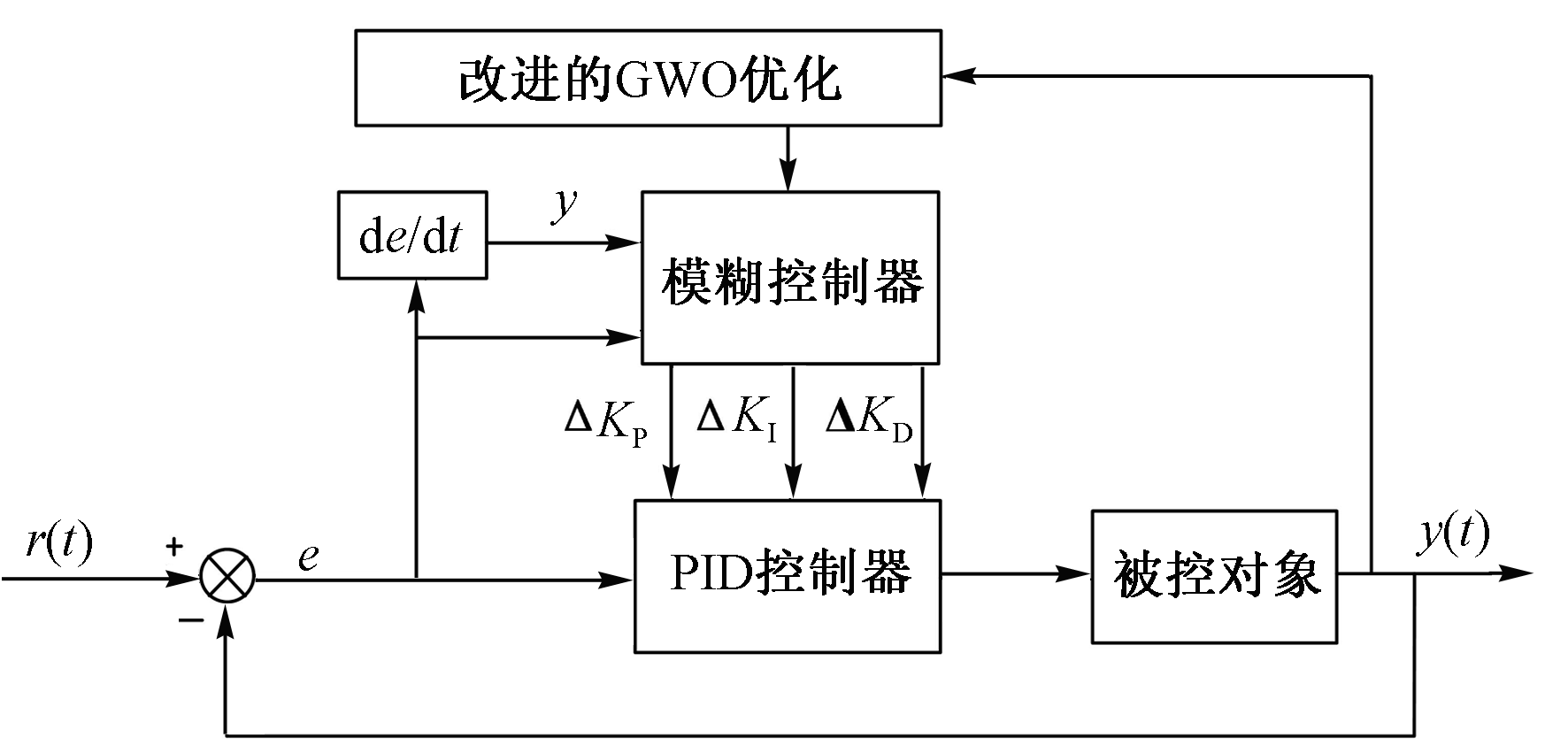
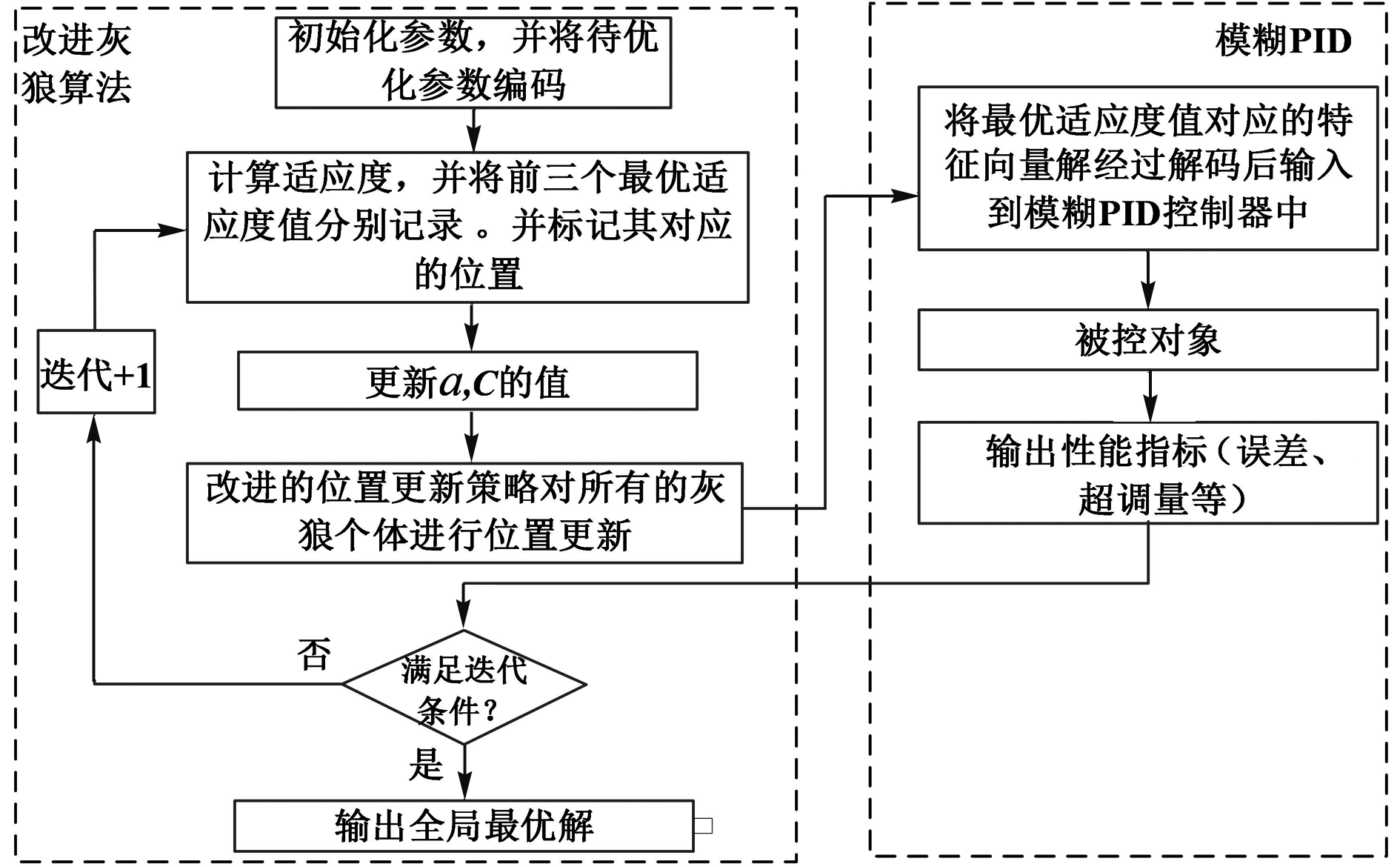
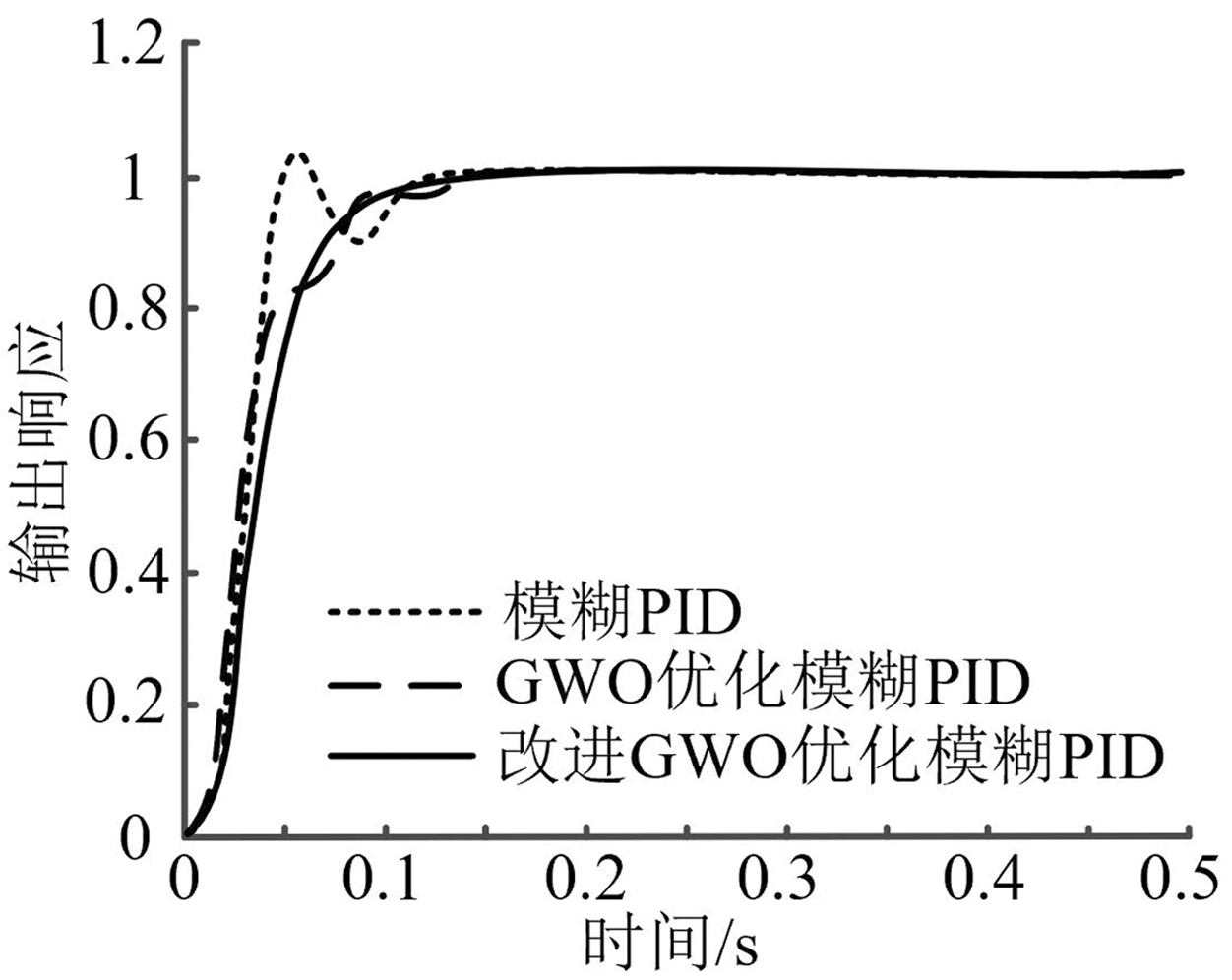
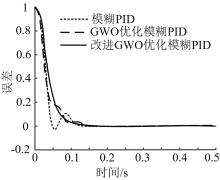
