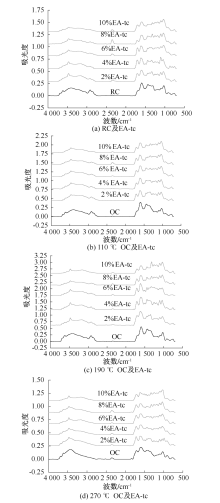
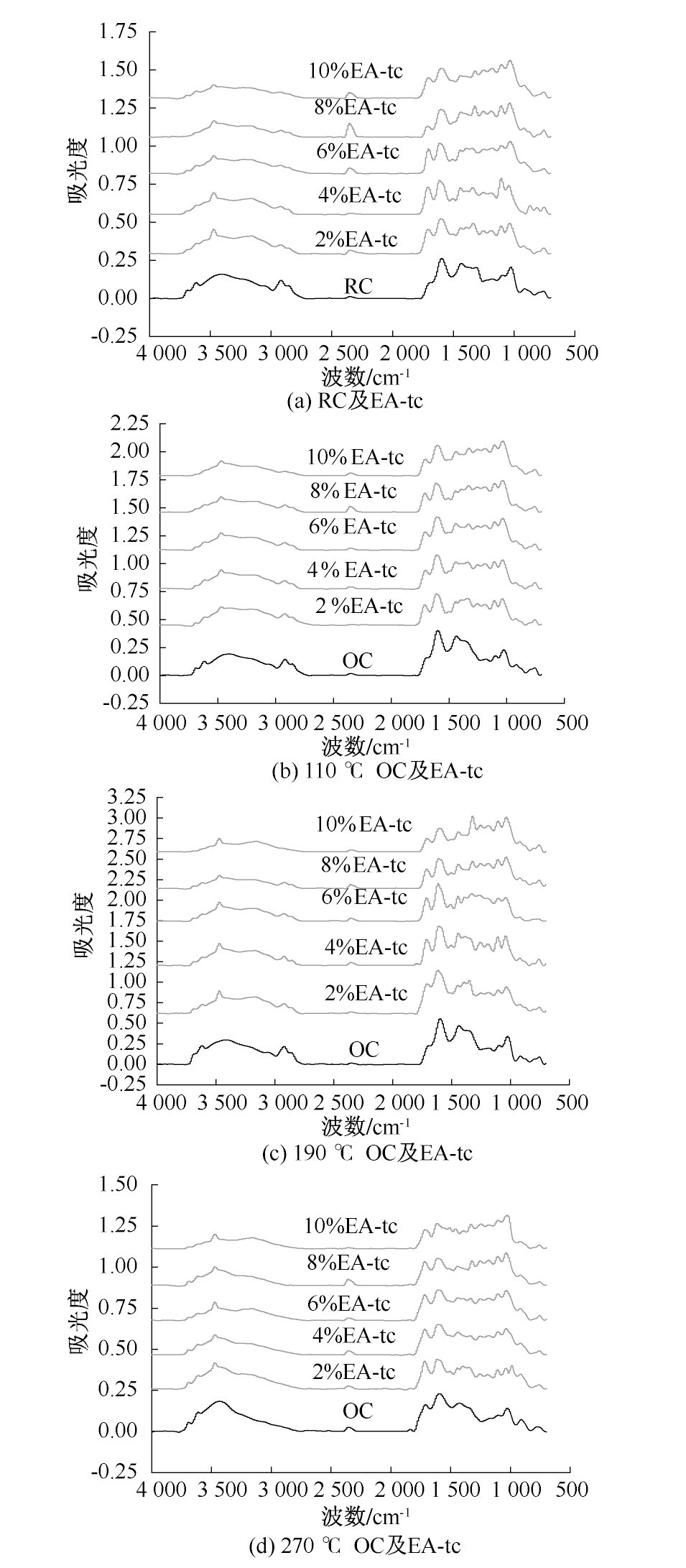
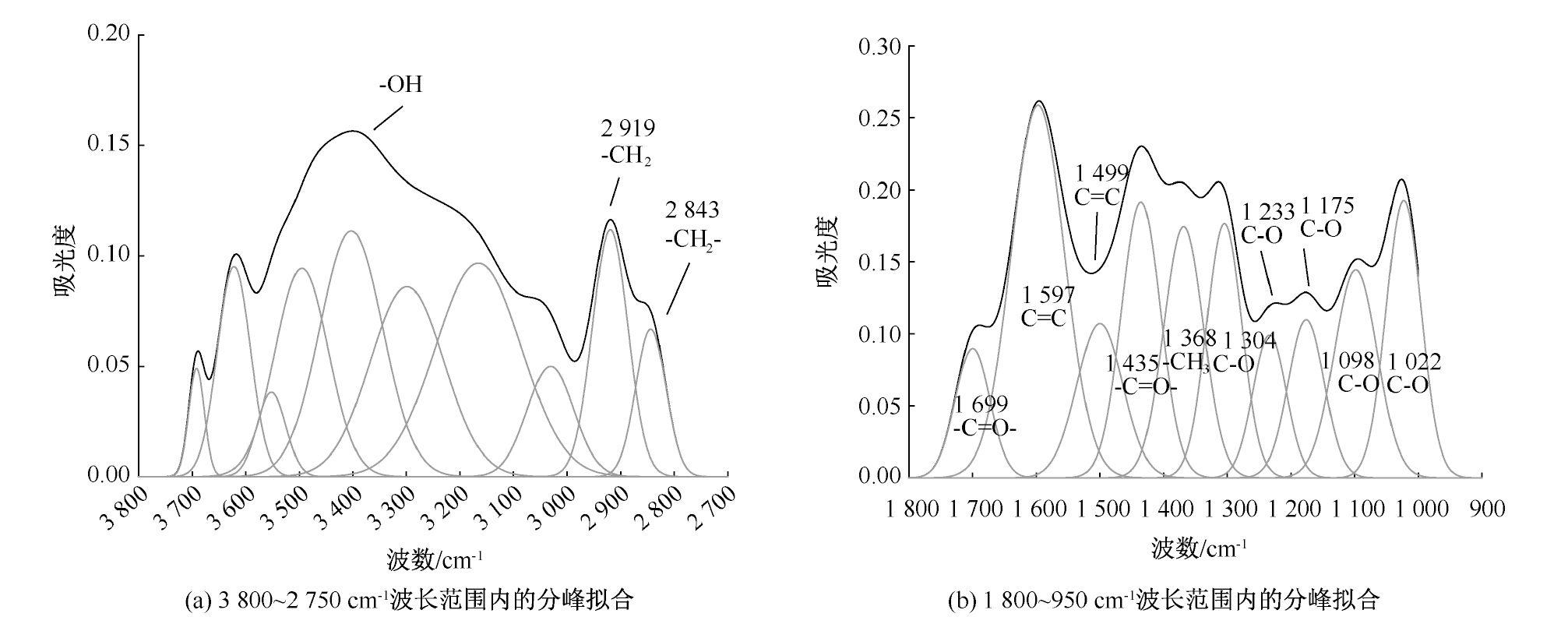
