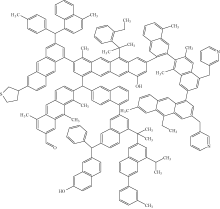
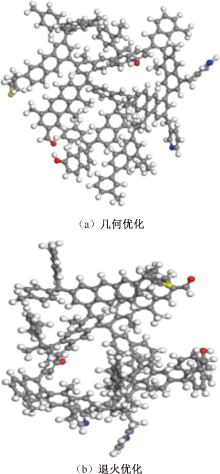
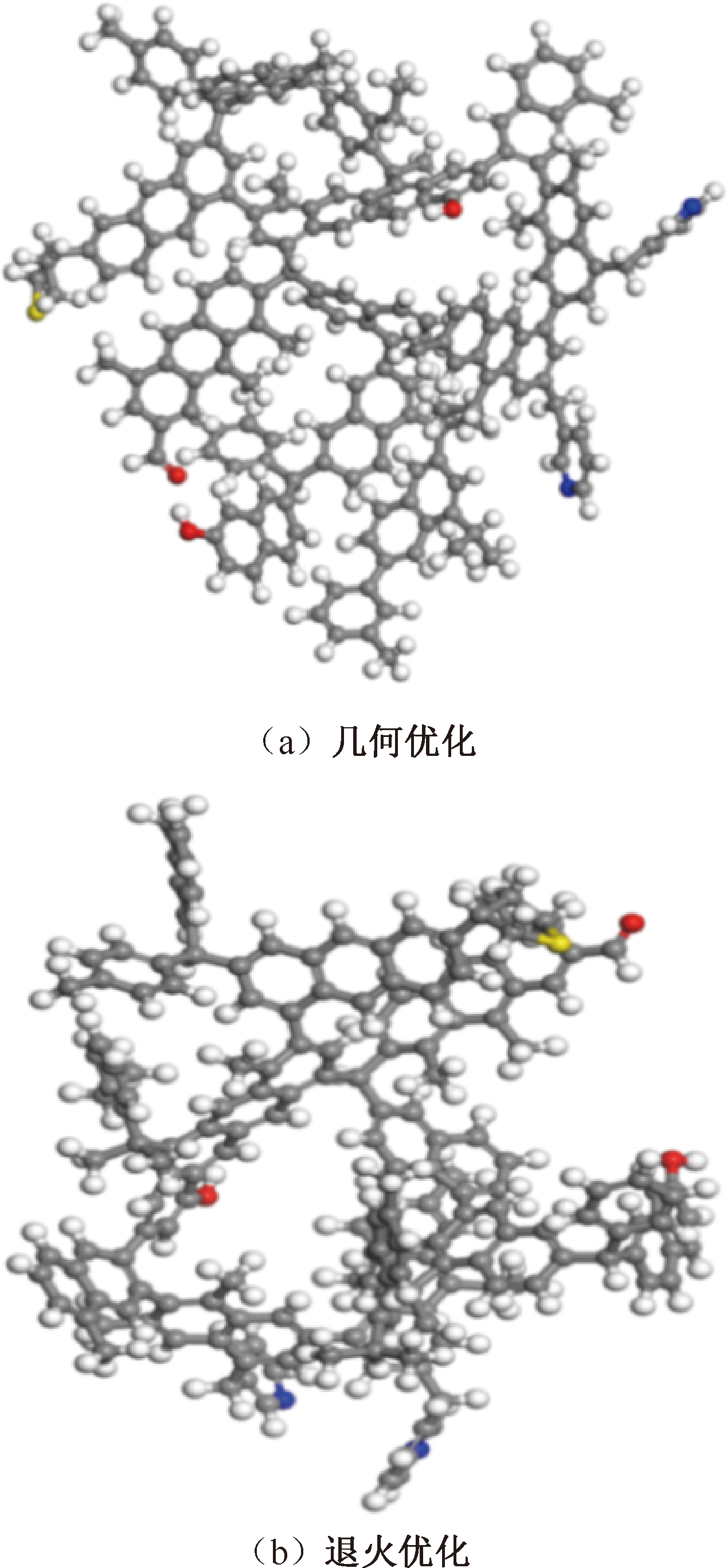
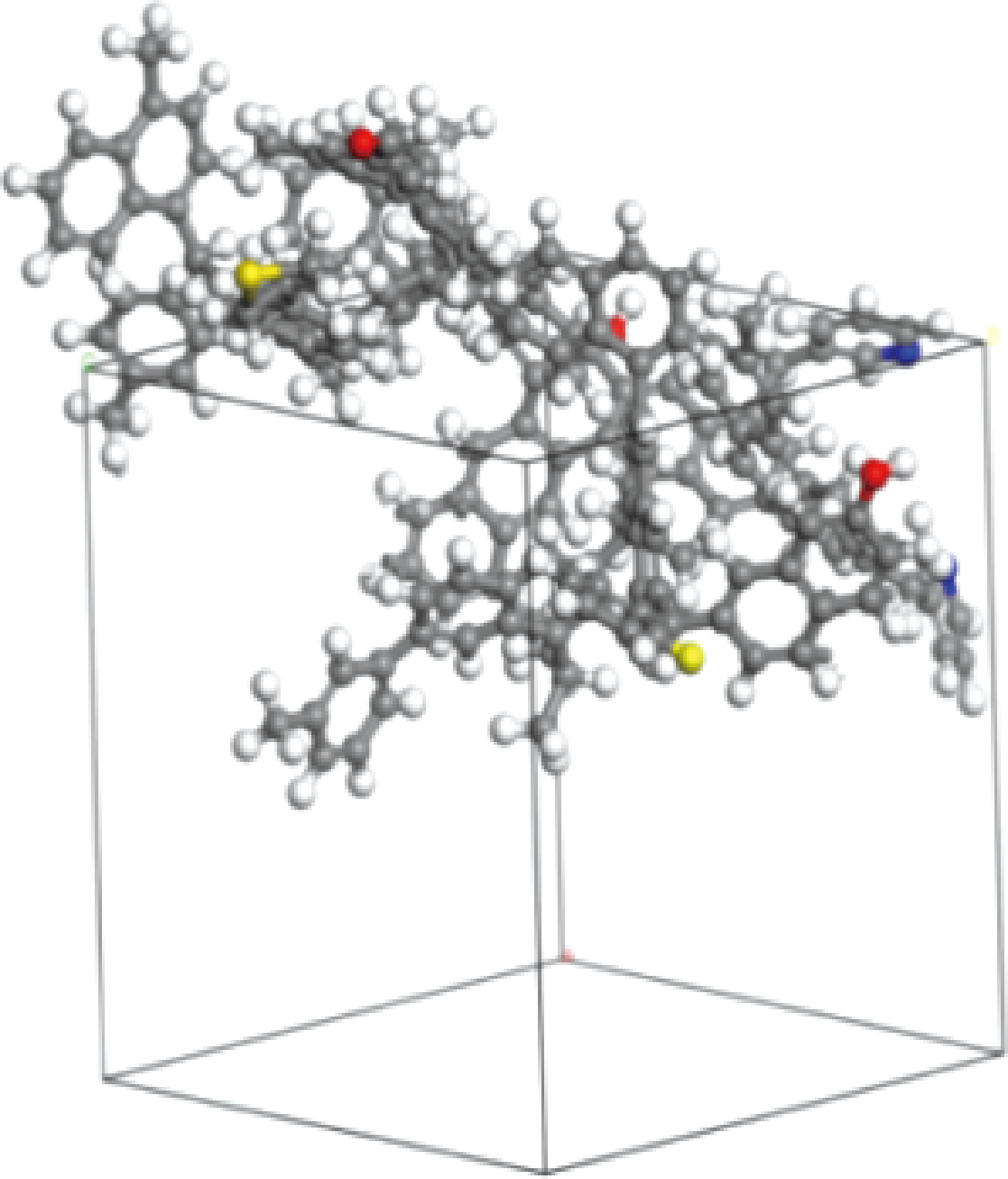
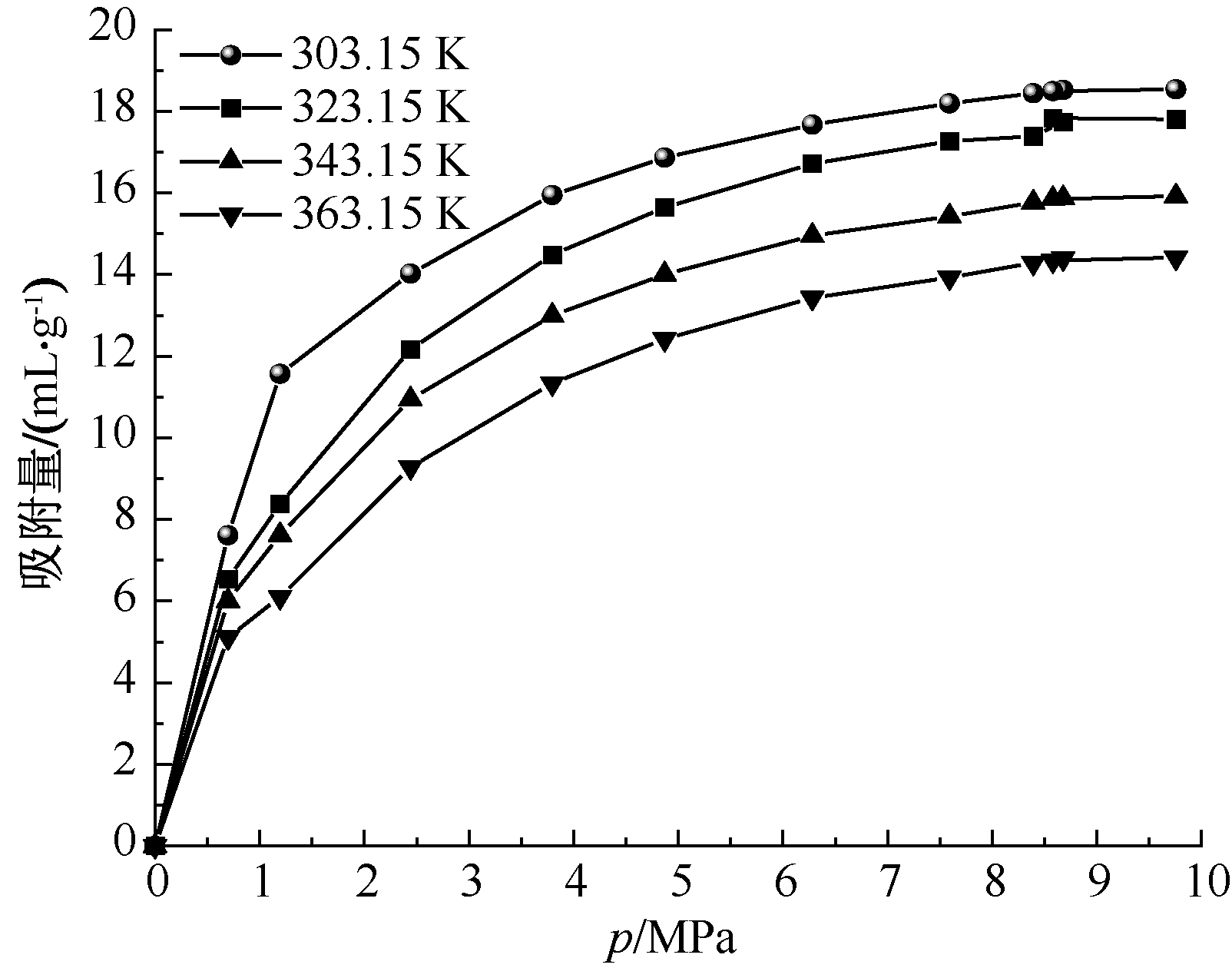
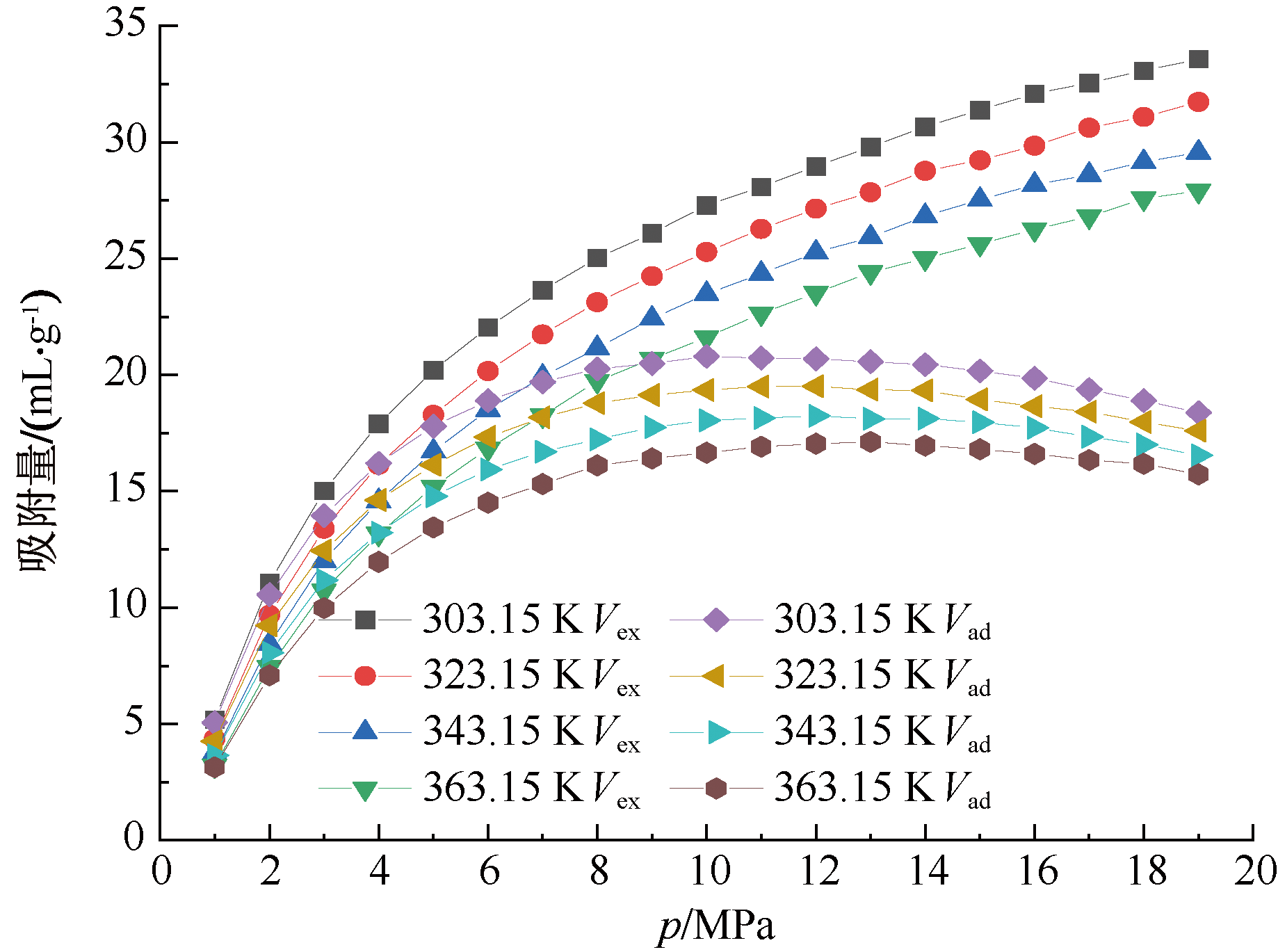
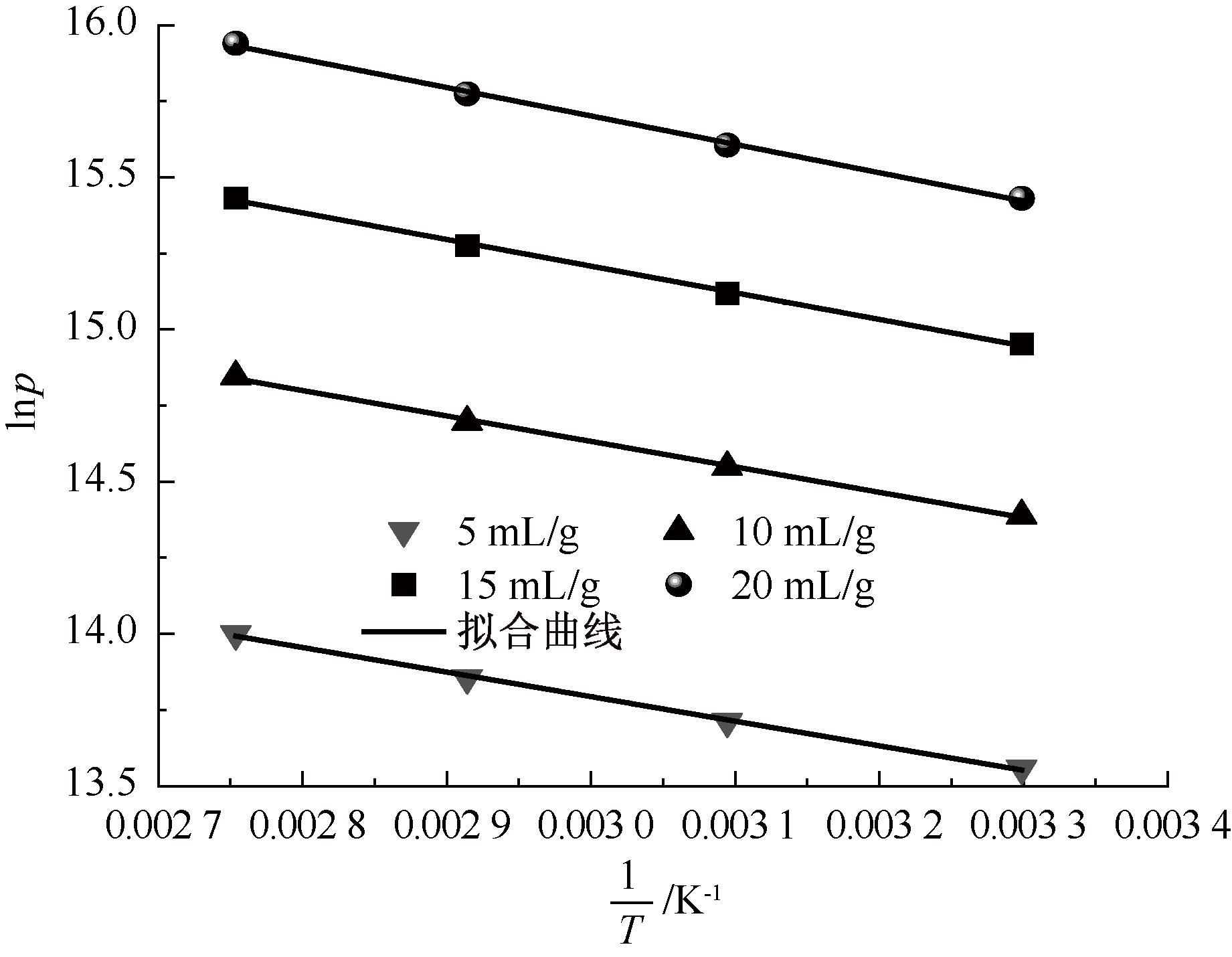
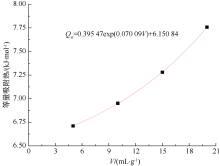
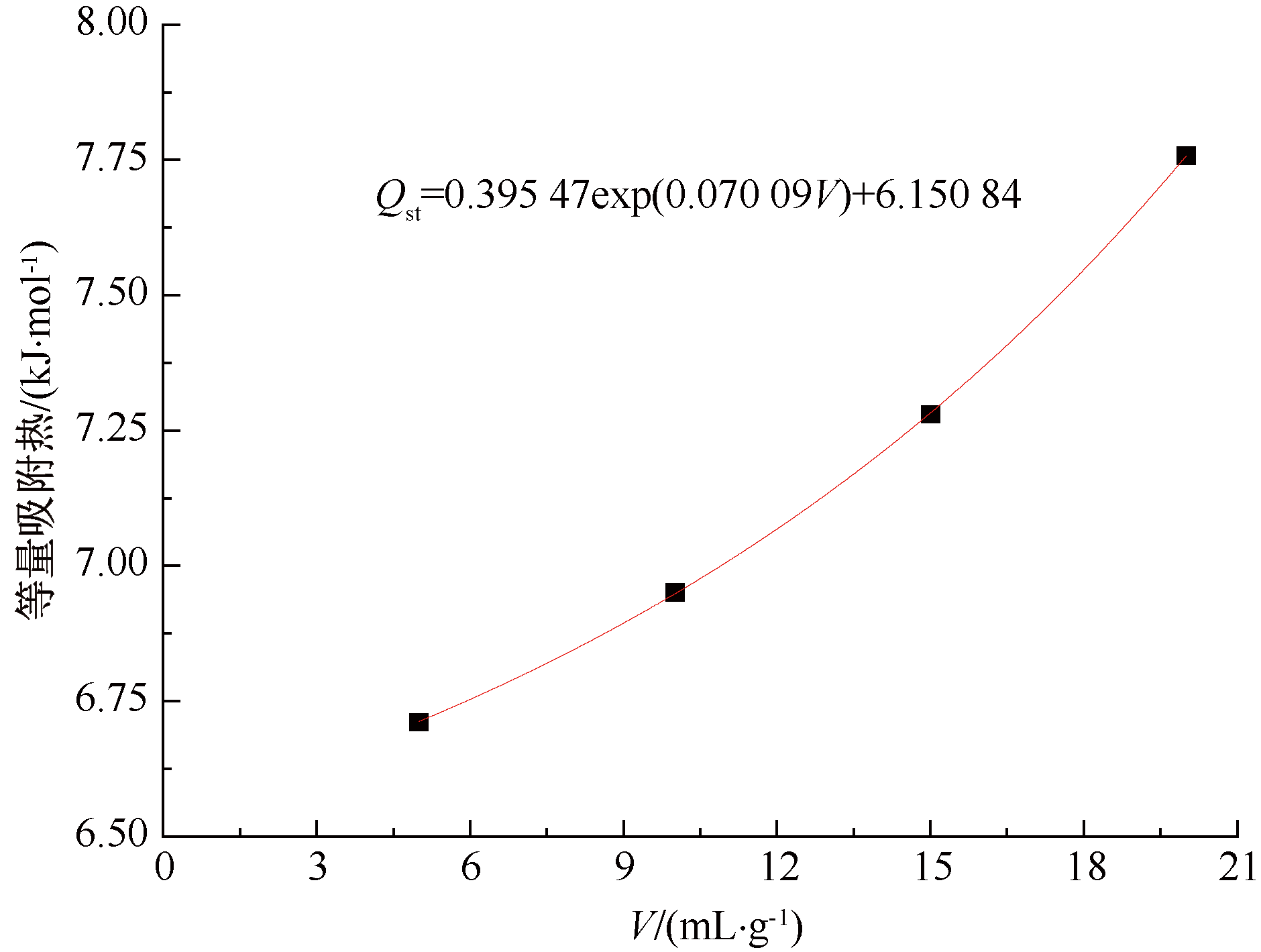
