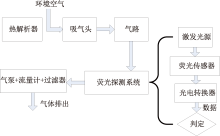
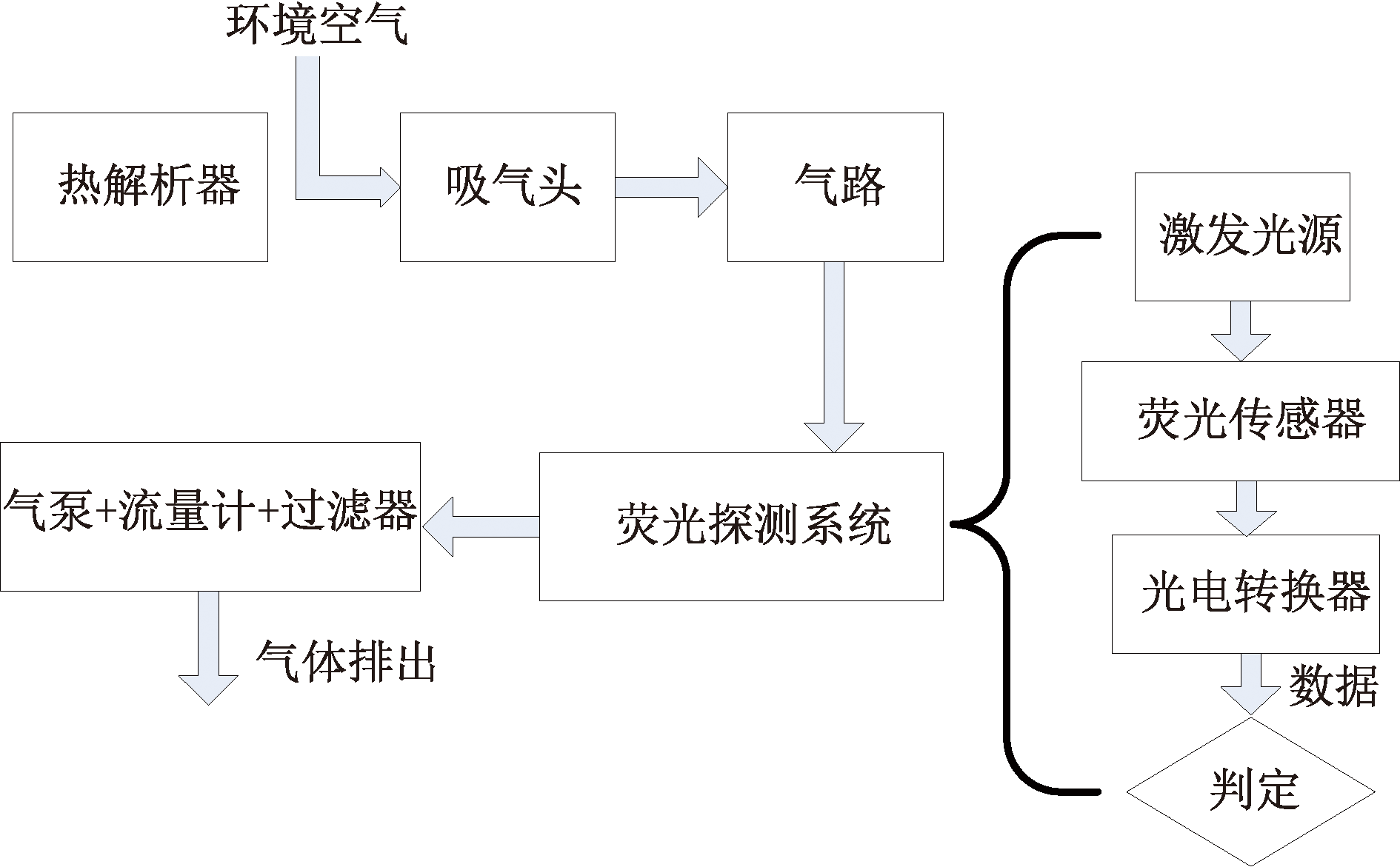
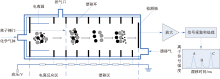
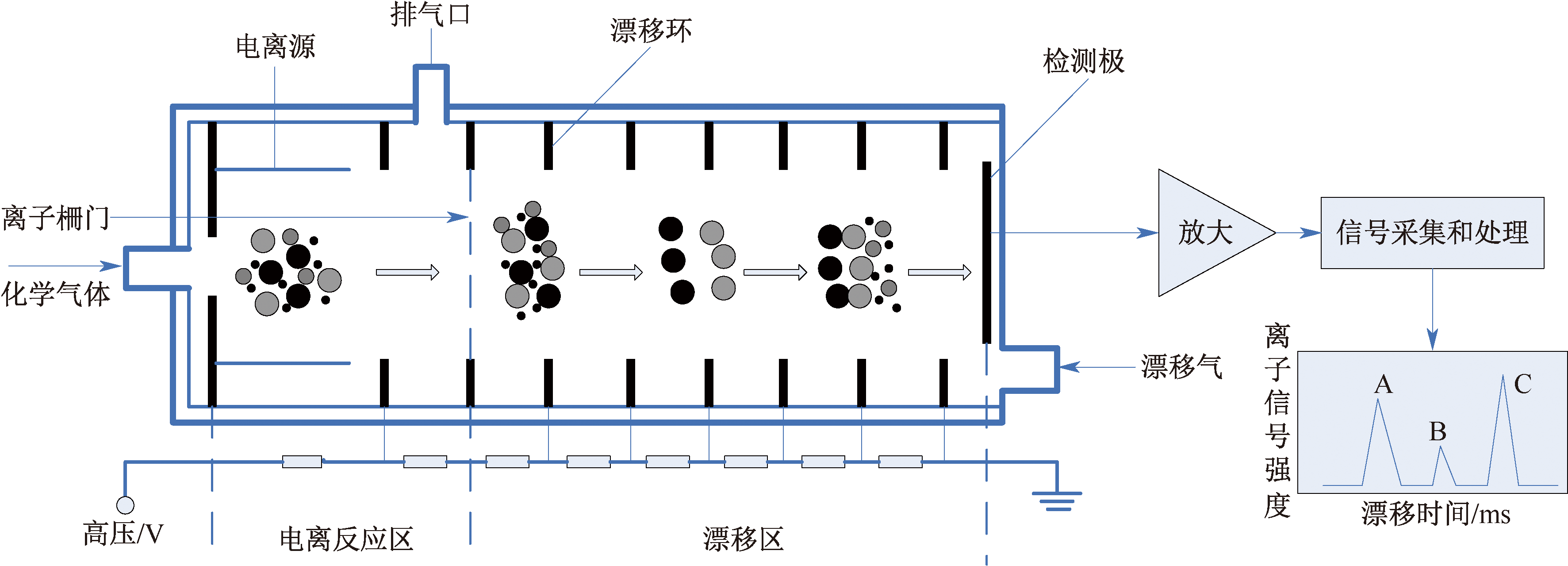
| [1] |
魏琳, 李丽华, 秦立强, 等. 城市地铁恐怖袭击事件应急能力综合评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(7):213-221.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.07.2285
|
|
WEI Lin, LI Lihua, QIN Liqiang, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of emergency response capability of urban subway terrorist attacks[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(7): 213-221.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.07.2285
|
| [2] |
许兴鹏, 许清风, 房志明, 等. 全球恐怖袭击发展趋势与伤亡风险分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(6):170-175.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.06.022
|
|
XU Xingpeng, XU Qingfeng, FANG Zhiming, et al. Development trend of global terrorist attacks and analysis on casualty risk[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(6): 170-175.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.06.022
|
| [3] |
US State Department. Global terrorism index 2013[R], 2014.
|
| [4] |
黄杰, 张显峰. 以南疆为例的区域暴恐袭击风险评估[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(2):192-199.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.02.026
|
|
HUANG Jie, ZHANG Xianfeng. Risk assessment of regional violent terrorist attacks in southern Xinjiang[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(2):192-199.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.02.026
|
| [5] |
方子龙. 兰姆波型声表面波爆炸物传感器研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2023.
|
|
FANG Zilong. Research on lamb type surface acoustic wave explosive sensor[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2023.
|
| [6] |
陈瑞. 面向安检透视成像应用的闪烁体光子计数X射线探测器[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2023.
|
|
CHEN Rui. A scintillation photon-counting X-ray detector for security inspection imaging[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2023.
|
| [7] |
周烨. 近场毫米波人体成像仿真设计与优化研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2020.
|
|
ZHOU Ye. Research on simulation design and optimization of near-field millimeter wave personnel screening[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020.
|
| [8] |
刘伏龙, 王浩然, 薄楠, 等. 基于核共振吸收法开展爆炸物检测的原理验证研究[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2022, 56(增1):258-264.
