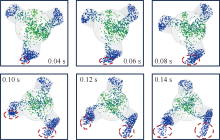
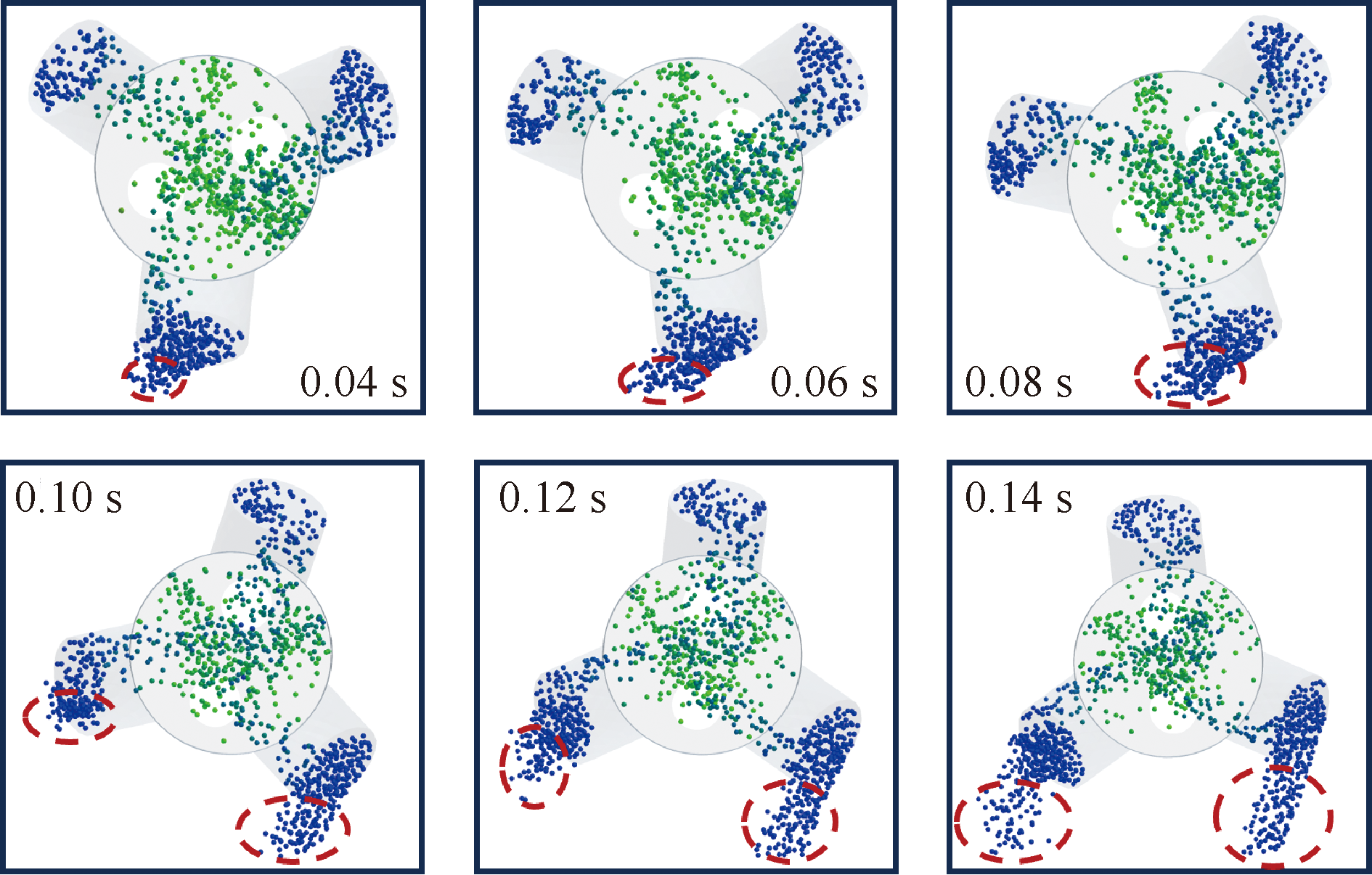
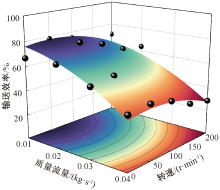
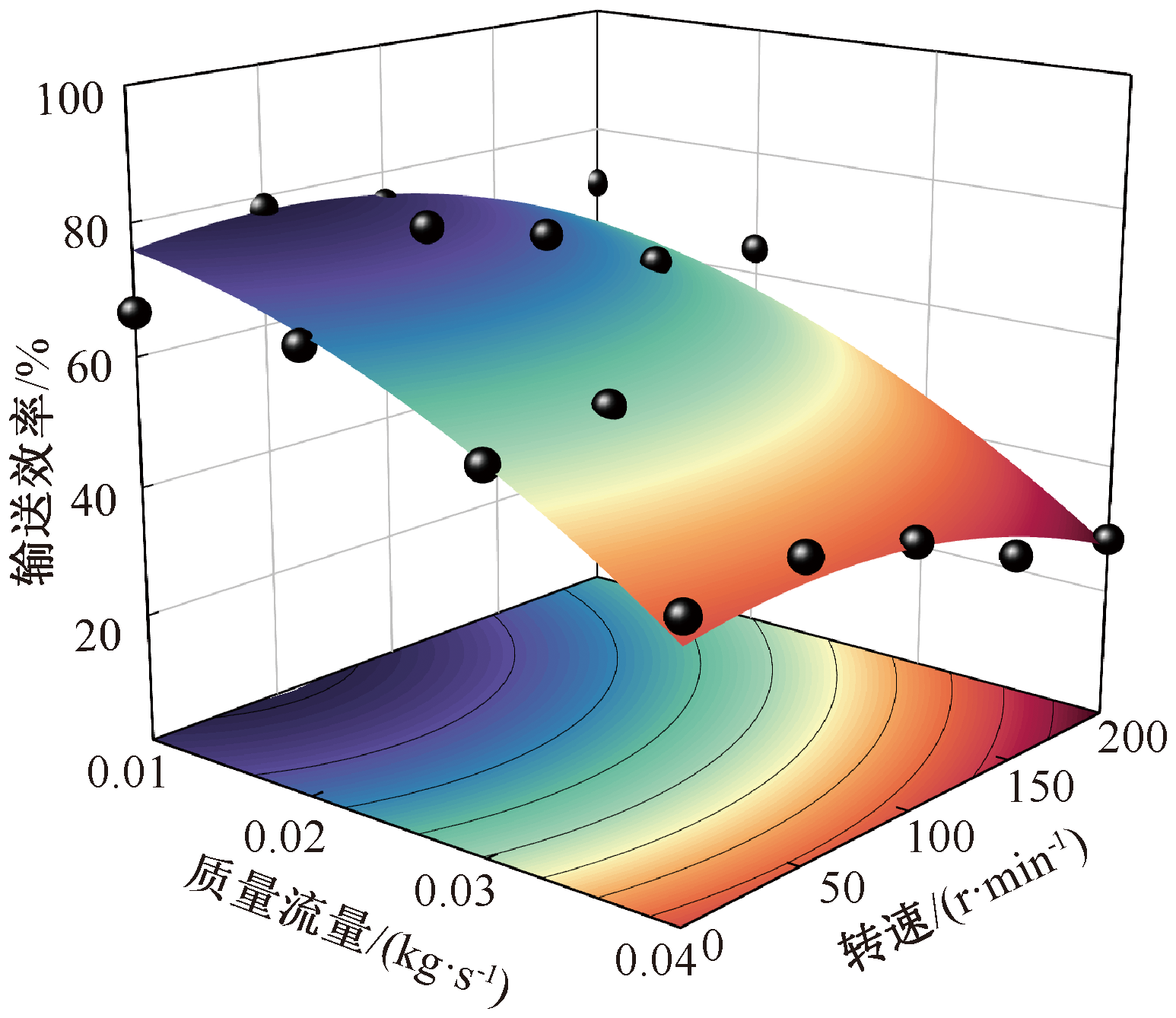
| [1] |
陈亮, 王恩元. 含瓦斯煤受载破坏瓦斯涌出的前兆特征研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(12): 79-84.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.12.011
|
|
CHEN Liang, WANG Enyuan. Study on precursory characteristics of gas emission from damaged coal containing gas[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(12): 79-84.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.12.011
|
| [2] |
林海飞, 高帆, 严敏, 等. 煤层瓦斯含量PSO-BP神经网络预测模型及其应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(9):80-87.
