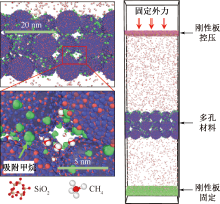
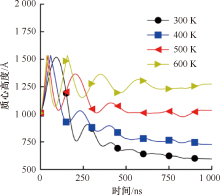
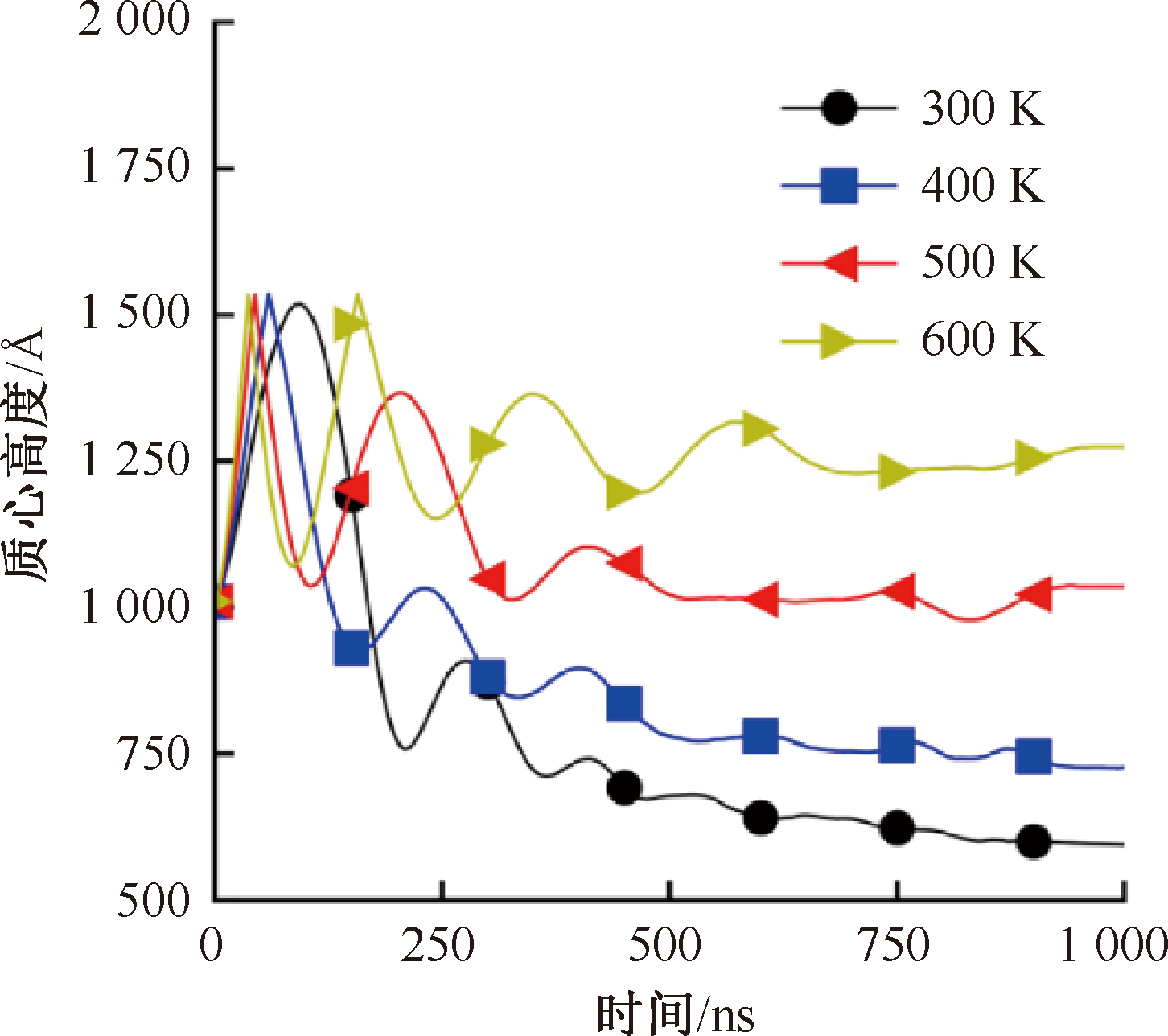
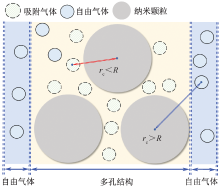
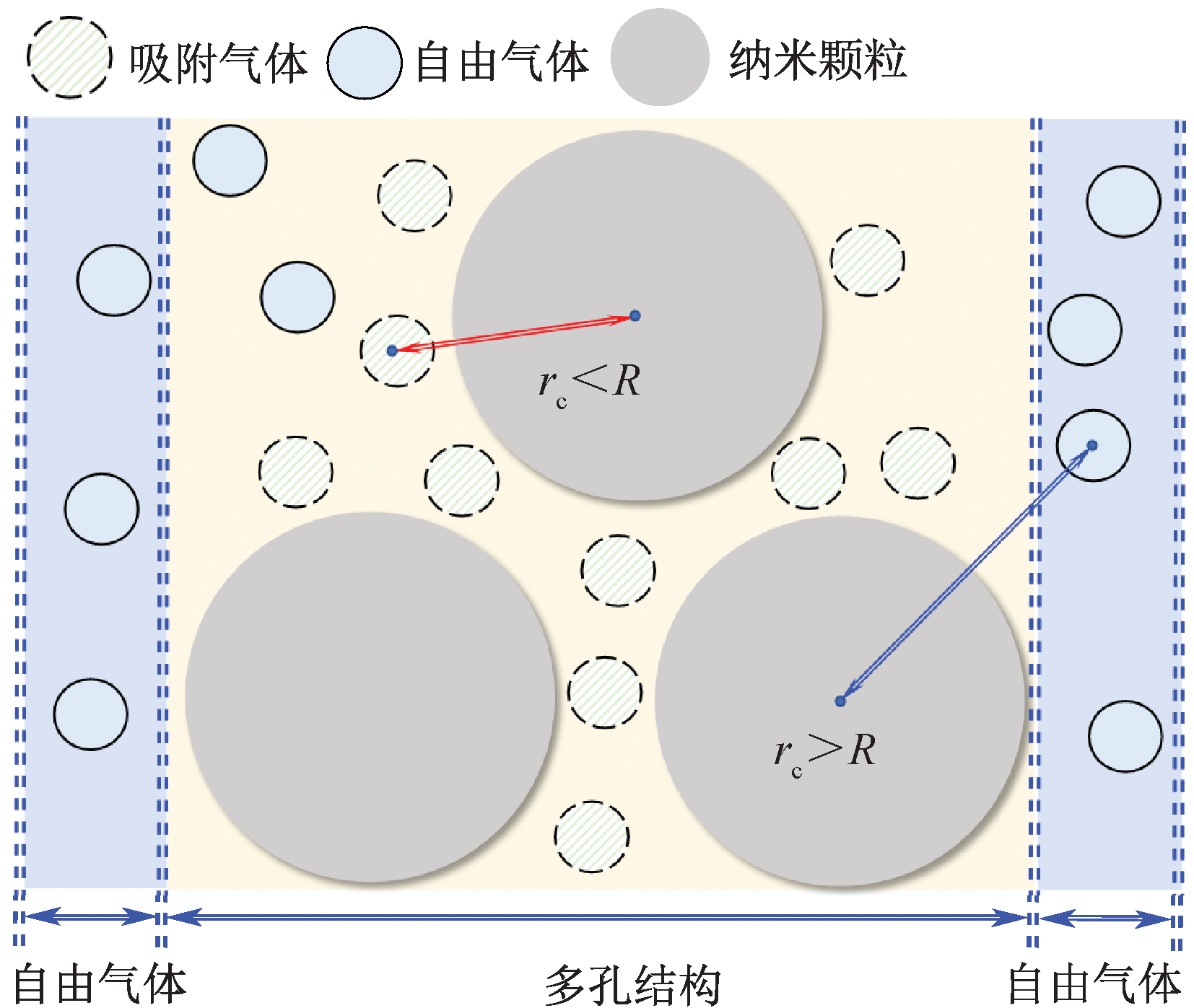