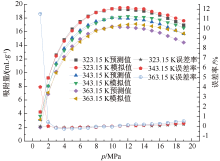
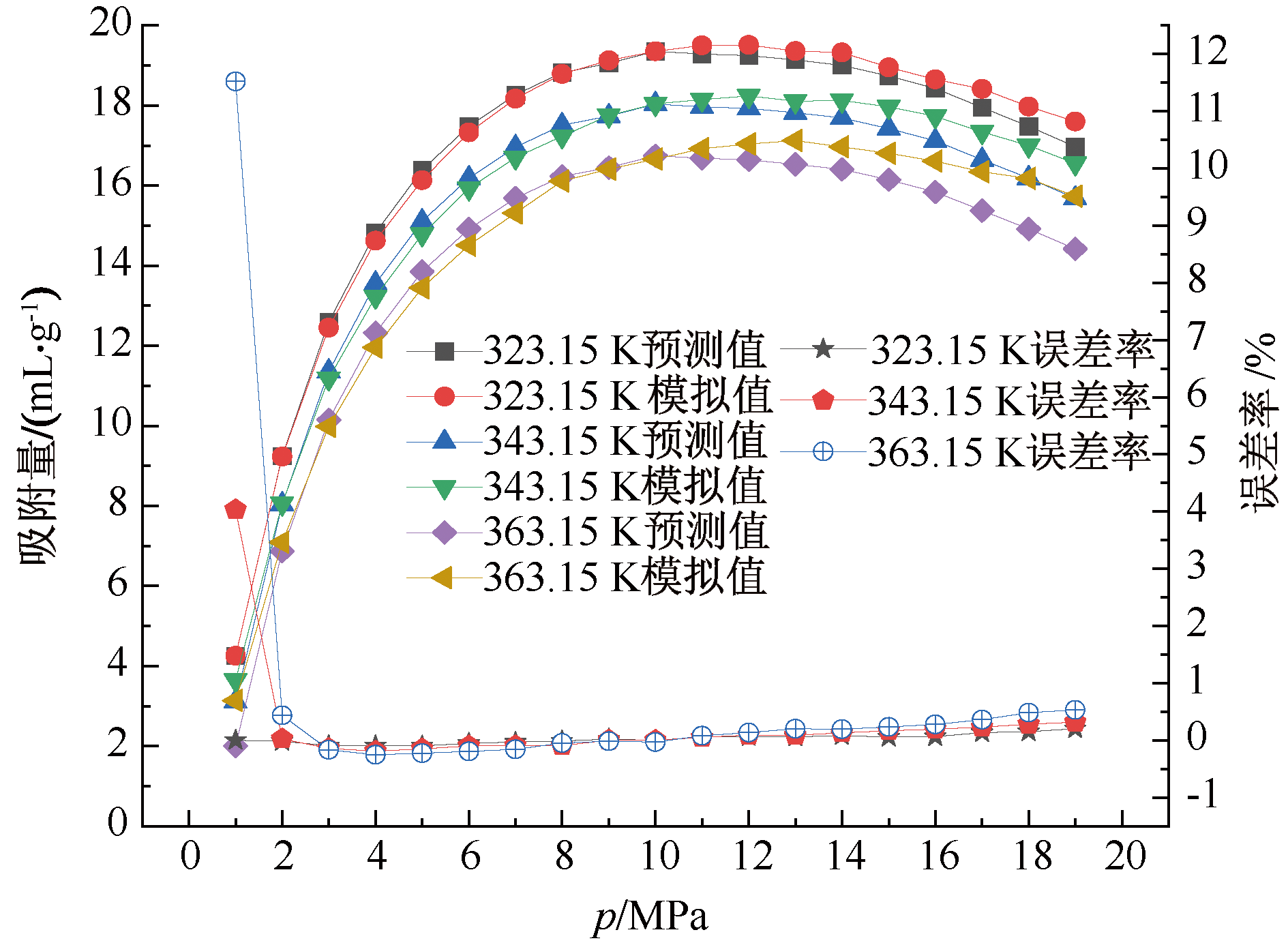
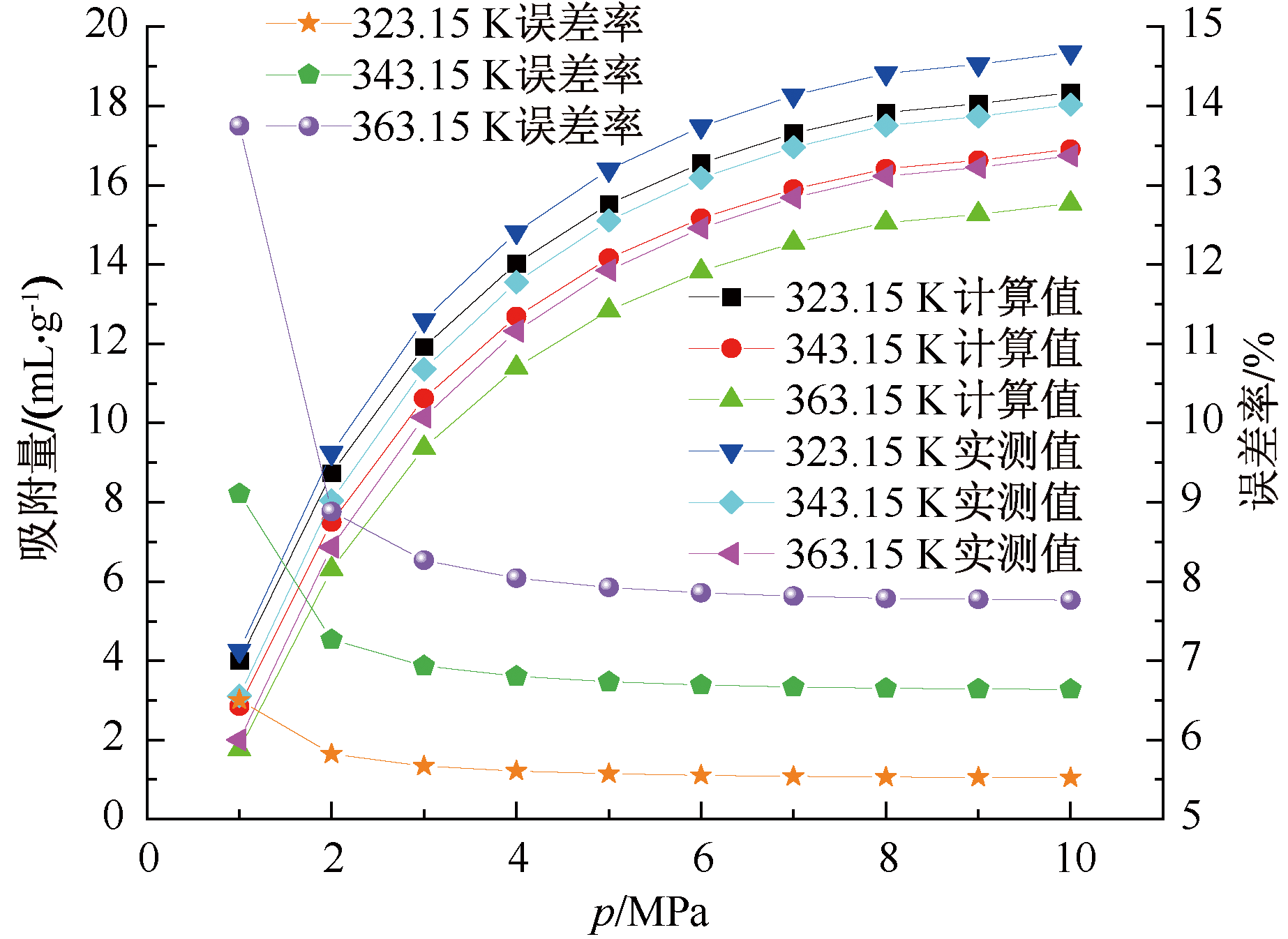
| [1] |
袁亮, 张农, 阚甲广, 等. 我国绿色煤炭资源量概念、模型及预测[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2018, 47(1): 1-8.
|
|
YUAN Liang, ZHANG Nong, KAN Jiaguang, et al. The concept, model and reserve forecast of green coal resources in China[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2018, 47(1): 1-8.
