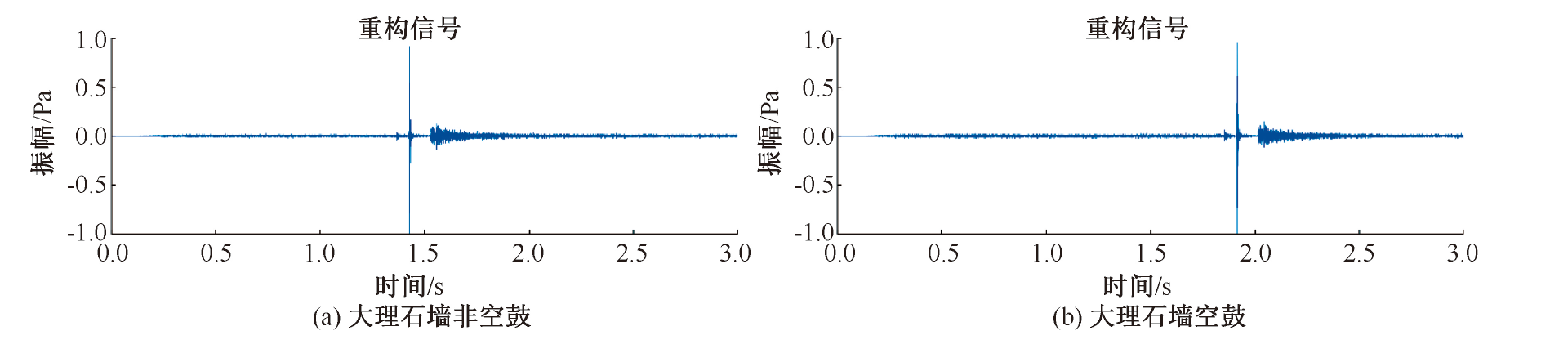
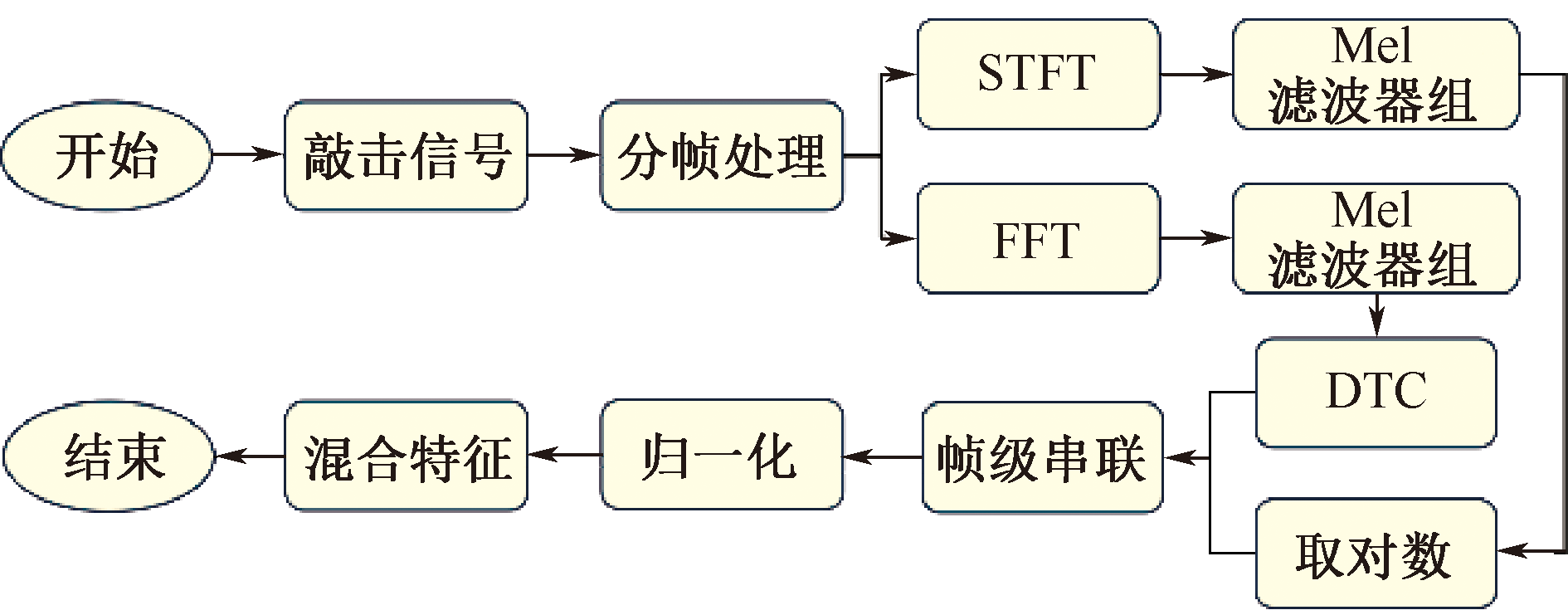
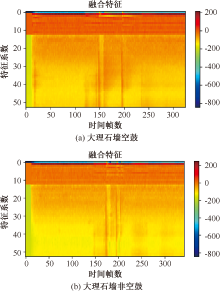
| [1] |
汪思迪. 粘贴保温板外保温体系分析:以设计视角看空鼓、开裂、脱落的过程[J]. 居舍, 2025(7):56-59.