|
|
LIN Haifei, GAO Fan, YAN Min, et al. Study on PSO-BP neural network prediction method of coal seam gas content and its application[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(9):80-87.
|
| [3] |
王俏, 王兆丰, 马树俊, 等. 冷冻取芯过程煤样温度变化特性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(2): 76-81.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.02.011
|
|
WANG Qiao, WANG Zhaofeng, MA Shujun, et al. Study on temperature variation of coal sample in process of freezing coring[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(2): 76-81.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.02.011
|
| [4] |
张宏图, 魏建平, 王云刚, 等. 煤层瓦斯含量测定定点取样方法研究进展[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2016, 12(1): 186-192.
|
|
ZHANG Hongtu, WEI Jianping, WANG Yungang, et al. Sampling methods for coalbed gas content direct determination[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2016, 12(1):186-192.
|
| [5] |
王庆, 张佳伟, 陶亮, 等. 古龙页岩油水平井扩径段岩屑运移数值模拟研究[J]. 石油机械, 2023, 51(12):44-51.
|
|
WANG Qing, ZHANG Jiawei, TAO Liang, et al. Numerical simulation on cuttings migration in hole enlargement section of horizontal well in gulong shale oil reservoir[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2023, 51(12):44-51.
|
| [6] |
AWAD A M, HUSSEIN I A, NASSER M S, et al. A CFD-RSM study of cuttings transport in non-Newtonian drilling fluids: impact of operational parameters[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 208: DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109613.
|
| [7] |
MAO Chunzhi, ZHANG Xinxin, LI Fenqiang, et al. On cutting transport for air reverse circulation in horizontal and inclined wells[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2023, 136: DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2023.105095.
|
| [8] |
张鑫鑫, 毛纯芝, 信伟卫, 等. 基于欧拉双流体模型的微小井眼环空岩屑运移数值模拟研究[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2023, 54(11):4413-4423.
|
|
ZHANG Xinxin, MAO Chunzhi, XIN Weiwei, et al. Numerical simulation research of cuttings transport in microhole annulus based on Eulerian two-fluid model[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2023, 54(11):4413-4423.
|
| [9] |
AKHSHIK S, BEHZAD M, RAJABI M. CFD-DEM simulation of the hole cleaning process in a deviated well drilling: the effects of particle shape[J]. Particuology, 2016, 25:72-82.
|
| [10] |
AKHSHIK S, BEHZAD M, RAJABI M. CFD-DEM approach to investigate the effect of drill pipe rotation on cuttings transport behavior[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2015, 127:229-244.
|
| [11] |
PANG Boxue, WANG Shuyan, JIANG Xiaoxue, et al. Effect of orbital motion of drill pipe on the transport of non-Newtonian fluid-cuttings mixture in horizontal drilling annulus[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 174:201-215.
doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.11.009
|
| [12] |
胡金帅, 张光伟, 李峻岭, 等. 基于CFD-DEM耦合模型的岩屑运移数值模拟分析[J]. 断块油气田, 2022, 29(4):561-566.
|
|
HU Jinshuai, ZHANG Guangwei, LI Junling, et al. Numerical simulation of cuttings migration based on CFD-DEM coupling model[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2022, 29(4):561-566.
|
| [13] |
LI Botao, ZHANG Hongtu, WEI Jianping, et al. Coal particle transport behavior in a rotating drill pipe used for negative pressure pneumatic conveying[J]. Powder Technology, 2022, 402: DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2022.117369.
|
| [14] |
李博涛. 负压排渣钻孔定点取样过程煤屑-气流动特性研究[D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学, 2020.
|
|
LI Botao. Gas-solid flow characteristics of sampling method based on negative pressure pneumatic conveying[D]. Jiaozuo: Henan Polytechnic University, 2020.
|
| [15] |
宋先知, 李根生, 王海柱, 等. 盐穴储气库底部碎屑旋转射流冲洗数值模拟[J]. 天然气工业, 2010, 30(8):83-86.
|
|
SONG Xianzhi, LI Gensheng, WANG Haizhu, et al. Numerical simulation on rotating jet-flow washing for debris on the bottom of cavern underground storage[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2010, 30(8):83-86.
|