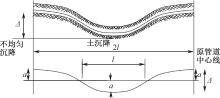
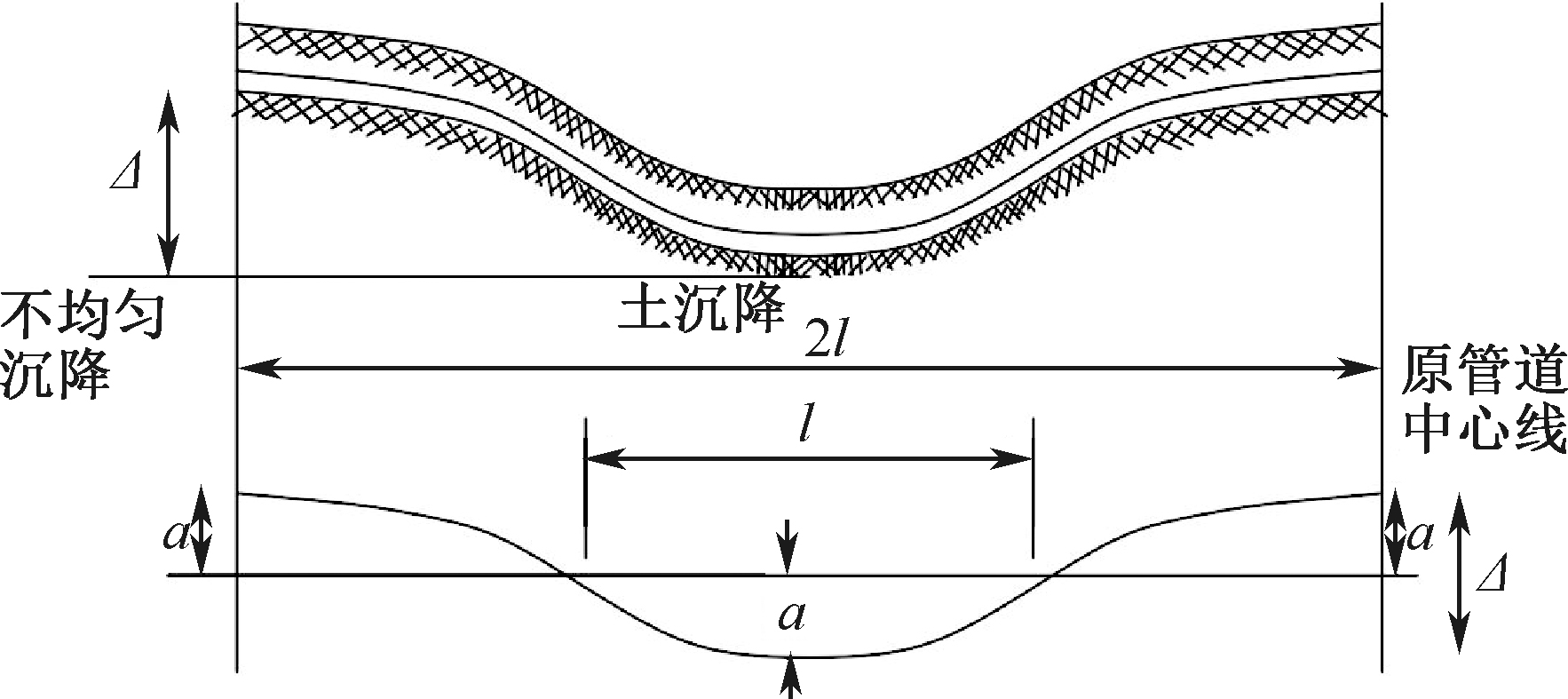
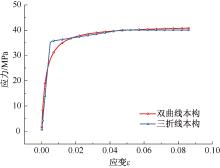
