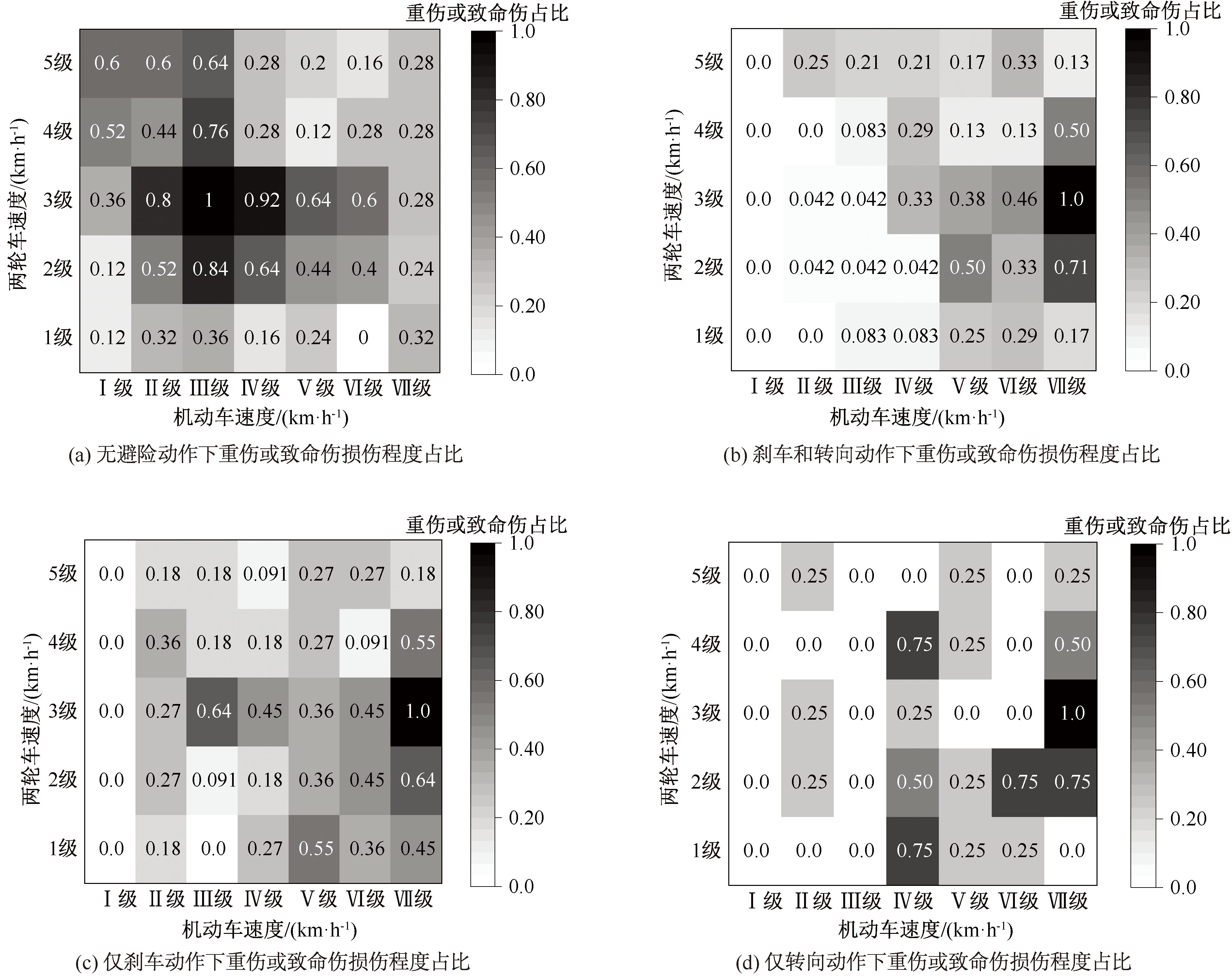
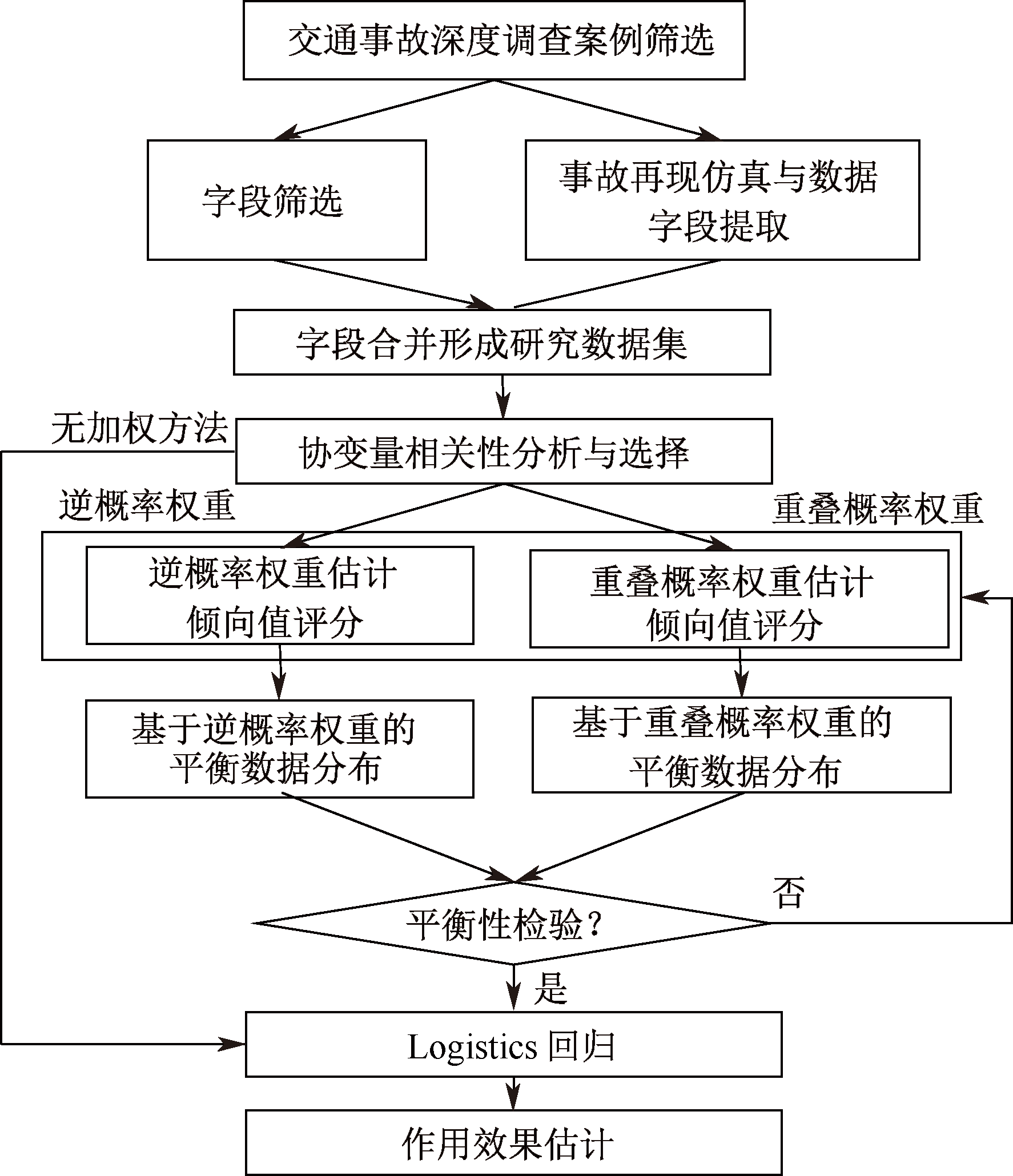
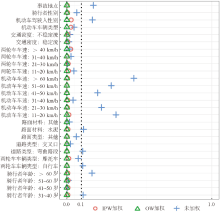
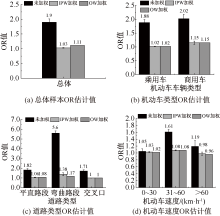
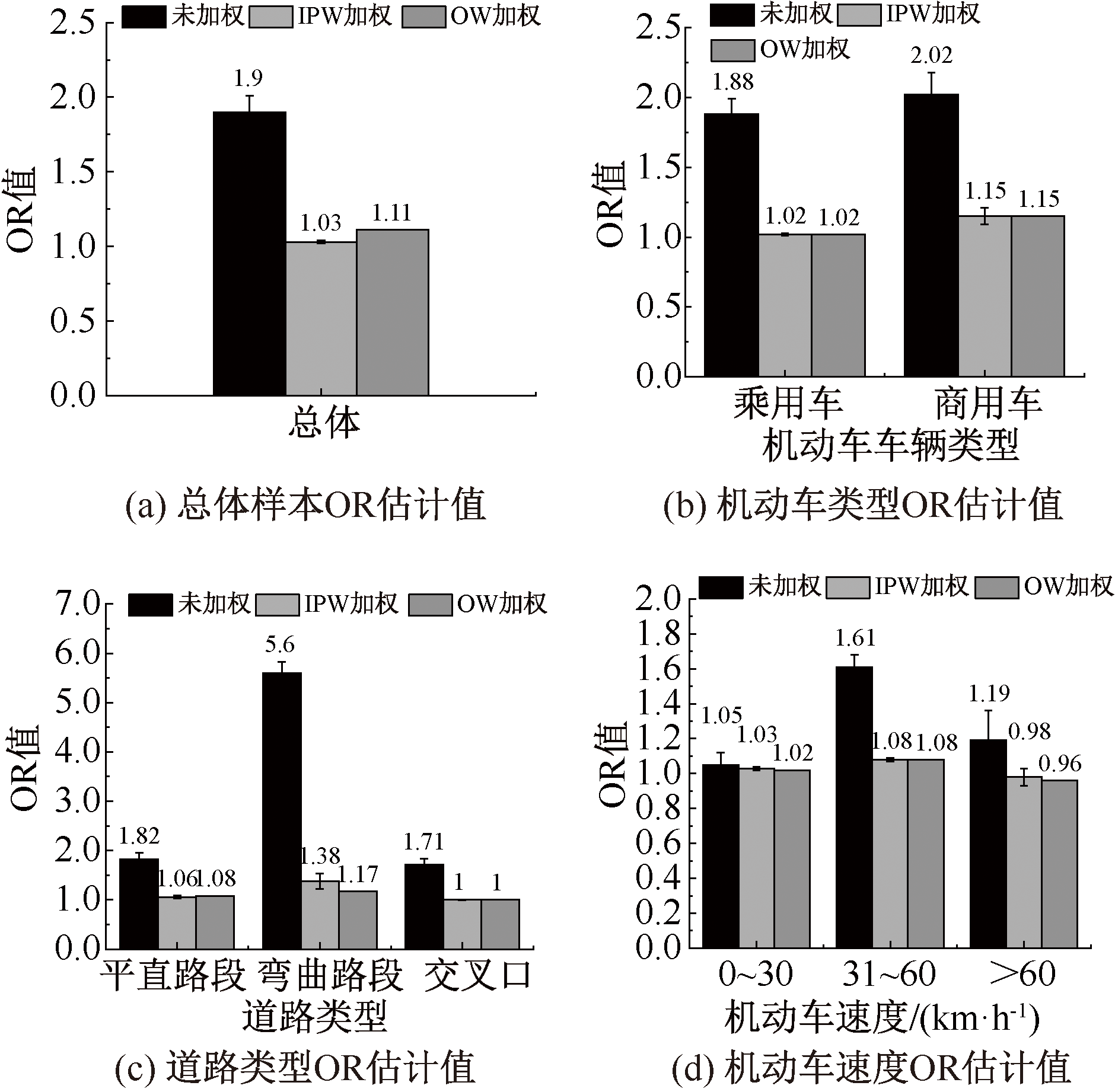
| [1] |
国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2022:771.
|
| [2] |
HUANG Yuan, ZHOU Qing, KOELPER C, et al. Are riders of electric two-wheelers safer than bicyclists in collisions with motor vehicles?[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2020, 134: DOI: 10.1016/j.aap.2019.105336.
|
| [3] |
LUBBE N, JEPPSSON H, STERNLUND S, et al. Injury risk curves to guide safe speed limits on Swedish roads using german crash data supplemented with estimated non-injury crashes[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2024, 202: DOI: 10.1016/j.aap.2024.107586.
|
| [4] |
