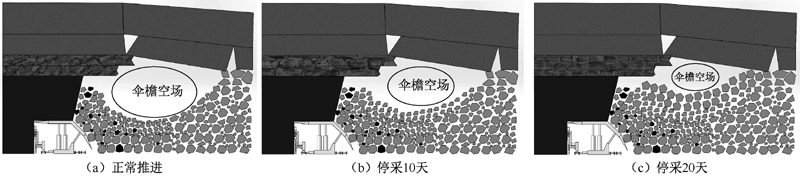
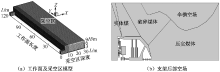
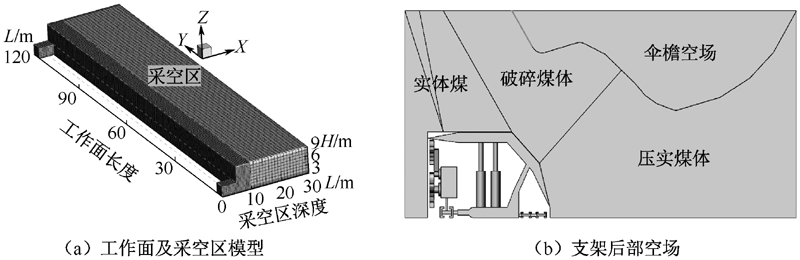
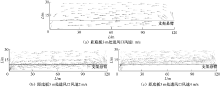
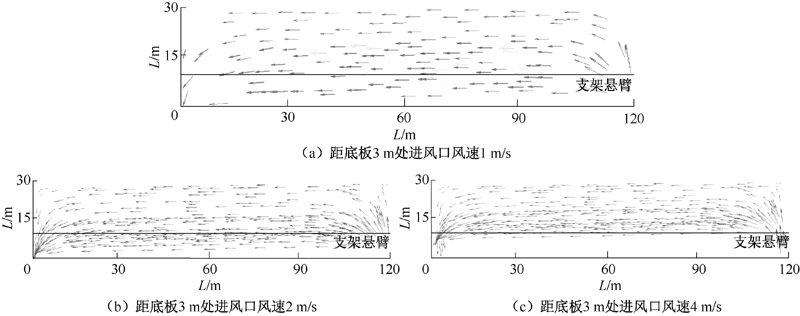
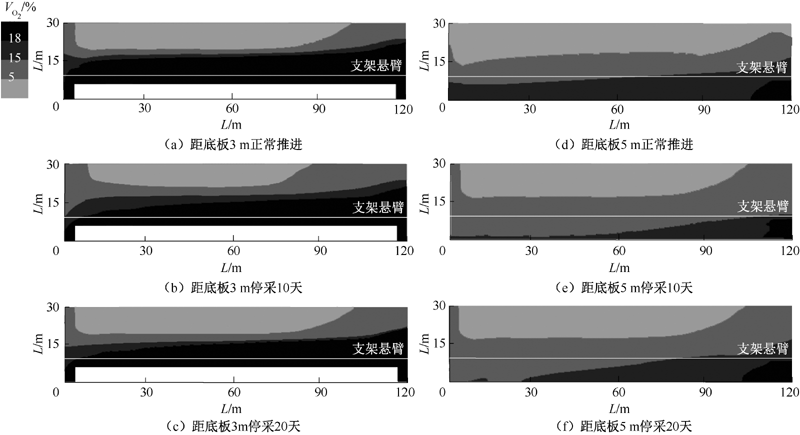
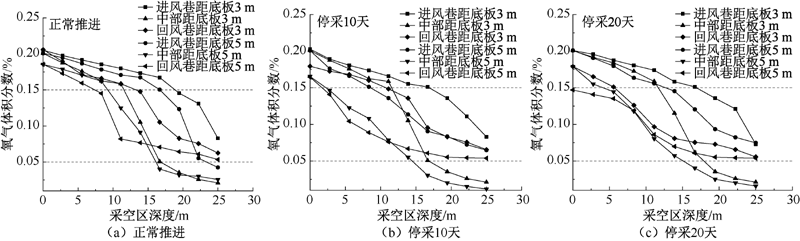
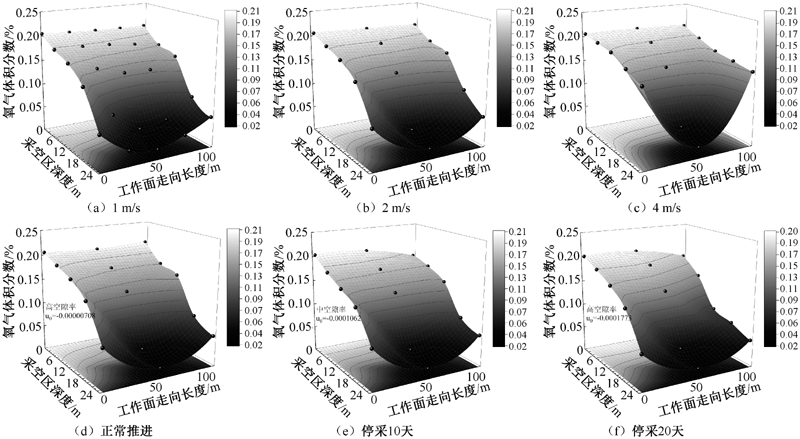
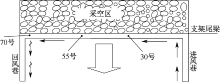
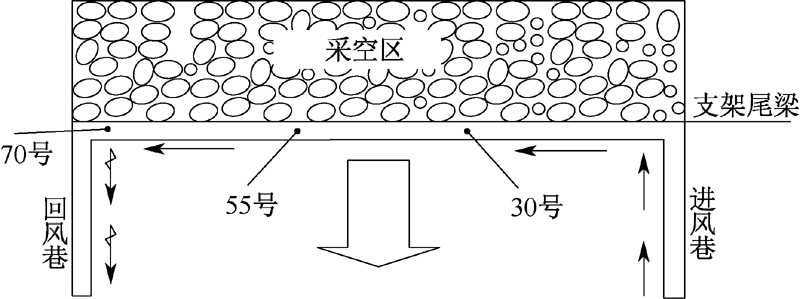
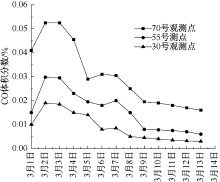
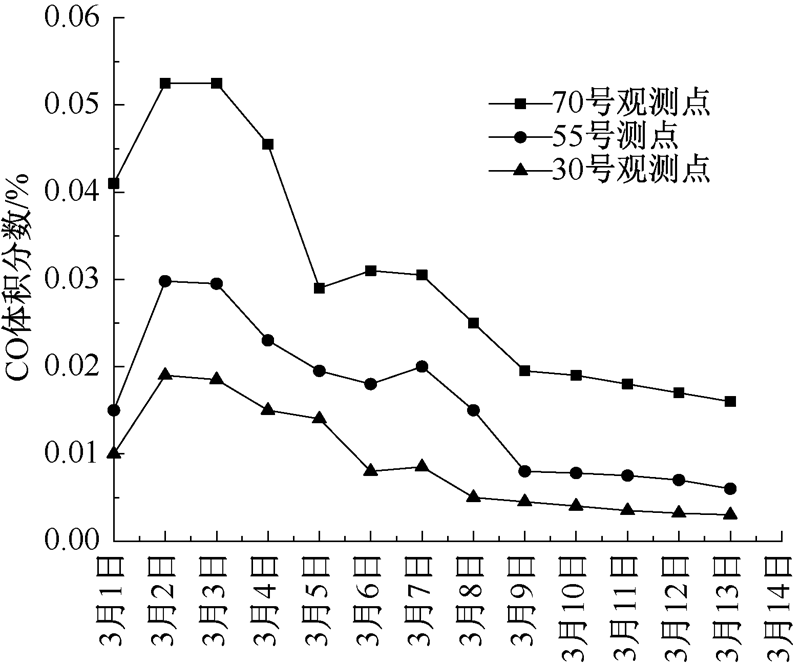
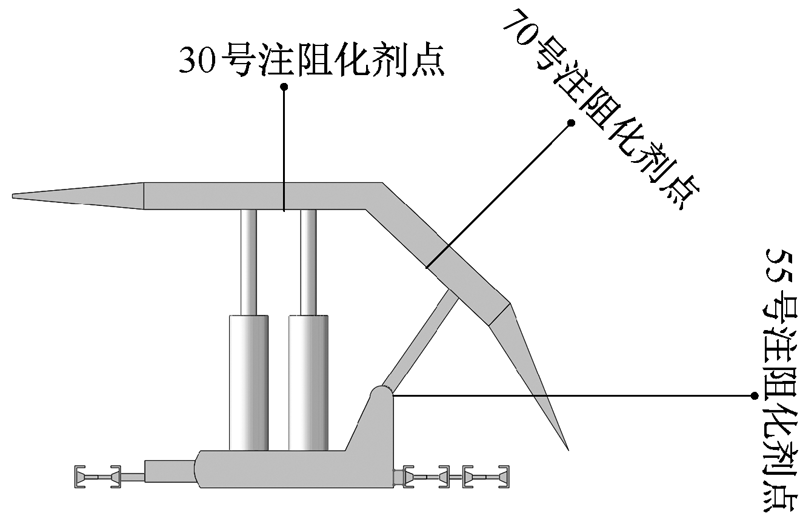
| [1] |
杨胜强, 张人伟, 邸志前, 等. 综采面采空区自燃“三带”的分布规律[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2000, 29(1):93-96.
|
|
YANG Shengqiang, ZHANG Renwei, DI Zhiqian, et al. Distribution reg ularity of spontaneous combustion “ Three-Zone” in goaf of fully-mechanized coal faces[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2000, 29(1):93-96.
|
| [2] |
汪东. 回采工作面配风量对采空区漏风及自燃影响分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2016, 44(12):96-101.
|
|
WANG Dong. Analysis on the effect of air quantity of coal mining face to air leakage and spontaneous combustion in goaf[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2016, 44(12) :96-101.
