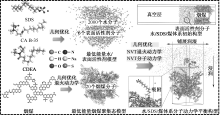
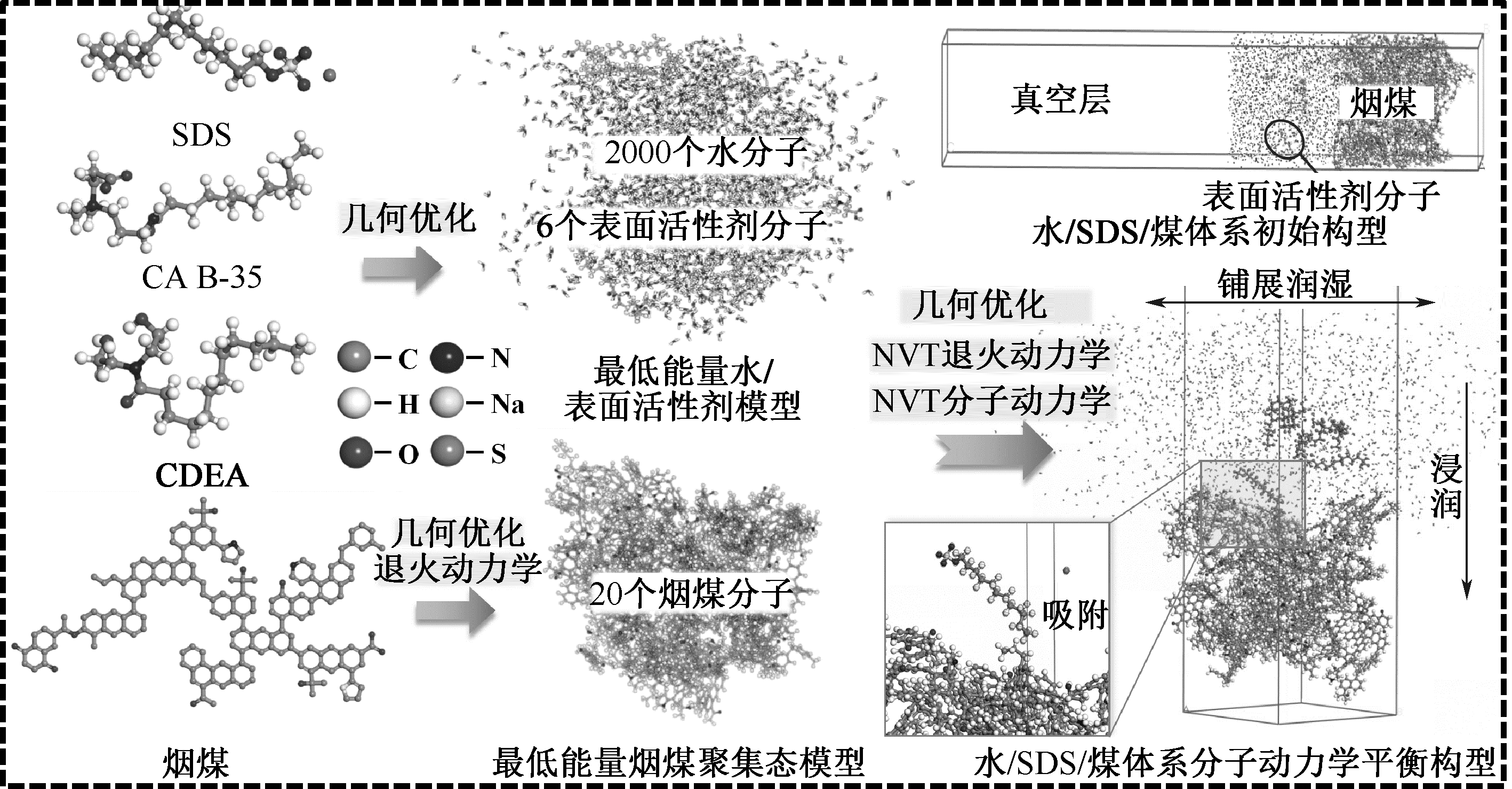
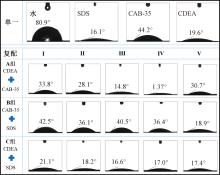
