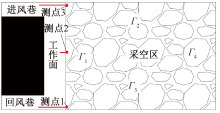
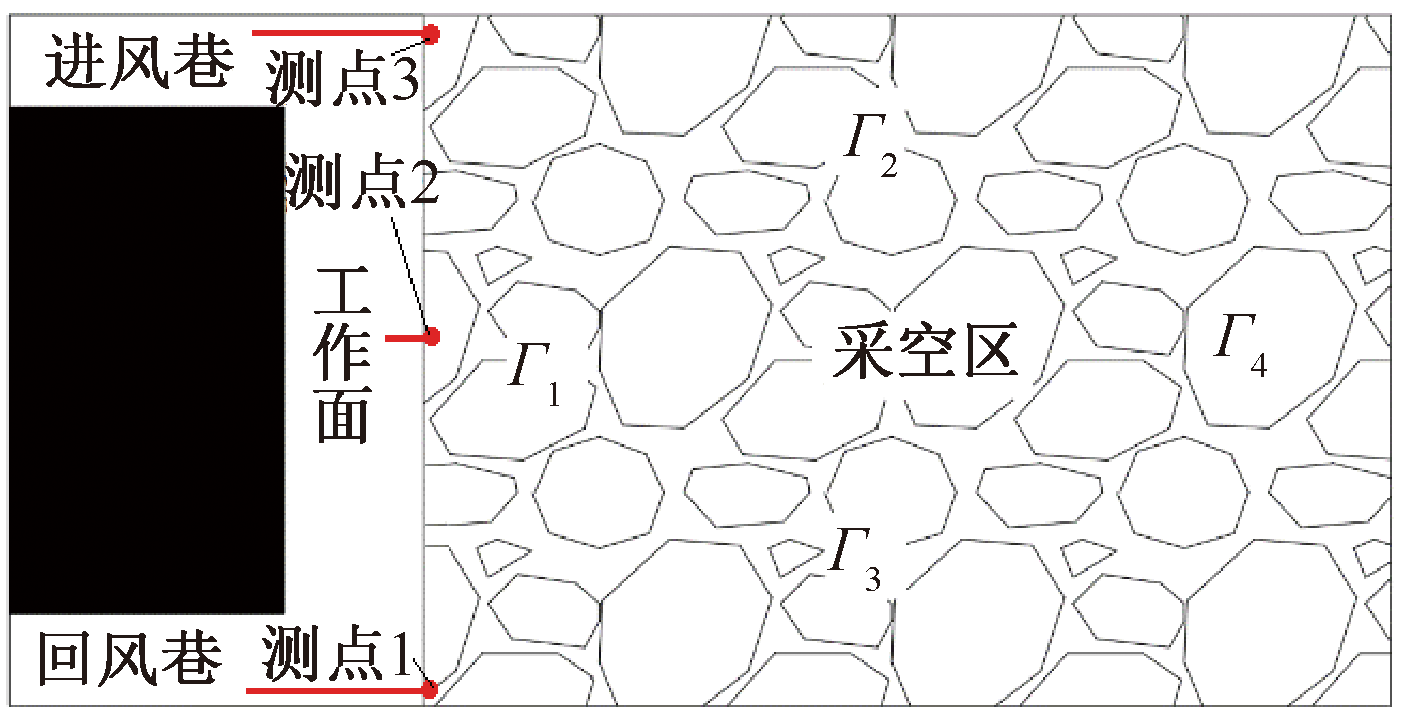
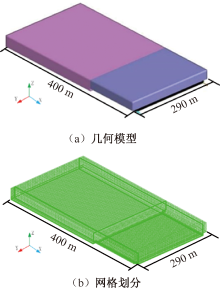
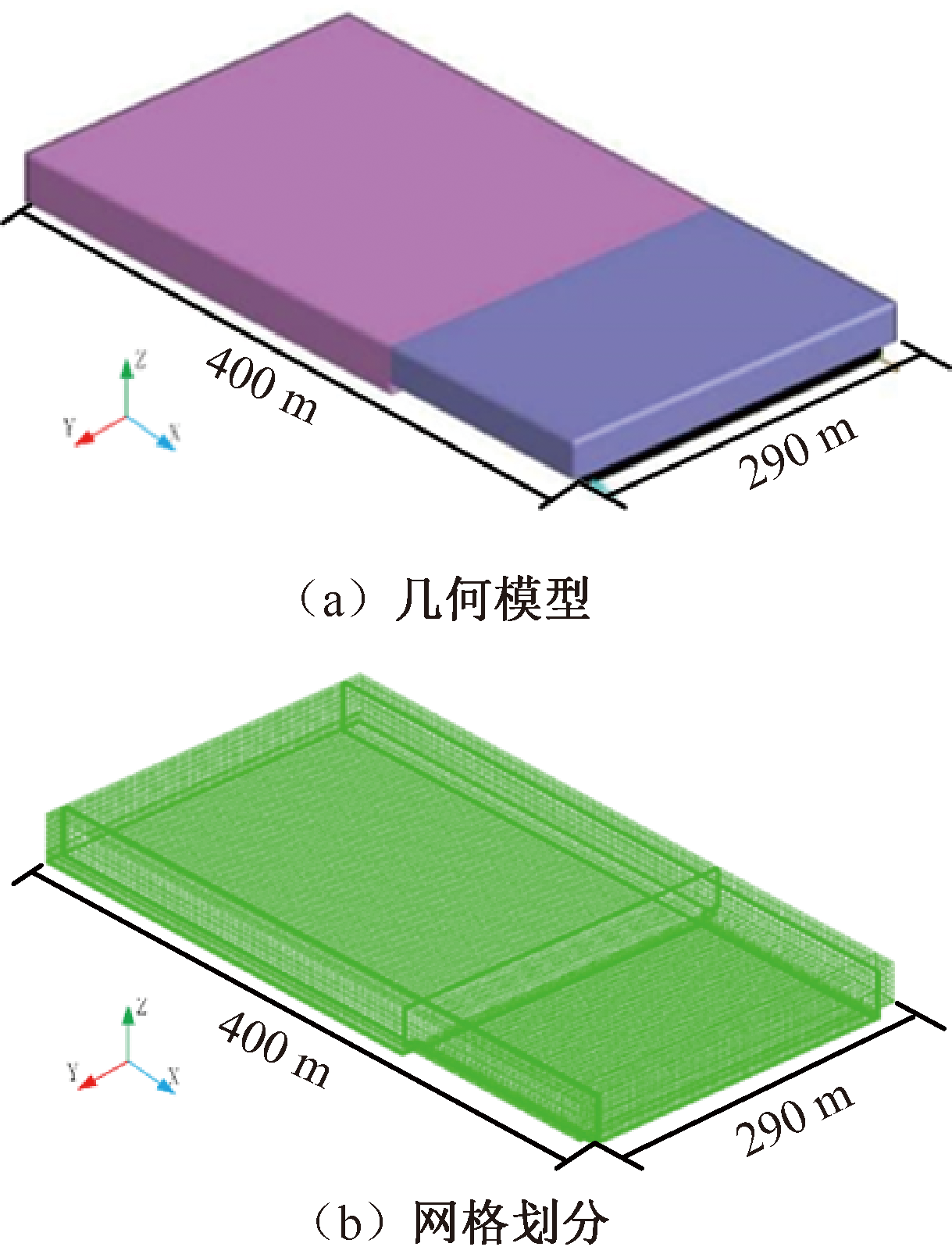