殷豪, 林淼, 王鹏, 等. 基于XGBoost的二轮车碾压事故致因研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2023, 30(5): 19-27,45.
|
|
YIN Hao, LIN Miao, WANG Peng, et al. Study on the cause of two-wheeler run-over accidents based on XGBoost[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2023, 30(5): 19-27,45.
|
| [5] |
王仲旭, 陈泽平, 鲁誉, 等. 两轮车事故影响因素分析及损伤机理研究[J]. 汽车技术, 2022(10): 56-62.
|
|
WANG Zhongxu, CHEN Zeping, LU Yu, et al. Research on factors affecting two-wheeler accidents and injury mechanisms[J]. Automobile Technology, 2022(10): 56-62.
|
| [6] |
周华, 张巧玉, 母尧尧, 等. 十字路口乘用车与二轮车典型危险场景聚类及推演[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(4): 100-107.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.016
|
|
ZHOU Hua, ZHANG Qiaoyu, MU Yaoyao, et al. Clustering and deduction of typical dangerous scenarios between passenger vehicles and two-wheelers at crossroads[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(4): 100-107.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.016
|
| [7] |
周华, 刘峰, 李平飞, 等. 电动二轮车侧倾角对骑车人头部损伤影响研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(5): 79-84.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.05.014
|
|
ZHOU Hua, LIU Feng, LI Pingfei, et al. Impact of electric bicycles' roll angle on cyclist's head injury[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(5): 79-84.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.05.014
|
| [8] |
REN Qiaoqiao, XU Min. Heterogeneity in crash patterns of autonomous vehicles: the latent class analysis coupled with multinomial logit model[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2025, 209: DOI: 10.1016/j.aap.2024.107827.
