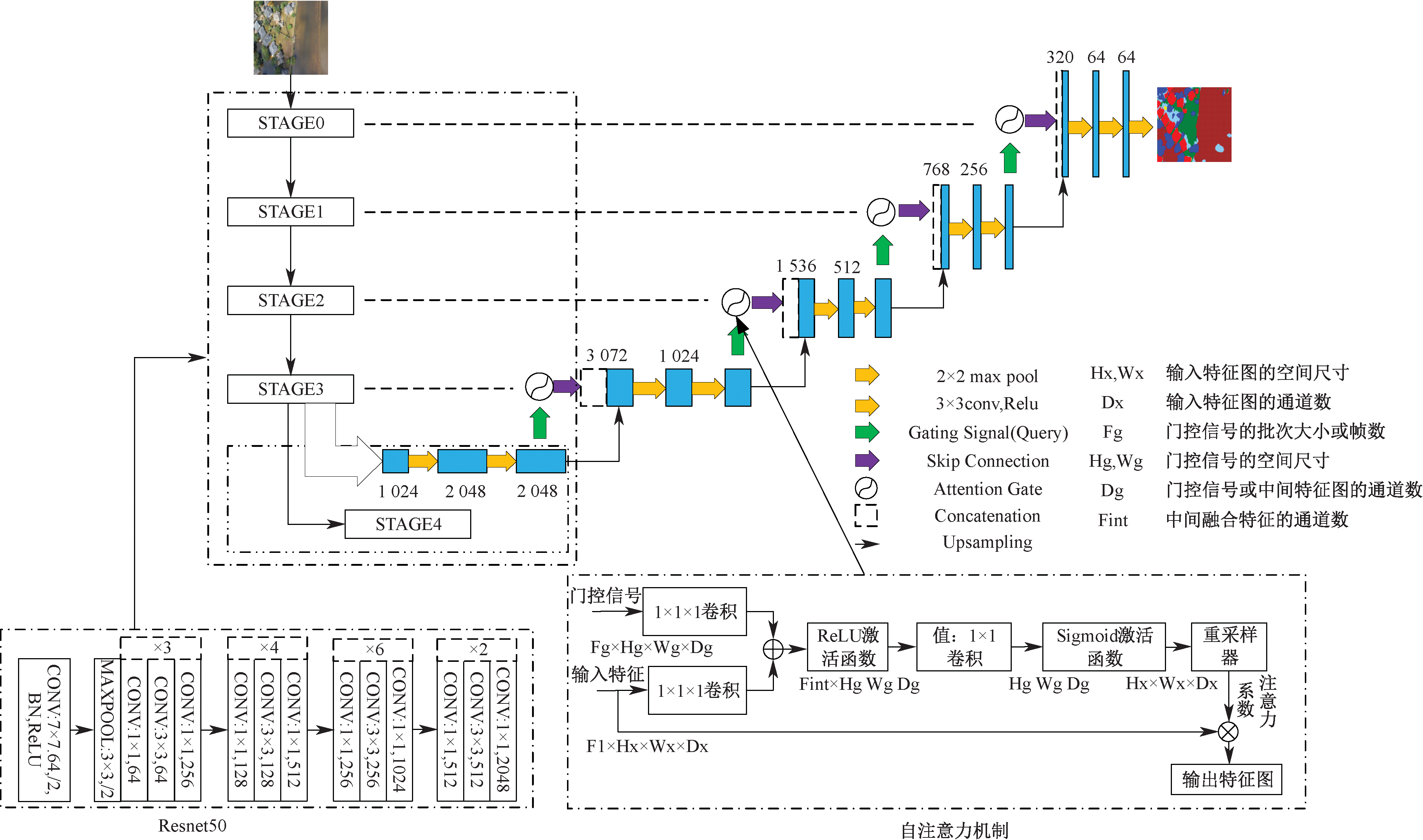
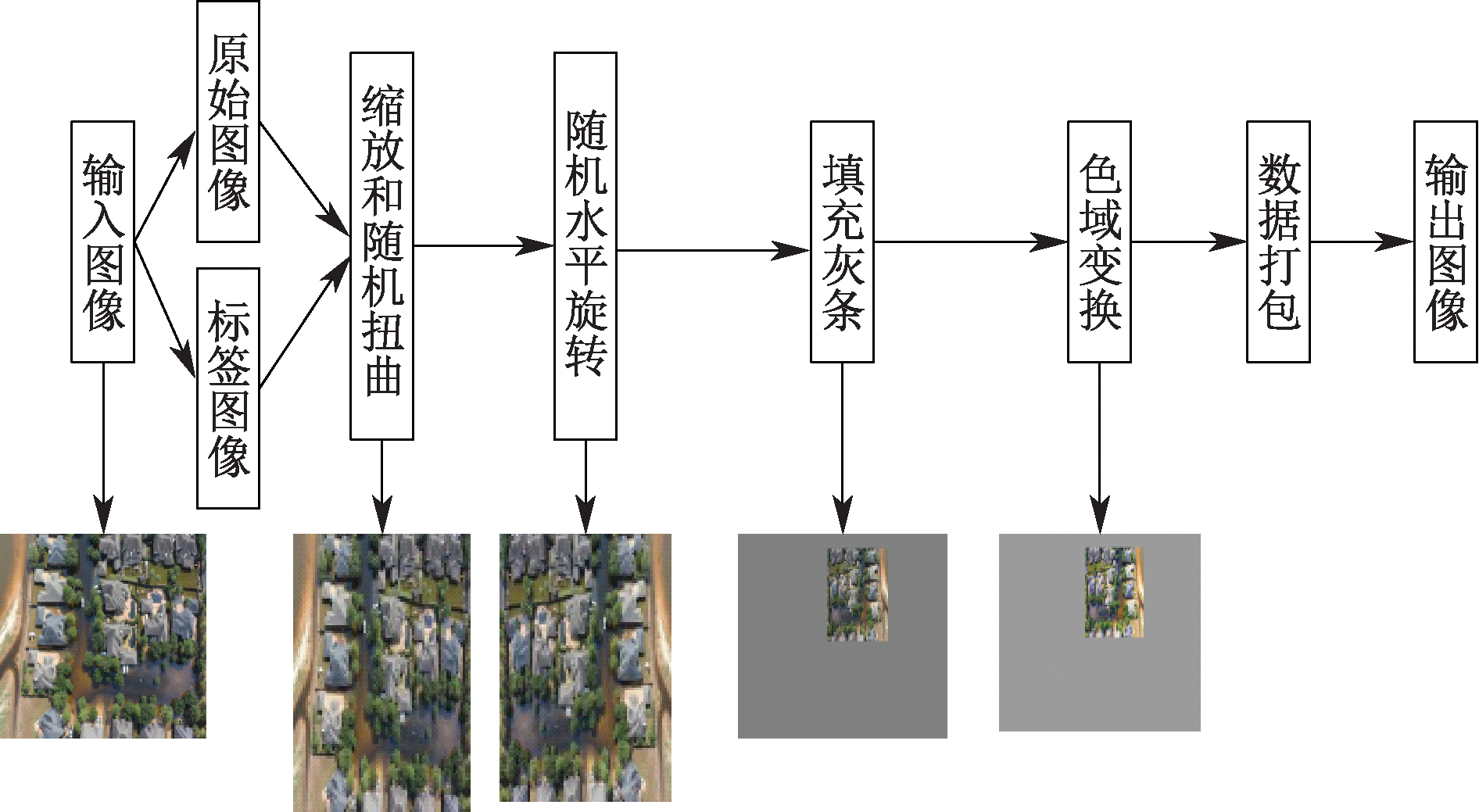
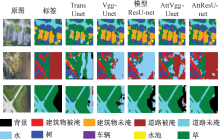
| [1] |
LATIF S, SIMONOVIC S P. Compounding joint impact of rainfall, storm surge and river discharge on coastal flood risk: an approach based on 3D fully nested Archimedean copulas[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2023,82:DOI: 10.1007/s12665-022-10719-9.
|
| [2] |
周月华, 彭涛, 史瑞琴. 我国暴雨洪涝灾害风险评估研究进展[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2019, 38(5):494-501.
|
|
ZHOU Yuehua, PENG Tao, SHI Ruiqin. Research progress on risk assessment of heavy rainfall and flood disasters in China[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 2019, 38(5):494-501.
|
| [3] |
张海凤, 孔锋, 方建. 超常规极端暴雨洪涝灾害应对的国际比较研究:以2021年中美德暴雨洪涝灾害为例[J]. 水利水电技术:中英文, 2023, 54(7):1-13.