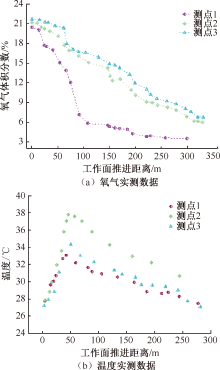
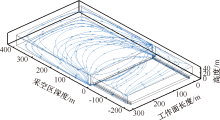
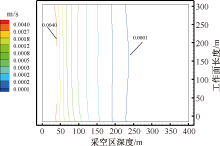
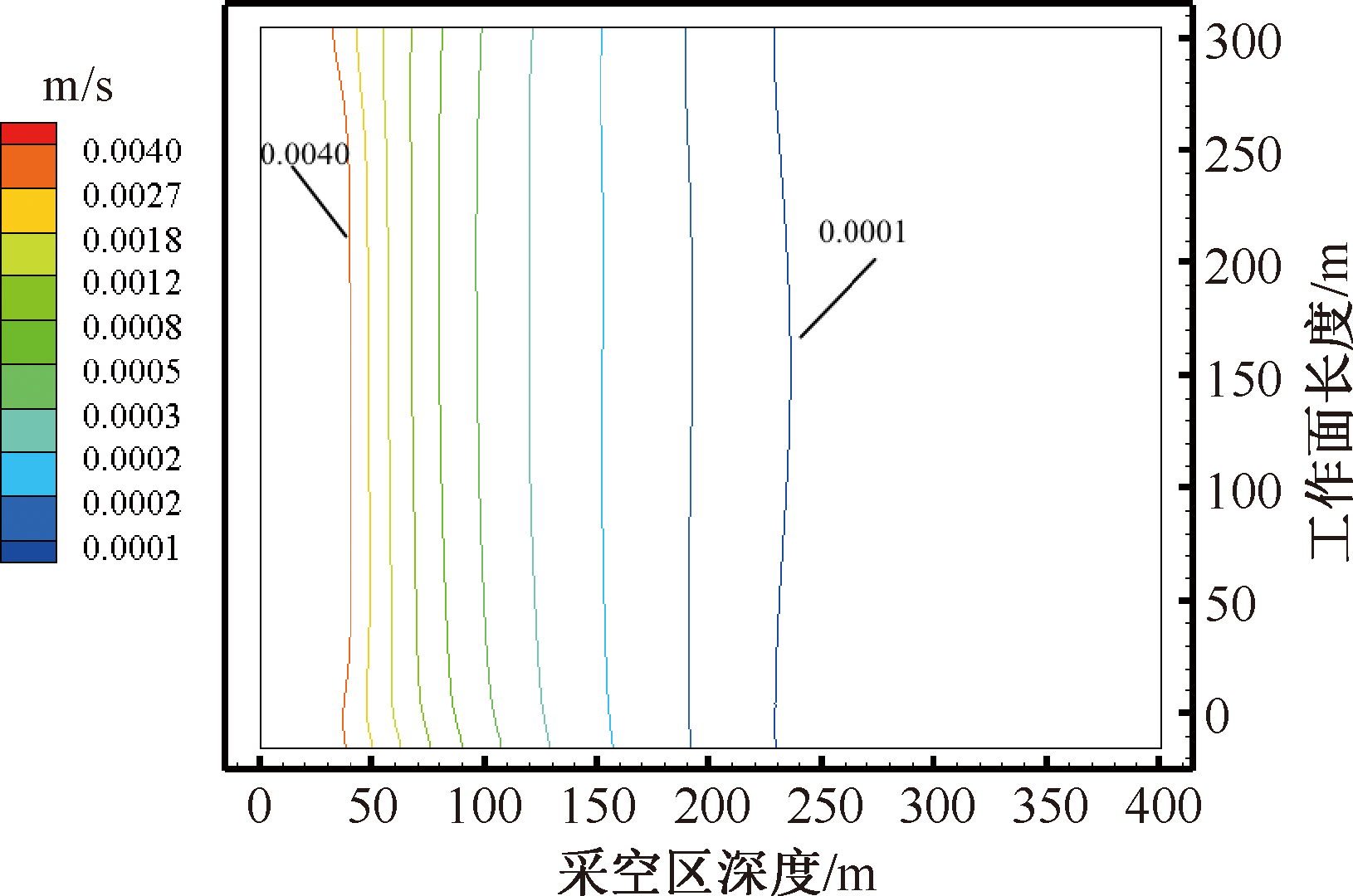
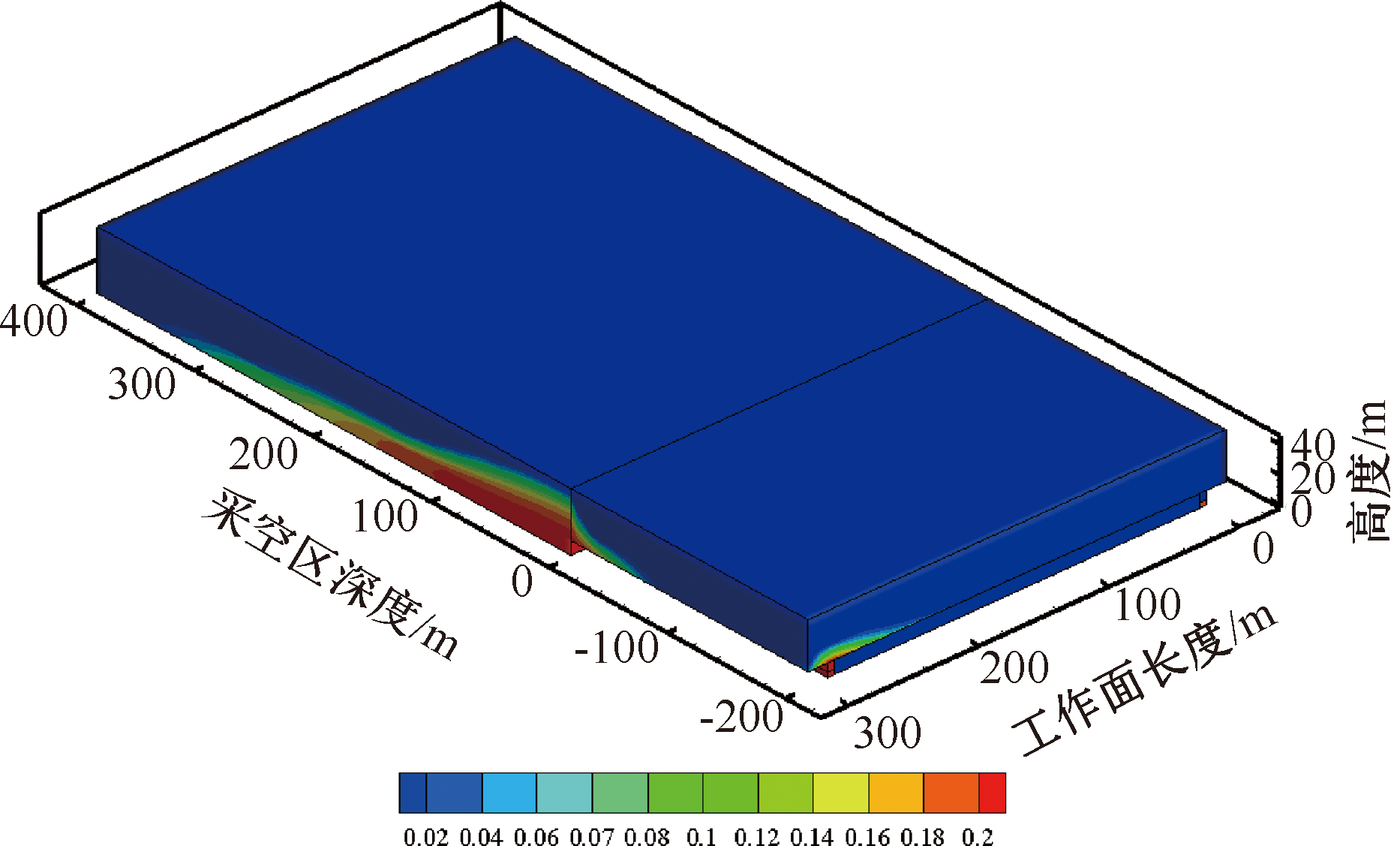
