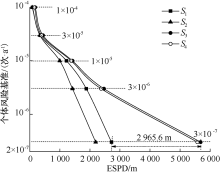
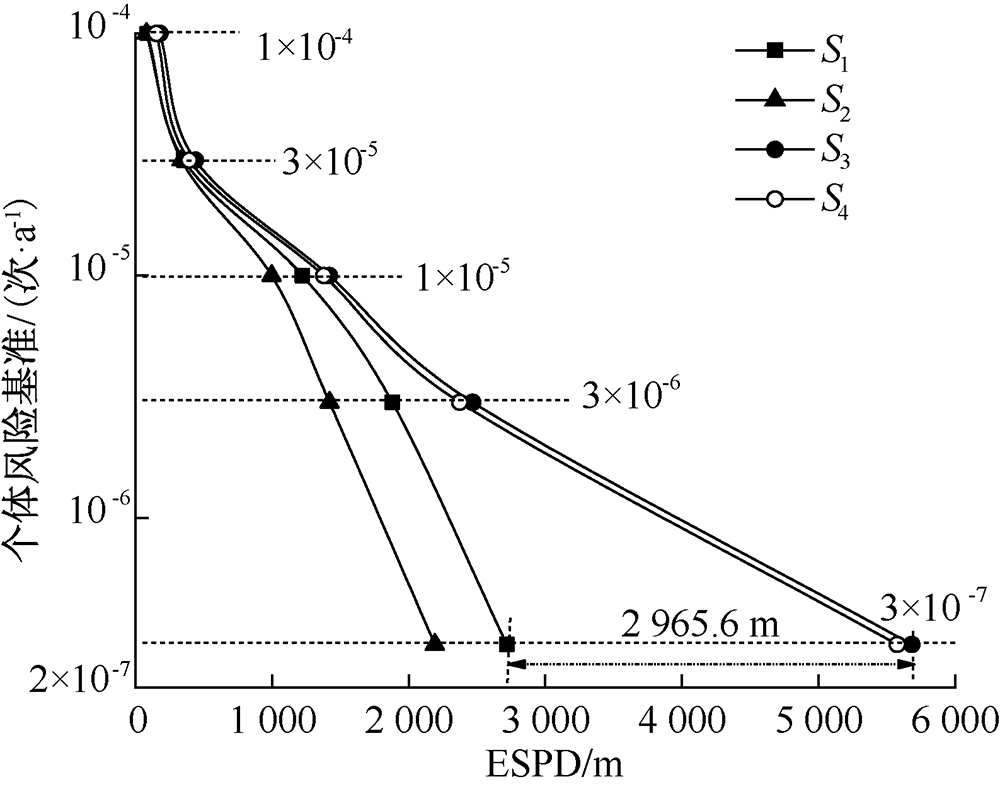
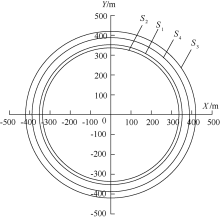
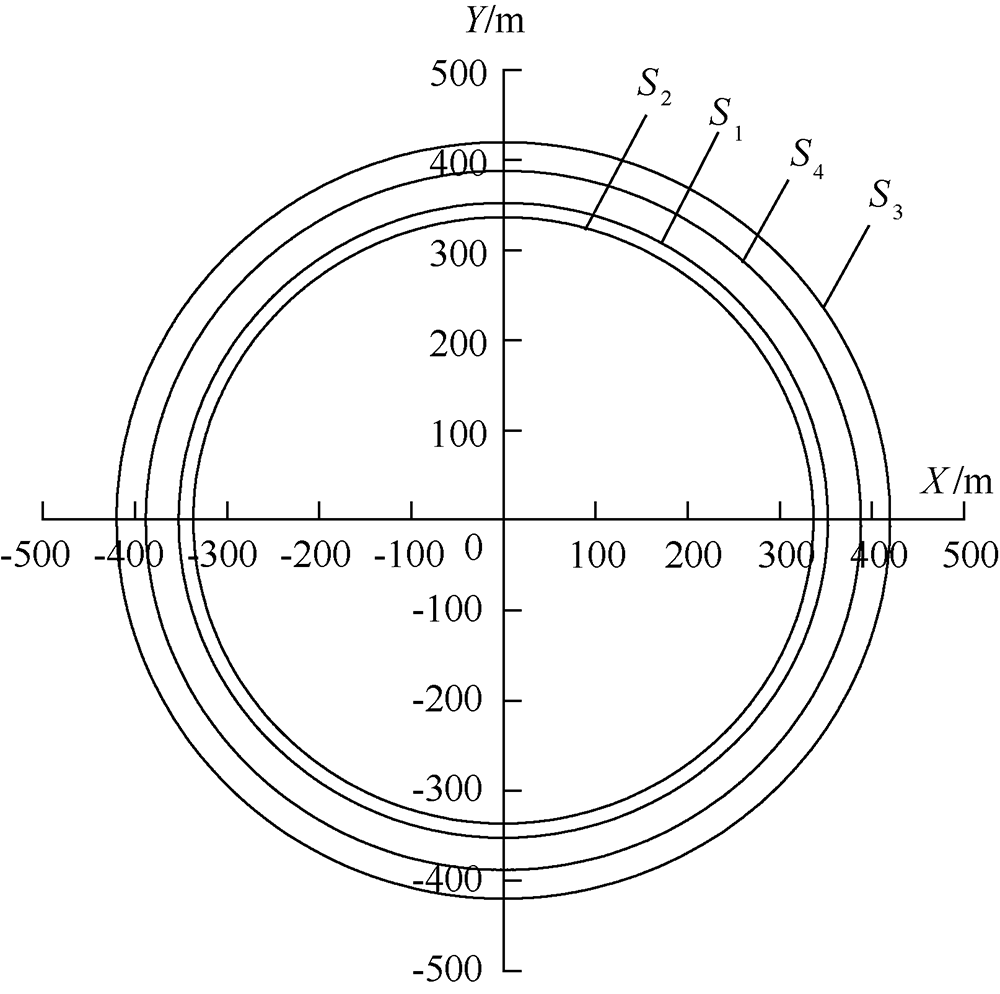
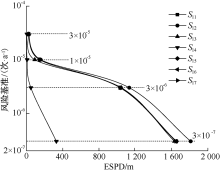
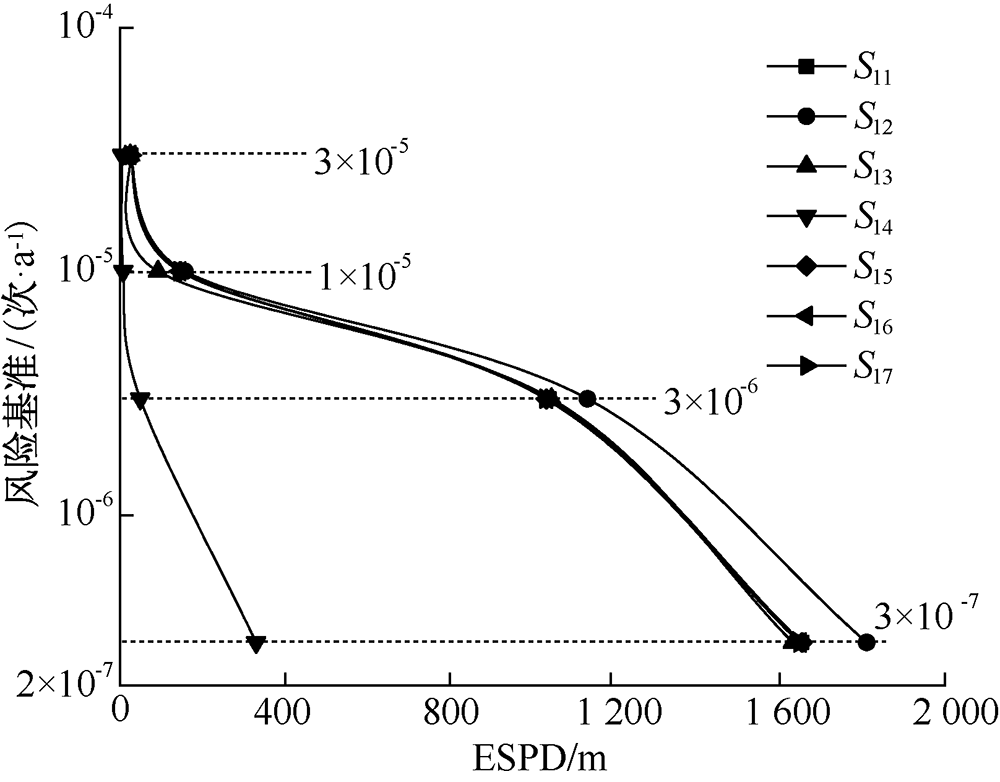
| [1] |
王志荣, 孙培培, 唐振华, 等. 密闭容器甲烷-空气混合物爆炸的尺寸效应[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(1): 60-66.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.01.009
|
|
WANG Zhirong, SUN Peipei, TANG Zhenhua, et al. Size effect of methane-air mixture explosion in closed vessel[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(1): 60-66.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.01.009
|
| [2] |
JÄKEL C, KELM S, VERFONDERN K, et al. Validation of a 3D multiphase-multicomponent CFD model for accidental liquid and gaseous hydrogen releases[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(17): 8807-8818.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.10.024
|
| [3] |
JIA Wenlong, BAN Jiuqing, LIANG Fangjian, et al. A new homogeneous non-equilibrium model to compute vapor-liquid two-phase critical pressure ratios of multicomponent hydrocarbon mixtures[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2020, 68(11): DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2020.104338.
doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2020.104338
|
| [4] |
PENG Dingyu, ROBINSON D B. New two-constant equation of state[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals, 1976, 15(1): 3069-3078.
|
| [5] |
FRANC$\dot{U}$ J, MIKYŠKA J. An alternative model of multicomponent diffusion based on a combination of the Maxwell-Stefan theory and continuum mechanics[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2020, 400(1): DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2019.108962.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2019.108962
|
| [6] |
FILLO A J, SCHLUP J, BEARDSELL G, et al. A fast, low-memory, and stable algorithm for implementing multicomponent transport in direct numerical simulations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2020, 406(4): DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2019.109185.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2019.109185
|
| [7] |
YANG W, XIA J, WANG X, et al. Predicting evaporation dynamics of a multicomponent gasoline/ethanol droplet and spray using non-ideal vapour-liquid equilibrium models[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 168(4): DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.120876.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.120876
|
| [8] |
王铭明, 于浩, 汪晨, 等. 多组分气体混合物在煤的孔隙中运动特性研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(3): 162-166.
|
|
WANG Mingming, YU Hao, WANG Chen, et al. Study on transport characteristics of multi-component gaseous mixtures through coal pore[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48 (3): 162-166.
|
| [9] |
胡百中, 陈序, 何泊龙, 等. 含硫天然气集输管道气体泄漏扩散三维数值模拟[J]. 重庆科技学院学报:自然科学版, 2019, 21(2): 21-25, 90.
|
|
HU Baizhong, CHEN Xu, HE Bolong, et al. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of gas leakage and diffusion in sulfur natural gas gathering[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Science and Technology:Natural Sciences Edition, 2019, 21(2): 21-25, 90.
|
| [10] |
DAVID W J, JEFFREY D M. The importance of multiphase and multicomponent modeling in consequence and risk analysis[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2003, 104(3): 51-64.
doi: 10.1016/S0304-3894(03)00234-6
|
| [11] |
辛保泉, 喻健良, 党文义, 等. 复杂地形高含硫天然气风洞扩散实验及安全防护距离[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(11): 149-158.
|
|
XIN Baoquan, YU Jianliang, DANG Wenyi, et al. Wind tunnel dispersion experiments and safety protection distances of high sulfur natural gas in complex terrains[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40 (11): 149-158.
|
| [12] |
International Association of Oil and Gas Producers. Process release frequencies[R], 2010.
|
| [13] |
任乐峰, 孟祥坤, 陈国明. 滩海油气管道泄漏风险演化与评估[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(1): 159-164.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.01.023
|
|
REN Lefeng, MENG Xiangkun, CHEN Guoming. Risk evolution and evaluation for oil and gas leakage of pipeline in shallow sea[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31 (1): 159-164.
|
| [14] |
GB 36894—2018, 危险化学品生产装置和储存设施风险基准[S].
|
|
GB 36894-2018, Risk criteria for hazardous chemicals production unit and storage installations[S].
|
| [15] |
辛保泉, 党文义, 喻健良, 等. 石化过程蒸气云爆炸抗爆设防荷载定量评估方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(9): 113-118.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.09.016
|
|
XIN Baoquan, DANG Wenyi, YU Jianliang, et al. Quantitative evaluation method of blast-resistant and defense loads for VCE in petrochemical process[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(9): 113-118.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.09.016
|