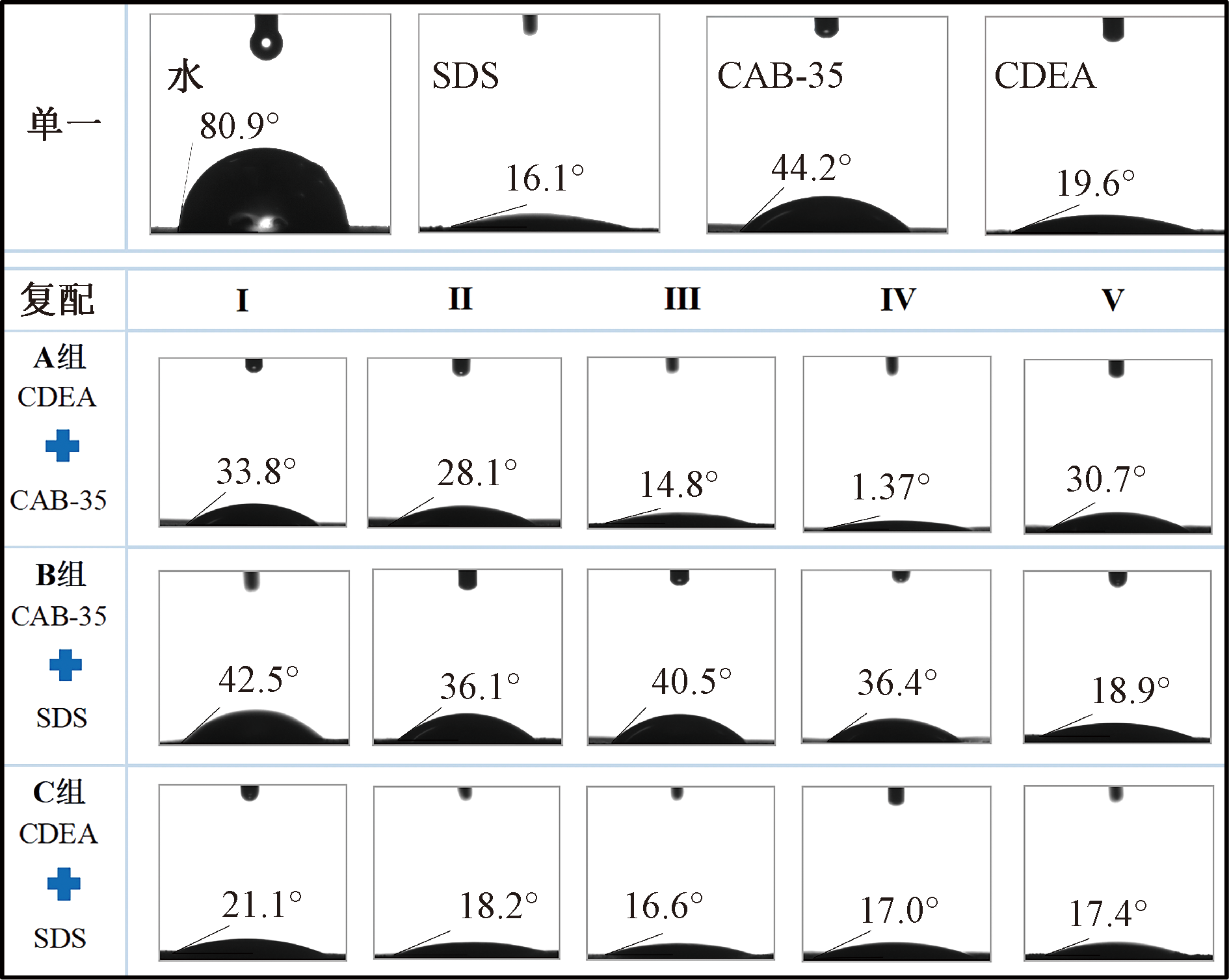
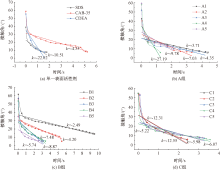
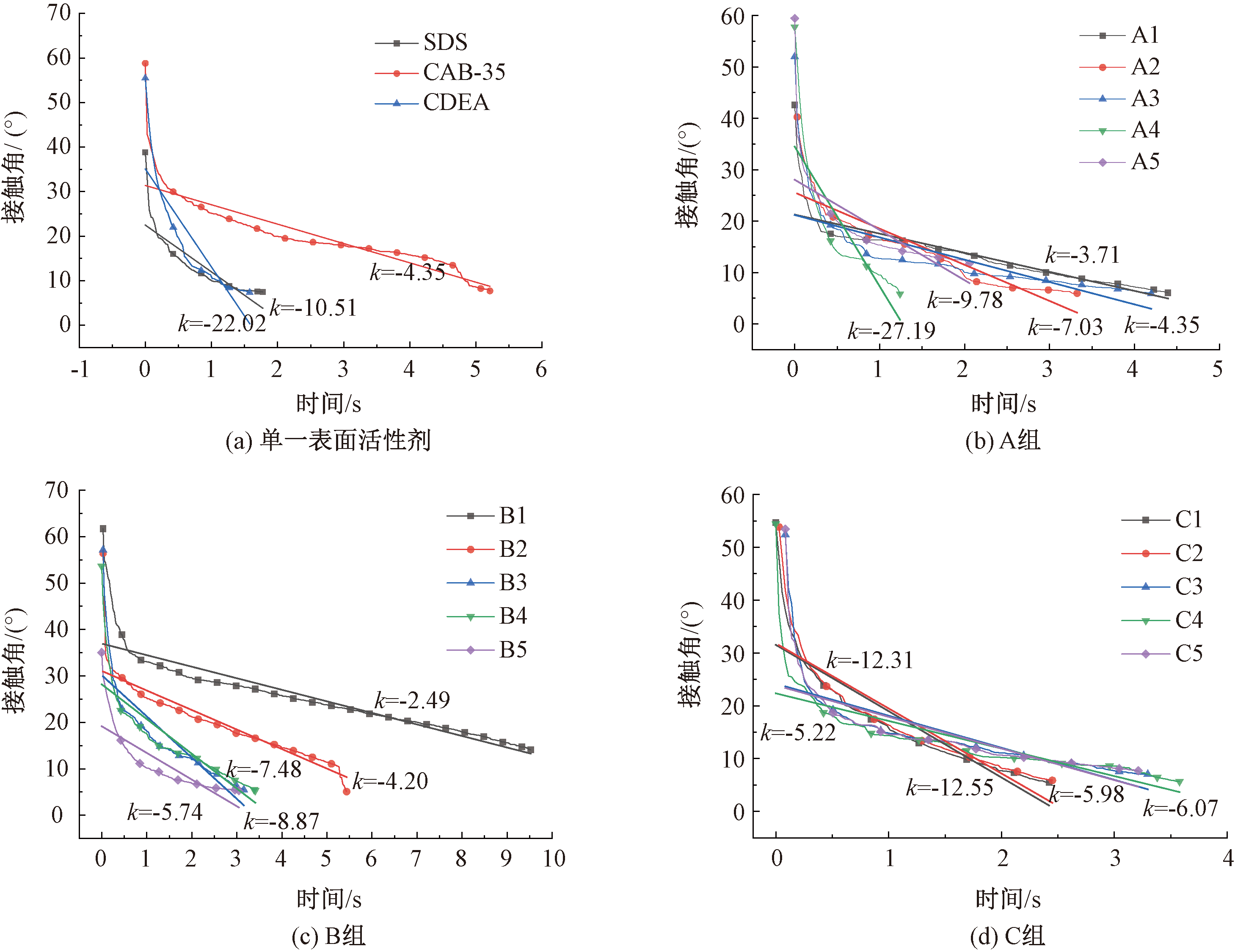
