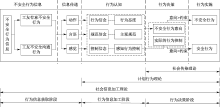
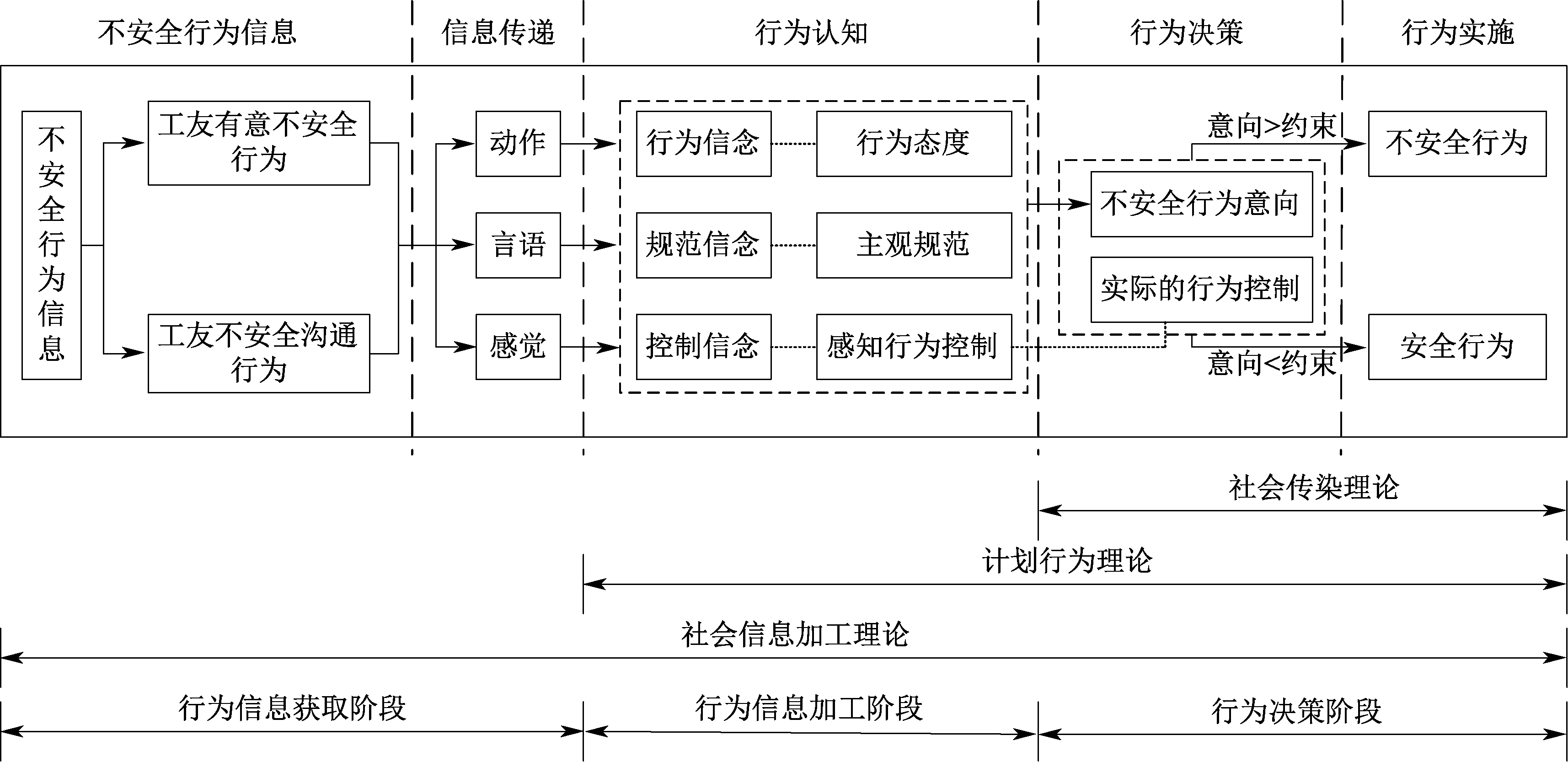
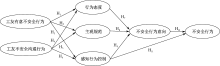
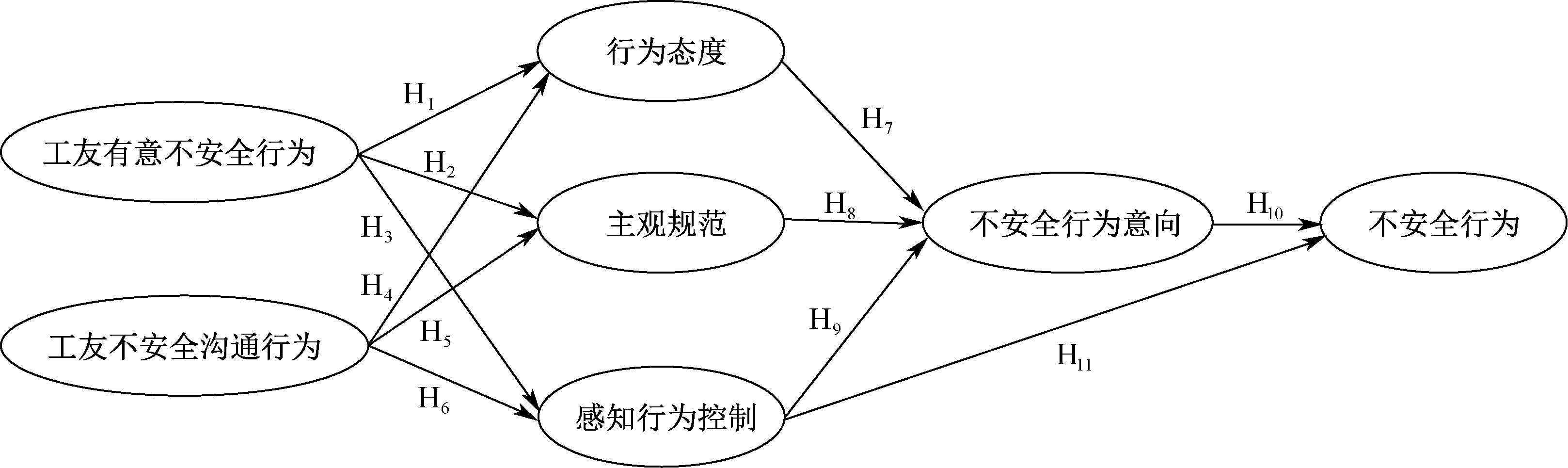
| [1] |
MITROPOULOS P, ABDELHAMID T S, HOWELL G A. Systems model of construction accident causation[J]. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 2005, 131(7):816-825.
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9364(2005)131:7(816)
|
| [2] |
HASLAM R A, HIDE S A, GIBBA G F, et al. Contributing factors in construction accidents[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2005, 36(4):401-415.
doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2004.12.002
pmid: 15892935
|
| [3] |
FERGUSON M J. From bad to worse: a social contagion model of organizational misbehavior[D]. Nashville: Vanderbilt University, 2007.
|
| [4] |
章少康, 谭钦文, 刘娟, 等. 基于大五人格特质理论的有意不安全行为研究[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2020, 46(6):51-55.
|
|
ZHANG Shaokang, TAN Qinwen, LIU Juan, et al. A study of intentional unsafe behavior based on big-five personality trait theory[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 46(6):51-55.
|
| [5] |
周彪, 吴春林, 汪涛, 等. 建设项目员工责任心对安全行为的影响[J]. 土木工程学报, 2018, 51(8):89-95.
|
|
ZHOU Biao, WU Chunlin, WANG Tao, et al. The influence of conscientiousness to safety behavior in construction projects[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2018, 51(8):89-95.
|
| [6] |
DONG Shuang, LI Heng, SKITMORE M, et al. An experimental study of intrusion behaviors on construction sites:the role of age and gender[J]. Safety Science, 2019, 115:425-434.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2019.02.035
|
| [7] |
叶贵, 越宏哲, 冯新怡, 等. 建筑工人不安全行为的认知失效致因仿真研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(11):6-12.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.11.002
|
|
YE Gui, YUE Hongzhe, FENG Xinyi, et al. Simulation study on causes of cognitive failure of construction workers' unsafe behavior[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(11):6-12.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.11.002
|
| [8] |
杨高升, 程欣. 专业技能对建筑工人不安全行为的影响:有调节的中介作用[J]. 工程管理学报, 2019, 33(5):130-134.
