| [1] |
向雪梅, 赖玉香, 刘春辉, 等. 微合金化元素Sn对Al-Mg-Si合金高温时效强化相析出路径的改变[J]. 金属学报, 2018, 54(9): 1273-1280.
doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2018.00125
|
|
XIANG Xuemei, LAI Yuxiang, LIU Chunhui, et al. Sn-induced modification of the precipitation pathways upon high-temperature ageing in an Al-Mg-Si alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2018, 54(9): 1273-1280.
doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2018.00125
|
| [2] |
ZHANG Xinxin, ZHOU Xiaorong, NILSSON J. Corrosion behaviour of AA6082 Al-Mg-Si alloy extrusion: the influence of quench cooling rate[J]. Corrosion Science, 2019, 150: 100-109.
doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2019.01.030
|
| [3] |
TEICHMANN K, MARIOARA C D, ANDERSEN S J, et al. TEM study of β' precipitate interaction mechanisms with dislocations and β' interfaces with the aluminium matrix in Al-Mg-Si alloys[J]. Materials Characterization, 2013, 75: 1-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2012.10.003
|
| [4] |
张鑫. 高速列车用6系铝合金应力腐蚀性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2016.
|
|
ZHANG Xin. The stress corrosion behavior investigation of 6 series aluminum alloy for high-speed train[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology, 2016.
|
| [5] |
吕伟, 秦霜霜, 穆治国, 等. CRH380AL型高铁列车应急疏散及影响因素模拟研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(8):164-170.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.08.024
|
|
LYU Wei, QIN Shuangshuang, MU Zhiguo, et al. Simulation study on evacuation of CRH380AL high-speed train and its influencing factors[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(8): 164-170.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.08.024
|
| [6] |
赵江平, 徐恒, 党悦悦. 基于改进Faster R-CNN的铁路客车螺栓检测研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(7):82-89.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.07.012
|
|
ZHAO Jiangping, XU Heng, DANG Yueyue. Research on bolt detection of railway passenger cars based on improved Faster R-CNN[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(7): 82-89.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.07.012
|
| [7] |
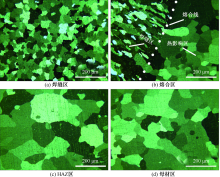
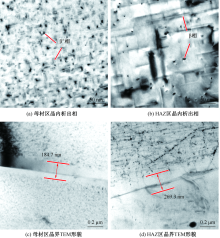
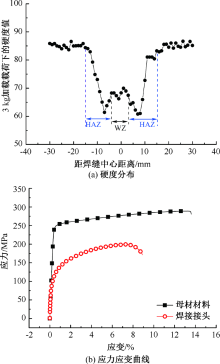
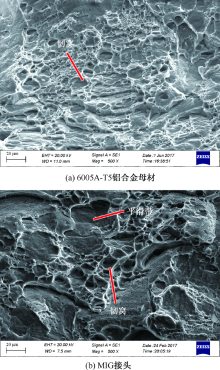
吉华, 邓运来, 邓建峰, 等. 焊接速度对6005A-T6铝合金双轴肩搅拌摩擦焊接头力学性能的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(5):24-29.
|
|
JI Hua, DENG Yunlai, DENG Jianfeng, et al. Effect of welding speed on mechanical properties of double-shaft shoulder friction stir welding joint of 6005A-T6 aluminum alloy[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(5):24-29.
|
| [8] |
张昱, 李冀东, 丁鑫健, 等. 6N01铝合金高频脉冲电流复合MIG焊接电信号和图像信号的采集与分析[J]. 热加工工艺, 2020, 49(1):152-154.
|
|
ZHANG Yu, LI Jidong, DING Xinjian, et al. Acquisition and analysis of electric signals and image signals of high frequency pulse current hybrid MIG welding of 6N01 aluminum alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2020, 49(1):152-154.
|
| [9] |
孟立春, 刘春辉, 赖玉香, 等. 6N01-7N01铝合金T型焊接接头的微观组织与性能的研究[J]. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 44(12):20-26.
|
|
MENG Lichun, LIU Chunhui, LAI Yuxiang, et al. The heterogeneity in microstructure and property of the welded joints between 6N01 and 7N01 aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Hunan University:Natural Science, 2017, 44(12):20-26.
|
| [10] |
GB/T 228.1—2010, 金属材料拉伸试验第1部分:室温试验方法[S].
|
|
GB/T 228.1—2010, Metallic materials-tensile testing part 1: method of test at room temperature[S].
|
| [11] |
HB 5254—1983, 变形铝合金拉伸应力腐蚀.试验方法[S].
|
| [12] |
LIN Sen, DENG Yunlai, LIN Huaqiang, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties and stress corrosion behavior of friction stir welded joint of Al-Mg-Si alloy extrusion[J]. Rare Metals, 2018: doi: 10.1007/s12598-018-1126-7.
doi: 10.1007/s12598-018-1126-7
|
| [13] |
ZHANG Liang, LI Xiaoyan, NIE Zuoren, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a new Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy joints welded by laser beam[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 83: 451-458.
|
| [14] |
CHU Qiaoling, BAI Ruixiang, JIAN Haigen, et al. Microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of 6061 aluminum laser beam welded joints[J]. Materials Characterization, 2018, 137: 269-276.
doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2018.01.030
|
| [15] |
YANG Wenchao, JI Shouxun, ZHANG Qian, et al. Investigation of mechanical and corrosion properties of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy under various ageing conditions and interface analysis of η' precipitate[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 85: 752-761.
|
| [16] |
LIN Y C, ZHANG Jinlong, LIU Guan, et al. Effects of pre-treatments on aging precipitates and corrosion resistance of a creep-aged Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 83: 866-875.
|
| [17] |
LI Hai, ZHAO Peipei, WANG Zhixiu, et al. The intergranular corrosion susceptibility of a heavily overaged Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2016, 107: 113-122.
doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2016.02.025
|