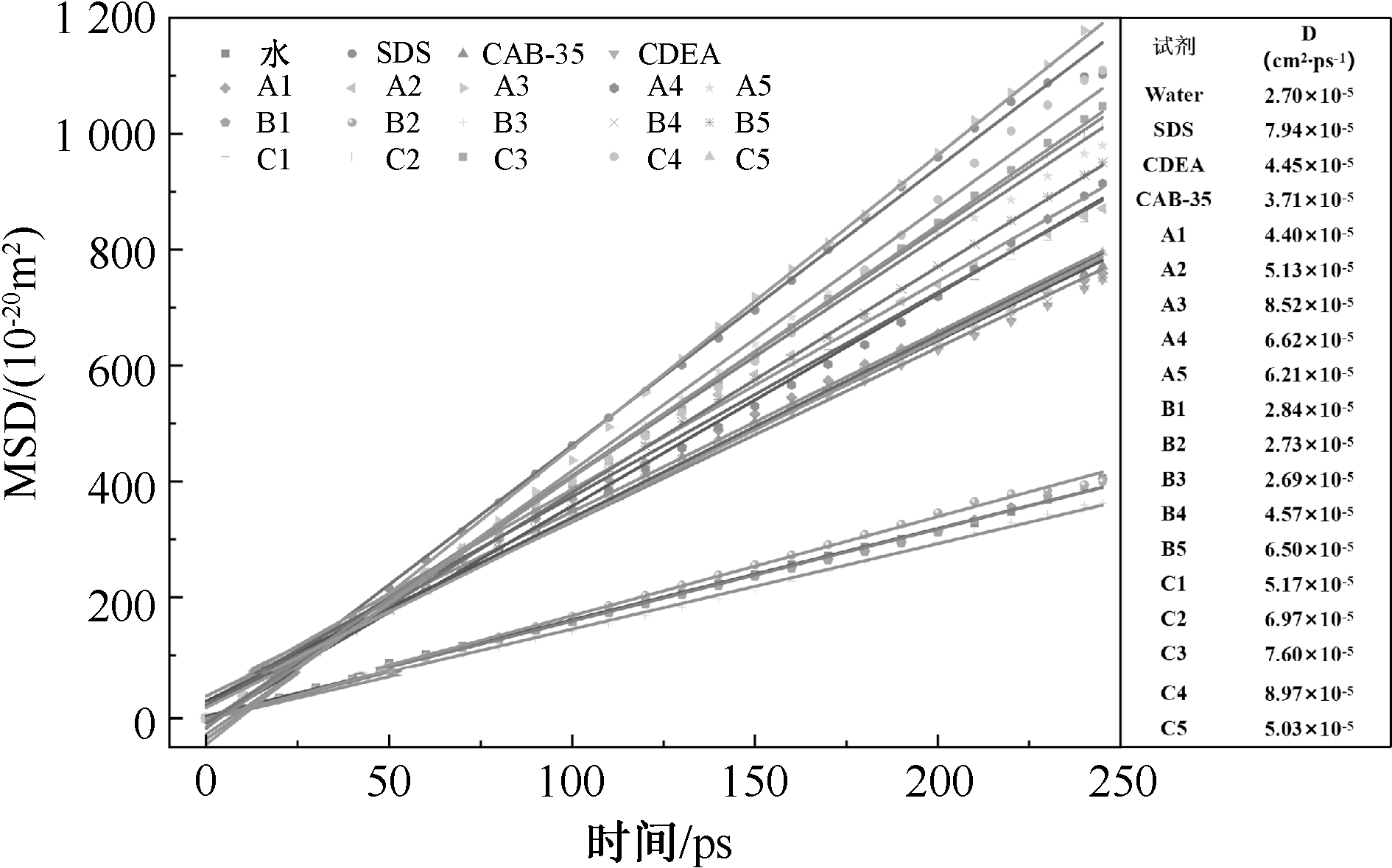
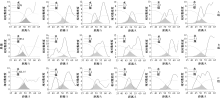
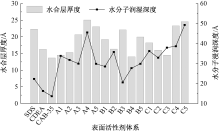
