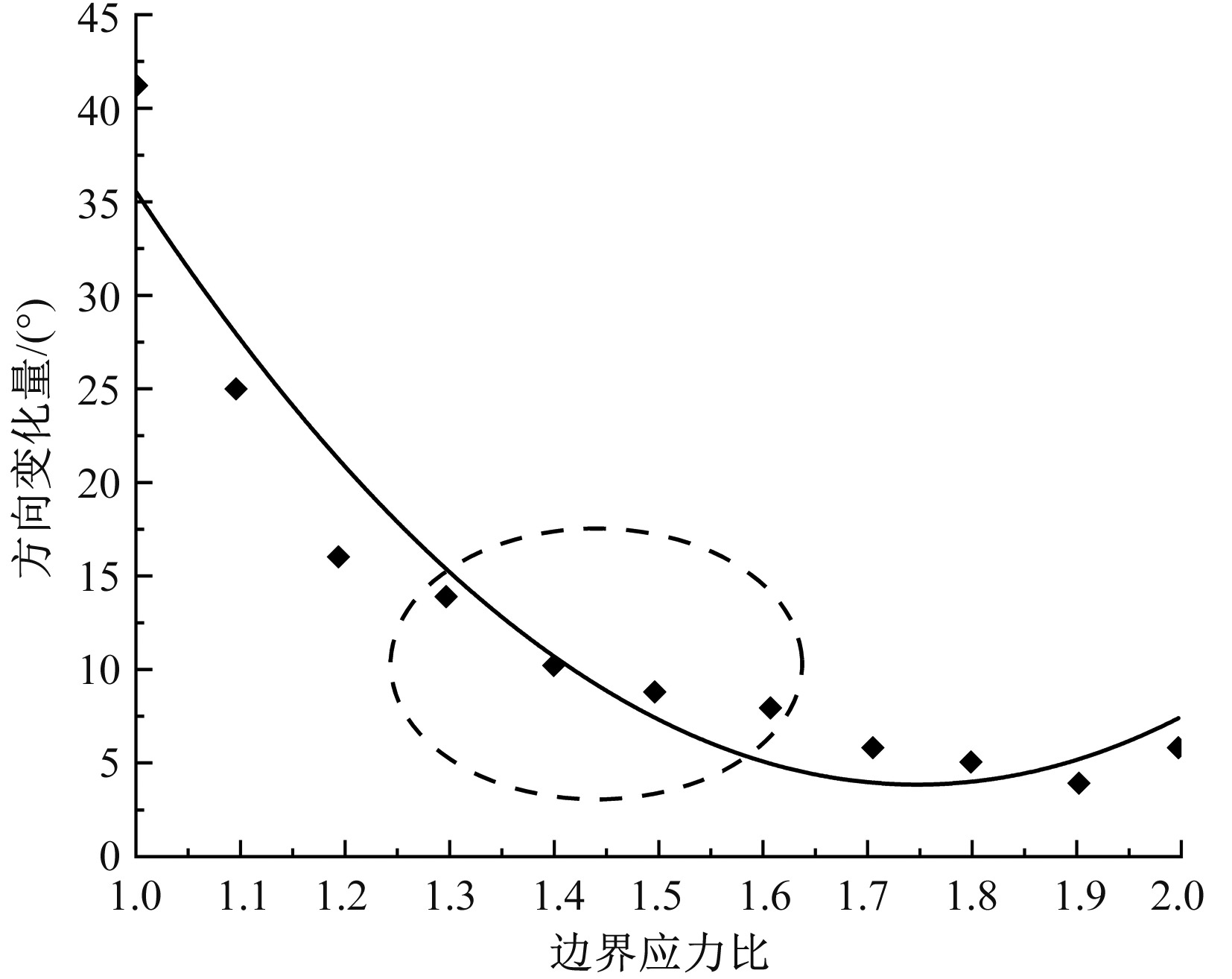
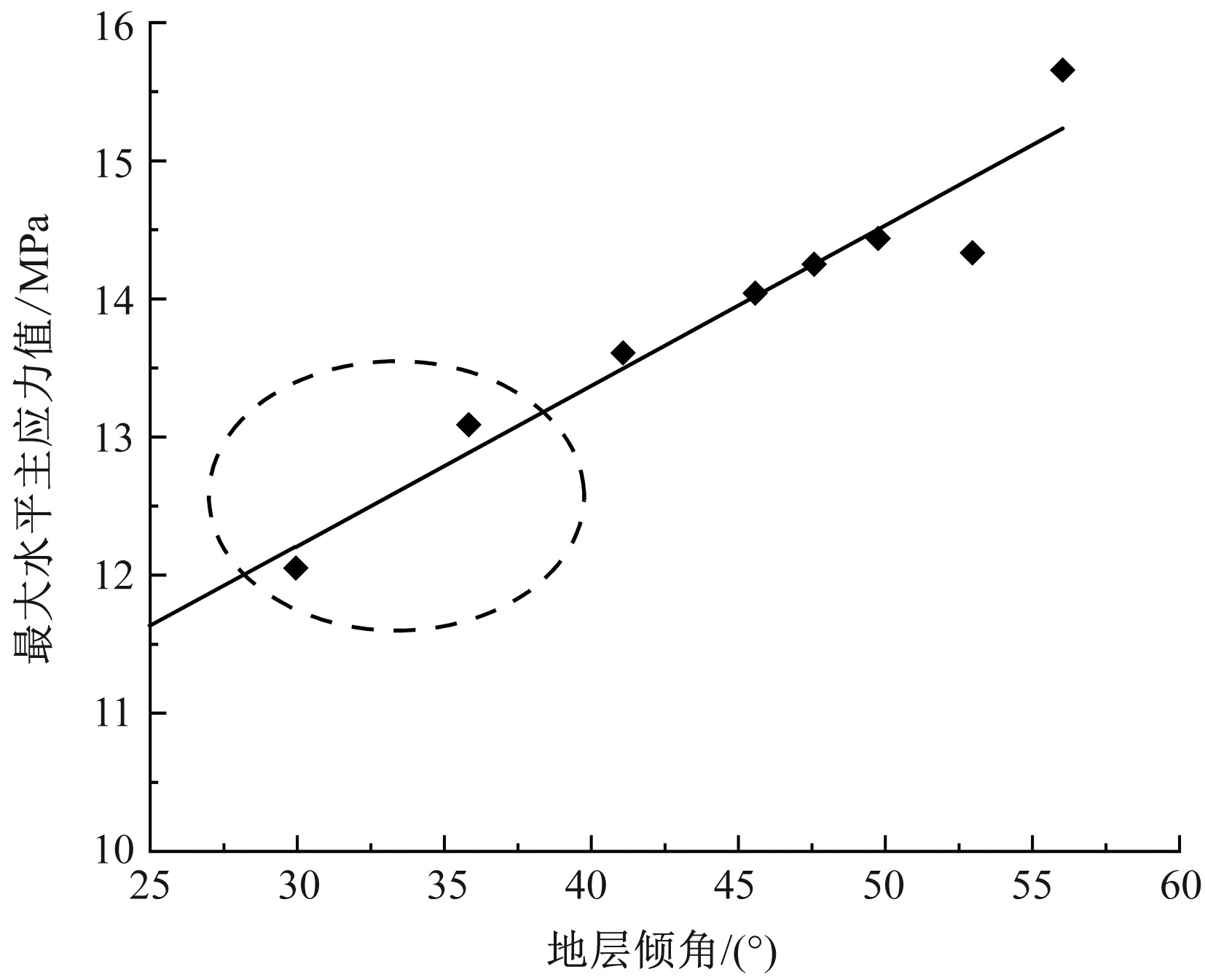
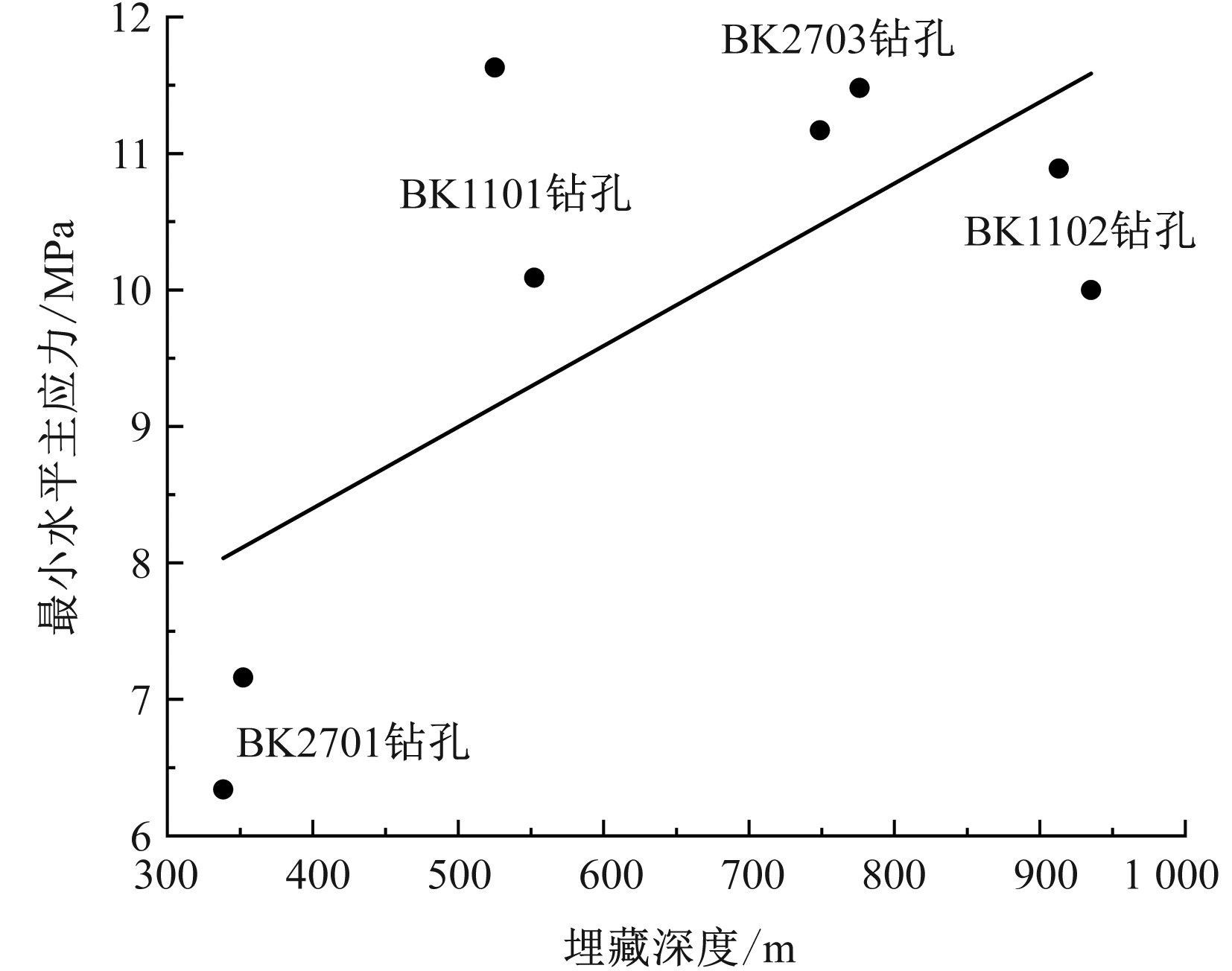
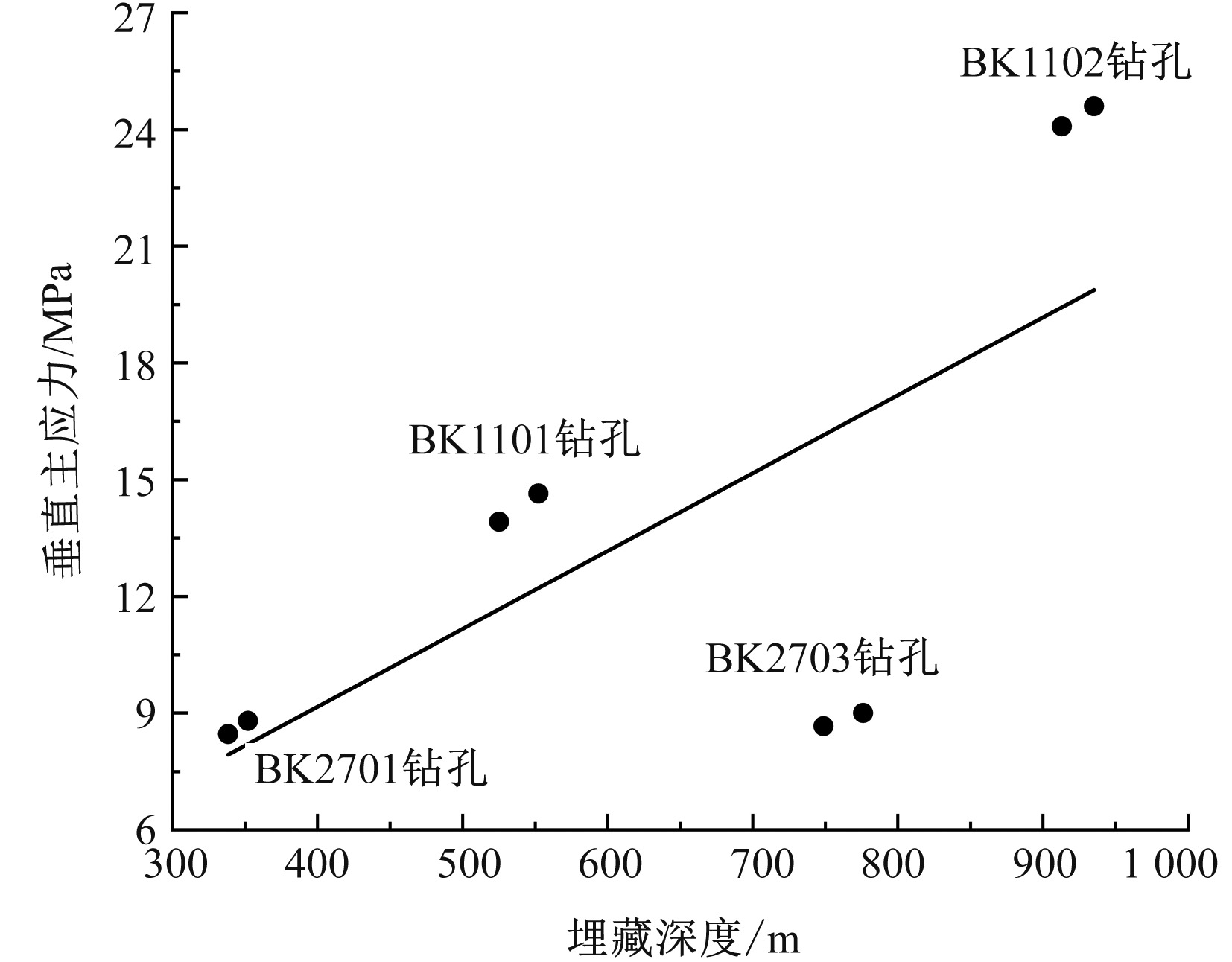
| [1] |
康红普. 我国煤矿巷道围岩控制技术发展70年及展望[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(1):1-30.
|
|
KANG Hongpu. Seventy years development and prospects of strata control technologies for coalmine roadways in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(1):1-30.
|
| [2] |
