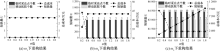
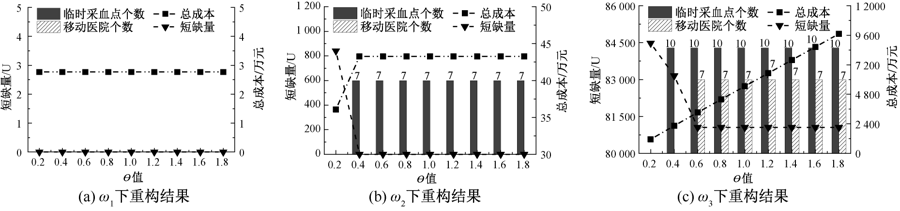
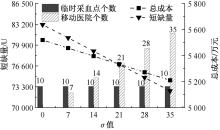
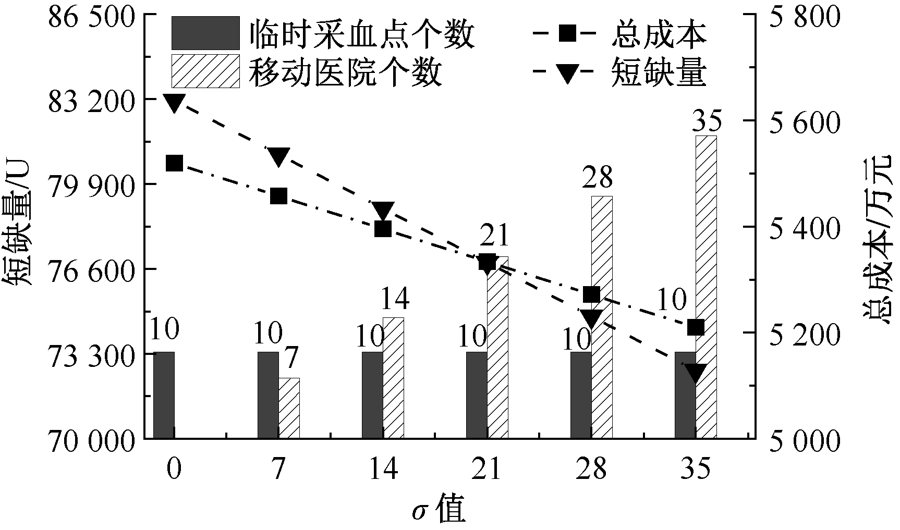
| [1] |
RITCHIE H, ROSER M. Natural disasters[R]. Our World in Data, 2014.
|
| [2] |
World Health Organization. Action framework to advance universal access to safe, effective and quality-assured blood products 2020-2023[EB/OL].[2020-02-17].
|
| [3] |
OSORIO A F, BRAILSFORD S C, SMITH H K. A structured review of quantitative models in the blood supply chain: a taxonomic framework for decision-making[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2015, 53(24):7191-7212.
doi: 10.1080/00207543.2015.1005766
|
| [4] |
陈思, 邓晓臻. 自然灾害下节点失效的运输网络关键节点识别[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(6):177-183.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.06.029
|
|
CHEN Si, DENG Xiaozhen. Identification of key nodes in transportation network with node failure in natural disasters[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(6):177-183.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.06.029
|
| [5] |
宋英华, 马连隆, 杨丽娇, 等. 基于模糊BN的企业业务中断风险分析:以洪涝灾害情景为例[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(6):1-6.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.06.001
|
|
SONG Yinghua, MA Lianlong, YANG Lijiao, et al. Business interruption risk analysis based on fuzzy BN: a case study of flood disaster[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(6):1-6.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.06.001
|
| [6] |
KOKS E E, ROZENBERG J, ZORN C, et al. A global multi-hazard risk analysis of road and railway infrastructure assets[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(9):451-479.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08394-9
|
| [7] |
BLACKWELL T, BOSSE M. Use of an innovative design mobile hospital in the medical response to Hurricane Katrina[J]. Annals of Emergency Medicine, 2007, 49(5):580-588.
doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2006.06.037
|
| [8] |
宋宫儒, 焦艳波, 安丽娜, 等. 我国国家卫生应急救援队的实践与改进探索[J]. 中华灾害救援医学, 2019, 7(4):18-21.
|
|
SONG Gongru, JIAO Yanbo, AN Li'na, et al. Chinese national health emergency rescue teams: disaster relief activities and suggestions for improvement[J]. Chinese Journal of Disaster Medicine, 2019, 7(4):18-21.
|
| [9] |
马祖军, 周愉峰. 国家血液战略储备库选址-库存问题[J]. 管理科学学报, 2018, 21(3):59-73.
|
|
MA Zujun, ZHOU Yufeng. Location-inventory problem for national strategic blood reserves[J]. Journal of Management Sciences in China, 2018, 21(3):59-73.
|
| [10] |
WANG Changjun, CHEN Shutong. A distributionally robust optimization for blood supply network considering disasters[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2020, 134:1-30.
|
| [11] |
WS 399—2012, 血液储存要求[S].
|
|
WS 399-2012, Standards for blood storage[S].
|
| [12] |
清华大学土木结构组, 西南交通大学土木结构组, 北京交通大学土木结构组. 汶川地震建筑震害分析[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2018, 29(4):1-9.
|
|
Civil and Structural Groups of Tsinghua University, Xinan Jiaotong University and Beijing Jiaotong University. Analysis on building seismic damage in Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2018, 29(4):1-9.
|
| [13] |
MA Zujun, WANG Keming, DAI Ying. An emergency blood allocation approach considering blood group compatibility in disaster relief operations[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Science, 2018, 10(1):74-88.
doi: 10.1007/s13753-018-0212-7
|
| [14] |
SHARMA B, RAMKUMAR M, SUBRAMANIAN N, et al. Dynamic temporary blood facility location-allocation during and post-disaster periods[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2019, 283(5):705-736.
doi: 10.1007/s10479-017-2680-3
|
| [15] |
CHEN Shutong, WANG Changjun. Incorporating a Bayesian network into two-stage stochastic programming for blood bank location-inventory problem in case of disasters[J]. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2019:DOI:10.1155/2019/7214907.
|
| [16] |
HAGHJOO N, TAVAKKOLI-M R, SHAHMORADI-M H, et al. Reliable blood supply chain network design with facility disruption: A real-world application[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 90: 1-18.
|
| [17] |
JABBARZADEH A, FAHIMNIA B, SEURING S. Dynamic supply chain network design for the supply of blood in disasters: a robust model with real world application[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2014, 70:225-244.
doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2014.06.003
|
| [18] |
严军雄, 黄露, 伍武彪. 地震灾害对献血者献血行为的影响及原因分析[J]. 中国输血杂志, 2008 (8):615-616.
|