|
|
YANG Gaosheng, CHENG Xin. The effect of professional skills on the unsafe behaviors of construction workers:a mediating role of regulation[J]. Journal of Engineering Management, 2019, 33(5):130-134.
|
| [9] |
NEWAZ M T, DAVIS P, JEFFERIES M, et al. The psychological contract: a missing link between safety climate and safety behaviour on construction sites[J]. Safety Science, 2019, 112:9-17.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2018.10.002
|
| [10] |
杨振宏, 万雨欣, 马健. 基于多群组SEM的有感领导对群体不安全行为影响研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2017, 17(3):999-1002.
|
|
YANG Zhenhong, WAN Yuxin, MA Jian. Impact of the sensitive leading style on the unsafe behaviors of the workers based on the multi-group SEM[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2017, 17(3):999-1002.
|
| [11] |
HE Changquan, JIA Guangshe, MCCABE B, et al. Relationship between leader-member exchange and construction worker safety behavior: the mediating role of communication competence[J]. International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics, 2021, 27(2):371-383.
doi: 10.1080/10803548.2019.1579484
|
| [12] |
NIKOLAEV B N, WOOD M S. Cascading ripples: contagion effects of entrepreneurial activity on self-employment attitudes and choices in regional cohorts[J]. Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, 2018, 12(4):455-481.
doi: 10.1002/sej.2018.12.issue-4
|
| [13] |
AJZEN I. Perceived behavioral control, self-efficacy, locus of control, and the theory of planned behavior[J]. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 2002, 32(4):665-683.
doi: 10.1111/jasp.2002.32.issue-4
|
| [14] |
陈岩英, 谢朝武, 张凌云, 等. 旅游危机中线上媒体声量信号对潜在旅游者安全沟通行为的影响机制[J]. 南开管理评论, 2020, 23(1):40-52.
|
|
CHEN Yanying, XIE Chaowu, ZHANG Lingyun, et al. The influence mechanism of online media volume signals on potential tourists' safety communication behavior in tourism crisis situation[J]. Nankai Business Review, 2020, 23(1):40-52.
|
| [15] |
杨高升, 杨鹏, 李秀云. 建筑工人流动性对施工安全水平的影响分析[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2015, 11(1):116-120.
|
|
YANG Gaosheng, YANG Peng, LI Xiuyun. Analysis on influence by liquidity of construction workers to construction safety level[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2015, 11(1):116-120.
|
| [16] |
李超平, 徐世勇. 管理与组织研究常用的60个理论[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2019:397-398.
|
| [17] |
AJZEN I. The theory of planned behavior[J]. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 1991, 50(2):179-211.
doi: 10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T
|
| [18] |
程恋军. 矿工不安全行为形成机制及其双重效应研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2015.
|
|
CHENG Lianjun. Research on forming mechanism of miners' unsafe behaviors and its dual effect[D]. Fuxin:Liaoning University of Engineering and Technology, 2015.
|
| [19] |
SIMONS-MORTON B G. Prospective analysis of peer and parent influences on smoking initiation among early adolescents[J]. Prevention Science, 2002, 3(4):275-283.
doi: 10.1023/A:1020876625045
|
| [20] |
叶贵, 陈梦莉, 汪红霞. 建筑工人不安全行为意向TPB修正模型研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2015, 25(1):145-151.
|
|
YE Gui, CHEN Mengli, WANG Hongxia. Study on model for construction workers unsafe behavior intention[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2015, 25(1):145-151.
|
| [21] |
ZHANG Mengchun, FANG Dongping. A cognitive analysis of why Chinese scaffolders do not use safety harnesses in construction[J]. Construction Management and Economics, 2013, 31(3):207-222.