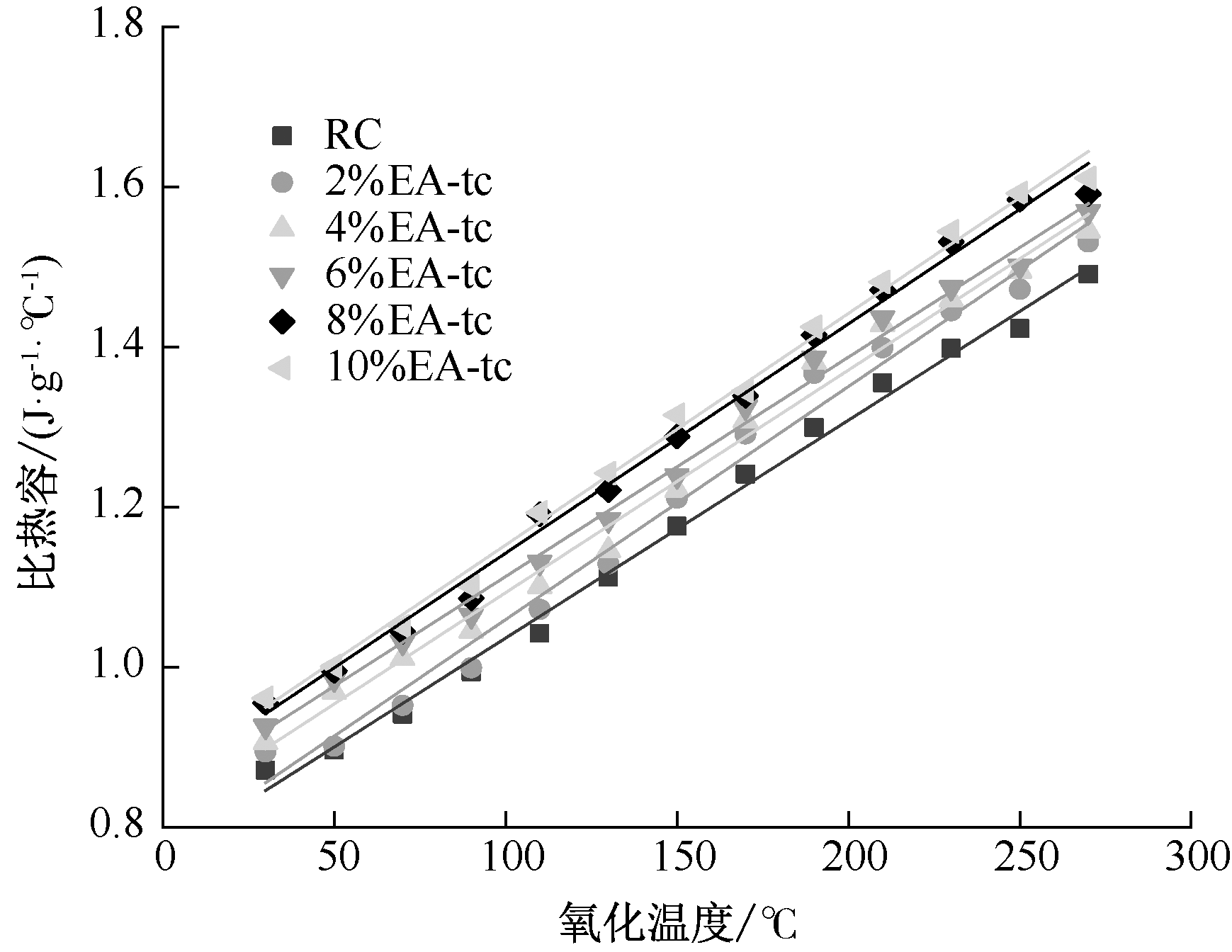
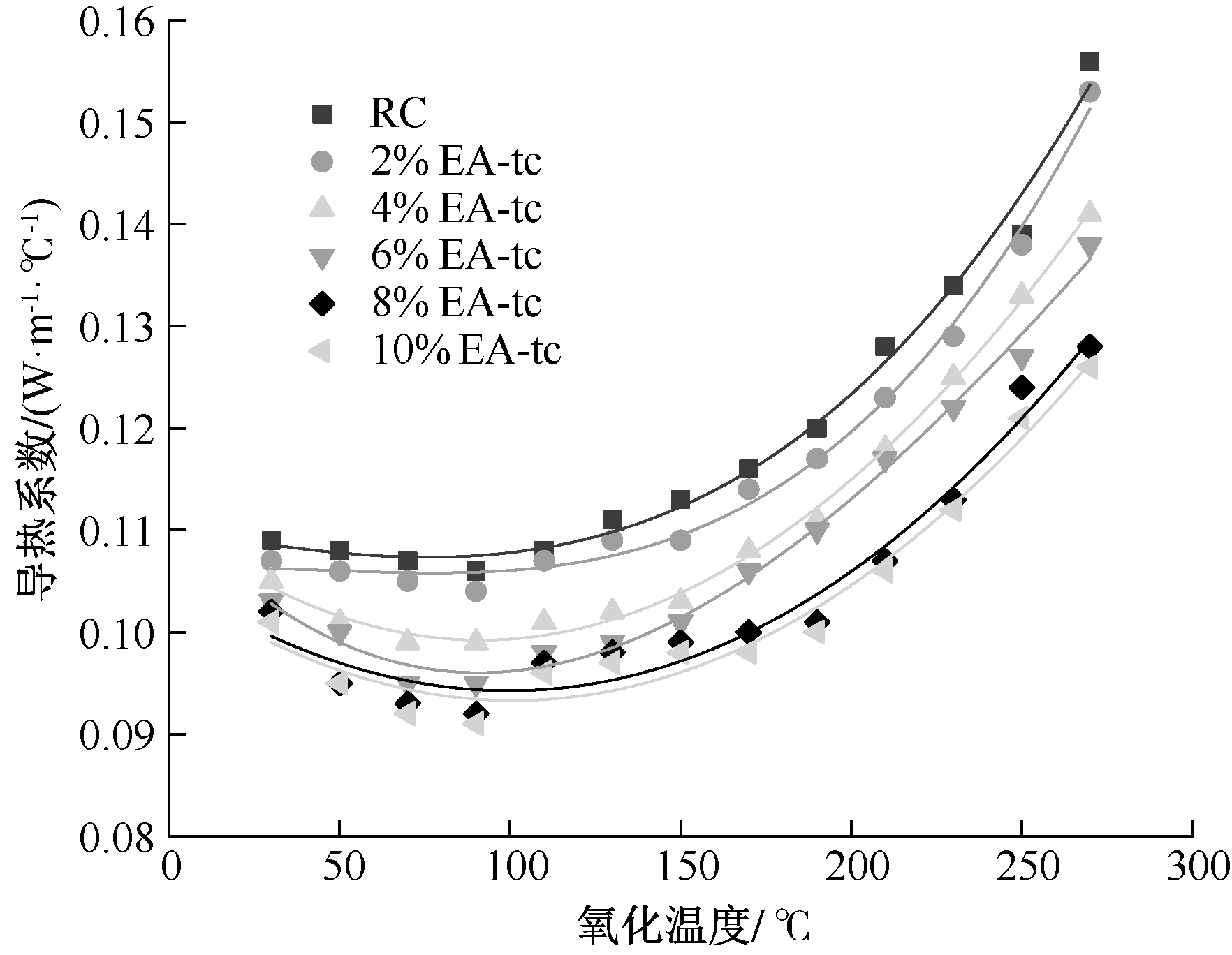
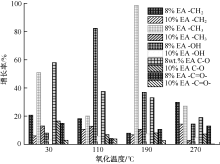