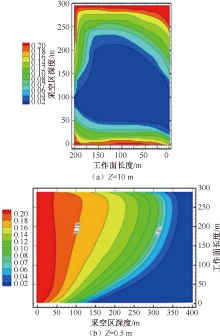
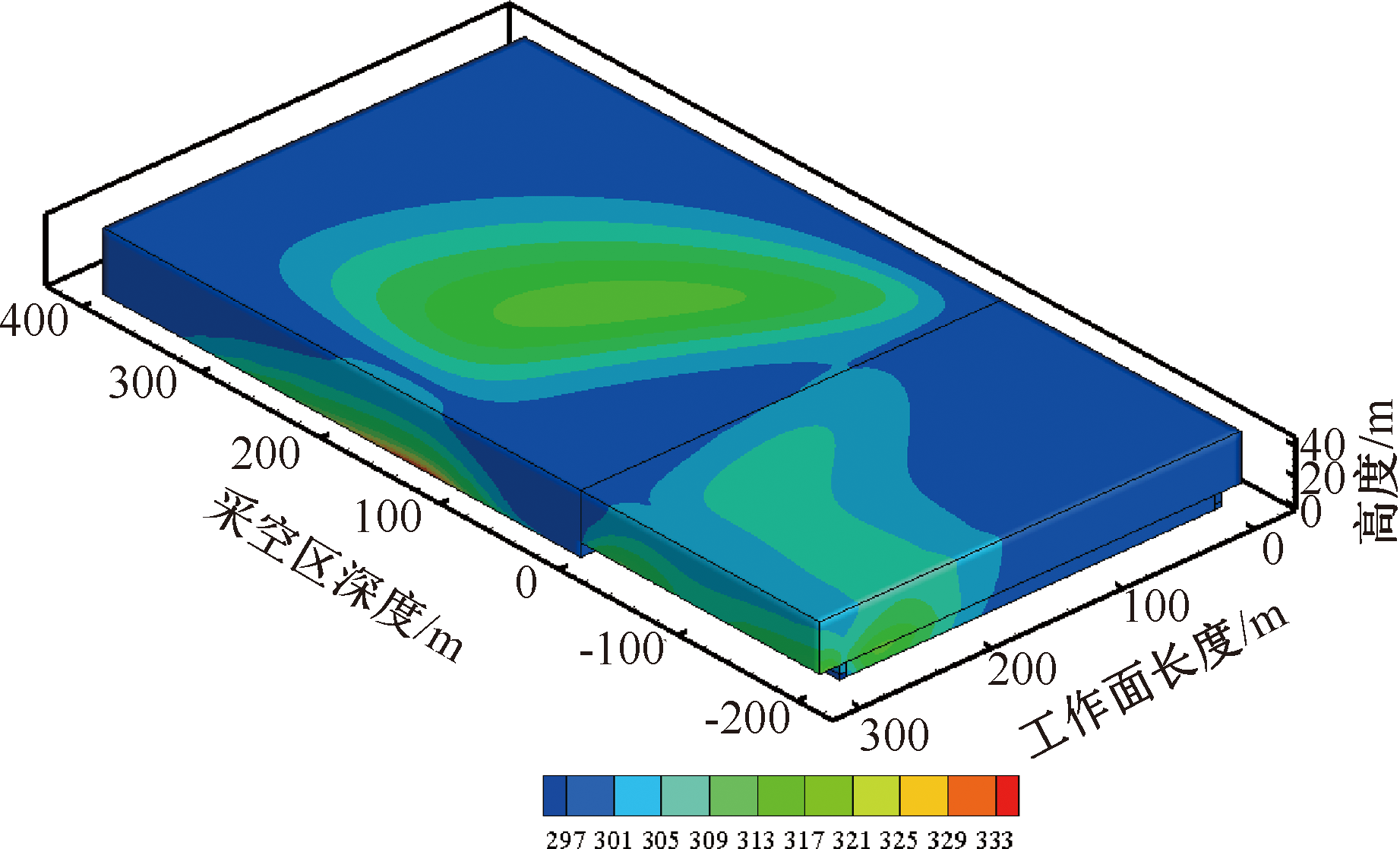
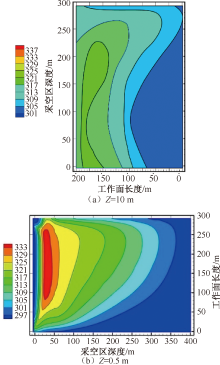
| [1] |
QIAO Ming, REN Ting, ROBERTS Jon, et al. New insight into proactive goaf inertisation for spontaneous combustion management and control[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 161(4):739-757.
|
| [2] |
STRACHER G B, TAYLOR T P. Coal fires burning out of control around the world: thermodynamic recipe for environmental catastrophe[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2004, 59(1/2):7-17.
