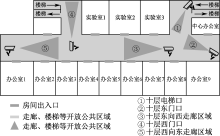
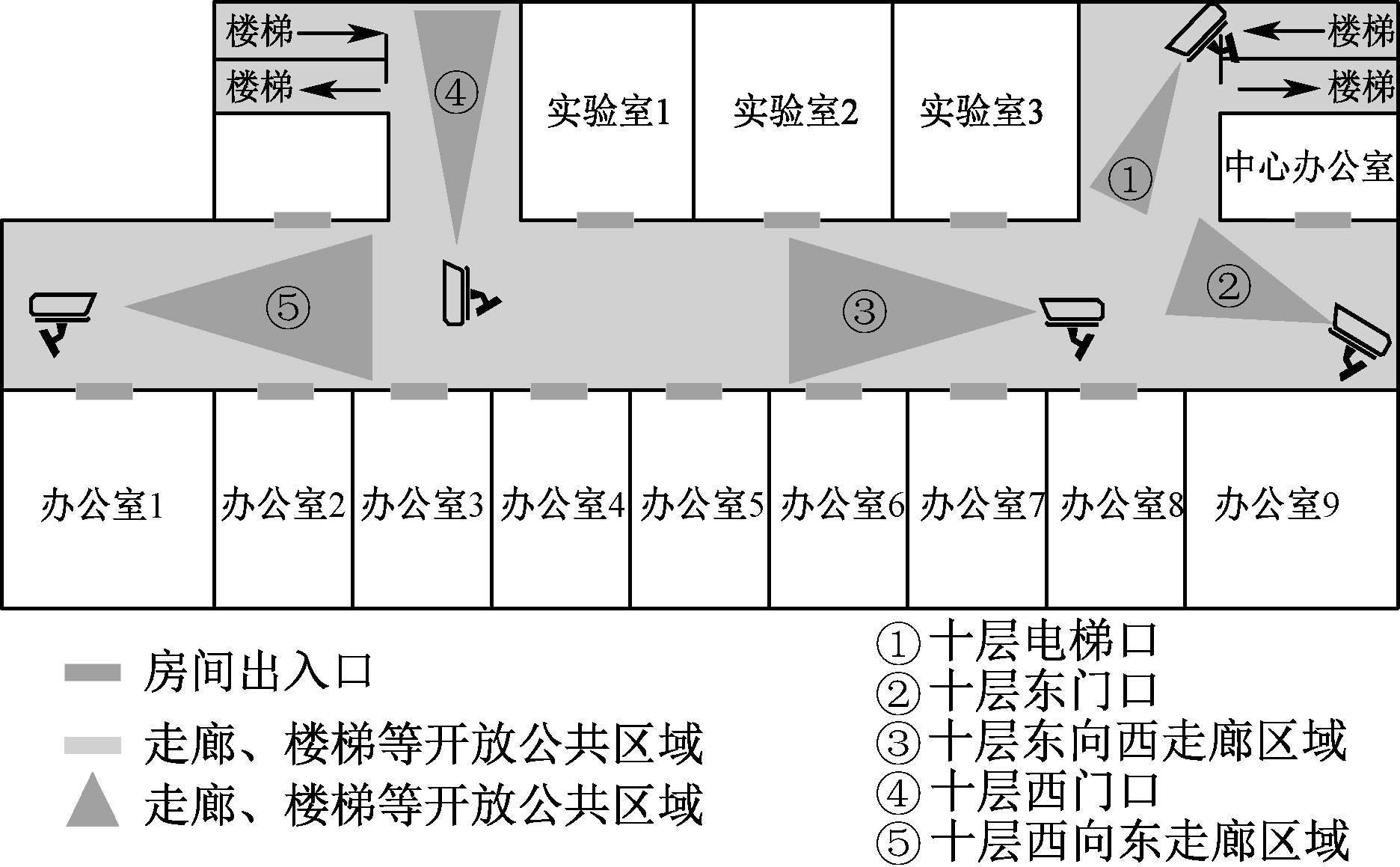
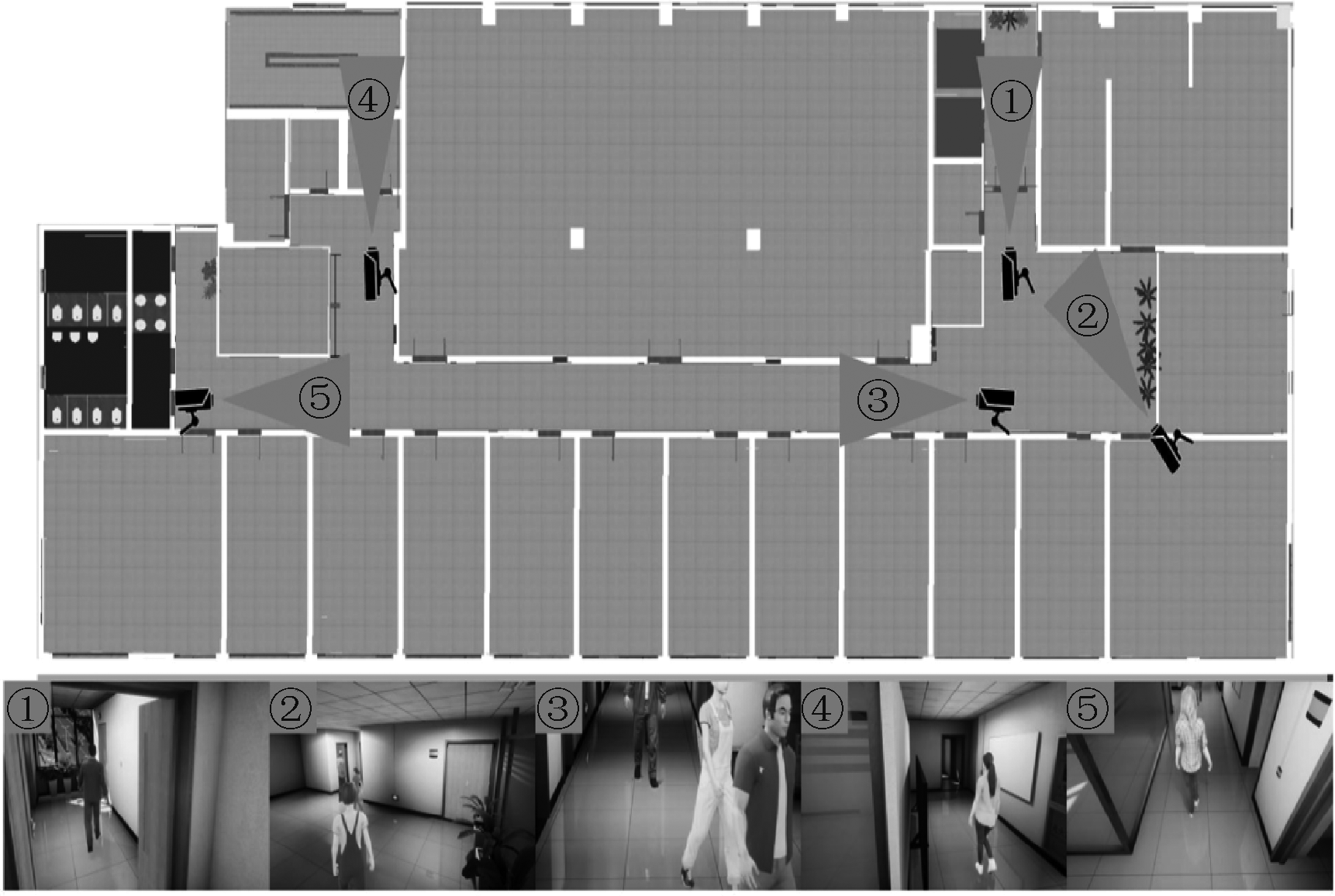
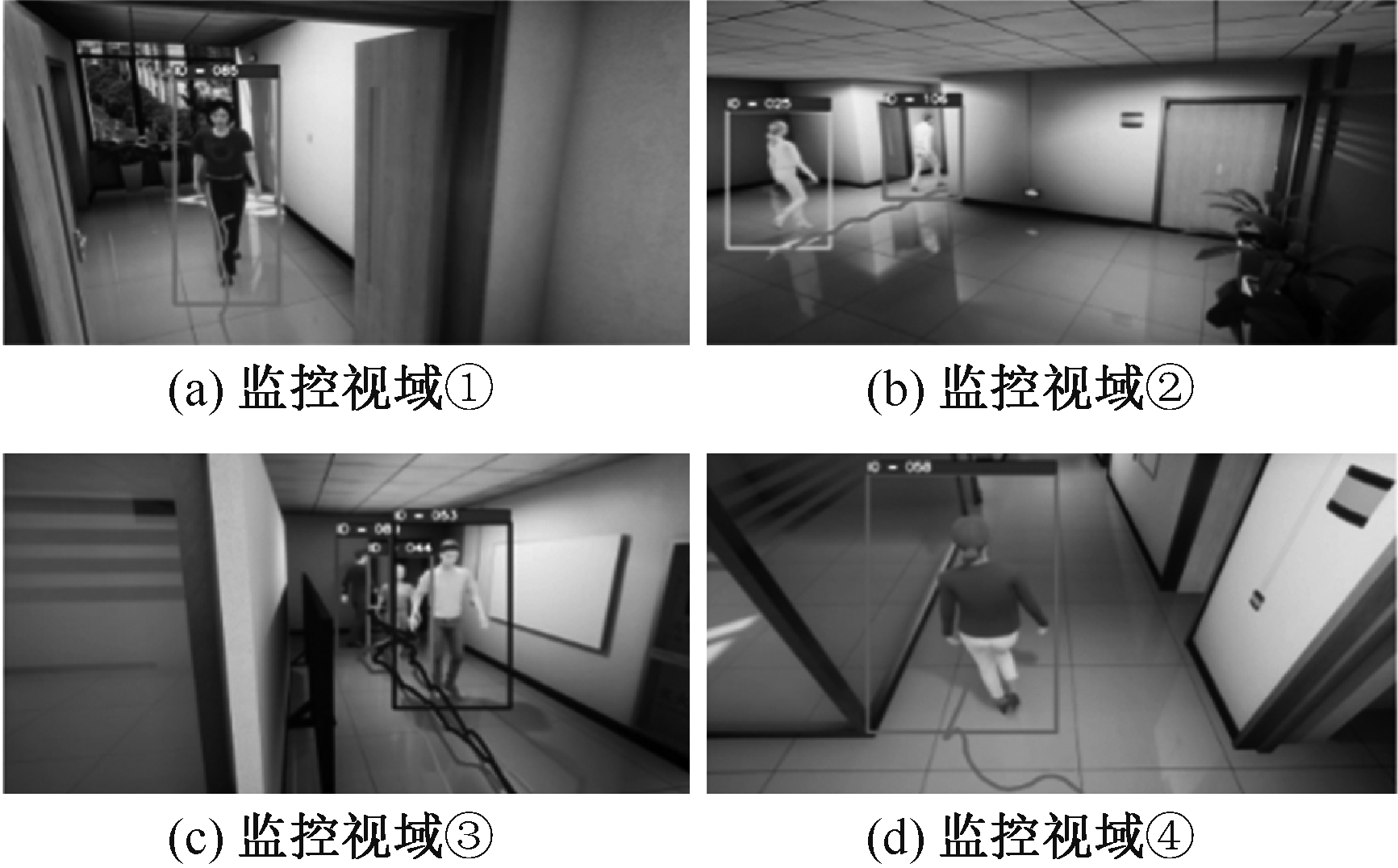
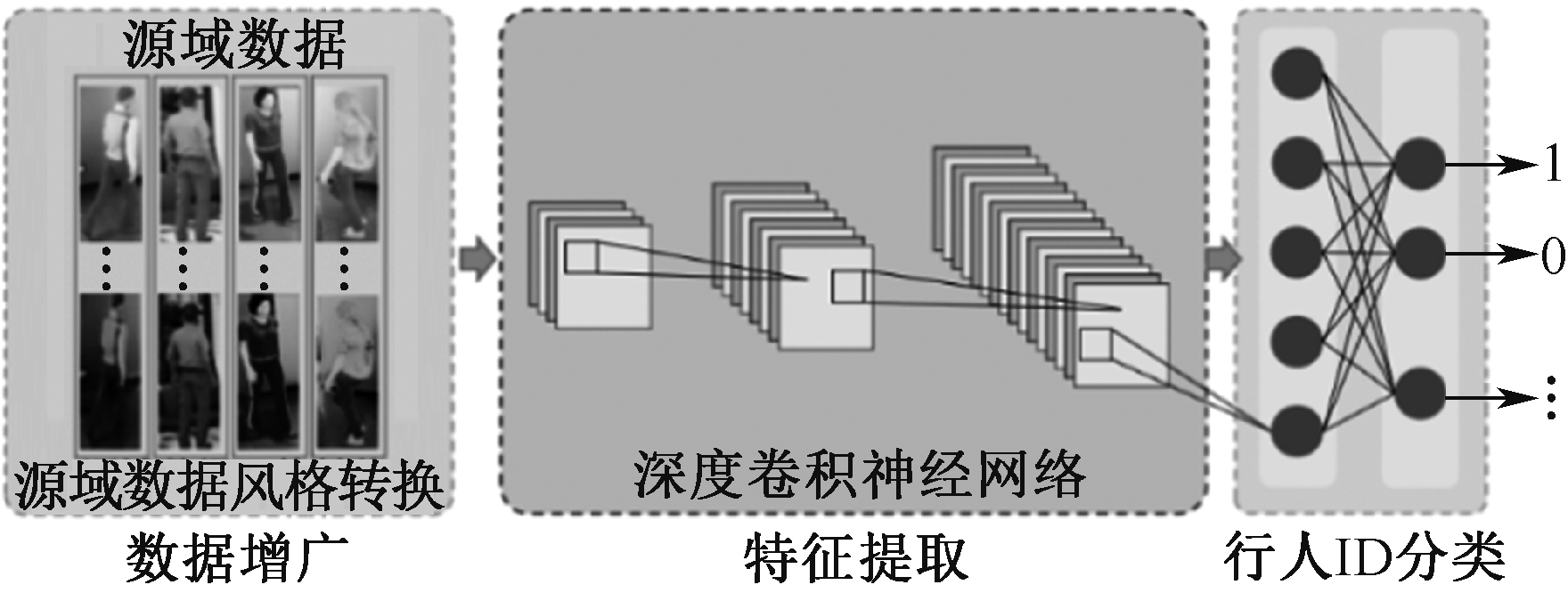
