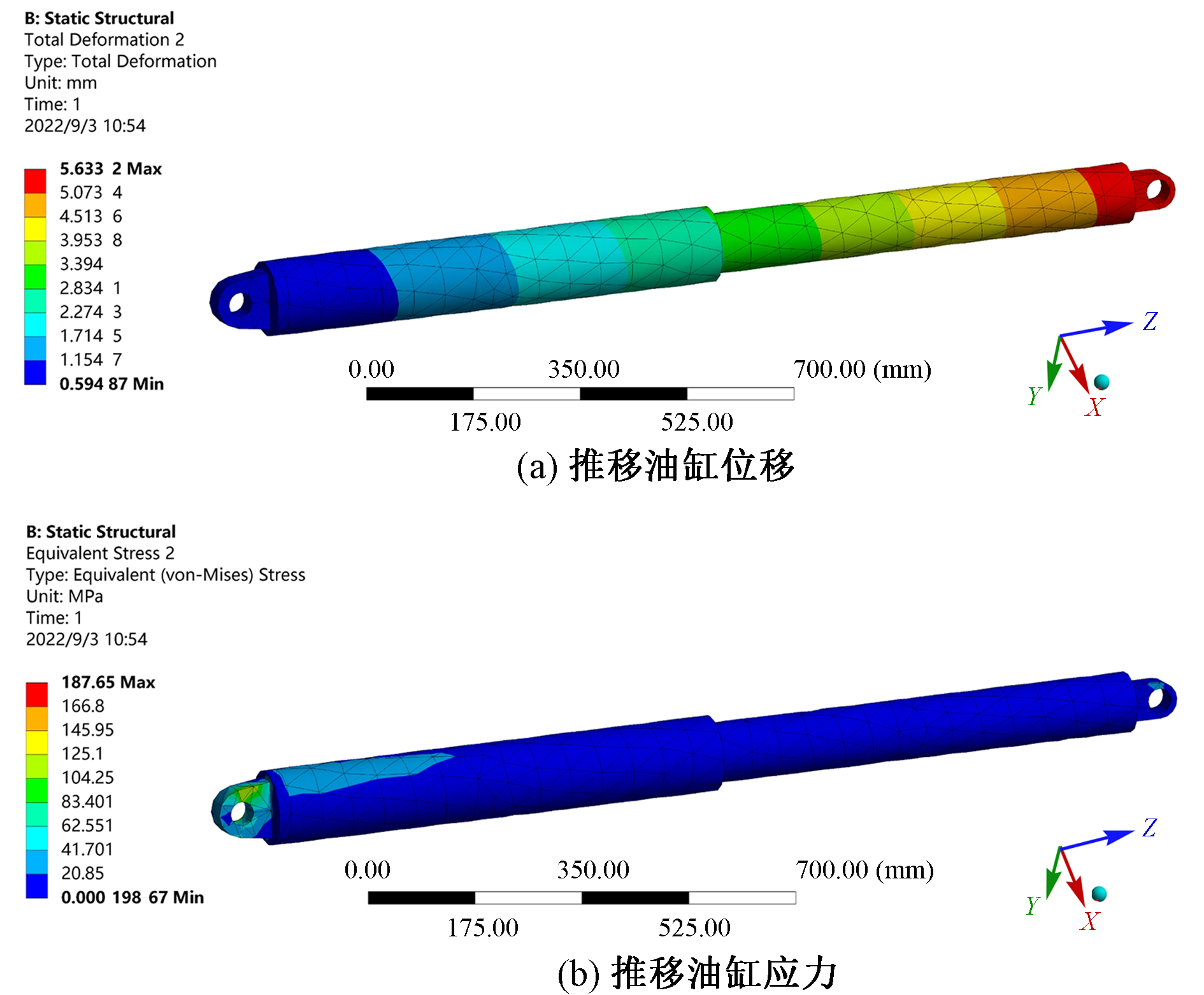
| [1] |
张进鹏, 刘立民, 刘传孝, 等. 深部大倾角煤岩层巷道断面形状与耦合支护[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 52(11):4074-4 087.
|
|
ZHANG Jinpeng, LIU Limin, LIU Chuanxiao, et al. Cross-section shape and coupling support of deep and large-inclined coal and rock roadway[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2021, 52(11):4074-4 087.