|
| [3] |
齐庆杰, 祁云, 周新华, 等. 供风量对采空区自燃动态影响及防灭火技术[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(4):120-126.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.04.019
|
|
QI Qingjie, QI Yun, ZHOU Xinhua, et al. Dynamic effects of air supply volume on spontaneous combustion in goafs and fire prevention and extinguishing technology[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(4):120-126.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.04.019
|
| [4] |
李宗翔, 海国治, 秦书玉, 等. 采空区风流移动规律的数值模拟与可视化显示[J]. 煤炭学报, 2001, 26(6):76-78.
|
|
LI Zongxiang, HAI Guozhi, QIN Shuyu, et al. Numerical simulation and visual display of air flow pattern in goaf[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2001, 26(6):76-78.
|
| [5] |
司俊鸿, 程根银, 朱建芳, 等. 采空区非均质多孔介质渗透特性三维建模及应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(5):220-224.
|
|
SI Junhong, CHENG Genyin, ZHU Jianfang, et al. Three-dimensional modeling and application of permeability characteristics of heterogeneous porous media in goaf[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(5):220-224.
|
| [6] |
李树刚, 钱鸣高, 石平五, 等. 综放开采覆岩离层裂隙变化及空隙渗流特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2000, 19(5):604-607.
|
|
LI Shugang, QIAN Minggao, SHI Pingwu, et al. Study on bed separated fissursed of overlying staratum and interstice permeability in fully-mechanized top coal caving[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2000, 19(5):604-607.
|
| [7] |
谢军, 薛生. 综放采空区空间自燃三带划分指标及方法研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2011, 39(1):65-68.
|
|
XIE Jun, XUE Sheng. Study on index and method of three zones of space spontaneous combustion in fully mechanized goaf[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2011, 39(1):65-68.
|
| [8] |
王家臣, 王兆会. 综放开采顶煤裂隙扩展的应力驱动机制[J]. 煤炭学报, 2018, 43(9) : 2376-2388.
|
|
WANG Jiachen, WANG Zhaohui. Propagating mechanism of top-coal fracture in longwall top-coal caving mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(9) : 2376-2388.
|
| [9] |
车强. 采空区气体三维多场耦合规律研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京),2010.
|
|
CHE Qiang. Study on coupling law of mixed gas study on coupling law of mixed gas three-dimensional multi-field in goaf[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology(Beijing), 2010.
|
| [10] |
王少锋, 王德明, 曹凯, 等. 采空区及上覆岩层空隙率三维分布规律[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 45(3):833-839.
|
|
WANG Shaofeng, WANG Deming, CAO Kai, et al. Distribution law of 3D fracture field of goaf and overlying strata[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2014, 45(3):833-839.
|
| [11] |
周佩玲, 袁飞, 赵鹏霞, 等. 动态采空区非线性氧化升温相似试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(11):95-100.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.11.014
|
|
ZHOU Peiling, YUAN Fei, ZHAO Pengxia, et al. Similar experimental study on non-linear oxidation heating up process of coal in dynamic gob areas[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(11): 95-100.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.11.014
|
| [12] |
ZHU Jianfang, HE Ning, LI Dengji, et al. The relationship between oxygen consumption rate and temperature during coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Elsevier, 2012, 50(4):842-845.
|
| [13] |
梁运涛, 张腾飞, 李树刚, 等. 采空区孔隙率非均质模型及其流场分布模拟[J]. 煤炭学报, 2009, 34(9):1203-1207.
|
|
LIANG Yuntao, ZHANG Tengfei, LI Shugang, et al. Heterogeneous model of porosity in goaf and its airflow field distribution[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2009, 34(9):1203-1207.
|
| [14] |
董子文, 齐庆杰, 韩光, 等. 采空区氧化带与发火期动态演化规律模拟研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(7):45-51.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.07.008
|
|
DONG Ziwen, QI Qingjie, HAN Guang, et al. Numerical simulation study on dynamical evolution rule of spontaneous combustion oxidation zone and period[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(7):45-51.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.07.008
|
| [15] |
王立杰, 王继仁, 张勋, 等. 采空区高位钻孔注浆防灭火浆液扩散特性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(10):71-77.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.10.011
|
|
WANG Lijie, WANG Jiren, ZHANG Xun, et al. Study on slurry diffusion law of high level drilling grouting fire prevention and control in goaf[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(10):71-77.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.10.011
|
| [16] |
赵文彬, 赵娟, 李振武, 等. 厚煤层窄工作面采空区立体自燃带分布规律研究[J] .煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(12): 123-130.
|
|
ZHAO Wenbin, ZHAO Juan, LIN Zhenwu, et al. Study on regularity of three-dimensional spontaneous combustion zone in gob of narrow face with thick coal seam[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(12): 123-130.
|
| [17] |
褚廷湘, 韩学锋, 余明高, 等. 承压破碎煤体低温氧化特征与宏观致因分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(9):77-83.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.09.012
|
|
CHU Tingxiang, HAN Xuefeng, YU Minggao, et al. Low-temperature oxidation characteristics of compacted broken coal and macroscopic cause analysis[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(9):77-83.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.09.012
|