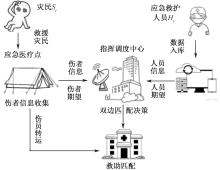
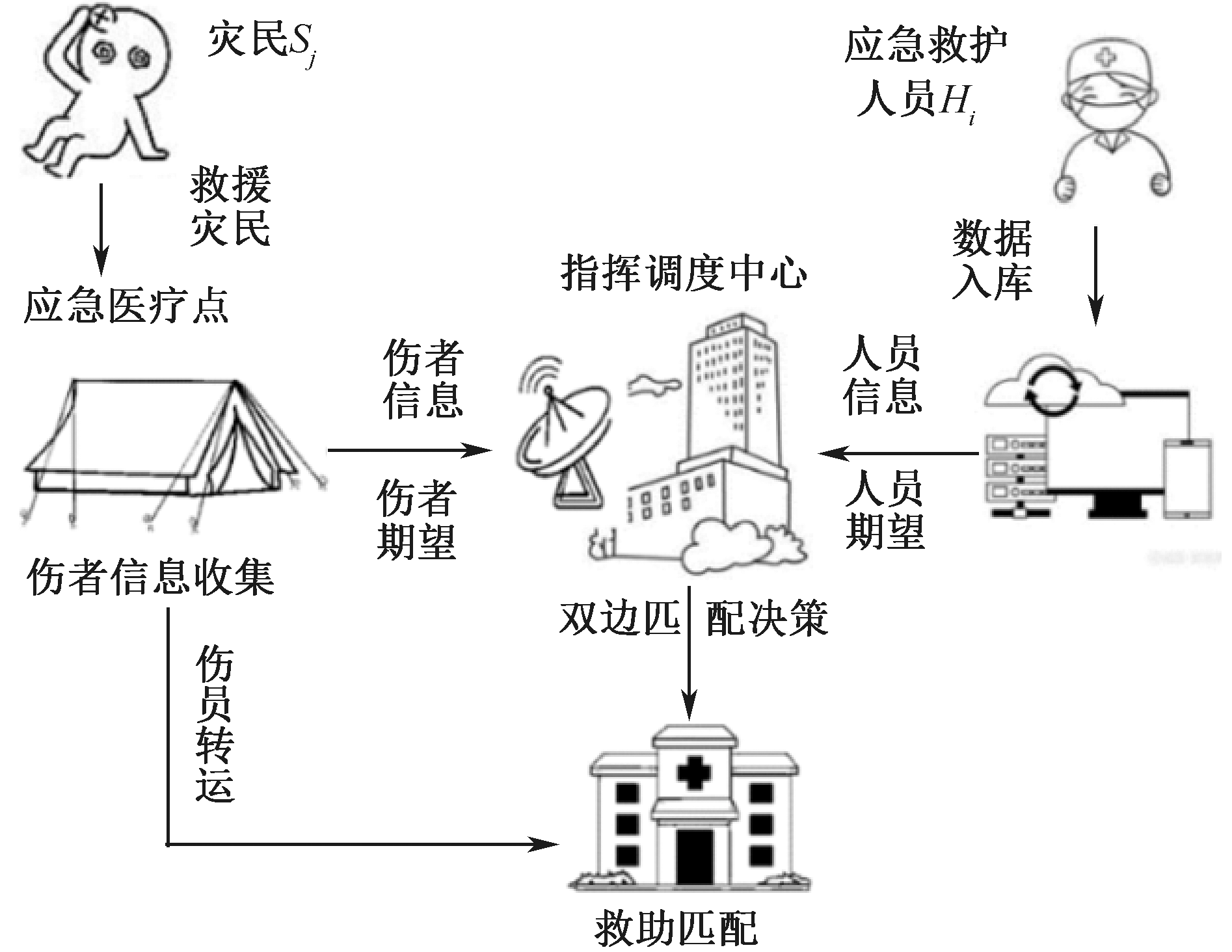
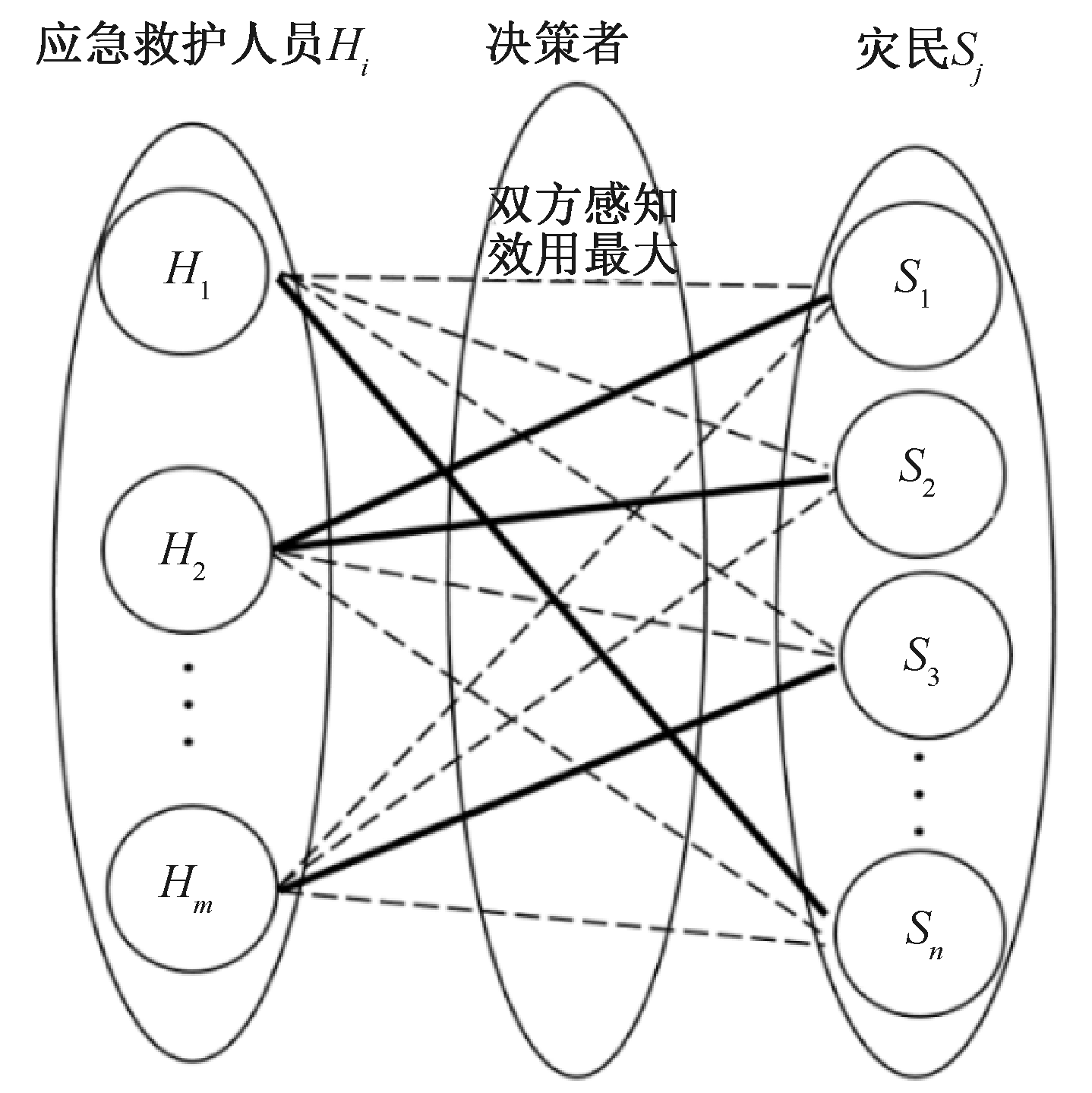
| [1] |
王欣, 方成勇, 唐小川. 泸定Ms 6.8地震诱发滑坡应急评价研究[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2023, 48(1):25-35.
|
|
WANG Xin, FANG Chengyong, TANG Xiaochuan, et al. Research on emergency evaluation of landslides induced by the Luding Ms 6.8 earthquake[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2023, 48(1):25-35.
|
| [2] |
张晨晓, 祝蕊, 刘海月, 等. 考虑伤员心理状况的应急医疗救护问题研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2017, 25(10):187-196.
|
|
ZHANG Chenxiao, ZHU Rui, LIU Haiyue, et al. The emergency victims rescue problem considering psychological condition[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2017, 25 (10): 187-196.
|
| [3] |
陈圣群, 王应明, 郑晶, 等. 考虑同群效应的志愿者与应急任务匹配方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2015, 25(11):156-162.
|
|
CHEN Shengqun, WANG Yingming, ZHENG Jing, et al. A method considering peer effect for matching volunteers with emergence tasks[J]. China Safety Sciences Journal, 2015, 25 (11): 156-162.
|
| [4] |
李铭洋, 曲晓宁, 李博, 等. 考虑多救援点的突发事件应急救援人员派遣模型[J]. 运筹与管理, 2018, 27(8):50-56.
doi: 10.12005/orms.2018.0180
|
|
LI Mingyang, QU Xiaoning, LI Bo, et al. Model for emergency rescuers assignment considering multiple disaster areas[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2018, 27(8):50-56.
doi: 10.12005/orms.2018.0180
|
| [5] |
姜艳萍, 梁霞, 张浩. 考虑后悔与失望行为的应急方案选择方法[J]. 运筹与管理, 2019, 28(11):91-97.