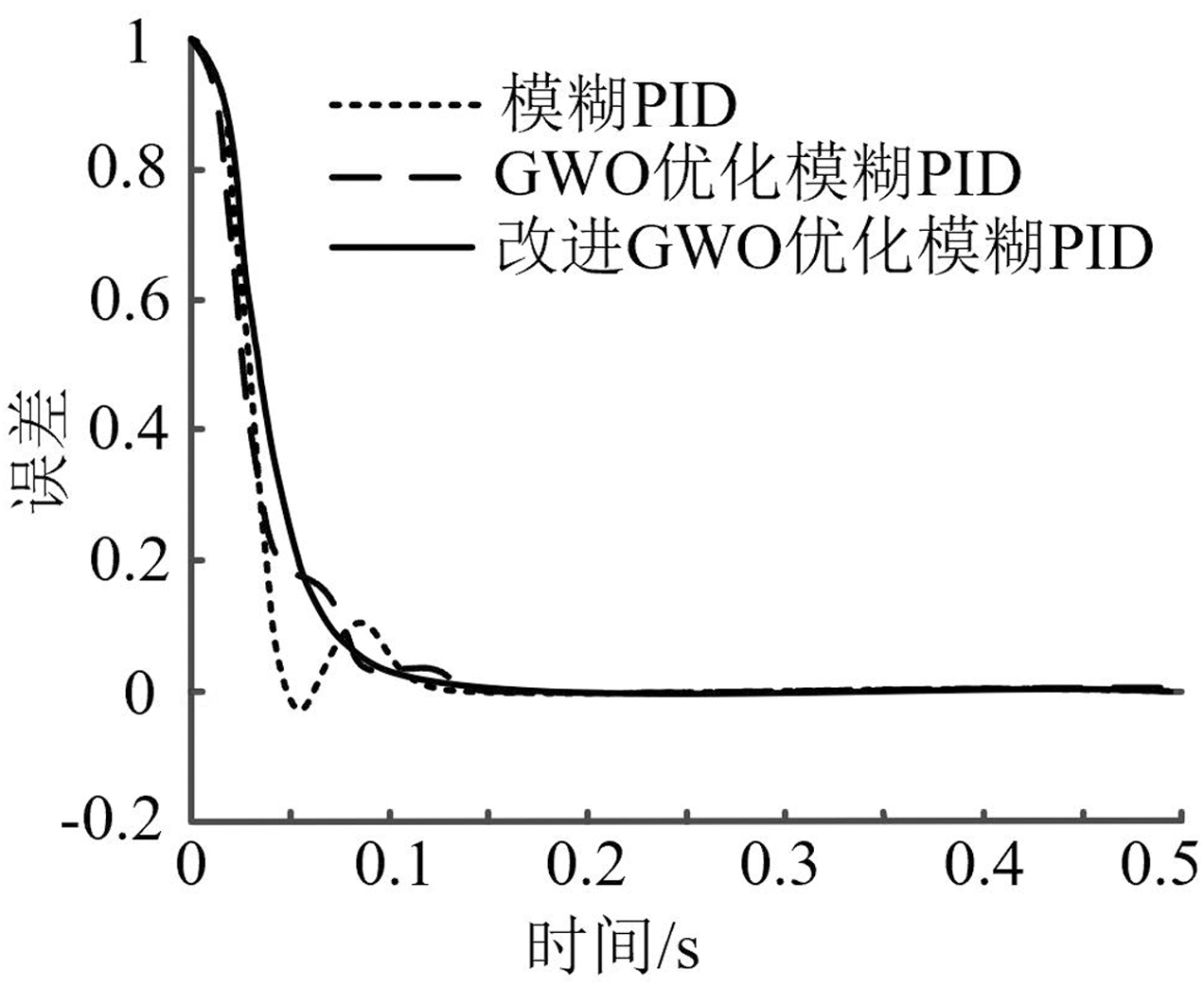
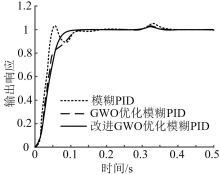
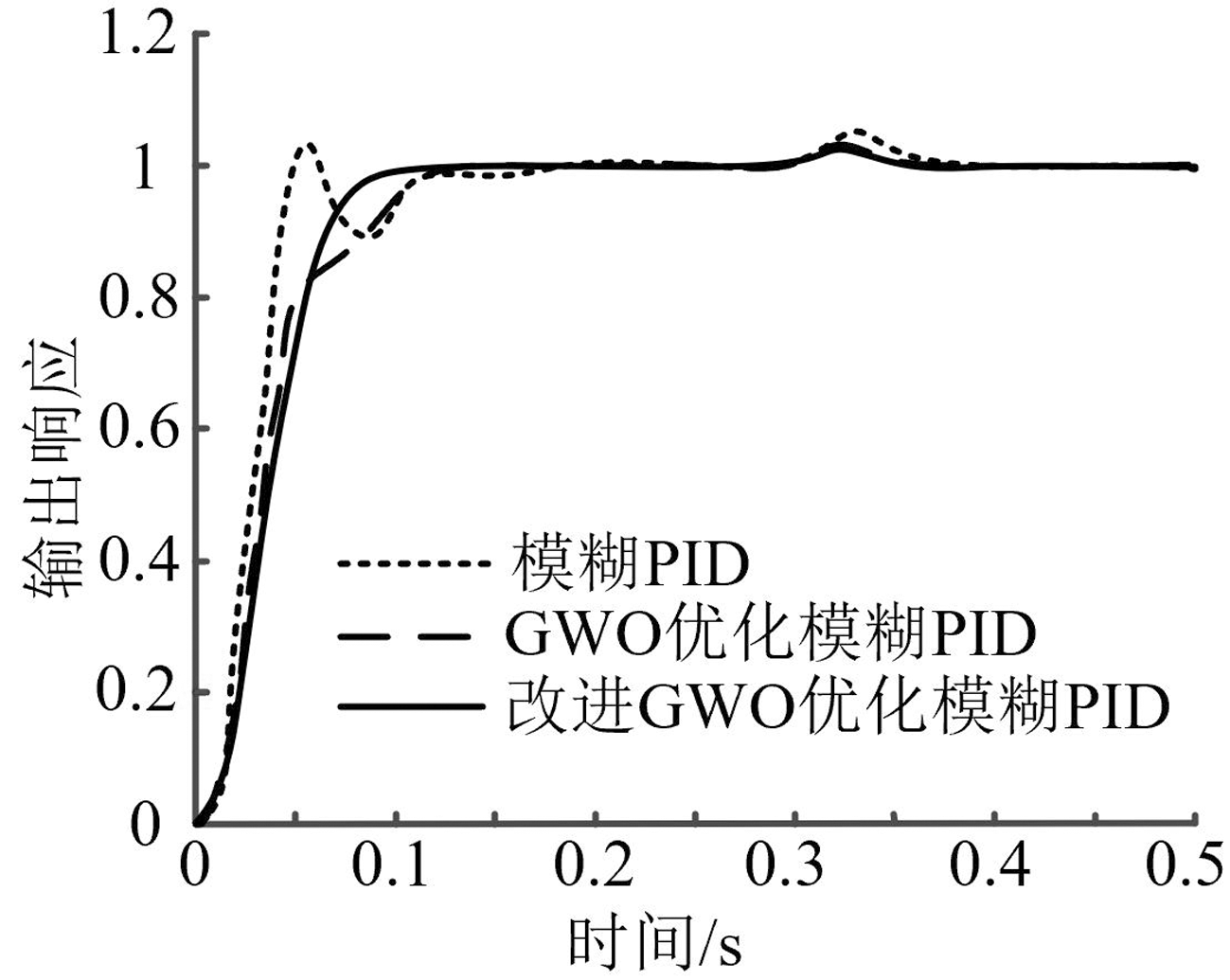
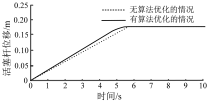
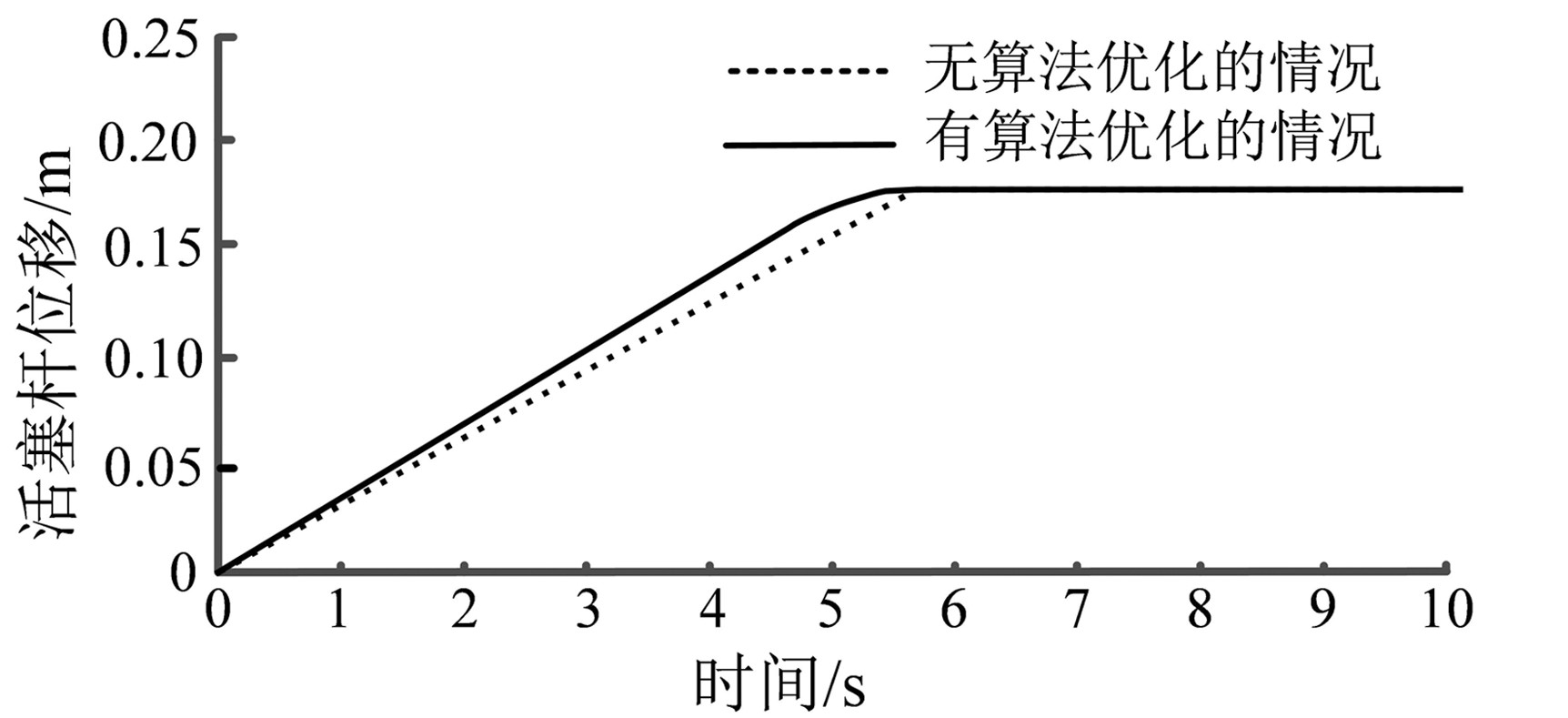
| [1] |
蒋向明. “双碳”背景下煤炭行业与地热产业双重发展机遇[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2022, 34(增1):1-6.
|
|
JIANG Xiangming. Double development opportunities for coal industry and geothermal industry under carbon peaking and carbon neutrality background[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2022, 34(S1):1-6.
|
| [2] |
高宏杰. 煤炭行业发展现状和供需形势分析[J]. 中国煤炭工业, 2022(3):75-77.
|
| [3] |
王国法. 《智能化示范煤矿验收管理办法(试行)》:从编写组视角进行解读[J]. 智能矿山, 2022, 3(6):2-10.
|
| [4] |
孔祥利, 王建行, 杨春学, 等. 可伸缩带式输送机自移机尾改造设计与应用[J]. 煤矿机械, 2022, 43(9):141-143.
|
|
KONG Xiangli, WANG Jianhang, YANG Chunxue, et al. Retrofit design and application of self-moving tail of retractable belt conveyor[J]. Coal Mine Machinery, 2022, 43 (9): 141-143.