|
| [2] |
史洪恺, 祁云, 张国恩, 等. 组合赋权-灰色聚类的煤与瓦斯突出危险评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33 (增1):52-57.
|
|
SHI Hongkai, QI Yun, ZHANG Guoen, et al. Risk assessment of coal and gas outburst based on combination weighting and grey clustering[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(S1): 52-57.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.S1.0593
|
| [3] |
仇悦, 龙航, 白杨, 等. 温度效应下煤体吸附瓦斯热力学及动力学特征[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(7):147-155.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.07.1934
|
|
QIU Yue, LONG Hang, BAI Yang, et al. Thermodynamic and kinetic characteristics of gas adsorption by coal under temperature effect[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(7):147-155.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.07.1934
|
| [4] |
高宇, 刘佳, 秦跃平. 不同粒径与压力下煤粒瓦斯吸附数学模型研究[J]. 煤矿安全, 2023, 54(7): 109-117.
|
|
GAO Yu, LIU Jia, QIN Yueping. Study on mathematical model of coal particles gas adsorption under different particle sizes and pressures[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(7): 109-117.
|
| [5] |
刘高峰, 李宝林, 张震, 等. 不同变质煤的瓦斯膨胀能演化特征及其突出预测启示[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2023, 51(10): 1-8.
|
|
LIU Gaofeng, LI Baolin, ZHANG Zhen, et al. Gas expansion energy of coals with different metamorphic degrees: evolutionary characteristics and their implications for the outburst prediction[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2023, 51(10): 1-8.
|
| [6] |
岳基伟, 王兆丰, 董家昕, 等. 受载煤自发渗吸过程水分运移规律及其影响机理[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(11): 4069-4082.
|
|
YUE Jiwei, WANG Zhaofeng, DONG Jiaxin, et al. Law of water migration during spontaneous imbibition in loaded coal and its influence mechanism[J]. Journal of Coal Society, 2022, 47(11): 4069-4082.