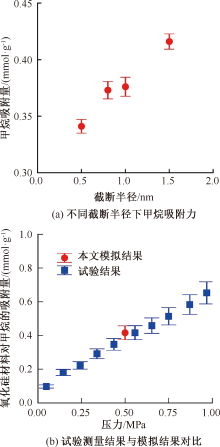
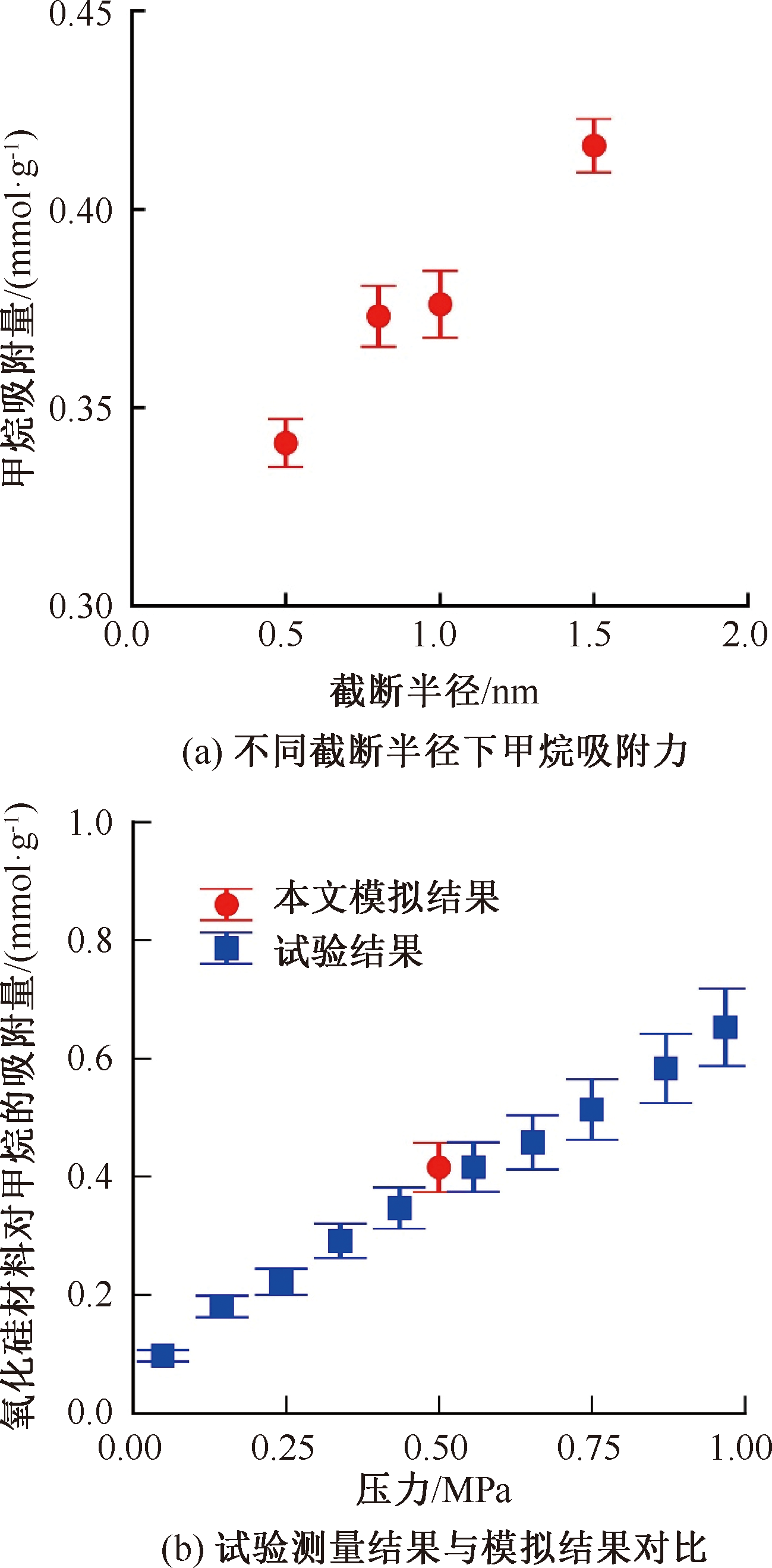
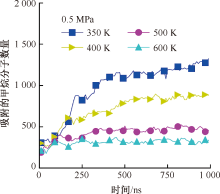
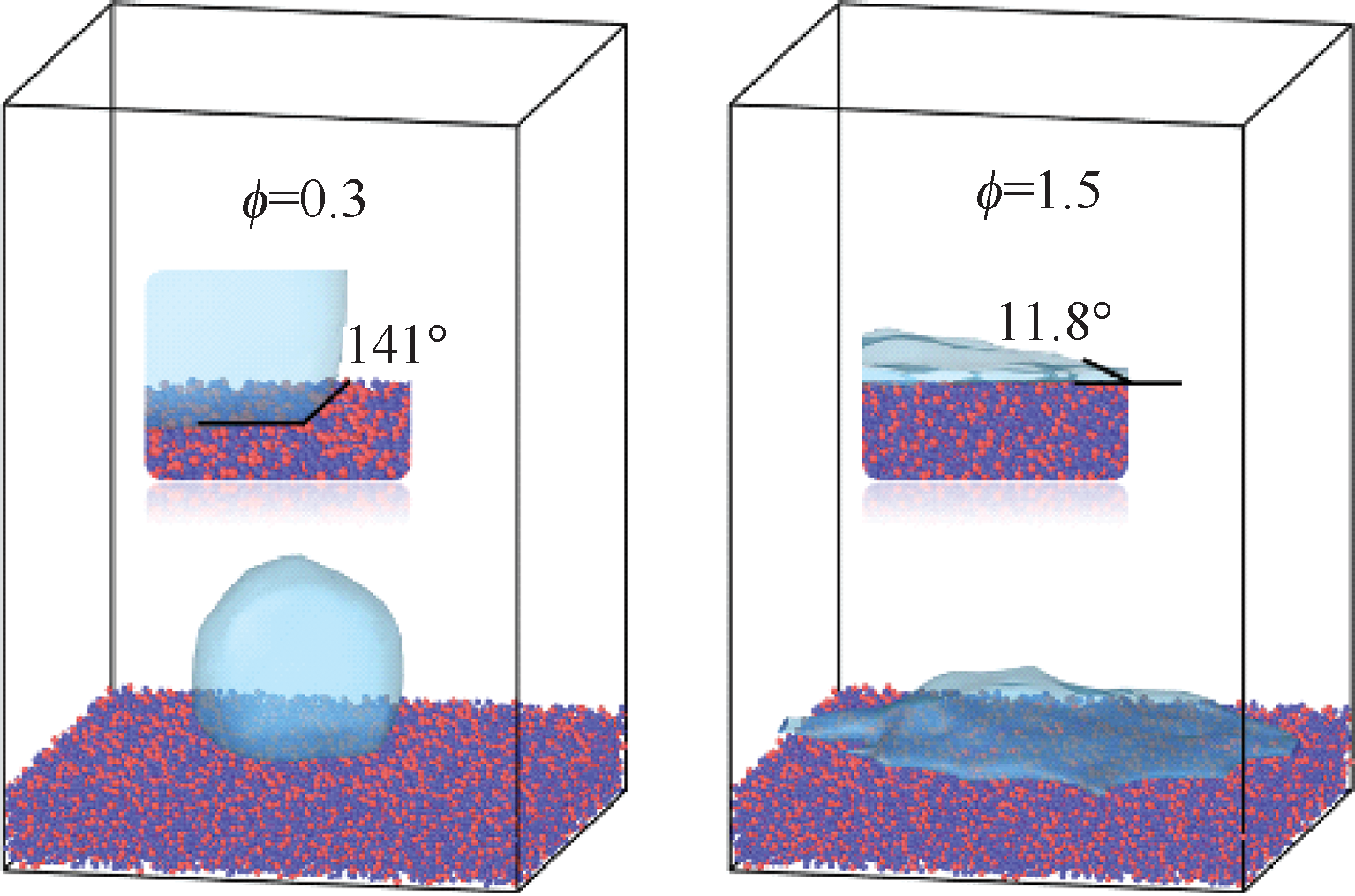