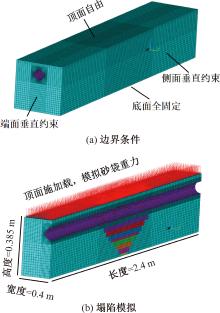
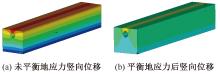
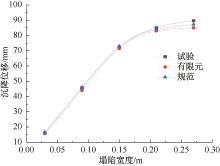
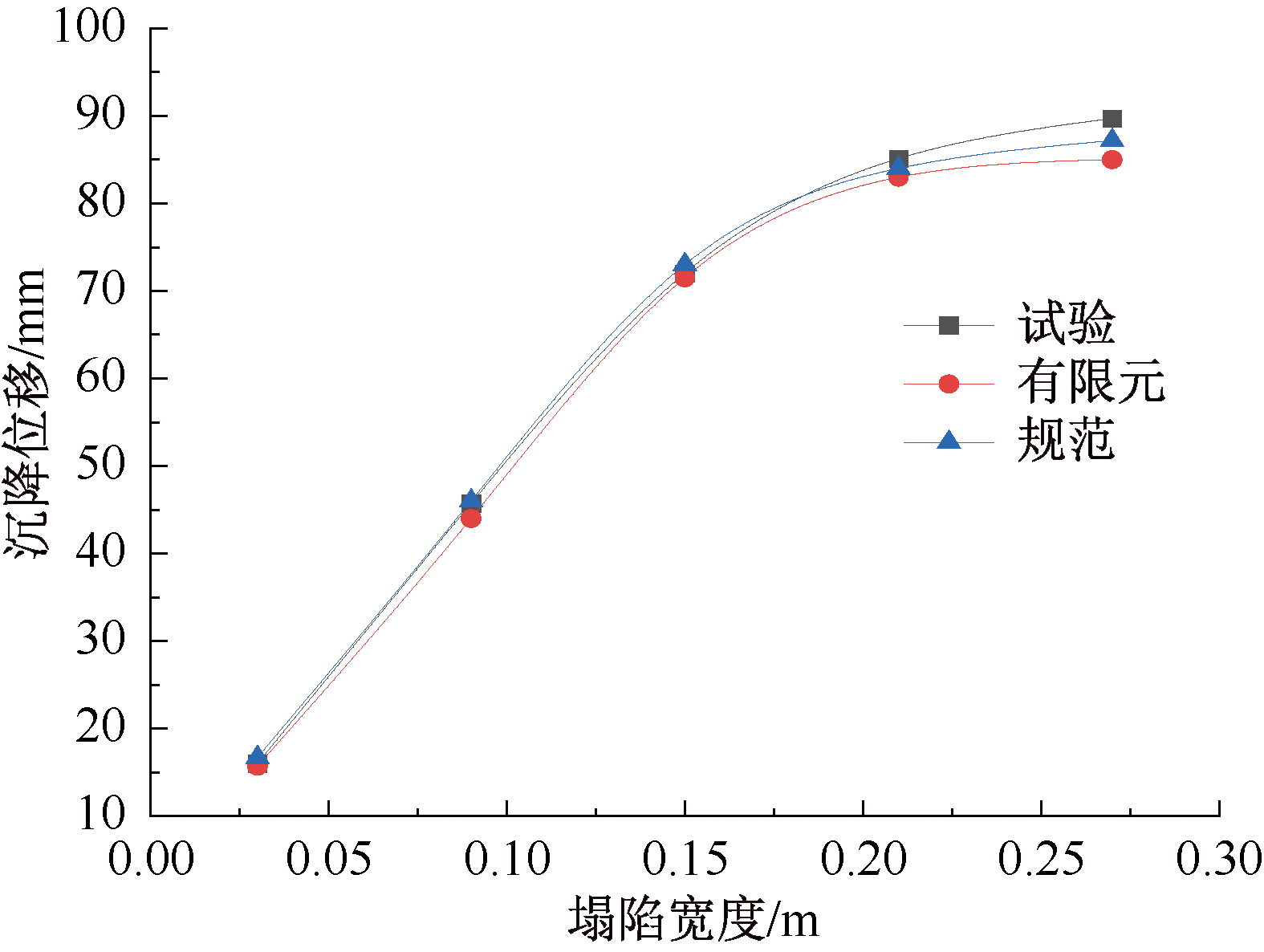
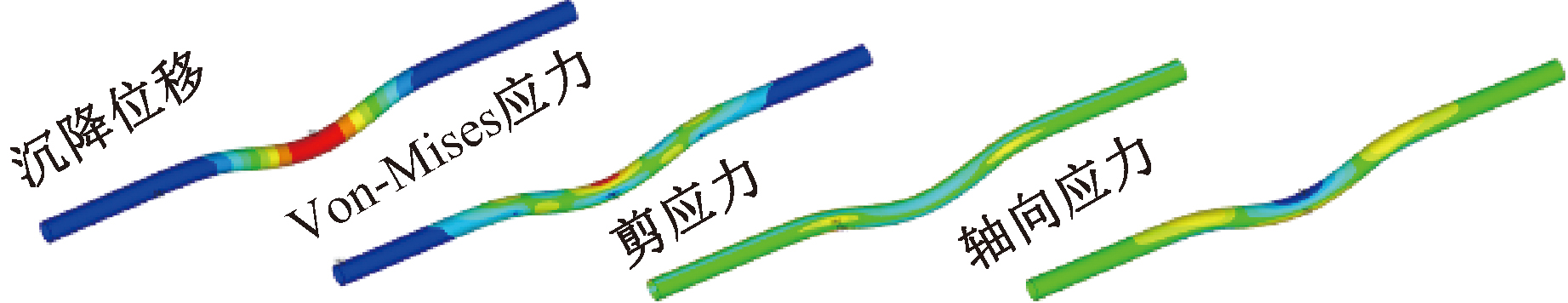
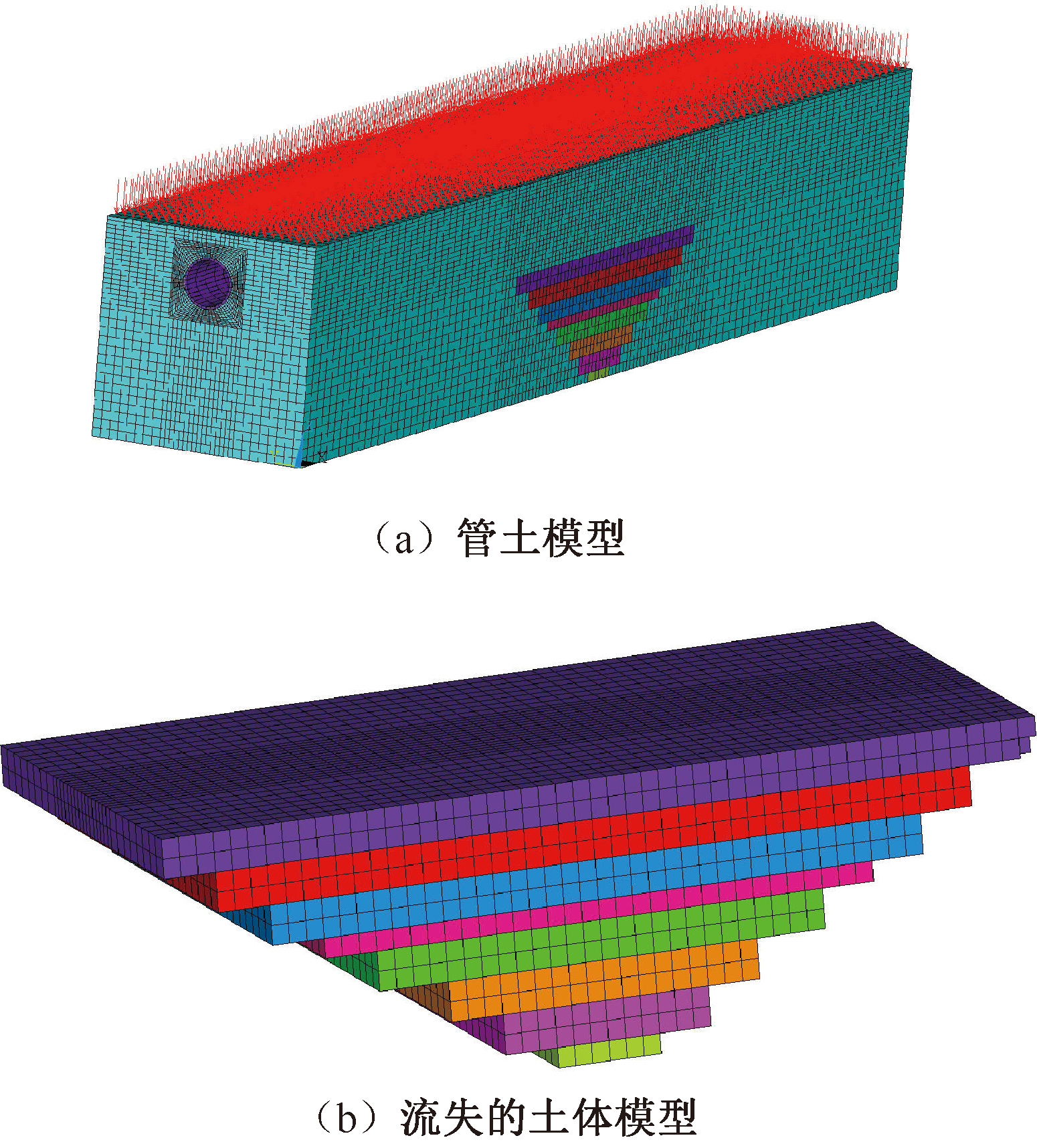