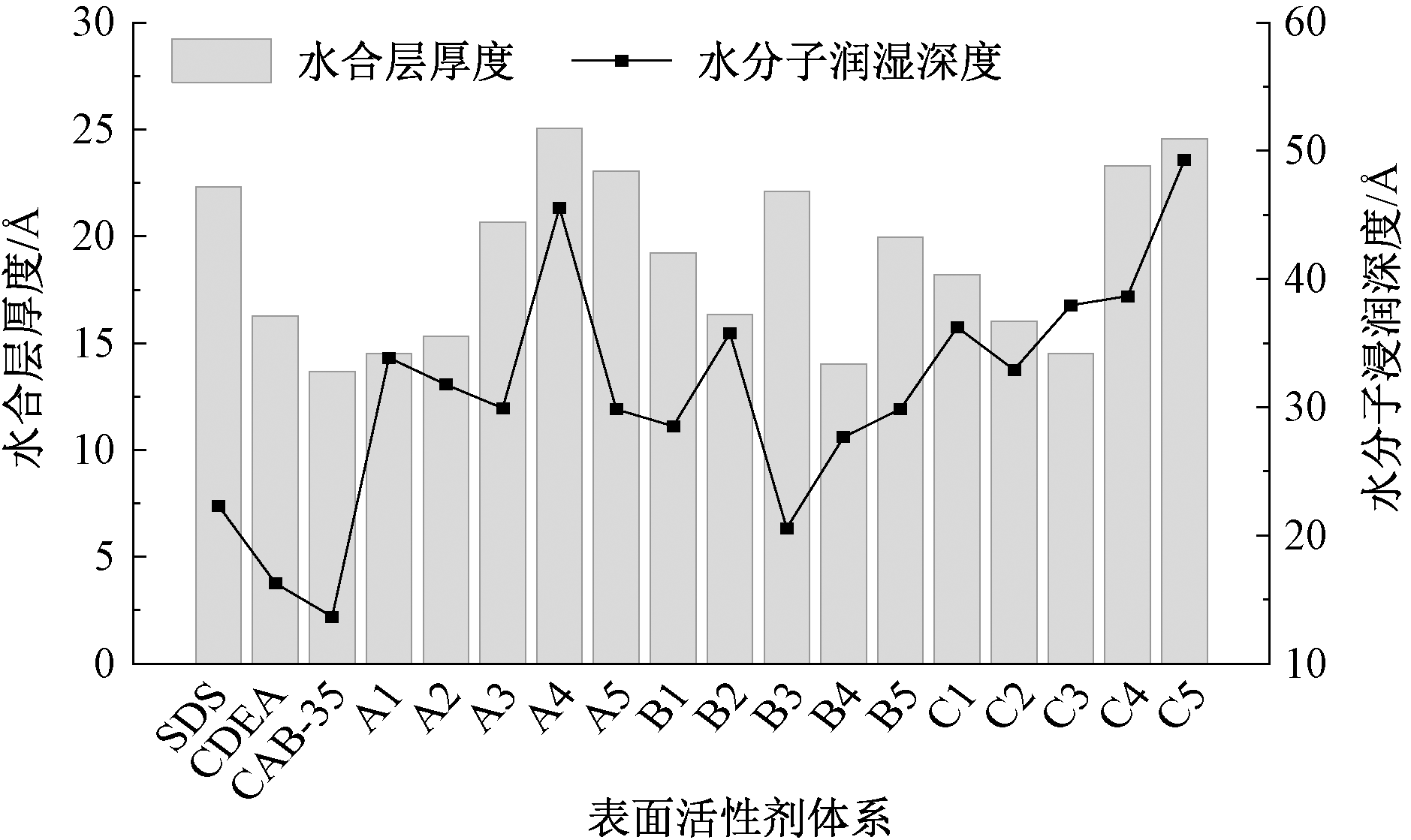
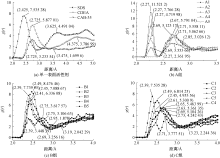
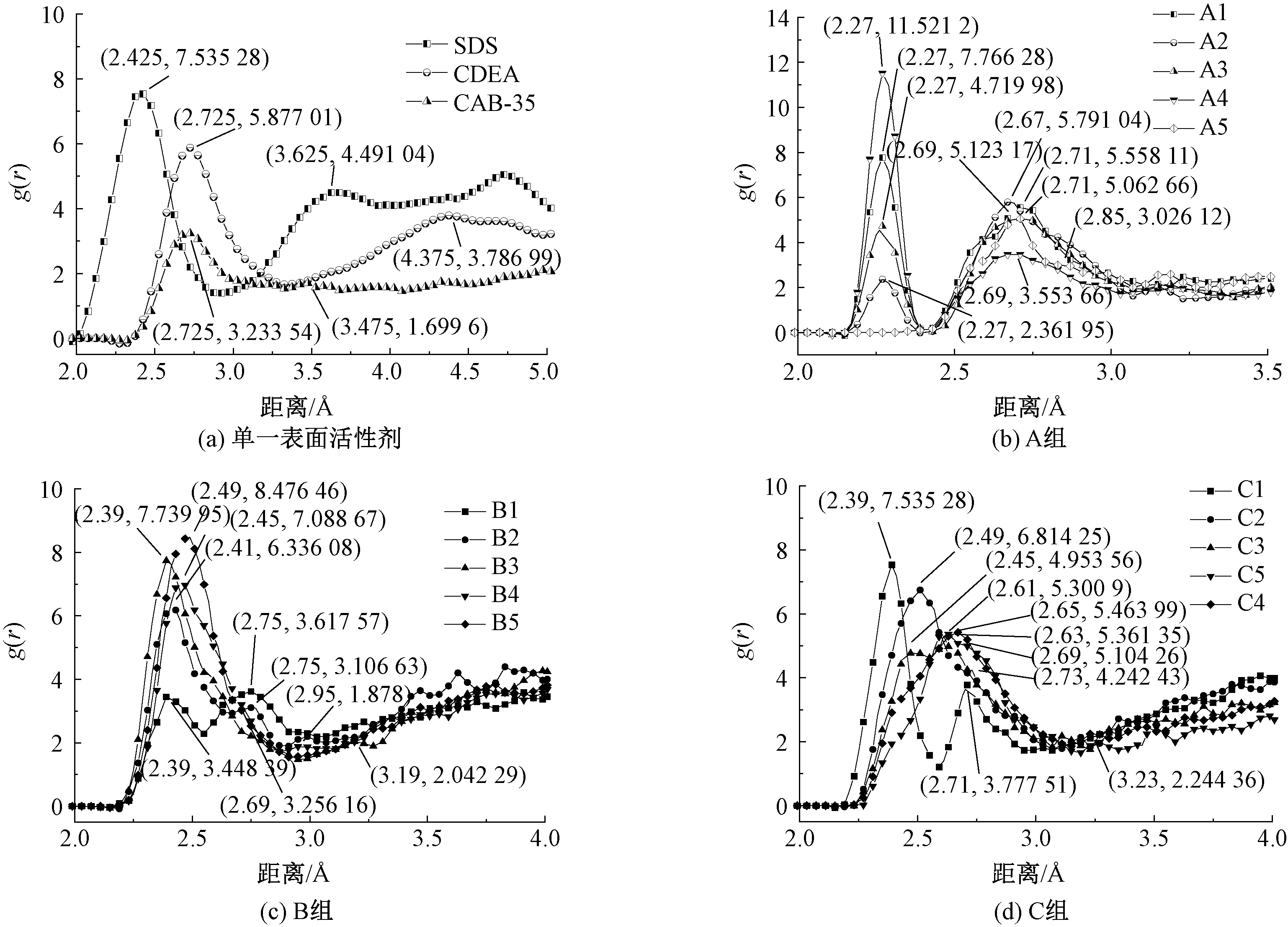