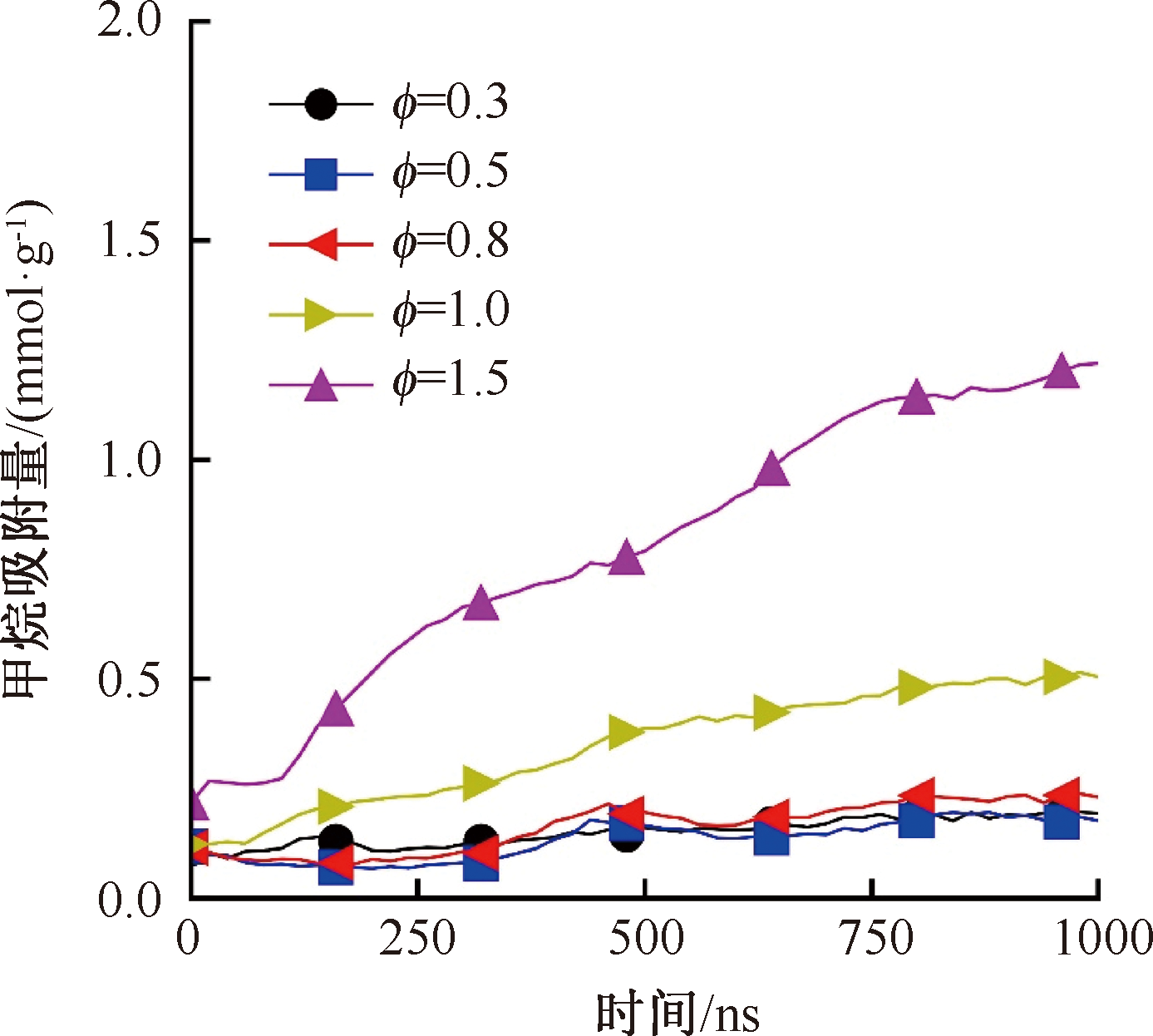
| [1] |
申晓静, 岳基伟, 梁跃辉, 等. 高温高压氛围下煤体吸附瓦斯特性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(2):176-184.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.02.1453
|
|
SHEN Xiaojing, YUE Jiwei, LIANG Yuehui, et al. Study on gas adsorption characteristics of coal under high temperature and high pressure atmosphere[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(2):176-184.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.02.1453
|
| [2] |
李云赫, 闵秀博, 余忆玄, 等. 甲烷与氮气吸附分离研究进展[J]. 石油学报:石油加工, 2022, 38(6):1520-1530.