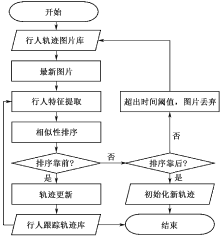
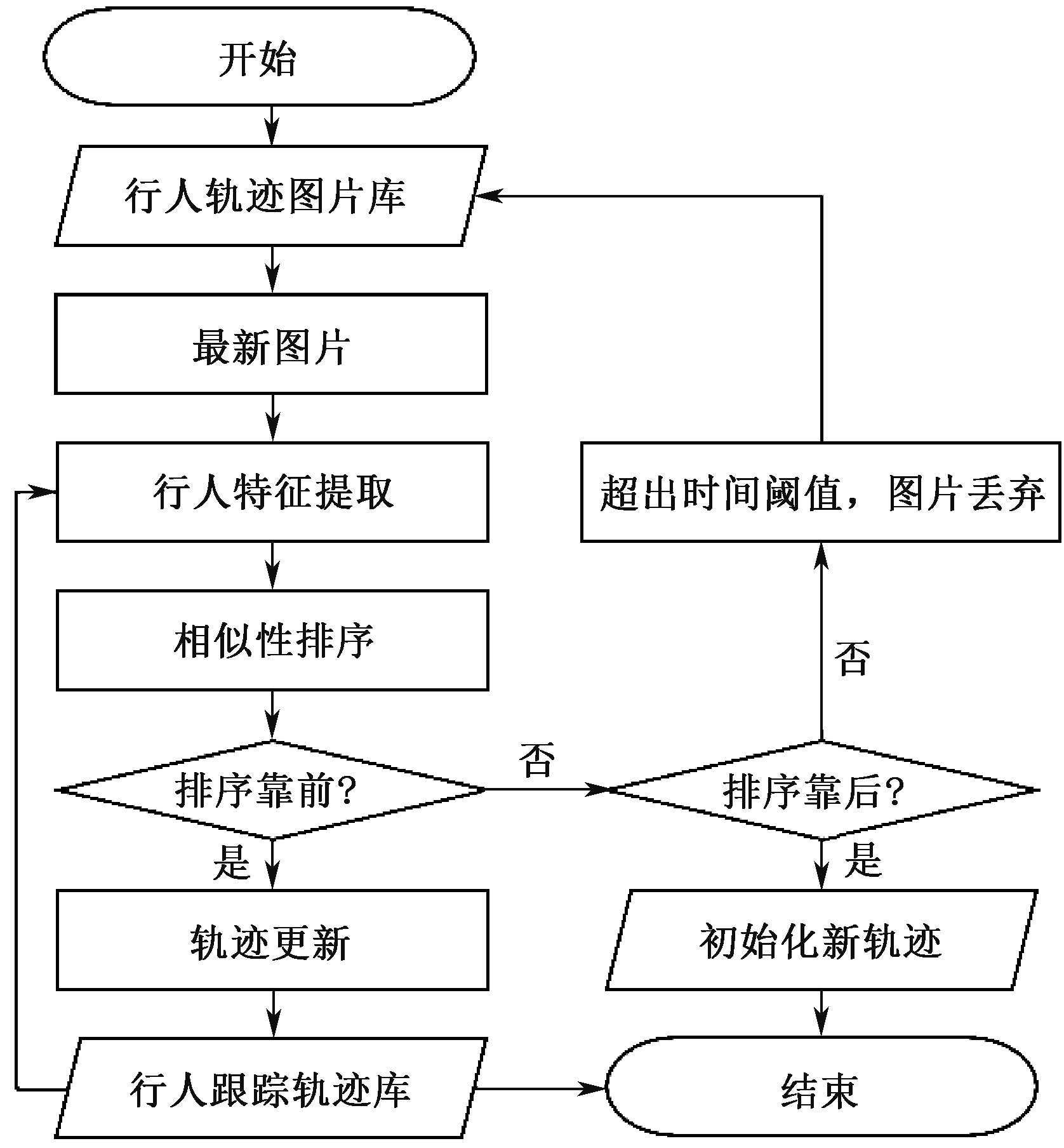
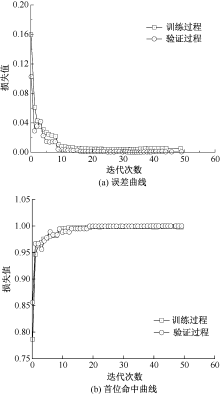
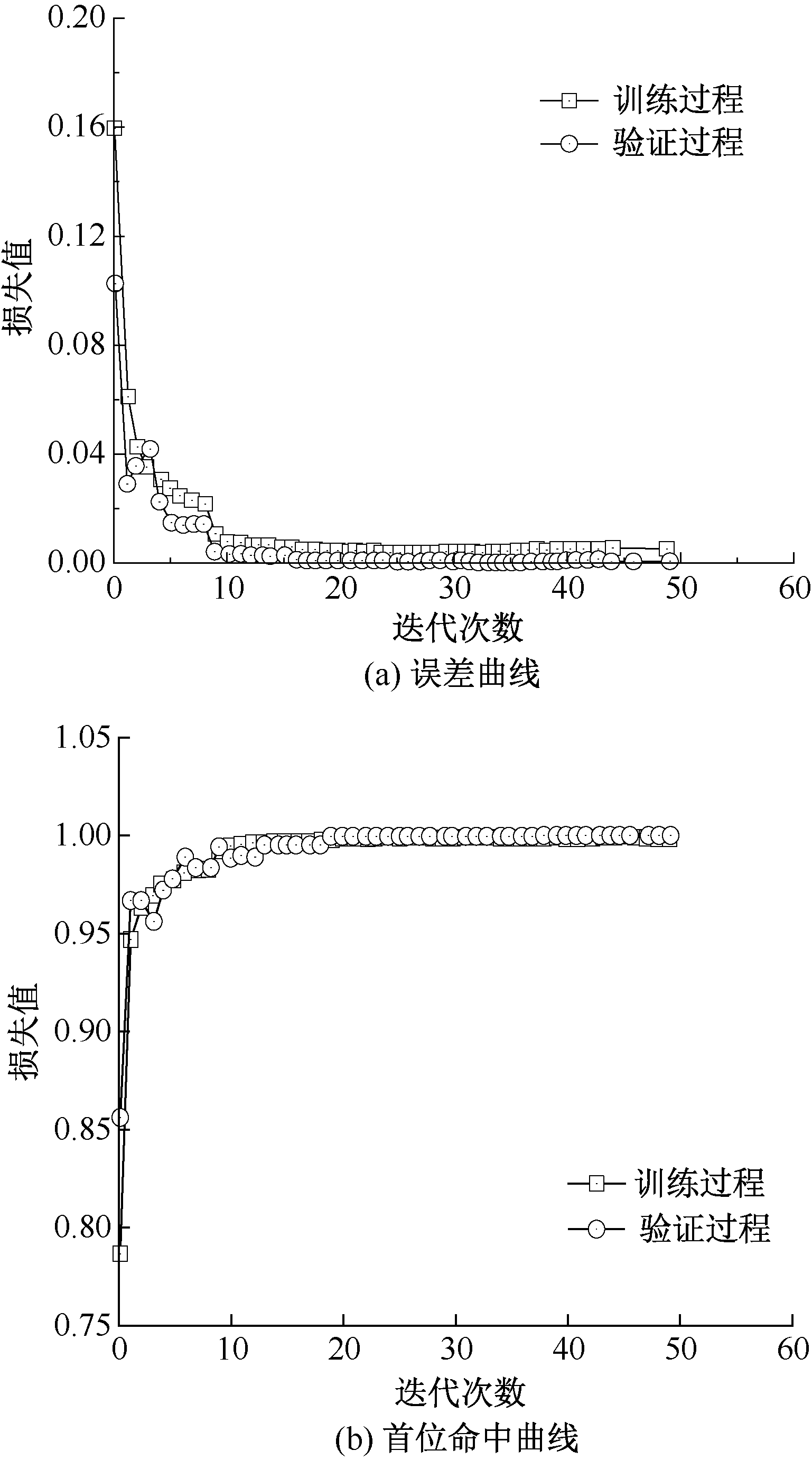