|
| [2] |
谢苗, 李晓婧, 刘治翔, 等. 掘进机扰动下超前支架动态响应特性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(4):65-71.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.04.012
|
|
XIE Miao, LI Xiaojing, LIU Zhixiang, et al. Analysis and study of dynamic response characteristics of advance support disturbed by roadheader[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28 (4): 65-71.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.04.012
|
| [3] |
范东林, 王巍. 大采高工作面回风巷道支护参数优化研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(增2):166-171.
|
|
FAN Donglin, WANG Wei. Study on support parameter optimization of mining roadway in working face with large mining height[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(S2): 166-171.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.S2.0098
|
| [4] |
尚玺. 深部顶板夹煤层软岩巷道承载结构失效分析及返修技术[D]. 湘潭: 湖南科技大学, 2022.
|
|
SHANG Xi. Failure analysis and repair technology of bearing structure of soft rock roadway with coal seam in deep roof[D]. Xiangtan: Hunan University of Science and Technology, 2022.
|
| [5] |
段燕伟. 不同巷道断面形状对围岩稳定性的数值模拟研究[J]. 价值工程, 2022, 41(6):131-133.
|
|
DUAN Yanwei. Numerical simulation of stability of surrounding rock with different roadway section shapes[J]. Value Engineering, 2022, 41 (6): 131-133.
|
| [6] |
安通. 大断面拱形巷道综掘掘支作业合理空顶距探讨[J]. 江西煤炭科技, 2020(2):28-30.
|
|
AN Tong. Discussion on reasonable empty roof distance of comprehensive excavation and supporting operation in large-scale arched roadway[J]. Jiangxi Coal Science & Technology, 2020 (2): 28-30.
|
| [7] |
杜健. 半煤岩拱形巷道临时支护设备力学分析及优化[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2013.
|
|
DU Jian. The mechanical analysis and optimization of temporary support equipment used in arched seni-coal rock roadway[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning University of Engineering and Technology, 2013.
|
| [8] |
LI Li, XIANG Songkong, WEI Yang, et al. A study of anchor cable and c-shaped tube support for the roadway of shuangliu coal mine[J]. Symmetry, 2023, 15(9):78-85.
doi: 10.3390/sym15010078
|
| [9] |
YU Haijun, LIU Honglin, XIA Yang, et al. A study on the deformation mechanism of the rock surrounding a weakly cemented cross-layer roadway, under tectonic stress[J]. Energies, 2023, 16(6):2546-2 548.
doi: 10.3390/en16010546
|
| [10] |
JIA Ce, LI Sheng, FAN Chaojun, et al. Supporting optimization of thick seam roadway with top coal based on orthogonal matrix analysis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1):933-933.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27817-8
pmid: 36650226
|
| [11] |
任增超. 基于顶板破碎段的掘进巷道支护技术应用[J]. 矿业装备, 2023(11):76-77.
|
|
REN Zengchao. Application of support technology for excavation tunnels based on roof fragmentation section[J]. Mining Equipment, 2023 (11): 76-77.
|
| [12] |
赵兴远. 巷道破坏机理与支护形式的选择[J]. 科技资讯, 2006(27):91-93.
|
|
ZHAO Xingyuan. The mechanism of tunnel failure and the selection of support forms[J]. Technology Information, 2006(27): 91-93.
|
| [13] |
王建霖. 临时支护装置在煤矿掘进工作面的应用[J]. 矿业装备, 2023(12):19-21.
|
|
WANG Jianlin. The application of temporary support devices in coal mine excavation working face[J]. Mining Equipment, 2023 (12): 19-21.
|
| [14] |
程光鹏. 掘进工作面过顶板破碎带支护方式研究[J]. 山西化工, 2023, 43(11):166-168.
|
|
CHENG Guangpeng. Research on support methods for broken zone passing through roof in excavation face[J]. Shanxi Chemical Industry, 2023, 43 (11): 166-168.
|
| [15] |
王建波, 李洋, 常庆. 基于数值模拟的软岩巷道支护优化研究[J]. 山东煤炭科技, 2023, 41(11):57-60.
|
|
WANG Jianbo, LI Yang, CHANG Qing. Optimization study of soft rock roadway support based on numerical simulation[J]. Shandong Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 41 (11): 57-60.
|