|
| [3] |
ROSEMA A, GUAN H, VELD H. Simulation of spontaneous combustion, to study the causes of coal res in the Rujigou basin[J]. Scientific Reports, 2001, 80(1):7-16.
|
| [4] |
ALEX C S, LI Yuan. Simulation of spontaneous heating in longwall gob area with a bleederless ventilation system[J]. Mining Engineering, 2008, 60(8):61-66.
|
| [5] |
DICK S, JAN H D, JAN W V H. A model for the spontaneous heating of coal[J]. Fuel, 1985, 64(7):963-972.
|
| [6] |
李宗翔, 李海洋, 贾进章. Y形通风采空区注氮防灭火的数值模拟[J]. 煤炭学报, 2005, 30(5): 51-55.
|
|
LI Zongxiang, LI Haiyang, JIA Jinzhang. Numerical simulation of preventing spontaneous combustion by nitrogen injection in goaf of Y-type ventilation face[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2005, 30(5): 51-55.
|
| [7] |
卞晓锴, 包宗宏, 史美仁. 采空区温度场模拟及煤自燃状态预测[J]. 南京化工大学学报, 2000, 22(2):43-47.
|
|
BIAN Xiaokai, BAO Zonghong, SHI Meiren, et al. Numerical simulation of temperature field for worked-out section of coal mines and prediction of spontaneous combustion[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Chemical Technology, 2000, 22(2):43-47.
|
| [8] |
谭允祯, 张东俭, 杨东岳, 等. 综采放顶煤工作面采空区自燃区的划分[J]. 山东科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2002, 21(1):69-71.
|
|
TAN Yunzhen, ZHANG Dongjian, YANG Dongyue, et al. The division of spontaneous combustion areas in the goaf of fully mechanized caving face[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology :Natural Science, 2002, 21(1):69-71.
|
| [9] |
余为, 李强, 黄伟, 等. 破碎岩体中的气体渗流规律研究[J]. 燕山大学学报, 2007, 31(4):317-321.
|
|
YU Wei, LI Qiang, HUANG Wei, et al. Study on the laws of gas flow in over-broken rock mass[J]. Journal of Yanshan University, 2007, 31(4):317-321.
|
| [10] |
唐明云, 戴广龙, 秦汝祥, 等. 综采工作面采空区漏风规律数值模拟[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 43(4):1 494-1 498.
|
|
TANG Mingyun, DAI Guanglong, QIN Ruxiang, et al. Numerical analysis of air-leakage law in goaf of fully mechanized face[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2012, 43(4):1 494-1 498.
|
| [11] |
刘伟. 采空区自然发火的多场耦合机理及三维数值模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2014.
|
|
LIU Wei. Multi-physics coupling mechanism and three-dimensional numerical simulation of spontaneous combustion of goaf[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining & Technology (Beijing), 2014.
|
| [12] |
朱建芳, 蔡卫, 秦跃平. 基于移动坐标的采空区自然发火模型研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2009, 34(8):1 095-1 099.
|
|
ZHU Jianfang, CAI Wei, QIN Yueping. Mathematical model for spontaneous combustion m goaf in the moving coordinates[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2009, 34(8):1 095-1 099.
|
| [13] |
车强. 采空区气体三维多场耦合规律研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2010.
|
|
CHE Qiang. Study on coupling law of mixed gas three-dimensional multi-field in goaf[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining & Technology(Beijing), 2010.
|
| [14] |
王月红. 移动坐标下采空区自然发火的有限体积法模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2009.
|
|
WANG Yuehong. Study on simulation of spontaneous combustion in goaf on the moving coordinate with finite volume method[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining & Technology (Beijing), 2009.
|
| [15] |
刘伟, 秦跃平, 乔珽, 等. 煤耗氧速率与CO生成速率的计算及实验论证[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2016, 45(6):1 141-1 147.
|
|
LIU Wei, QIN Yueping, QIAO Ting, et al. Experimental demonstration on calculation of oxygen consumption rate andCO generation rate in coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2016, 45(6):1 141-1 147.
|