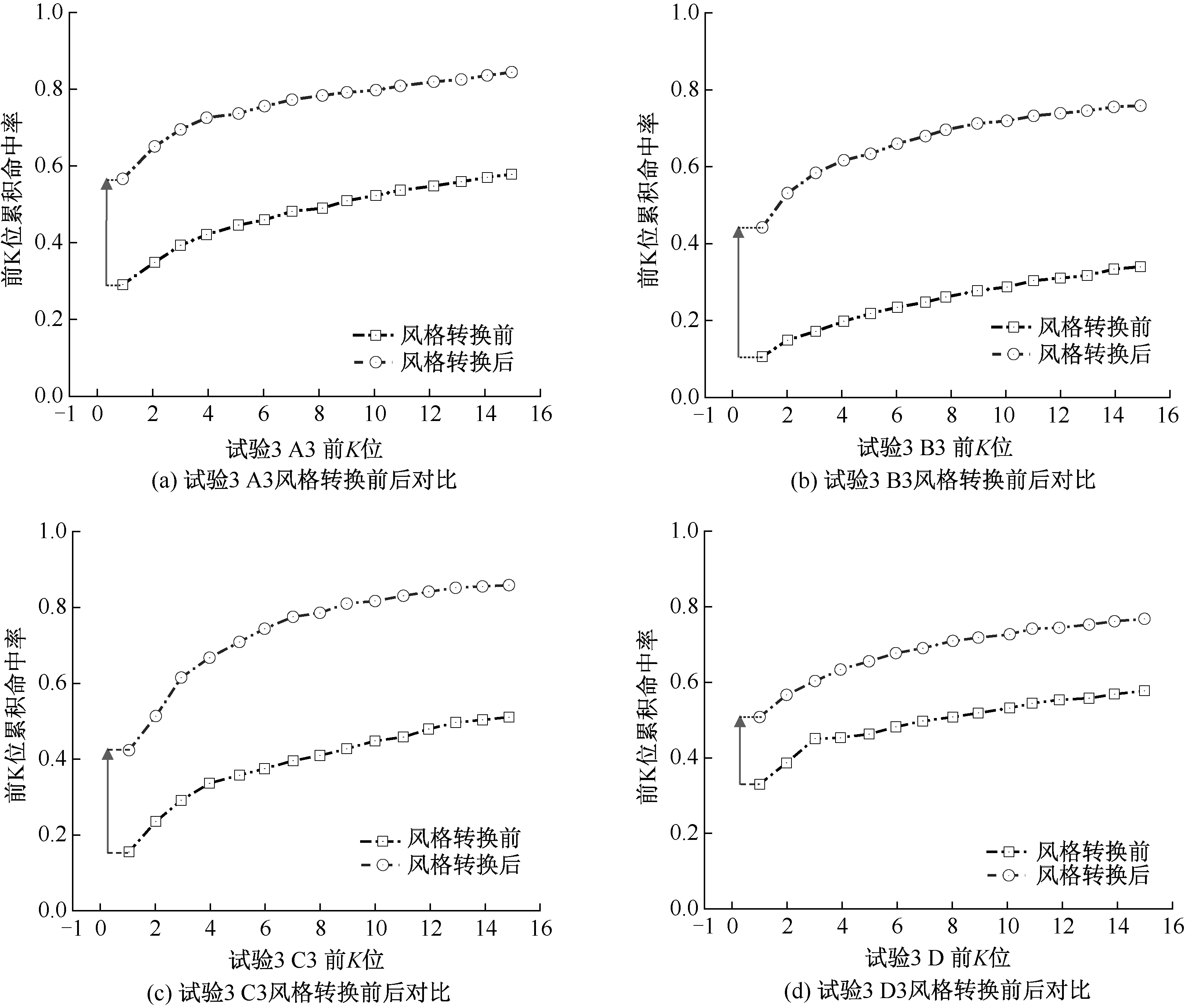
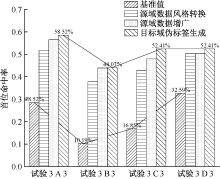
| [1] |
ZHOU Bolei, TANG Xiaoou, WANG Xiaogang. Learning collective crowd behaviors with dynamic pedestrian-agents[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 111:50-58.
|
| [2] |
TOMASTIK R, LIN Yiqing, BANASZUK A. Video-based estimation of building occupancy during emergency egress[C]. 2008 American Control Conference. IEEE, 2008:894-901.
|
| [3] |
马亚萍, 吴楠, 高远, 等. 基于分布式建筑控制策略的人员疏散系统[J]. 清华大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 55(8):927-932.
|
|
MA Yaping, WU Nan, GAO Yuan, et al. Building fire smoke control strategies simulation using fire and evacuation information[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University:Natural Science Edition, 2015, 55(8):927-932.
|
| [4] |
CHUO Y H, SHEU R K, CHEN Lunchi. Design and implementation of a cross-camera suspect tracking system[C]. 2019 International Automatic Control Conference (CACS), IEEE, 2019:1-6.