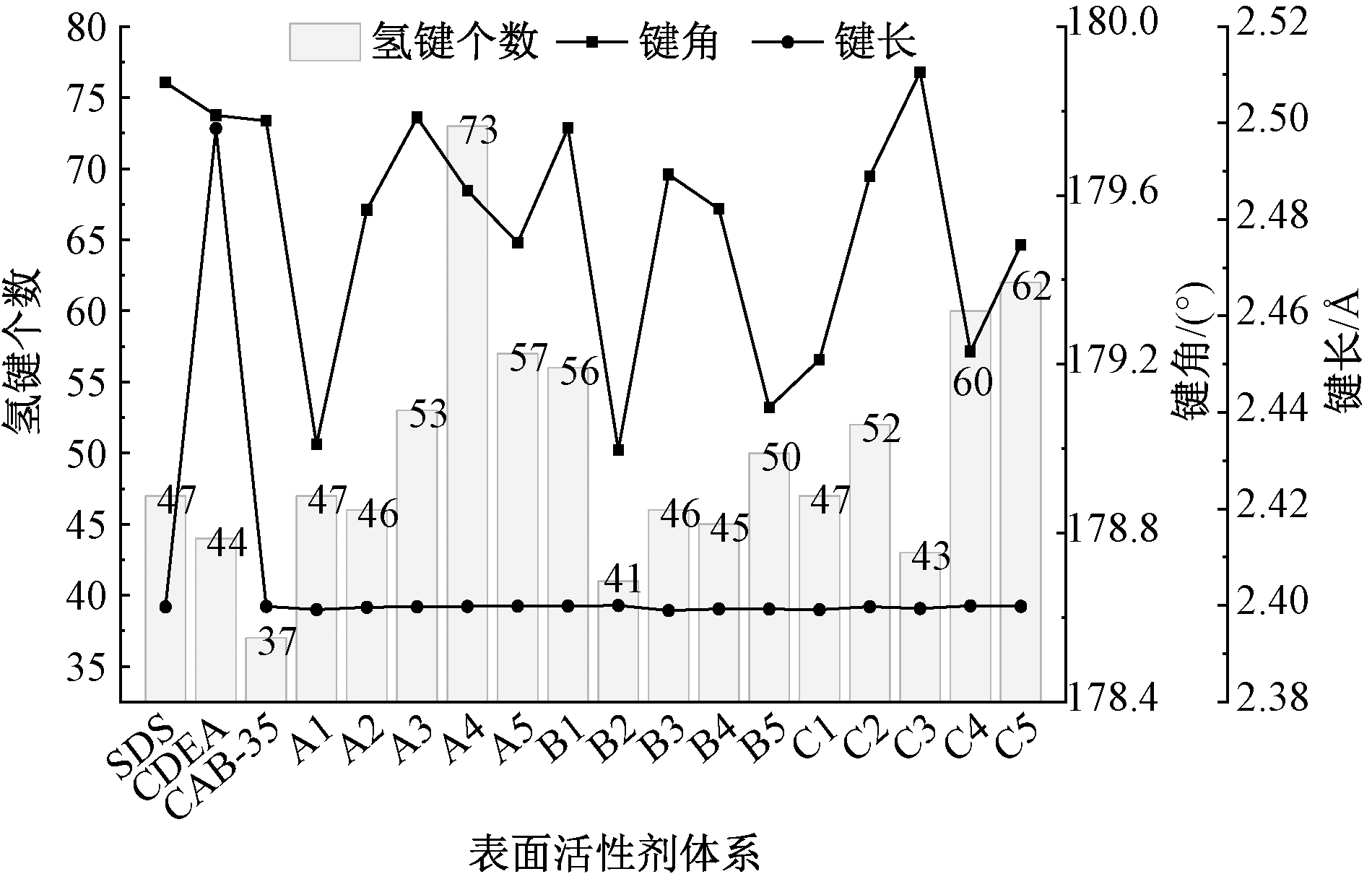
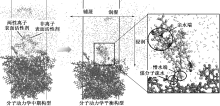
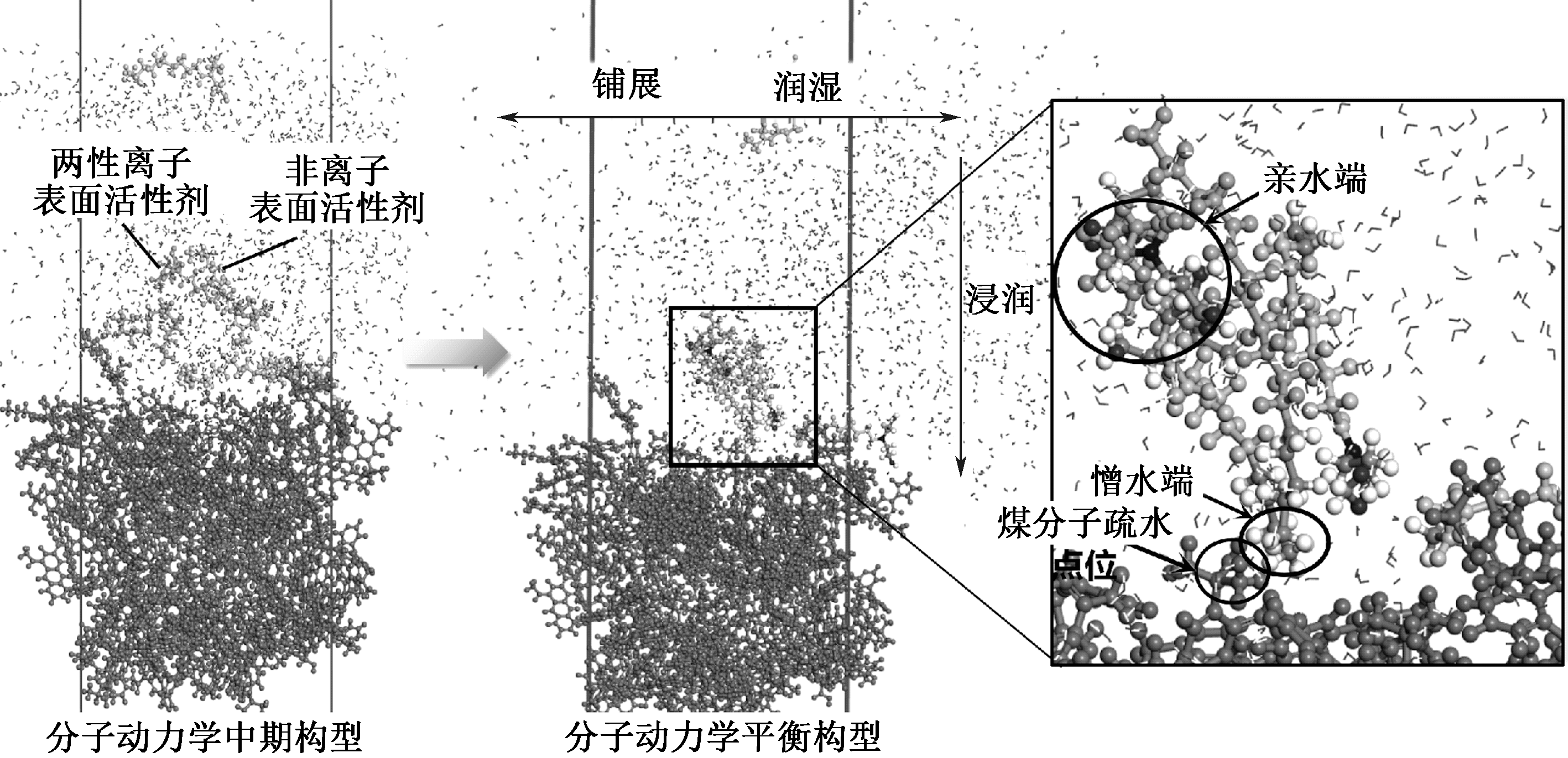