|
|
LIU Fulong, WANG Haoran, BO Nan, et al. Proof-of-principle study of explosive detection based on nuclear resonance absorption[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2022, 56(S1): 258-264.
|
| [9] |
华仁军, 刘伟鹏, 许鑫鑫, 等. 核电四极矩共振信号强度检测模型修正[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2021, 41(3):524-527.
|
|
HUA Renjun, LIU Weipeng, XU Xinxin, et al. Modification of signal strength detection model for nuclear quadrupole resonance[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2021, 41(3): 524-527.
|
| [10] |
谷天予, 张大成, 冯中琦, 等. 痕量爆炸物的激光诱导击穿光谱快速鉴别方法[J]. 现代应用物理, 2023, 14(2):106-111,132.
|
|
GU Tianyu, ZHANG Dacheng, FENG Zhongqi, et al. Identification of trace explosives by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2023, 14(2): 106-111, 132.
|
| [11] |
叶倩, 洪欢欢, 周峰, 等. 基于机器学习的直接电离质谱爆炸物检测方法[J]. 分析测试学报, 2021, 40(4):589-595.
|
|
YE Qian, HONG Huanhuan, ZHOU Feng, et al. Detection of explosives by direct ionization mass spectrometry based on machine learning algorithm[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2021, 40(4): 589-595.
|
| [12] |
吴昊天, 王广发, 窦新存. 比色法在爆炸物检测中的研究进展[J]. 分析测试学报, 2021, 40(4):468-477.
|
|
WU Haotian, WANG Guangfa, DOU Xincun. Advances on colorimetry in explosives detection[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2021, 40(4): 468-477.
|
| [13] |
孙宁, 胡庭溪, 徐澍, 等. 基于远程遥控方式训练松鼠识别毒品和爆炸物气味[J]. 中国药物依赖性杂志, 2024, 33(1):28-35.
|
|
SUN Ning, HU Tingxi, XU Shu, et al. Experiment of training squirrels to recognize the odor of drugs and explosives based on remote control[J]. Chinese Journal of Drug Dependence, 2024, 33(1): 28-35.
|
| [14] |
窦新存, 王广发, 代卓华. 非制式爆炸物比色/荧光传感研究进展(特邀)[J]. 光子学报, 2022, 51(8):121-135.
|
|
DOU Xincun, WANG Guangfa, DAI Zhuohua. Recent progress in colorimetric/fluorescent sensing toward improvised explosives (invited)[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2022, 51(8): 121-135.
|
| [15] |
程传钦. 高光稳定性共组装荧光传感材料的开发及在爆炸物检测方面的应用[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2022.
|
|
CHENG Chuanqin. Development of high-photostability co-assembled fluorescence sensing materials and their application in explosives detection[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022.
|
| [16] |
金洁, 疏天民. 离子迁移管中湿度变化对毒品和烟酰胺检测的影响[J]. 分析试验室, 2021, 40(9):1 044-1 048.
|
|
JIN Jie, SHU Tianmin. Effect of humidity changes in ion migration tubes on drug and nicotinamide detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2021, 40(9):1 044-1 048.
|
| [17] |
代渐雄, 赵忠俊, 朱爽, 等. 微波诱导等离子体离子迁移谱用于痕量爆炸物检测的研究[J]. 分析化学, 2018, 46(8):1 238-1 244.
|
|
DAI Jianxiong, ZHAO Zhongjun, ZHU Shuang, et al. Microwave induced plasma ionization ion mobility spectrometry for detection of trace explosives[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(8): 1 238-1 244.
|
| [18] |
金洁, 尤晓明. 离子迁移谱(第三版)[M]. 上海: 复旦大学出版社, 2021:2-3.
|
| [19] |
薛伟. 有机聚合物复合荧光纤维及其传感性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京邮电大学, 2020.
|
|
XUE Wei. Organic polymer composite fluorescence fibers and their sensing properties[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2020.
|
| [20] |
郭海军, 吴昱辰, 唐寒露, 等. HMX基钝感传爆药制备技术[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(2):139-144.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.02.019
|
|
GUO Haijun, WU Yuchen, TANG Hanlu, et al. Preparation technology of HMX-based insensitive booster explosives[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(2): 139-144.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.02.019
|
| [21] |
母鸿斌. 新型三过氧化三丙酮(TATP)荧光探针的设计、合成与性能研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2022.
|
|
MU Hongbin. Design, synthesis and performance study of novel fluorescent probes for triacetone triperoxide (TATP)[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2022.
|