|
| [5] |
CHENG De, GONG Yihong, WANG Jinjun, et al. Part-aware trajectories association across non-overlapping uncalibrated cameras[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 230:30-39.
|
| [6] |
KOHL P, SPECKER A, SCHUMANN A, et al. The mta dataset for multi-target multi-camera pedestrian tracking by weighted distance aggregation[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2020: 4 489-4 498.
|
| [7] |
张建平, 何田丰, 林佳瑞, 等. 基于BIM的建筑空间与设备拓扑信息提取及应用[J]. 清华大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 58(6):587-592.
|
|
ZHANG Jianping, HE Tianfeng, LIN Jiarui, et al. Building space and equipment topology information extraction and application based on BIM[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University:Natural Science Edition, 2018, 58(6):587-592.
|
| [8] |
YE Mang, SHEN Jianbing, LIN Gaojie, et al. Deep learning for person re-ide.pngication: a survey and outlook[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 44(6): 2872-2893.
|
| [9] |
杜培军, 林聪, 陈宇, 等. 多时相遥感影像样本迁移模型与地表覆盖智能分类[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 50(7):955-966.
|
|
DU Peijun, LIN Cong, CHEN Yu, et al. Training sample transfer learning from multi-temporal remote sensing images for dynamic and intelligent land cover classification[J]. Journal of Tongji University:Natural Science, 2022, 50(7):955-966.
|
| [10] |
陈述, 孙孟文, 陈云, 等. 基于无监督LDA的水电工程施工安全事故致因分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(10): 79-85.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.10.1924
|
|
CHEN Shu, SUN Mengwen, CHEN Yun, et al. Causal analysis of construction safety accidents in hydropower projects based on unsupervised LDA[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(10): 79-85.
|
| [11] |
LI Jianing, ZHANG Shiliang. Joint visual and temporal consistency for unsupervised domain adaptive person re-ide.pngication[C]. Computer Vision-ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, 2020: 483-499.
|
| [12] |
ZHAI Yunpeng, LU Shijian, YE Qixiang, et al. Ad-cluster: augmented discriminative clustering for domain adaptive person re-ide.pngication[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2020: 9021-9030.
|
| [13] |
LI Hui, XIAO Jimin, SUN Mingjie, et al. Progressive sample mining and representation learning for one-shot person re-ide.pngication[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2021, 110: DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107614.
|
| [14] |
LLOYD S. Least squares quantization in PCM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1982, 28(2): 129-137.
|
| [15] |
ESTER M, KRIEGEL H P, SANDER J, et al. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise[C]. KDD-96 Proceedings, 1996, 96(34): 226-231.
|
| [16] |
邓社军, 虞宇浩, 张俊林, 等. 基于行人恐慌情绪解析的改进社会力模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(2):45-52.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.02.1277
|
|
DENG Shejun, YU Yuhao, ZHANG Junlin, et al. Improved social force model based on analysis of pedestrian panic emotion[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(2):45-52.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.02.1277
|
| [17] |
QIU Weichao, YUILLE A. Unrealcv: connecting computer vision to unreal engine[C]. Computer Vision-ECCV 2016 Workshop, 2016: 909-916.
|
| [18] |
叶晨, 关玮. 生成式对抗网络的应用综述[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版2020, 48(4):591-601.
|
|
YE Chen, GUAN Wei. Training sample transfer learning from multi-temporal remote sensing images for dynamic and intelligent land cover classification[J]. Journal of Tongji University:Natural Science, 2020, 48(4):591-601.
|
| [19] |
FAN Hehe, ZHENG Liang, YAN Chenggang, et al. Unsupervised person re-ide.pngication: clustering and fine-tuning[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM), 2018, 14(4): 1-18.
|
| [20] |
马博渊, 周佳城, 班晓娟, 等. 基于视觉检测的非接触式膏体浓度识别方法[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2023, 54(5):1942-1953.
|
|
MA Boyuan, ZHOU Jiacheng, BAN Xiaojuan, et al. Non-contact recognition method of paste concentration based on visual inspection[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2023, 54(5):1942-1953.
|