|
| [2] |
肖翠翠, 远航. 基于红外热成像技术的建筑外墙渗漏及空鼓检测研究[J]. 北方建筑, 2025, 10(1):70-73.
|
|
XIAO Cuicui, YUAN Hang. Research on building exterior wall leakage and hollowing detection based on infrared thermography technology[J]. Northern Architecture, 2025, 10(1): 70-73.
|
| [3] |
赵响, 丁勇, 李登华. 基于融合特征的CNN-Transformer墙体瓷砖粘贴空鼓检测算法[J]. 现代电子技术, 2024, 47(18):163-171.
|
|
ZHAO Xiang, DING Yong, LI Denghua. Fused feature based CNN-Transformer algorithm for empty drum detection of pasting tile in exterior wall[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2024, 47(18): 163-171.
|
| [4] |
赵仕兴, 马麟涛, 许浒, 等. 建筑饰面砖空鼓缺陷无人机识别关键参数试验研究[J/OL]. 土木与环境工程学报:中英文:1-13.[2025-03-19]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/50.1218.tu.20241028.2110.007.
|
|
ZHAO Shixing, MA Lintao, XU Hu, et al. Experimental study on key parameters for identification of hollowing defects via UAV in facade tiles[J/OL]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering: 1-13.[2025-03-19]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/50.1218.tu.20241028.2110.007.
|
| [5] |
刘向开, 司敏. 基于无人机红外热成像技术的建筑外墙检测应用[J]. 建材世界, 2024, 45(2):107-109.
|
|
LIU Xiangkai, SI Min. Application of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) infrared thermography technology for exterior wall inspection in buildings[J]. The World of Building Materials, 2024, 45(2): 107-109.
|
| [6] |
周浩, 梁军汀, 卢杰. 基于MFCC和GMM的瓷砖空鼓率识别系统及方法[J]. 无损检测, 2024, 46(3):28-32,55.
|
|
ZHOU Hao, LIANG Junting, LU Jie. Ceramic tile hollow drum rate identification system and method based on MFCC and GMM[J]. Nondestructive Testing, 2024, 46(3): 28-32,55.
|
| [7] |
廖健. 某建筑采用无人机搭载红外热像技术对外墙饰面砖空鼓状况分析[J]. 广东建材, 2023, 39(10):39-41.
|
| [8] |
沈吉才. 基于涡流的建筑物外墙空鼓快速检测技术研究[D]. 上海: 上海应用技术大学, 2023.
|
|
SHEN Jicai. Rapid detection technology of building exterior wall hollowing based on eddy current[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Technology, 2023.
|
| [9] |
LIU Yuchen, LIU Fuzheng, JIANG Mingshun. Research on YOLO algorithm for lightweight PCB defect detection based on MobileViT[J/OL]. Optoelectronics Letters, 1-8[2025-03-19]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-025-4292-5.
|
| [10] |
王浚银, 文斌, 沈艳军, 等. 基于改进YOLOv7-tiny的铝型材表面缺陷检测方法[J]. 浙江大学学报:工学版, 2025, 59(3):523-534.
|
|
WANG Junyin, WEN Bin, SHEN Yanjun, et al. Surface defect detection method for aluminum profiles based on improved YOLOv7-tiny[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Engineering Science, 2025, 59(3): 523-534.
|
| [11] |
YOO H, KIM Y. Development of a crack recognition algorithm from non-routed pavement images using artificial neural network and binary logistic regression[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2016, 20(4): 1151-1162.
doi: 10.1007/s12205-015-1645-9
|
| [12] |
王超群, 梁伟, 梁晓斌. CEEMD-FCM模型下的管道缺陷识别方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(1):87-93.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.01.014
|
|
WANG Chaoqun, LIANG Wei, LIANG Xiaobin. Pipeline defect recognition method based on CEEMD-FCM[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(1): 87-93.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.01.014
|
| [13] |
李苗, 李凌波, 左志恒, 等. 基于机器学习的成品油管道运行工况识别[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(6):127-135.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.06.1410
|
|
LI Miao, LI Lingbo, ZUO Zhiheng, et al. Machine learning-based recognition for recognizing operating conditions of multi-product pipelines[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(6): 127-135.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.06.1410
|
| [14] |
郭震, 贾笑岩, 李富民, 等. 基于机器学习的建筑火灾蔓延快速预测[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(11):117-125.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.11.2219
|
|
GUO Zhen, JIA Xiaoyan, LI Fumin, et al. Fast prediction for building fire spread based on machine learning[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(11): 117-125.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.11.2219
|
| [15] |
张凯, 张科. 基于LightGBM算法的边坡稳定性预测研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(7):113-120.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.07.1473
|
|
ZHANG Kai, ZHANG Ke. Prediction study on slope stability based on LightGBM algorithm[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(7): 113-120.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.07.1473
|