|
| [5] |
冯国庭. 智能薄煤层等高综采工作面关键技术与装备[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2022, 50(增1):264-268.
|
|
FENG Guoting. Key technologie and equipment for intelligent fully-mechanized working face with equal height in thin coal seam[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(S1):264-268.
|
| [6] |
刘志明. 基于CAN总线的带式输送机自移机尾电液控制系统设计研究[J]. 煤, 2021, 30(5):77-79.
|
|
LIU Zhiming. Design and research on electro-hydraulic control system of belt conveyor self-moving tail based on CAN bus[J]. Coal, 2021, 30(5):77-79.
|
| [7] |
刘震, 李洋, 闫建伟. 皮带自移机尾电液控制系统设计[J]. 机械工程与自动化, 2022(4):176-177.
|
|
LIU Zhen, LI Yang, YAN Jianwei. Design of electro-hydraulic control system for belt self-moving tail[J]. Mechanical Engineering and Automation, 2022(4):176-177.
|
| [8] |
宋康, 聂永朝, 兰春森. 顺槽带式输送机智能化机尾的研究[J]. 煤矿机械, 2022, 43(9):122-124.
|
|
SONG Kang, NIE Yongchao, LAN Chunsen. Research on intelligent tail of through belt conveyor[J]. Coal Mine Machinery, 2022, 43(9):122-124.
|
| [9] |
任乐乐, 张幸福, 李春鹏. 缓冲阀控制系统在输送带自移机尾上的应用及性能研究[J]. 煤矿机械, 2022, 43(10):156-158.
|
|
REN Lele, ZHANG Xingfu, LI Chunpeng. Application and performance research on buffer valve control system on self-advancing tail piece of conveyor[J]. Coal Mining Machinery, 2022, 43(10):156-158.
|
| [10] |
卢飞, 陈昊南. 基于PID的陆区航路纵向碰撞风险控制[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(9):86-93.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.09.1126
|
|
LU Fei, CHEN Haonan. Longitudinal collision risk control in land route based on PID[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(9):86-93.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.09.1126
|
| [11] |
门飞, 蒋欣. 求解露天矿低碳运输调度问题的改进灰狼优化算法[J]. 工矿自动化, 2020, 46(12):90-94.
|
|
MEN Fei, JIANG Xin. Improved gray wolf optimization algorithm for solving low-carbon transportation scheduling problem in open-pit mines[J]. Journal of Mine Automation, 2020, 46(12):90-94.
|
| [12] |
李敬明. 萤火虫群智能优化算法及其应用研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2018.
|
|
LI Jingming. Reasearch on swarm intelligent optimization algorithm of glowworm and its application[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2018.
|
| [13] |
孟团兴. 基于双引导机制灰狼优化算法的研究与应用[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2022.
|
|
MENG Tuanxing. Research and application of gray wolf optimization algorithm based on dual guidance mechanism[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2022.
|
| [14] |
李星. 灰狼优化算法的改进及应用研究[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学, 2022.
|
|
LI Xing. Research on the improvement and application of gray wolf optimization algorithm[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2022.
|
| [15] |
杨婷婷. 基于神经网络与灰狼优化算法的物种分布模型的研究与应用[D]. 兰州: 西北民族大学, 2022.
|
|
YANG Tingting. Research and application of species distribution model based on neural network and gray wolf optimization algorithm[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Minzu University, 2022.
|
| [16] |
李龙. 基于机电液联合仿真的2000 kN五轴模锻液压机同步特性研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2014.
|
|
LI Long. Study on the synchronization characteristics of 2000 kN five-axis die forging hydraulic press based on electromechanical and hydraulic co-simulation[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2014.
|
| [17] |
张道兵, 朱川曲, 刘泽, 等. 基于Matlab优化工具箱的煤巷顶板锚杆支护结构可靠性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2007(9):131-134,179.
|
|
ZHANG Daobing, ZHU Chuanqu, LIU Ze, et al. Reliability analysis on bolt support structure of coal roadway roof based on matlab's optimization toolbox[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2007(9):131-134,179.
|