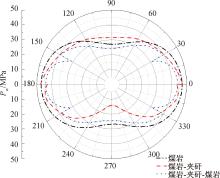
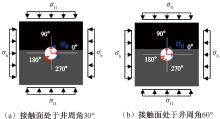
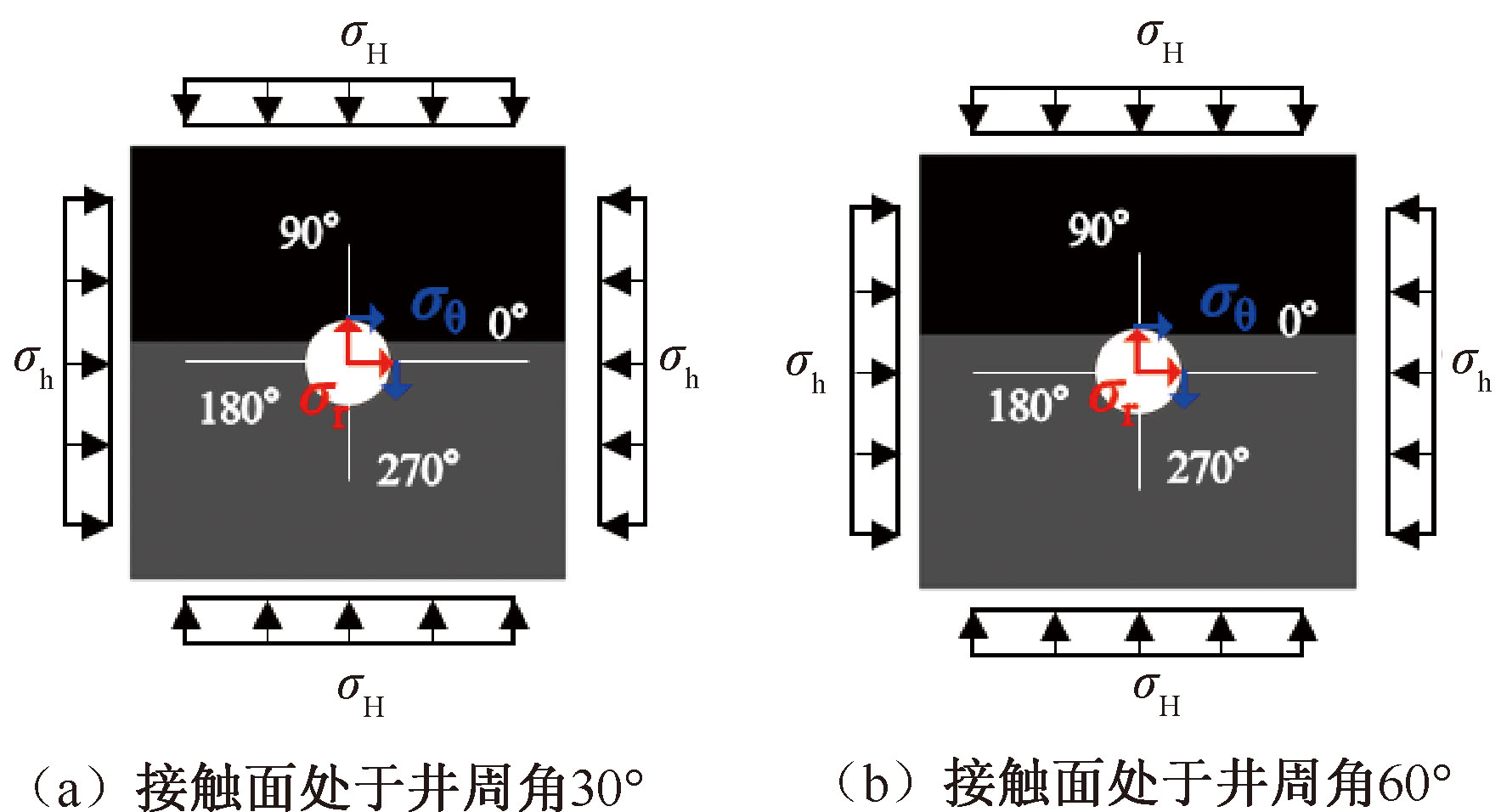
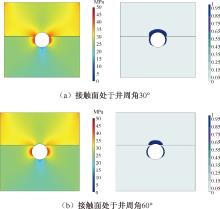
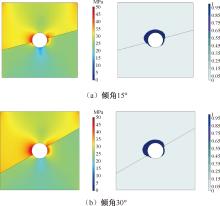
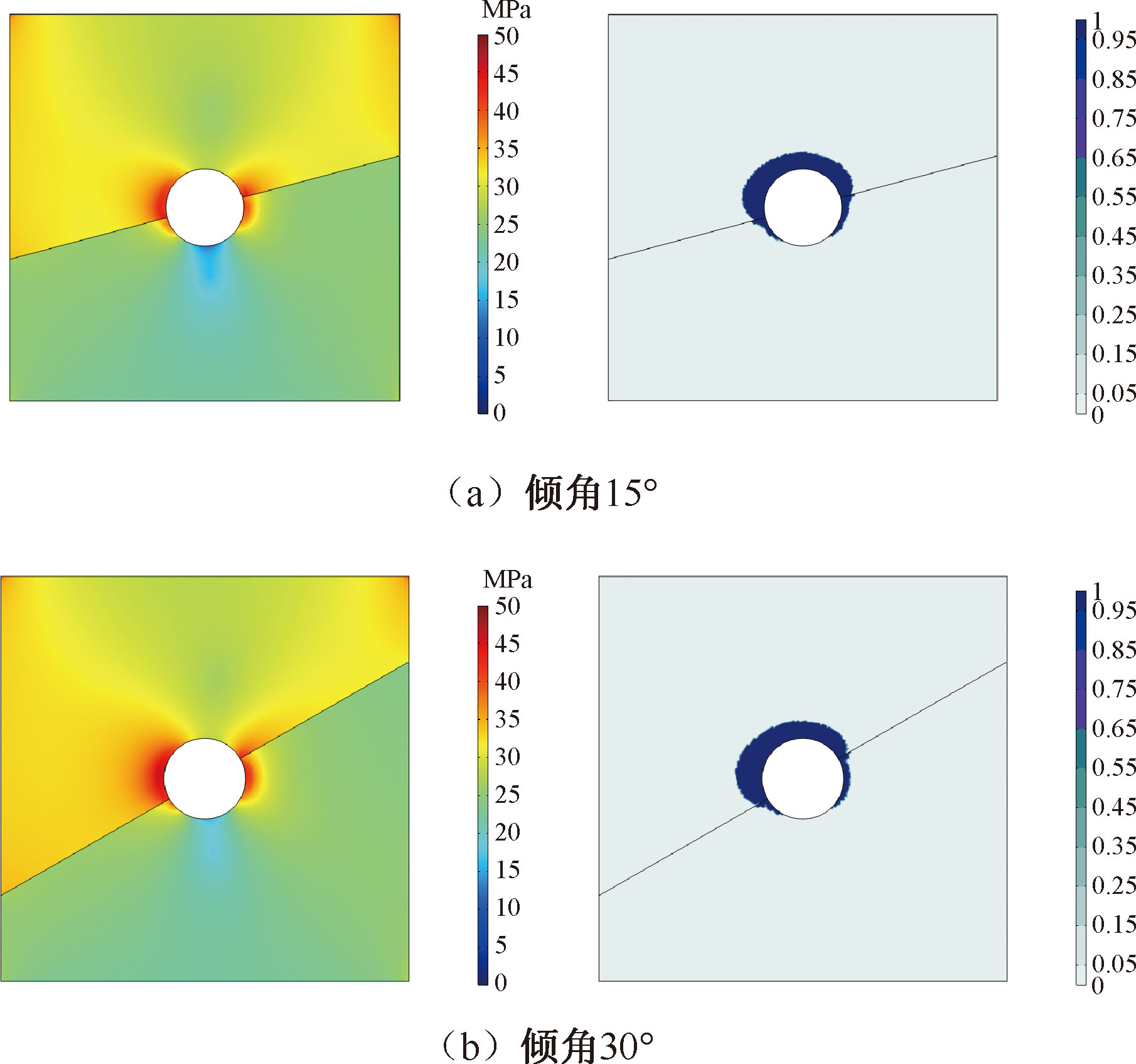
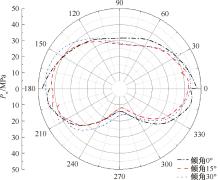
| [1] |
XU Fengyin, HOU Wei, XIONG Xianyue, et al. The status and development strategy of coalbed methane industry in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(4): 765-783.
doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(23)60427-6
|
| [2] |
ZHANG Yongping, YANG Yanhui, SHAO Guoliang, et al. Problems in the development of high-rank CBM horizontal wells in the Fanzhuang-Zhengzhuang block in the Qinshui basin and countermeasures[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2017, 4(6): 423-431.
doi: 10.1016/j.ngib.2017.09.013
|
| [3] |
WANG Heyuan, FENG Fuping, ZHANG Jianwei, et al. Impact of rock strength degradation by fluid intrusion on borehole stability in shale[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2024, 11(6): 553-568.
doi: 10.1016/j.ngib.2024.09.004
|
| [4] |
LI Hangyu, LAU Honchuan, HUANG Shan. China's coalbed methane development: a review of the challenges and opportunities in subsurface and surface engineering[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 166: 621-635.
doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.03.047
|
| [5] |
GAO Deli, BI Yansen, XIAN Baoan. Technical advances in well type and drilling & completion for high-efficient development of coalbed methane in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2022, 9(6): 561-577.
doi: 10.1016/j.ngib.2022.11.006
|
| [6] |
FENG Fuping, WANG Heyuan, HAN Xu, et al. Dynamic coupling mechanism of shale drilling fluid invasion depth, fracture width, and rock strength[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2025, 37: DOI: 10.1063/5.0271691.
|
| [7] |
王在明, 陈金霞, 沈园园, 等. JN1H 井煤岩气长水平段钻井井壁稳定技术[J]. 钻井液与完井液, 2023, 40(3): 356-362.
|
|
WANG Zaiming, CHEN Jinxia, SHEN Yuanyuan, et al. Borehole wall stabilization technology for drilling the long horizontal section coal rock gas well JN1H[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2023, 40(3): 356-362.
|
| [8] |
肖晓春, 樊玉峰, 吴迪, 等. 组合煤岩力学性质与声-电荷信号关系研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2018, 14(2): 126-132.
|
|
XIAO Xiaochun, FAN Yufeng, WU Di, et al. Study on relationship between mechanical properties and acoustic emission-charge signals of combined coal-rock[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2018, 14(2): 126-132.
|
| [9] |
陆菜平. 组合煤岩的强度弱化减冲原理及其应用[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2008.
|
|
LU Caiping. Intensity weakening theory for rock burst of compound coal-rock and its application[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2008.
|
| [10] |
SHAN Tiancheng, LI Zhonghui, ZHANG Xin, et al. Pressure stimulated current in progressive failure process of combined coal-rock under uniaxial compression: Response and mechanism[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2024, 34(2): 227-243.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2023.12.008
|
| [11] |
张晨阳. 底煤厚度对巷道底板冲击启动的影响规律研究[D]. 北京: 煤炭科学研究总院, 2018.
|
|
ZHANG Chenyang. Research of the influence laws of bottom coal thickness on roadway floor burst start-up[D]. Beijing: China Coal Research Institute, 2018.
|
| [12] |
樊玉峰, 肖晓春, 丁鑫, 等. 岩煤分界面力学性质对组合煤岩力学行为影响机制[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(4): 1487-1501.
|
|
FAN Yufeng, XIAO Xiaochun, DING Xin, et al. Influence mechanism of contact surface mechanical properties on mechanical behavior of coal rock combination[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(4): 1487-1501.
|
| [13] |
解北京, 栾铮, 刘天乐, 等. 静水压下原生组合煤岩动力学破坏特征[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(5):2153-2167.
|
|
XIE Beijing, LUAN Zheng, LIU Tianle, et al. Dynamic failure characteristics of primary coal-rock combination under hydrostatic pressure[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(5): 2153-2167.
|
| [14] |
马智会, 马智勇, 潘荣锟, 等. 三维静载与循环冲击共同作用下组合煤岩体力学特性试验研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2024, 20 (8): 58-67.