|
|
ZHANG Haifeng, KONG Feng, FANG Jian. International comparative study on coping with flood waterlogging disaster from extraordinary rainstorm: taking rainstorm flood waterlogging disasters in China, America and Germany in 2021 as study cases[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2023, 54(7):1-13.
|
| [4] |
YANG Kaixin, ZHANG Sujie, YANG Xinran, et al. Flood detection based on unmanned aerial vehicle system and deep learning[J]. Complexity, 2022, 2022(1):1-9.
|
| [5] |
孙世金, 孙永玲, 刘晓, 等. 基于Landsat 8影像的冰川边界提取方法研究:以喀喇昆仑区域为例[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2024, 39(6):1363-1372.
doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2024.6.1363
|
|
SUN Shijin, SUN Yongling, LIU Xiao, et al. Research on glacier boundary extraction method based on Landsat-8 image: taking the Karakoram region as an example[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2024, 39(6):1363-1372.
|
| [6] |
MIAO Tian, ZENG Hongcheng, WANG He, et al. A fast extraction method of flood areas based on iterative threshold segmentation using spaceborne SAR data[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(9):2760-2768.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.09.08
|
| [7] |
李昕悦, 张锦, 贾笑怡, 等. 适用于城市洪水的水体提取方法对比与分析[J]. 地下水, 2020, 42(5):179-183.
|
|
LI Xinyue, ZHANG Jin, JIA Xiaoyi, et al. Comparison and analysis of water extraction methods suitable for urban flood[J]. Ground Water, 2020, 42(5):179-183.
|
| [8] |
王敬明, 王世新, 王福涛, 等. 基于Sentinel-1 SAR数据洪水淹没提取方法研究[J]. 灾害学, 2021, 36(4):214-220.
|
|
WANG Jingming, WANG Shixin, WANG Futao, et al. Flood inundation region extraction method based on Sentinel-1 SAR data[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2021, 36(4):214-220.
|
| [9] |
郭玮, 袁宏永, 薛明, 等. SAR影像洪水淹没范围深度学习提取方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(4):177-184.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.04.026
|
|
GUO Wei, YUAN Hongyong, XUE Ming, et al. Flood inundation area extraction method of SAR images based on deep learning[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(4):177-184.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.04.026
|
| [10] |
LI Wenning, LI Yi, GONG Jianhua, et al. Urban water extraction with UAV high-resolution remote sensing data based on an improved U-NET model[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(16):DOI: 10.3390/rs13163165.
|
| [11] |
ZHAO Jie, LI Yu, MATGEN P, et al. Urban-aware U-NET for large-scale urban flood mapping using multitemporal Sentinel-1 intensity and interferometric coherence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022,60:1-21.
|
| [12] |
KIM J, KIM H, KIM D, et al. Deep learning-based flood area extraction for fully automated and persistent flood monitoring using cloud computing[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(24):DOI: 10.3390/rs14246373.
|
| [13] |
FENG Wenqing, SUI Haigang, HUANG Weiming, et al. Water body extraction from very high-resolution remote sensing imagery using deep U-NET and a super pixel-based conditional random field model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 16(4):618-622.
doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2879492
|
| [14] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,2016:770-778.
|
| [15] |
OKTAY O, SCHLEMPER J, FOLGOC L L, et al. Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas[J]. arXiv Preprint arXiv, 2018:DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1804.03999.
|
| [16] |
RAHNEMOONFAR M, CHOWDHURY T, SARKAR A, et al. Flood net: a high-resolution aerial imagery dataset for post flood scene understanding[J]. IEEE Access, 2021,9:89 644-89 654.
|
| [17] |
徐康, 朱茂, 贺秋华, 等. 一种基于TransUNet的SAR影像水体提取及洲滩面积变化监测应用[J]. 测绘科学, 2024, 49(2):55-64.
|
|
XU Kang, ZHU Mao, HE Qiuhua, et al. Water extraction from SAR images based on TransUNet and its application in sandbar area change monitoring[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2024, 49(2):55-64.
|
| [18] |
WU Ji, JIN Yaqiu, SHI Jiancheng, et al. Special issue on the 2016 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(6):2428-2430.
doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.4609443
|
| [19] |
江松, 李研博, 何旭乾, 等. 基于无人机影像深度学习的滑坡灾害智能识别[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(7):229-238.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.07.2092
|
|
JIANG Song, LI Yanbo, HE Xuqian, et al. Intelligent identification of landslide disaster based on deep learning of UAV images[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(7):229-238.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.07.2092
|