| [1] |
ZHANG Yutao, LIU Yurui, SHI Xueqiang, et al. Risk evaluation of coal spontaneous combustion on the basis of auto-ignition temperature[J]. Fuel, 2018, 233: 68-76.
|
| [2] |
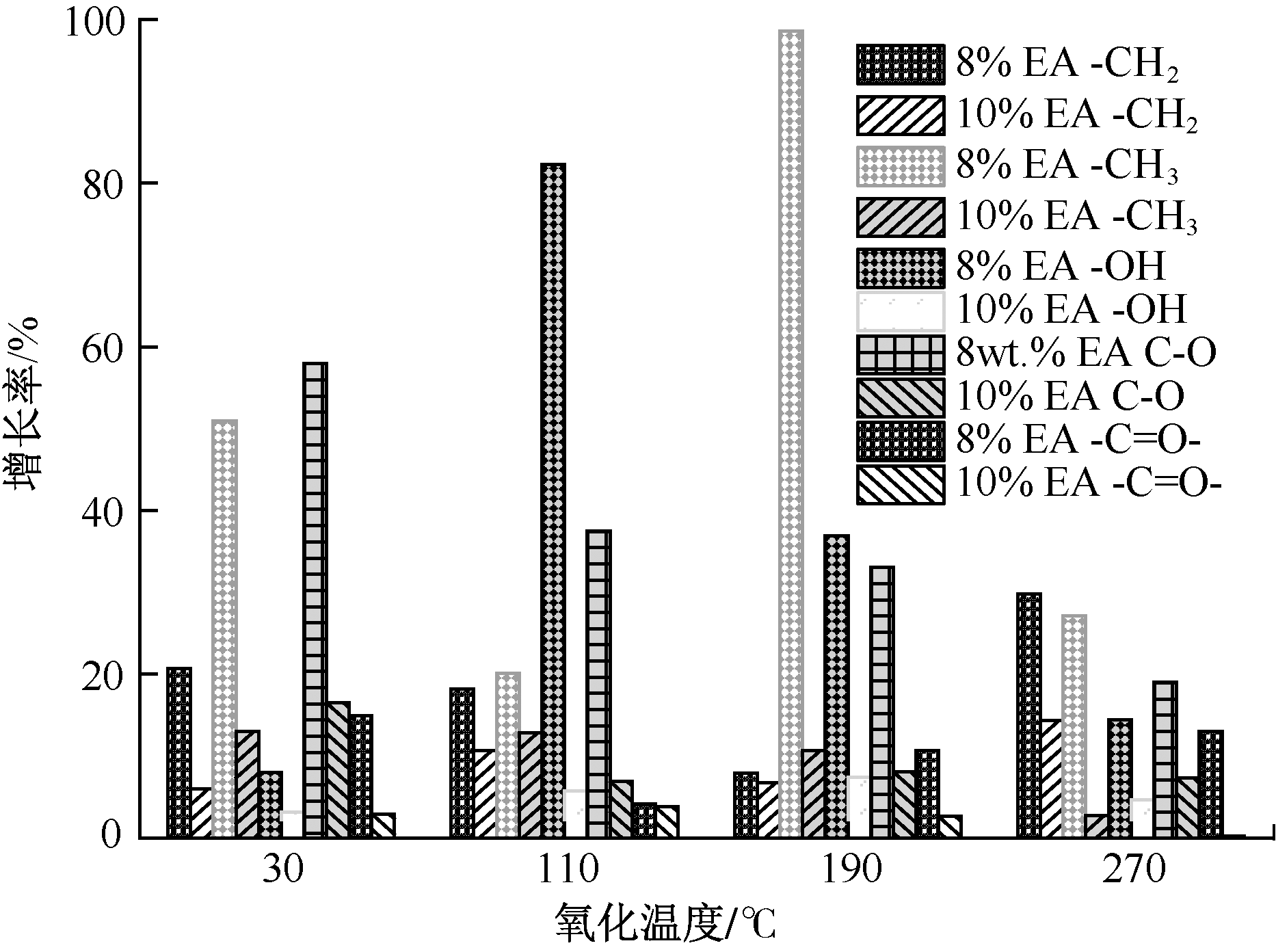
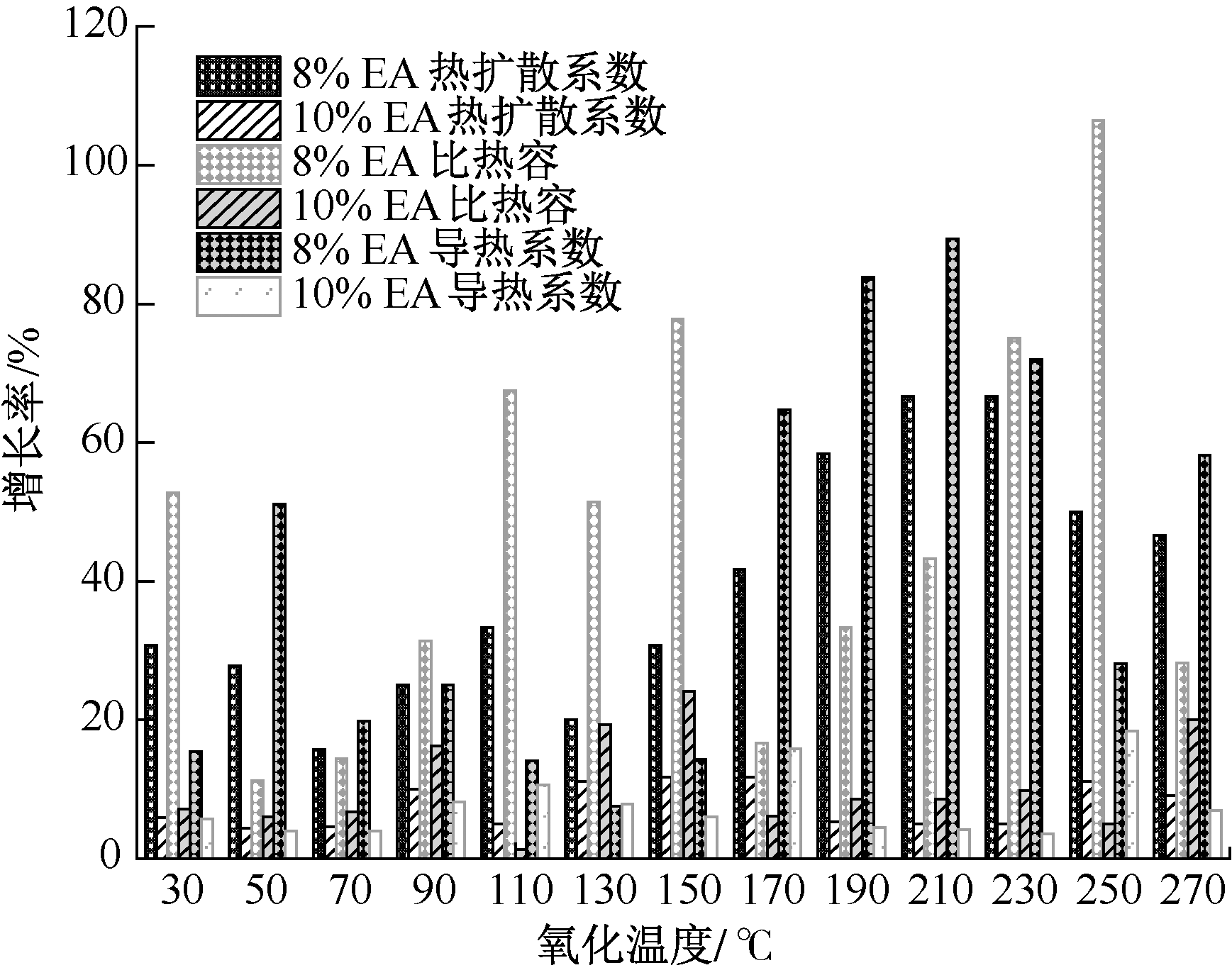
张嬿妮, 舒盼, 刘春辉, 等. 乙二胺四乙酸微胶囊阻化煤自燃性能研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2022, 50(8): 108-117.