蔡美峰. 地应力测量原理和方法的评述[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 1993(3):275-283.
|
|
CAI Meifeng. A Review of principles and methods of geostress measurements[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 1993(3):275-283.
|
| [3] |
蔡美峰, 乔兰, 于波, 等. 金川二矿区深部地应力测量及其分布规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 1999(4):46-50.
|
|
CAI Meifeng, QAO Lan, YU Bo, et al. Study on deep geostress measurement and its distribution pattern in Jinchuan No.2 mining area[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 1999(4):46-50.
|
| [4] |
蔡美峰, 陈长臻, 彭华, 等. 万福煤矿深部水压致裂地应力测量[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(5):1 069-1 074.
|
|
CAI Meifeng, CHEN Changzhen, PENG Hua, et al. In-situ stress measurement bu hydraulic fracturing technique in deep position of Wanfu coal mine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(5):1 069-1 074.
|
| [5] |
秦向辉, 谭成轩, 孙进忠, 等. 地应力与岩石弹性模量关系试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2012(6): 1 689-1 695.
|
|
QIN Xianghui, TAN Chengxuan, SUN Jinzhong, et al. Experimental study of relation between in-situ crustal stress and rock elastic modulus[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012(6): 1 689-1 695.
|
| [6] |
尹健民, 周春华, 李云安, 等. 北疆深埋隧洞地应力与区域应力场相关性研究[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2014, 31(11):42-46.