doi: 10.12005/orms.2019.0253
|
|
JIANG Yanping, LIANG Xia, ZHANG Hao. Method of selecting emergency alternative considering regret and disappointment behaviors of decision maker[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2019, 28 (11): 91-97.
doi: 10.12005/orms.2019.0253
|
| [6] |
宋英华, 白明轩, 马亚萍, 等. 考虑多主体心理效应的应急资源调度超网络模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(2):158-166.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.02.022
|
|
SONG Yinghua, BAI Mingxuan, MA Yaping, et al. Super-network model of emergency resource scheduling considering multi-agent psychological effect[J]. China Safety Sciences Journal, 2021, 31 (2): 158-166.
|
| [7] |
车萤, 雷中杰, 何成奇, 等. 188例芦山地震伤员伤情分类及早期康复策略[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2013, 13(6):657-661.
|
|
CHE Ying, LEI Zhongjie, HE Chengqi, et al. Injury categorization and early rehabilitation strategy of 188 victims of Lushan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine, 2013, 13(6):657-661.
|
| [8] |
夏哲远, 殷婷婷, 黄榕, 等. 护理人员参与“6·7”公交爆炸批量伤员救护体验的质性研究[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2013, 30(14):5-8.
|
|
XIA Zheyuan, YIN Tingting, HUANG Rong, et al. Qualitative research of nurses' mental experience for "6·7" mass blast patients rescu[J]. Military Nursing, 2013, 30 (14): 5-8.
|
| [9] |
张绮珊, 赖锦佳, 黄蝶卿, 等. 急诊科灾害专科护士工作体验的质性研究[J]. 护理学杂志, 2023, 38(3):58-61.
|
|
ZHANG Qishan, LAI Jinjia, HUANG Dieqing, et al. Qualitative study on working experience of disaster specialist nurses in emergency department[J]. Journal of Nursing Science, 2023, 38 (3): 58-61.
|
| [10] |
袁铎宁, 姜艳萍, 梁海明. 考虑属性优先性的择期手术医患双边稳定匹配模型[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2020, 40(9):2367-2 378.
|
|
YUAN Duoning, JIANG Yanping, LIANG Haiming. Two-sided stable matching model between selective operation patients and surgeons considering the priority of attributes[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2020, 40 (9): 2 367-2 378.
|
| [11] |
郑国管, 王小合, 钱宇, 等. 患者满意度测评问题与治理路径思考[J]. 中国卫生政策研究, 2019, 12(3):8-16.
|
|
ZHENG Guoguan, WANG Xiaohe, QIAN Yu, et al. Study of the challenges in the evaluation of patient satisfaction and the thinking of government path[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Policy, 2019, 12 (3): 8-16.
|
| [12] |
刘冉, 尤筱玥, 林辉, 等. 基于主客观赋权的企业专利组合质量评价[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2023, 51(5):667-673.
|
|
LIU Ran, YOU Xiaoyue, LIN Hui, et al. Firm patent portfolio quality evaluation based on combinatorial weighting method[J]. Journal of Tongji University:Natural Science, 2023, 51 (5): 667-673.
|
| [13] |
喻寅昀, 徐伟. 考虑顾客容忍区间的服务质量测评[J]. 统计与决策, 2019, 35(13):177-180.
|
|
YU Yinyun, XU Wei. Service quality evaluation considering customer tolerance interval[J]. Statistics & Decision, 2019, 35 (13): 177-180.
|
| [14] |
李丽, 周荣义, 王凌睿, 等. 基于后悔理论的危化品公路桥梁运输风险评估[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2022, 29(2):71-77.
|
|
LI Li, ZHOU Rongyi, WANG Lingrui, et al. Risk assessment of road bridge transportation of hazardous chemicals based on regret theory[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29 (2): 71-77.
|
| [15] |
许鹏, 刘敬贤, 陈淑楣, 等. 基于AHP群决策的三峡后续工作规划航运项目实施评估模型[J]. 中国航海, 2021, 44(3):84-91,111.
|
|
XU Peng, LIU Jingxian, CHEN Shumei, et al. Implementation assessment model for waterway transport project of three gorges follow-up work plan based on AHP group decision making[J]. Navigation of China, 2021, 44 (3): 84-91,111.
|
| [16] |
汪新凡, 周浪, 朱远芳, 等. 基于后悔理论的概率犹豫模糊双边匹配决策方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2022, 37(9):2380-2388.
|
|
WANG Xinfan, ZHOU Lang, ZHU Yuanfang, et al. Two-sided matching decision making method with probabilistic hesitant fuzzy information based on regret theory[J]. Control and Decision, 2022, 37 (9): 2380-2388.
|