|
| [9] |
MILTON J C, SHANKAR V N, MANNERING F L. Highway accident severities and the mixed Logit model: an exploratory empirical analysis[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2008, 40(1): 260-266.
|
| [10] |
WANG Chenzhu, ABDEL-ATY M, HAN Lei. Effects of speed difference on injury severity of freeway rear-end crashes: insights from correlated joint random parameters bivariate probit models and temporal instability[J]. Analytic Methods in Accident Research, 2024, 42: DOI: 10.1016/j.amar.2024.100320.
|
| [11] |
ZHANG Pengxiang, MAHMUD A, VIKASH V, et al. Comparison of safety effect estimates from propensity scores-potential outcomes framework and empirical Bayes before-after method: case study of adaptive traffic signal control[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2024, 91: 258-270.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsr.2024.09.011
pmid: 39998528
|
| [12] |
董傲然. 面向骑行者保护的电动两轮车事故重建优化与损伤仿真研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2023.
|
|
DONG Aoran. Research on accident reconstruction optimization and damage simulation of electric two-wheeled for cyclist protection[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2023.
|
| [13] |
李明, 唐姣, 宋欣筑, 等. 基于响应面法的抑尘剂组分配比优选模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(1): 88-94.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.01.0175
|
|
LI Ming, TANG Jiao, SONG Xinzhu, et al. Optimization model of dust suppressant component ratio based on response surface methodology[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(1): 88-94.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.01.0175
|
| [14] |
CRAMER H. Mathematical methods of statistics[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1999:286.
|
| [15] |
ROSENBAUM P R, RUBIN D B. The central role of the propensity score in observational studies for causal effects[J]. Biometrika, 1983, 70(1): 41-55.
|
| [16] |
LI Yan, LI Liang. Propensity score analysis methods with balancing constraints: a monte carlo study[J]. Statistical Methods in Medical Research, 2021, 30(4): 1119-1142.
doi: 10.1177/0962280220983512
pmid: 33525962
|
| [17] |
涂博祥, 秦婴逸, 吴骋, 等. 倾向性评分加权方法介绍及R软件实现[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2022, 22(3): 365-372.
|
|
TU Boxiang, QIN Yingyi, WU Cheng, et al. Introduction of propensity score weighting methods and implementation by R software[J]. Chinese Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine, 2022, 22(3): 365-372.
|
| [18] |
韩贺东. 基于稳定权重目标最大似然估计模型的研究及其在真实世界研究中的应用[D]. 上海: 中国人民解放军海军军医大学, 2020.
|
|
HAN Hedong. Modeling of stabilized weight based targeted maximum likelihood estimation and its application in real-world studies[D]. Shanghai: Naval Medical University, 2020.
|
| [19] |
MOLINA J, SUED M, VALDORA M. Models for the propensity score that contemplate the positivity assumption and their application to missing data and causality[J]. Stats in Medicine, 2017, 37(24): 3503-3518.
|
| [20] |
高绒绒, 高倩, 王彤. 倾向性评分逆概率加权法中极端权重的处理方法[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2023, 40(6): 956-960.
|
|
GAO Rongrong, GAO Qian, WANG Tong. Treatment of extreme weight in inverse probability weighted method of propensity score[J]. China Health Statistics, 2023, 40(6): 956-960.
|
| [21] |
LI Fan, MORGAN K L, ZASLAVSKY A M. Balancing covariates via propensity score weighting[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2018, 113(521): 390-400.
|
| [22] |
LI Fan, THOMAS L E. Addressing extreme propensity scores via the overlap weights[J]. American Journal of Epidemiology, 2019, 188(1): 250-257.
doi: 10.1093/aje/kwy201
pmid: 30189042
|
| [23] |
于淼, 张生奎, 王利华, 等. 肝酶对钢铁工人代谢健康型肥胖与高尿酸血症关联影响[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(2): 231-238.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.02.1184
|
|
YU Miao, ZHANG Shengkui, WANG Lihua, et al. Effect of liver enzymes on association between metabolically healthy obesity and hyperuricemia in steelworkers[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(2): 231-238.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.02.1184
|
| [24] |
朱彤, 王驰恒, 李青, 等. 基于集成学习的驾驶人避险安全效果影响因素研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(6): 3243-3251.
|
|
ZHU Tong, WANG Chiheng, LI Qing, et al. Study on factors influencing the avoidance effect of drivers based on integrated learning[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(6): 3243-3251.
|
| [25] |
SUNBIN Y, KUMAGAI J, MORITA T, et al. Who to sacrifice? modeling the driver's dilemma[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2023, 178: DOI: 10.1016/j.tra.2023.103872.
|