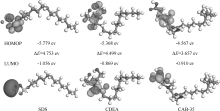
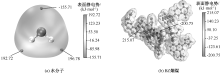
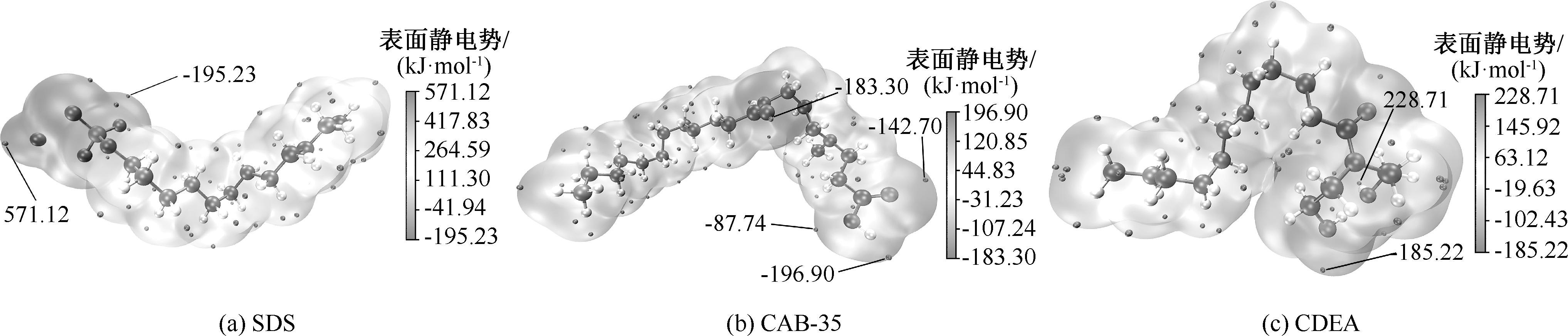
| [1] |
程卫民, 周刚, 陈连军, 等. 我国煤矿粉尘防治理论与技术20年研究进展及展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(2):1-20.