|
|
ZHANG Yanni, SHU Pan, LIU Chunhui, et al. Study on inhibition of coal spontaneous combustion by ethylenedia mine tetraacetic acid microcapsule[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(8): 108-117.
|
| [3] |
肖旸, 叶星星, 刘昆华, 等. 二次氧化煤自燃过程关键官能团的转变规律[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(增2): 989-1000.
|
|
XIAO Yang, YE Xingxing, LIU Kunhua, et al. Transformation law of key functional groups in the process of coal secondary oxidation[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(S2): 989-1000.
|
| [4] |
戚绪尧, 王涛, 张兰君, 等. 低共熔溶剂抑制煤自燃的机理研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2024, 49(4): 1 917-1 930.
|
|
QI Xuyao, WANG Tao, ZHANG Lanjun, et al. Mechanism of deep eutectic solvent on coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2024, 49(4): 1 917-1 930.
|
| [5] |
LI Jinhu, LI Zenghua, WANG Chaojie, et al. Experimental study on the inhibitory effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) on coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2018, 178: 312-321.
|
| [6] |
娄和壮, 贾廷贵. 惰性气氛对煤自燃过程的竞争吸附差异性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(4): 60-67.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.010
|
|
LOU Hezhuang, JlA Tinggui. Competitive adsorption differences during coal spontaneous combustion process in noble gas atmosphere[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(4): 60-67.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.010
|
| [7] |
LI Jinhu, LI Zenghua, YANG Yongliang, et al. Laboratory study on the inhibitory effect of free radical scavenger on coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2018, 171: 350-360.
|
| [8] |
WANG Deming, DOU Guolan, ZHONG Xiaoxing, et al. An experimental approach to selecting chemical inhibitors to retard the spontaneous combustion of coal[J]. Fuel, 2014, 117: 218-223.
|
| [9] |
GAO Ao, SUN Yong, HU Xiangming, et al. Substituent positions and types for the inhibitory effects of phenolic inhibitors in coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Fuel, 2022, 309: DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122104.
|
| [10] |
LIU Peiyu, LI Zenghua, ZHANG Xiaoyan, et al. Study on the inhibition effect of citric acid on coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Fuel, 2022, 310: DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122268.
|
| [11] |
王福生, 张朝阳, 刘向群, 等. 金属离子螯合剂抑制煤自燃试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2023, 51(增1): 1-8.
|
|
WANG Fusheng, ZHANG Chaoyang, LIU Xiangqun, et al. Experimental study on suppression of coal spontaneous combustion by metal ion chelating agents[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(S1): 1-8.
|
| [12] |
姜峰, 孙雯倩, 李珍宝, 等. 复合阻化剂抑制煤自燃过程的阶段阻化特性[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2022, 50(10): 68-75.
|
|
JIANG Feng, SUN Wenqian, LI Zhenbao, et al. Stage inhibition characteristics of composite inhibitor in process of inhibiting coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(10): 68-75.
|
| [13] |
WANG Kai, HU Lihong, DENG Jun, et al. Inhibiting effect and mechanism of polyethylene glycol-citric acid on coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Energy, 2023, 275: 127-522.
|
| [14] |
LI Dajiang, XIAO Yang, LYU Huifei, et al. Effects of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate on the exothermic and heat transfer characteristics of coal during low-temperature oxidation[J]. Fuel, 2020, 273: DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117589.
|