|
|
YIN Jianmin, ZHOU Chunhua, LI Yun'an, et al. Correlation between tunnel stress and regional stress field in north Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2014, 31(11):42-46.
|
| [7] |
尚晓光, 朱斯陶, 姜福兴, 等. 地面直井水压致裂防控巨厚硬岩运动型矿震试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(增2):639-650.
|
|
SHANG Xiaoguang, ZHU Sitao, JIANG Fuxing, et al. Experimental study on the prevention and control of mine earthquake by high pressure water fracturing of huge thick strata in vertical shaft[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(S2):639-650.
|
| [8] |
王成虎, 高桂云, 王洪, 等. 利用室内和现场水压致裂试验联合确定地应力与岩石抗拉强度[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(2):167-174.
|
|
WANG Chenghu, GAO Guiyun, WANG Hong, et al. Integrated determination of principal stress and tensile strength of rock based on the laboratory and field hydraulic fracturing tests[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(2):167-174.
|
| [9] |
祁云, 薛凯隆, 汪伟, 等. 矿井煤与瓦斯突出事故应急救援能力评估模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(2):225-230.
|
|
QI Yun, XUE Kailong, WANG Wei, et al. Assessment model of emergency response capability for coal and gas outburst accidents in mines[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(2):225-230.
|
| [10] |
祁云, 薛凯隆, 李绪萍, 等. 多策略改进SSA优化KELM的边坡稳定性预测模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2025, 35(3):92-98.
|
|
QI Yun, XUE Kailong, LI Xuping, et al. Slope stability prediction model based on multi-strategy improved SSA for optimizing KELM[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2025, 35(3):92-98.
|
| [11] |
WANG Wei, CUI Xinchao, QI Yun, et al. Prediction model of coal seam gas content based on kernel principal component analysis & IDBO-DHKELM[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2024, 35(11):DOI: 10.1088/1361-6501/ad6923.
|
| [12] |
张宏伟, 张文军, 南存全. 采矿工程中的原岩应力测量[J]. 阜新矿业学院学报:自然科学版, 1997(6):653-657.
|
|
ZHANG Hongwei, ZHANG Wenjun, NAN Cunquan. Stress measurement of original rock in mining engineering[J]. Journal of Fuxin Mining institute:Natural Science, 1997(6):653-657.
|
| [13] |
蒋健, 董志华, 周春华, 等. 新疆某高水头抽蓄电站地应力综合测量及应力场反演分析[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2025, 36(2):144-152.
|
|
JIANG Jian, DONG Zhihua, ZHOU Chunhua, et al. Comprehensive measurement of geostress and analysis of initial stress fieldinversion in a high-head pumped storage power station in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 2025, 36(2):144-152.
|
| [14] |
陈群策, 毛吉震, 侯砚和. 利用地应力实测数据讨论地形对地应力的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004(23): 3 990-3 995.
|
|
CHEN Qunce, MAO Jizhen, HOU Yanhe. Study on influence of topography on in-situ stress by interpretation of measurement data of in-situ stress[J]. Chinese Joural of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004(23): 3 990-3 995.
|
| [15] |
张军明, 张文, 马壮, 等. 基于实测数据的建庄煤矿地应力分布规律与影响因素研究[J]. 煤炭技术, 2025, 44(4):27-32.
|
|
ZHANG Junming, ZHANG Wen, MA Zhuang, et al. Study on distribution law and influencing factors of in-situ stress in jianzhuang coal mine based on measured data[J]. Coal Technology, 2025, 44(4):27-32.
|
| [16] |
李静, 刘晨, 刘惠民, 等. 复杂断层构造区地应力分布规律及其影响因素[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2021, 50(1):123-137.
|
|
LI Jing, LIU Chen, LIU Huimin, et al. Distribution and influencing factors of in situ stress incomplex fault tectonic region[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2021, 50(1):123-137.
|
| [17] |
翁剑桥, 曾联波, 吕文雅, 等. 断层附近地应力扰动带宽度及其影响因素[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(1):39-47.
|
|
WENG Jianqiao, ZENG Lianbo, LYU Wenya, et al. Width of stress disturbed zone near fault and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(1):39-47.