doi: 10.1080/01446193.2013.764000
|
| [22] |
GOH Y M, SA'ADON N F B. Cognitive factors influencing safety behavior at height: a multimethod exploratory study[J]. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 2015, 141(6): DOI: 10.1061/(asce)co.1943-7862.0000972.
|
| [23] |
梁化康. 建筑施工班组内安全违章社会传染机理研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.
|
|
LIANG Huakang. Research on the social contagion mechanism of safety violations within a construction crew[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019.
|
| [24] |
ZOHAR D, LURIA G. The use of supervisory practices as leverage to improve safety behavior: a cross-level intervention model[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2003, 34(5):567-577.
pmid: 14733991
|
| [25] |
CIGULAROV K, CHEN P Y, ROSECRANCE J. The effects of error management climate and safety communication on safety a multi-level study[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2010, 42:1498-1506.
doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2010.01.003
|
| [26] |
程恋军, 仲维清. 矿工不安全行为DARF形成机制实证研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2017, 13(2):107-113.
|
|
CHENG Lianjun, ZHONG Weiqing. Study on DARF formation mechanism of miners' unsafe behavior[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2017, 13(2):107-113.
|
| [27] |
WONG D B, LEE S G. Modelling the predictors of intention in workplace safety compliance of a multi-ethnic workforce[J]. Safety Science, 2016, 88: 155-165.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2016.05.003
|
| [28] |
刘晴. 建筑工人安全公民行为驱动机理及引导策略研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2018.
|
|
LIU Qing. Research on driving mechanism and guiding strategy of safety citizenship behaviors of construction workers[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2018.
|
| [29] |
YU Min, LI Jizu. Psychosocial safety climate and unsafe behavior among miners in China: the mediating role of work stress and job burnout[J]. Psychology, Health & Medicine, 2020, 25(7):793-801.
|
| [30] |
LI Jizu, ZHANG Yaping, WANG Xiaojia, et al. Relationship research between subjective well-being and unsafe behavior of coal miners[J]. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 2017, 13(11):7215-7221.
|
| [31] |
阮国祥. 建筑企业差错管理氛围对员工安全行为影响研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(1):140-145.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.01.025
|
|
RUAN Guoxiang. Research on effects of error management climate onemployees' safety behavior in construction firms[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(1):140-145.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.01.025
|
| [32] |
LIANG Qi, ZHOU Zhiyuan, YE Gui, et al. Unveiling the mechanism of construction workers' unsafe behaviors from an occupational stress perspective: a qualitative and quantitative examination of a stress-cognition-safety model[J]. Safety Science, 2022,145: DOI: 10.1016/j.ssci.2021.105486.
|
| [33] |
COOKE R, SNIEHOTTA F, SCHÜZ B. Predicting binge-drinking behaviour using an extended TPB: examining the impact of anticipated regret and descriptive norms[J]. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 2007, 42(2):84-91.
doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agl115
pmid: 17185302
|
| [34] |
FUGAS C S, SILVA S A, MELIÁ J L. Another look at safety climate and safety behavior: deepening the cognitive and social mediator mechanisms[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2012, 45:468-477.
doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2011.08.013
|
| [35] |
FUGAS C S, SILVA S A, MELIÁ J L. The "is" and the "ought": how do perceived social norms influence safety behaviors at work?[J]. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 2011, 16:67-79.
doi: 10.1037/a0021731
pmid: 21280945
|
| [36] |
DAVIS L E, AJZEN I, SAUNDERS J, et al. The decision of African American students to complete high school: an application of the theory of planned behavior[J]. Journal of Educational Psychology, 2002, 94(4):810-819.
doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.94.4.810
|
| [37] |
HAN H, HSU L T J, SHEU C. Application of the theory of planned behavior to green hotel choice: testing the effect of environmental friendly activities[J]. Tourism Management, 2010, 31(3):325-334.
doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2009.03.013
|
| [38] |
CONNER M, SHEERAN P, NORMAN P, et al. Temporal stability as a moderator of relationships in the theory of planned behaviour[J]. British Journal of Social Psychology, 2000, 39(4):469-493.
doi: 10.1348/014466600164598
|