|
| [7] |
姜海纳, 徐乐华, 程远平. 粉煤粒径对瓦斯吸附平衡时间的影响机制[J]. 煤矿安全, 2021, 52(6): 6-11.
|
|
JIANG Haina, XU Lehua, CHENG Yuanping. Influence of coal particle size on gas adsorption equilibrium time[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(6): 6-11.
|
| [8] |
王思琪, 张瑞林, 周银波. 温度对中等变质程度焦煤中甲烷吸附解吸特征的影响研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保, 2022, 49(6): 57-61, 78.
|
|
WANG Siqi, ZHANG Ruilin, ZHOU Yinbo. Study on the effect of temperature on the adsorption and desorption characteristics of methane in coking coal with medium metamorphic degree[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2022, 49(6): 57-61, 78.
|
| [9] |
SAKUROVS R, DAY S, WEIR S, et al. Temperature dependence of sorption of gases by coals and charcoals[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2008, 73: 250-258.
doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2007.05.001
|
| [10] |
李祥春, 张梦婷, 李忠备, 等. 气体吸附过程中煤比表面Gibbs函数变化规律[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(2): 509-519.
|
|
LI Xiangchun, ZHANG Mengting, LI Zhongbei, et al. Variation law of coal specific surface Gibbs function in gas adsorption process[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(2): 509-519.
|
| [11] |
TANG Xu, WANG Zhaofeng, RIPEPI N, et al. Adsorption affinity of different types of coal: mean isosteric heat of adsorption[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2015, 29(6): 3609-3615.
doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b00432
|
| [12] |
QI Lingling, PENG Xinshan, WANG Zhaofeng, et al. Study on the pore structures and adsorption characteristics of coking coal of Liulin mining in China under the condition of high temperature and high pressure[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2022, 10: DOI: 10.3389/feart.2022.877462.
|
| [13] |
CHEN Xiangjun, NIE Siyu, KANG Ningning. et al. Molecular simulation on adsorption difference of water and methane on long-flame coal[J]. Adsorption Science & Technology, 2023: DOI: 10.1155/2023/2615946.
|
| [14] |
YANG Yanhui, LIN Ling, LI Mengxi, et al. A multi-scale modeling of CH4 and H2O adsorption on coal molecules and the water blocking effect in coalbed methane extraction[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(16):DOI:10.3390/app9163421.
|
| [15] |
YAN Jingxue, JIA Baoshan, LIU Baogang, et al. Simulation study on molecular adsorption of coal in Chicheng coal mine[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(8):DOI:10.3390/molecules28083302.
|
| [16] |
岳基伟, 李宏, 孙永鑫, 等. 煤对甲烷及氘代甲烷吸附性能研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2022, 50(11): 93-99.
|
|
YUE Jiwei, LI Hong, SUN Yongxin, et al. Study on adsorption properties of coal for methane and deuterated methane[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(11): 93-99.
|
| [17] |
MOSHER K, HE Jiajun, LIU Yangyang, et al. Molecular simulation of methane adsorption in micro-and mesoporous carbons with applications to coal and gas shale systems[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2013, 109/110: 36-44.
doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2013.01.001
|
| [18] |
SONG Yu, ZHU Yanming. LI Wu. Macro molecule simulation and CH4 adsorption mechanism of coal vitrinite[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 396: 291-302.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.10.127
|
| [19] |
范志辉. 不同煤阶煤大分子建模及吸附机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.
|
|
FAN Zhihui. Study on macromolecular modeling and adsorption mechanism of coal with different coal rank[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020.
|
| [20] |
YAN Hongwei, NIE Baisheng, PENG Chao. Molecular model construction of low-quality coal and molecular simulation of chemical bond energy combined with materials sudio[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(21): 17 602-17 616.
|
| [21] |
苏现波, 林萌, 林晓英, 等. 吸附势理论在煤层甲烷吸附中的应用[J]. 中国煤层气, 2006, 3(2): :28-30.
|
|
SU Xianbo, LIN Meng, LIN Xiaoying, et al. Application of adsorption potential theory in coalbed methane adsorption[J]. China Coalbed Methane, 2006, 3(2):28-30.
|
| [22] |
薛培, 张丽霞, 梁全胜, 等. 页岩吸附超临界CH4的热力学特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(9): 1261-1270.
|
|
XUE Pei, ZHANG Lixia, LIANG Quansheng, et al. Thermodynamic characteristics of shale adsorption of supercritical CH4[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(9): 1261-1270.
|
| [23] |
李树刚, 白杨, 林海飞, 等. CH4、CO2和N2多组分气体在煤分子中吸附热力学特性的分子模拟[J]. 煤炭学报, 2018, 43(9): 2476-2483.
|
|
LI Shugang, BAI Yang, LIN Haifei, et al. Molecular simulation of adsorption thermodynamic properties of CH4, CO2 and N2 multicomponent gases in coal molecules[J]. Chinese Journal of Coal, 2018, 43(9): 2476-2483.
|