|
| [18] |
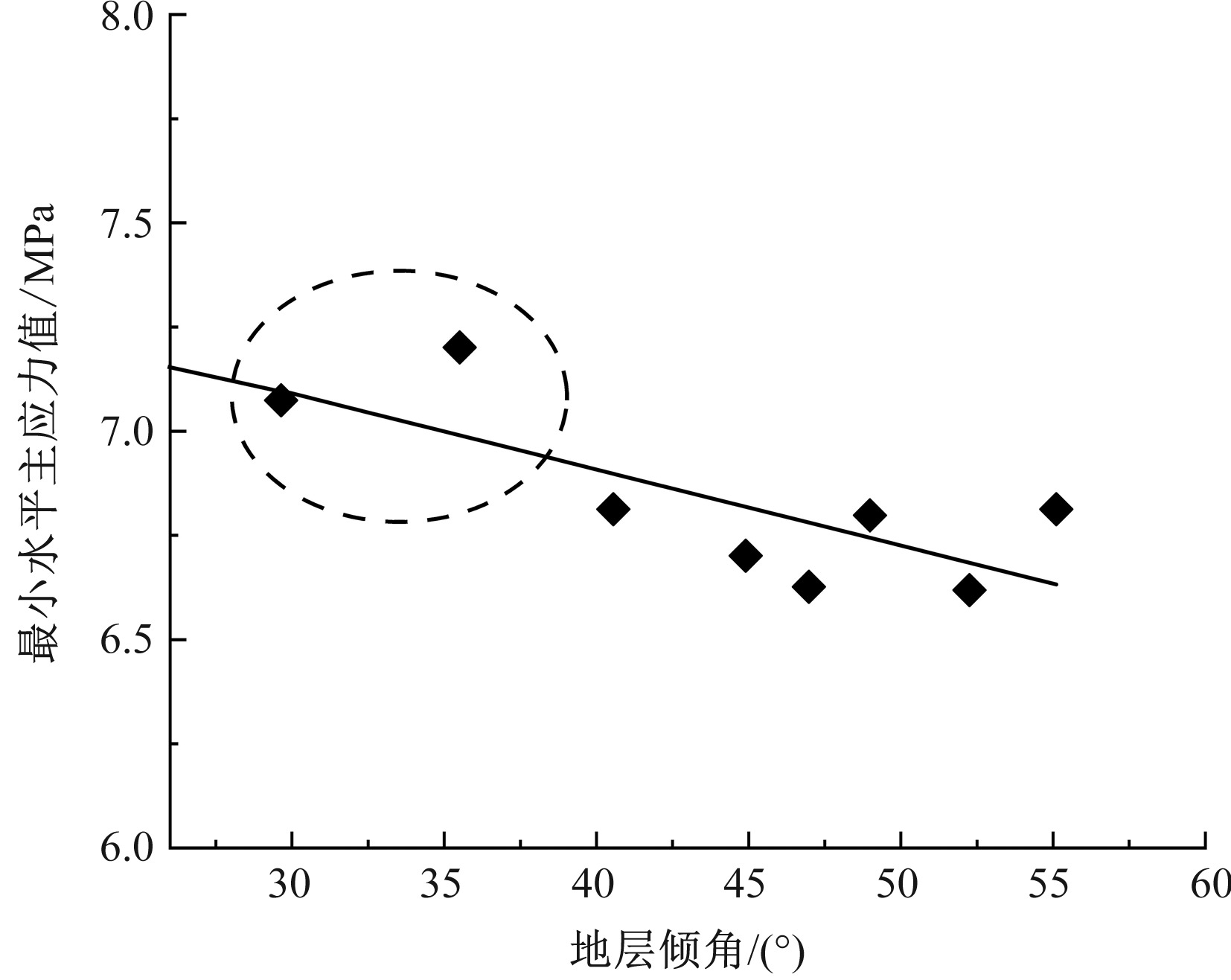
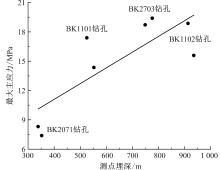
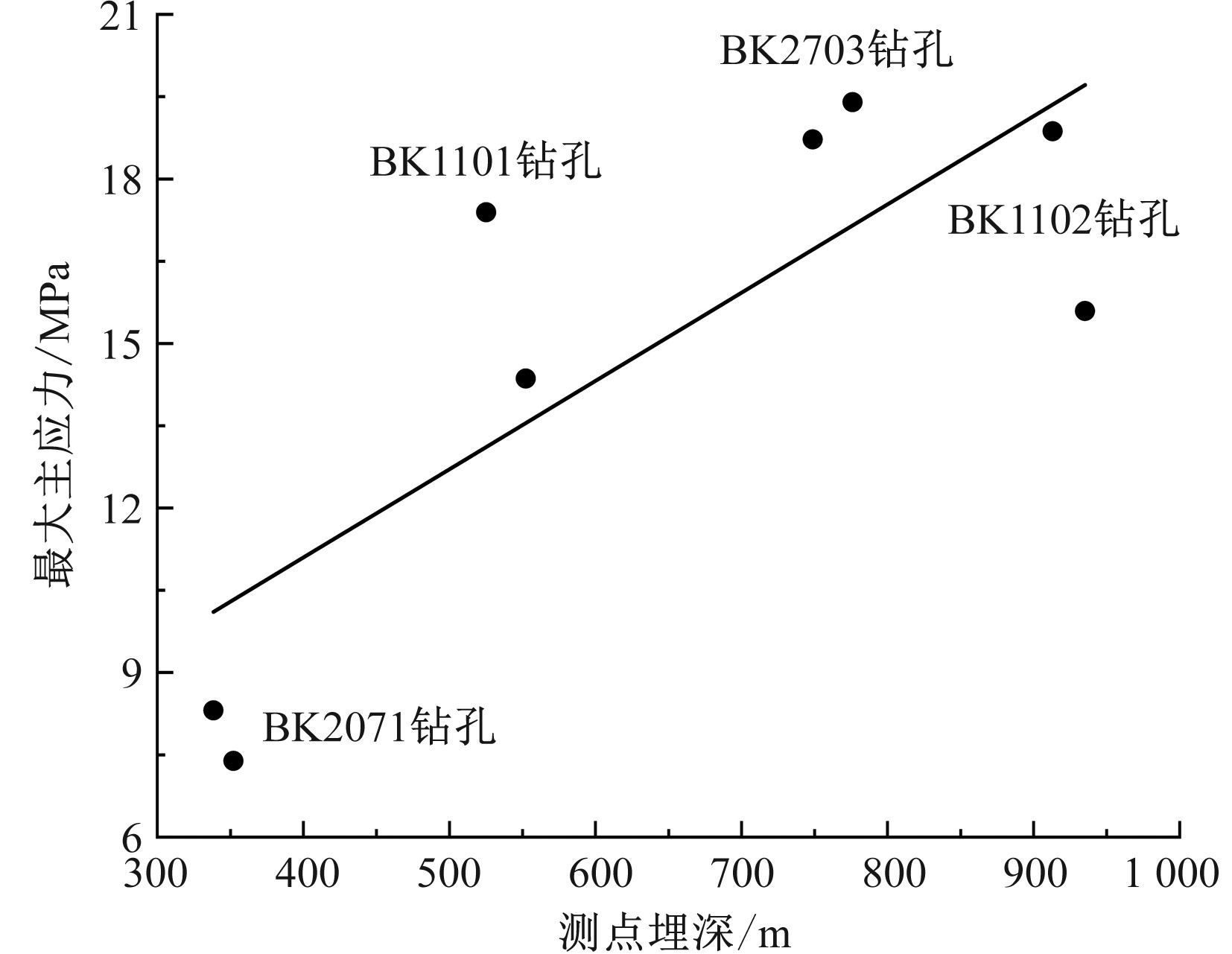
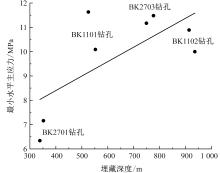
刘向阳, 刘永豪, 张顺峰, 等. 麦垛山煤矿地应力测量及井田应力场特征分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(增2):91-95.
|
|
LIU Xiangyang, LIU Yonghao, ZHANG Shunfeng, et al. In-situ stress measurement and characteristics analysis of mine field stress field in Maiduoshan coal mine[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(S1): 91-95.
|
| [19] |
张卫军, 张志佳, 胥海东, 等. 麦垛山煤矿巷道围岩地质力学测试试验[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(增2):18-22.
|
|
ZHANG Weijun, ZHANG Zhijia, XU Haidong, et al. Geo-mechanical testing of surrounding rocks in roadway of Maiduoshan coal mine[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(S2):18-22.
|