|
|
CHENG Weimin, ZHOU Gang, CHEN Lianjun, et al. Research progress and prospect of dust control theory and technology in China's coal mines in the past 20 years[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(2):1-20.
|
| [2] |
王鹏飞, 邬高高, 田畅, 等. 基于正交试验的内混式空气雾化喷嘴结构参数优化[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2023, 51(9):129-139.
|
|
WANG Pengfei, WU Gaogao, TIAN Chang, et al. Structural parameters optimization of internal mixing air atomizing nozzle based on orthogonal experiment[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(9):129-139.
|
| [3] |
CAO Yong, XIAO Yang, WANG Zhenping, et al. Recent progress and perspectives on coal dust sources, transport, hazards, and controls in underground mines[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2024,187:159-194.
|
| [4] |
WANG Yihan, YANG Wei, YANG Wenming, et al. Effect of AES anionic surfactant on the microstructure and wettability of coal[J]. Energy, 2024,289:130-118.
|
| [5] |
周群, 张文豪, 查舰, 等. 磁化与活性剂协同改善水湿润性能的作用机制[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(3):75-82.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.03.1178
|
|
ZHOU Qun, ZHANG Wenhao, ZHA Jian, et al. Synergistic mechanism between surfactants and magnetization on waterwetting characteristics[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(3):75-82.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.03.1178
|
| [6] |
李树刚, 郭豆豆, 白杨, 等. 不同质量分数SDBS对煤体润湿性影响的分子模拟[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(3):21-27.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.03.004
|
|
LI Shugang, GUO Doudou, BAI Yang, et al. Effect of SDBS of different mass fractions on coal's wettability by molecular simulation[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(3):21-27.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.03.004
|
| [7] |
聂文, 牛文进, 鲍秋, 等. 基于Dmol3模块的不同表面活性剂对煤尘润湿性的影响[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(3):1255-1266.
|
|
NIE Wen, NIU Wenjin, BAO Qiu, et al. Effect of different surfactants on the wettability of coal dust based on Dmol3 module[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(3):1255-1266.
|
| [8] |
荆德吉, 任帅帅, 葛少成. 不同磁化抑尘剂对煤粉润湿性影响规律的实验研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2019, 15(7):107-112.
|
|
JING Deji, REN Shuaishuai, GE Shaocheng. Experimental study on influence laws of different magnetized dust suppressants on wettability of pulverized coal[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2019, 15(7):107-112.
|
| [9] |
黄惠香. 煤矿复合降尘剂及其吸附降尘性能研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2023.
|
|
HUANG Huixiang. Research on composite dust reduction agent and its adsorption and dust reduction performance in coal mine[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology(Beijing), 2023.
|
| [10] |
孟祥曦. 表面活性剂对煤体的微观湿润机理及复配优选研究[D]. 葫芦岛: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2022.
|
|
MENG Xiangxi. Study on micro wetting mechanism and compound optimization of surfactant on coal[D]. Huludao: Liaoning Technical University, 2022.
|
| [11] |
张政, 葛少成, 孙丽英, 等. SDS对烟煤润湿性能和机理的分子模拟研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2023, 19(4):86-92.
|
|
ZHANG Zheng, GE Shaocheng, SUN Liying, et al. Molecular simulation study on wettability performance and mechanism of SDS on bituminous coal[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2023, 19(4):86-92.
|
| [12] |
姜丽, 袁树杰. 生物型表面活性剂在煤表面润湿吸附规律研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2019, 15(8):33-37.
|
|
JIANG Li, YUAN Shujie. Research on wetting and adsorbing regularities of biosurfactants on coal surface[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2019, 15(8):33-37.
|
| [13] |
刘硕. 矿井喷雾降尘表面活性剂作用机理的分子模拟研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2021.
|
|
LIU Shuo. Molecular simulation research on the spray dust reduction mechanism of surfactant in the underground coal mine[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021.
|
| [14] |
刘春福. 水分子/水合阳离子在微细石英颗粒表面的吸附机理研究[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2019.
|
|
LIU Chunfu. Research on adsorption mechanism of water molecules and hydrated cations on the fine quartz particle surface[D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2019.
|
| [15] |
ZHANG Kang, ZHANG Yixuan, ZHOU Lei, et al. Experimental and theoretical insight into the effect of a novel composite dispersant on the properties of coal pitch water slurry[J]. Fuel, 2024,365: DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2024.131281.
|
| [16] |
LI Wenfeng, WANG Hainan, LI Xin, et al. Effect of mixed cationic/anionic surfactants on the low-rank coal wettability by an experimental and molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Fuel, 2021,289: DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119886.
|