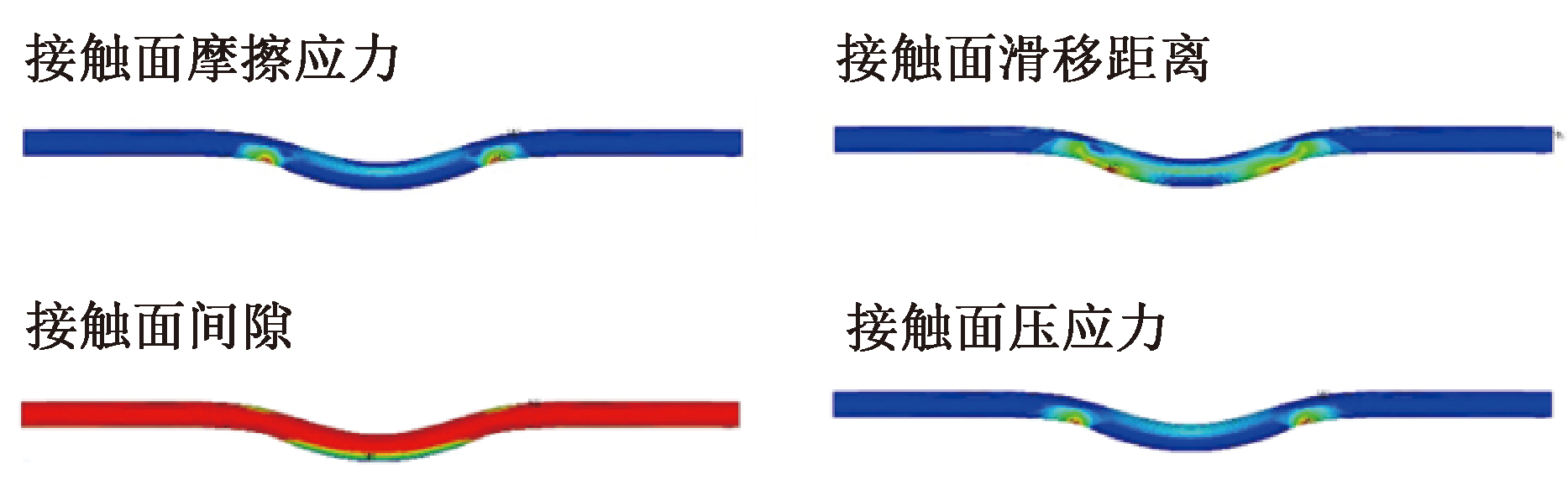
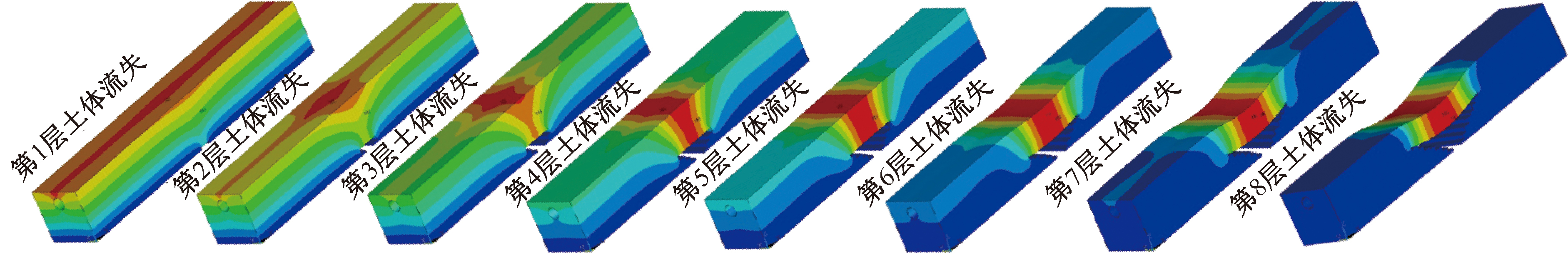
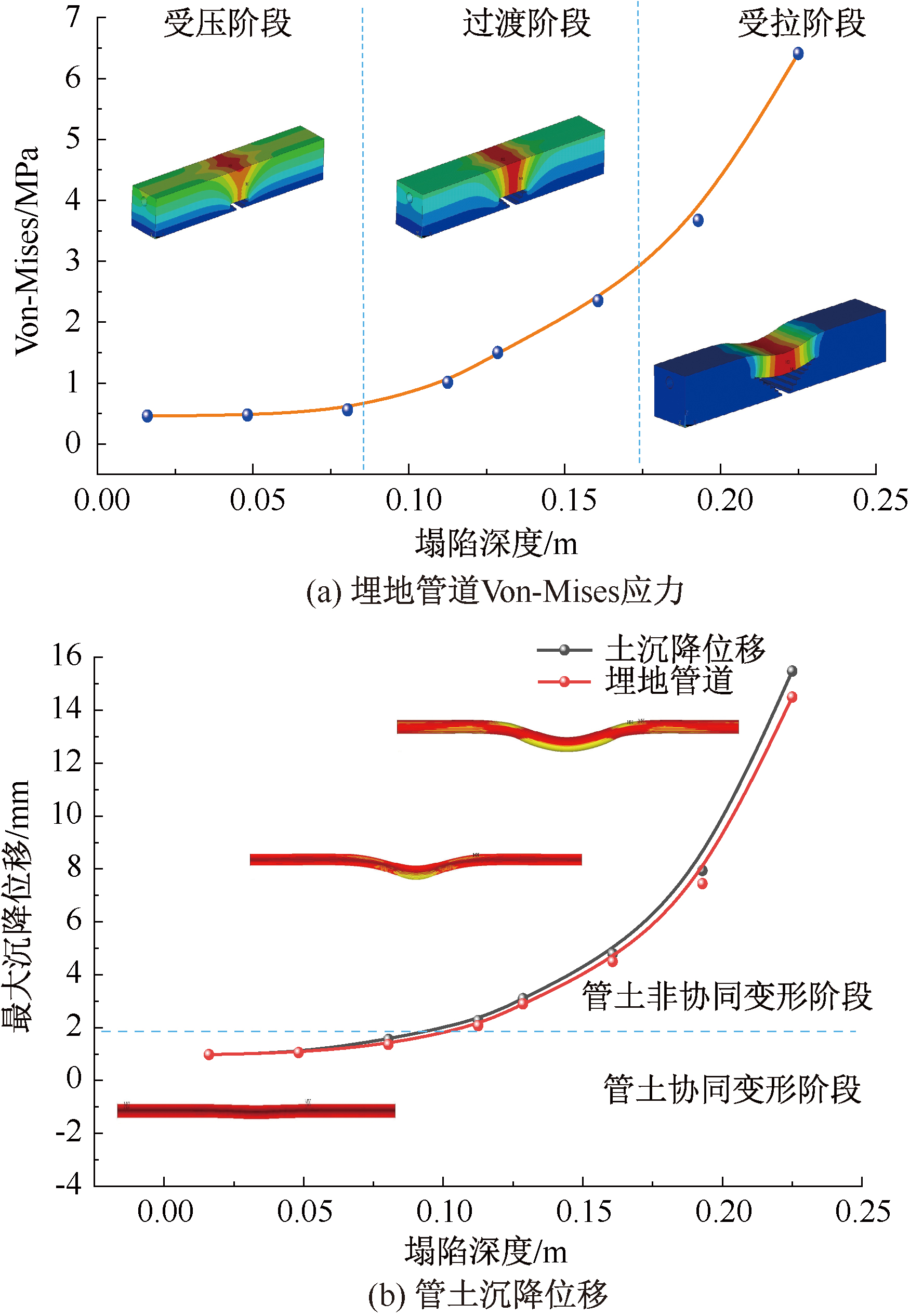
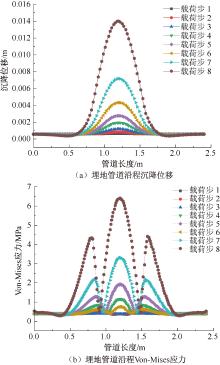
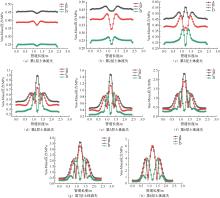
| [1] |
李乔楚, 杨瀚匀. 土体塌陷作用下埋地管道力学分析研究现状[J]. 焊管, 2022, 45(7):12-18,31.