|
|
LI Yunhe, MIN Xiubo, YU Yixuan, et al. Research progress in adsorption separation of methane and nitrogen[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica:Petroleum Processing Section, 2022, 38(6):1520-1530.
|
| [3] |
赵静, 张淮浩. 天然气吸附储存吸附剂成型实验研究[J]. 天然气化工:C1化学与化工, 2008, 33(6):15-18,23.
|
|
ZHAO Jing, ZHANG Huaihao. Experimental research on molding process of ANG powdery adsorbents[J]. Low-Carbon Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, 2008, 33(6):15-18,23.
|
| [4] |
PÉREZ-BOTELLA E, PALOMINO M, BÁFERO G B, et al. The influence of zeolite pore topology on the separation of carbon dioxide from methane[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2023, 72: DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2023.102490.
|
| [5] |
任俊豪, 任晓海, 宋海强, 等. 基于分子模拟的纳米孔内甲烷吸附与扩散特征[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(11):1366-1375.
|
|
REN Junhao, REN Xiaohai, SONG Haiqiang, et al. Adsorption and diffusion characteristics of methane in nanopores based on molecular simulation[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(11):1366-1375.
doi: 10.7623/syxb202011006
|
| [6] |
HE Jian, JU Yang, KULASINSKI K, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of methane transport in confined organic nanopores with high relative roughness[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2019, 62:202-213.
doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2018.12.010
|
| [7] |
WANG Dongbo, WANG Lin, ZHANG Li, et al. A modified model for estimating excess adsorption of methane in moist nanoporous silica[J]. Chemical Physics, 2020, 533: DOI: 10.1016/j.chemphys.2020.110740.
|
| [8] |
WU Hengan, CHEN Jie, LIU He. Molecular dynamics simulations about adsorption and displacement of methane in carbon nanochannels[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(24):13652-13 657.
|
| [9] |
CHAI Jingchun, LIU Shuyan, YANG Xiaoning. Molecular dynamics simulation of wetting on modified amorphous silica surface[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255(22):9078-9084.
|
| [10] |
YANG Mingyang, SHENG Qing, ZHANG Hu, et al. Water molecular bridge undermines thermal insulation of Nano-porous silica aerogels[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 349: DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118176.
|
| [11] |
MUNETOH S, MOTOOKA T, MORIGUCHI K, et al. Interatomic potential for Si-O systems using Tersoff parameterization[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2007, 39 (2):334-339.
|
| [12] |
YUE Wenping, LUO T, LIU Kaide. Trade-off between permeability and compressive strength for aerated concrete-based material with fly-ash under high pressure[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2023, 149 (3):669-685.
|
| [13] |
WANG Lu, YU Qingchun. Methane adsorption on porous nano-silica in the presence of water: an experimental and ab initio study[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 467:60-69.
doi: S0021-9797(15)30231-9
pmid: 26773609
|
| [14] |
YANG Mingyang, SHENG Qiang, GUO Lin, et al. How gas-solid interaction matters in graphene-doped silica aerogels[J]. Langmuir, 2022, 38(7):2238-2247.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c02777
pmid: 35129991
|