|
|
MA Zhihui, MA Zhiyong, PAN Rongkun, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of coal-rock combined body subjected to combined action of three-dimensional static load and cyclic impact[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2024, 20(8): 58-67.
|
| [15] |
|
|
PENG Yanyan, LI Yifan, YU Hu, et al. Mechanical properties of coal and rock with different dip angles based on true triaxial unloading test[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering, 2024, 6(2):DOI: 10.13532/jjmsce.cn10-1638/td.20231222.001.
|
| [16] |
郑建伟, 张修峰, 鞠文君, 等. 层面位置对煤岩组合体动态破坏特性影响规律研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2024, 52(10):97-105.
|
|
ZHENG Jianwei, ZHANG Xiufeng, JU Wenjun, et al. Influencing analysis of bedding plane location on the dynamic failure characteristics of coal-rock combinations[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2024, 52(10): 97-105.
|
| [17] |
WANG Shugang, DEREK E, LIU Jishan. Permeability evolution during progressive deformation of intact coal and implications for instability in underground coal seams[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2013, 58: 34-45.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.09.005
|
| [18] |
STEVEN A K, KRAMER D L, MICHAEL K. A numerical study on optimization of multilateral horizontal wellbore patterns for coalbed methane production in Southern Shanxi Province, China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2011, 86(4): 306-317.
doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2011.03.004
|
| [19] |
屈平, 申瑞臣, 付利, 等. 三维离散元在煤层水平井井壁稳定中的应用[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(1):1-5.
|
|
QU Ping, SHEN Ruichen, FU Li, et al. Application of three-dimensional discrete elements in the stabilization of coal seam horizontal well walls[J]. Journal of Petroleum, 2011, 32(1): 1-5.
|
| [20] |
QU Ping, SHEN Ruichen, LI Fu, et al. Time delay effect due to pore pressure changes and existence of cleats on borehole stability in coal seam[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2011, 85(2): 212-218.
doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2010.10.013
|
| [21] |
ERFAN S, QU Qingdong, AMINOSSADATI S M, et al. Horizontal borehole azimuth optimization for enhanced stability and coal seam gas production[J]. Rock Mechanics Bulletin, 2024, 3(1): DOI: 10.1016/j.rockmb.2023.100100.
|
| [22] |
ZHANG Lisong, YAN Xiangzhen, YANG Xiujuan, et al. An elastoplastic model of collapse pressure for deep coal seam drilling based on Hoek-Brown criterion related to drilling fluid loss to reservoir[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2015, 134:205-213.
doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2015.07.003
|
| [23] |
严俊涛, 孟英峰, 李皋, 等. 泥煤互层段井壁稳定分析新方法[J]. 钻采工艺, 2012, 35 (4): 19-21.
|
|
YAN Juntao, MENG Yingfeng, LI Gao, et al. A new method for well wall stability analysis of peat interbedded sections[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2012, 35(4): 19-21.
|
| [24] |
王岗, 潘一山, 肖晓春, 等. 组合煤岩体冲击倾向性及破坏特征的电荷规律试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26 (7): 135-140.
|
|
WANG Gang, PAN Yishan, XIAO Xiaochun, et al. Experimental study on charge law of coal-rock bodies rock burst tendency and failure characteristics[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(7): 135-140.
|
| [25] |
杜锋, 王凯, 孙加智, 等. 单轴压缩下不同倾角煤岩组合体力学特性及破坏特征[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(6):136-145.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.06.0785
|
|
DU Feng, WANG Kai, SUN Jiazhi, et al. Mechanical properties and failure characteristics of coal rock combinations with different inclination angles under uniaxial compression[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(6): 136-145.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.06.0785
|
| [26] |
伍永平, 闫壮壮, 罗生虎, 等. 煤岩组合体应力传递与强度特征倾角效应[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2023, 51(1):105-116.
|
|
WU Yongping, YAN Zhuangzhuang, LUO Shenghu, et al. Dip effect of stress transfer and structural instability mechanism of coal-rock combination[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(1): 105-116.
|
| [27] |
张恒. 煤矸组合结构破坏失稳的卸荷机制及前兆规律研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2021.
|
|
ZHANG Heng. Research on unloading mechanism and precursory laws of failure and instability of coal-rock parting compound structure[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology(Beijing), 2021.
|