|
|
LI Qiaochu, YANG Hanyun. Research status of mechanical analysis of buried pipeline under soil collapse[J]. Welded Pipe and Tube, 2022, 45(7):12-18,31.
|
| [2] |
殷鹰, 蓝朝逊, 李俊, 等. 埋地PE燃气管道地质沉降破坏数值分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(10):18-23.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.10.004
|
|
YIN Ying, LAN Chaoxun, LI Jun, et al. Numerical analysis of geological settlement failure of buried PE gas pipeline[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(10):18-23.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.10.004
|
| [3] |
KWAK T Y, WOO S I, KIM J, et al. Model test assessment of the generation of underground cavities and ground cave-ins by damaged sewer pipes[J]. Soils and Foundations, 2019, 59(3):586-600.
|
| [4] |
任建东, 王文, 董淼, 等. 开采沉陷区埋地管道变形及力学特征分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(10):82-89.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.10.012
|
|
REN Jiandong, WANG Wen, DONG Miao, et al. Analysis of deformation and mechanical characteristics of buried pipelines in mining subsidence areas[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(10):82-89.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.10.012
|
| [5] |
刘啸奔, 王宝栋, 张东, 等. 地表载荷作用下含缺陷燃气管道安全评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(10):127-135.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.018
|
|
LIU Xiaoben, WANG Baodong, ZHANG Dong, et al. Safety evaluation of gas pipelines with defects under surface load[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(10):127-135.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.018
|
| [6] |
李乔楚, 何沙. 基于单元生死技术的岩溶区域PE管道应力分析[J]. 应用力学学报, 2021, 38(4):1512-1522.
|
|
LI Qiaochu, HE Sha. Stress analysis of PE pipelines in karst areas based on unit life and death technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2021, 38(4):1512-1522.
|
| [7] |
潘钦锋, 张丙强, 黄志斌. 隧道下穿诱发既有管道-土体非协调变形解析研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(3):637-645.
|
|
PAN Qinfeng, ZhANG Bingqiang, HUANG Zhibin. Analytical study for uncoordinated interaction of existing tunnel-soil induced by tunnelling underneath[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(3):637-645.
|
| [8] |
伍颖, 李都. 基于生死单元技术的河流穿越管道力学规律研究[J/OL]. 应用力学学报:1-14[2023-12-24]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1112.O3.20230720.1013.002.html.
|
|
WU Ying, LI Du. Study on the mechanical laws of river crossing pipeline based on life and death units technology[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics:1-14[2023-12-24]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1112.O3.20230720.1013.002.html.
|
| [9] |
杨朝娜, 白晓红. 地基塌陷过程中埋地管线的有限元分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(33):266-271.
|
|
YANG Zhaona, BAI Xiaohong. Numerical Analysis for influnce of foundation collaps on buried pipelines[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(33):266-271.
|
| [10] |
MOHITOUR M, GOLSHAN H, MURRAY A, et al. Pipeline design & construction:a practical approach[M]. New York: American Socieiy of Mechanical Engineers Press, 2000:71-74.
|
| [11] |
LI Xiaoli, LI Chen, LIU Xiaoyan, et al. Mechanical simulation and electrochemical corrosion in a buried pipeline with corrosion defects situated in permafrost regions[J]. Surface Review and Letters, 2021, 28(3): DOI: 10.1142/s0218625x21500025.
|
| [12] |
SULEIMAN M T, COREE B J. Constitutive model for high density polyethylene material: systematic approach[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2004, 16(6):511-515.
|
| [13] |
刘爱华, 杨清, 吴均平. ANSYS三维地应力场数值模拟方法应用研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2013, 19(2):133-142.
|
|
LIU Aihua, YANG Qing, WU Junping. A practical ansys 3-D numerical simulation method for in-situ stress field[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2013, 19(2):133-142.
|
| [14] |
胡长明, 袁一力, 梅源, 等. 基于ABAQUS的地层-结构法模型的地应力平衡方法研究[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2018, 55(4):76-86.
|
|
HU Changming, YUAN Yili, MEI Yuan, et al. Initial geo-stress balance method for the finite-element model using the stratum-structure method[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2018, 55(4):76-86.
|
| [15] |
ZHANG Jie, XIE Rui, ZHENG Ting, et al. Buckling behavior of buried pipe crossing stratum subsidence area[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2022, 135: DOI: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106130.
|