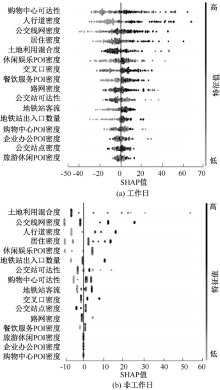
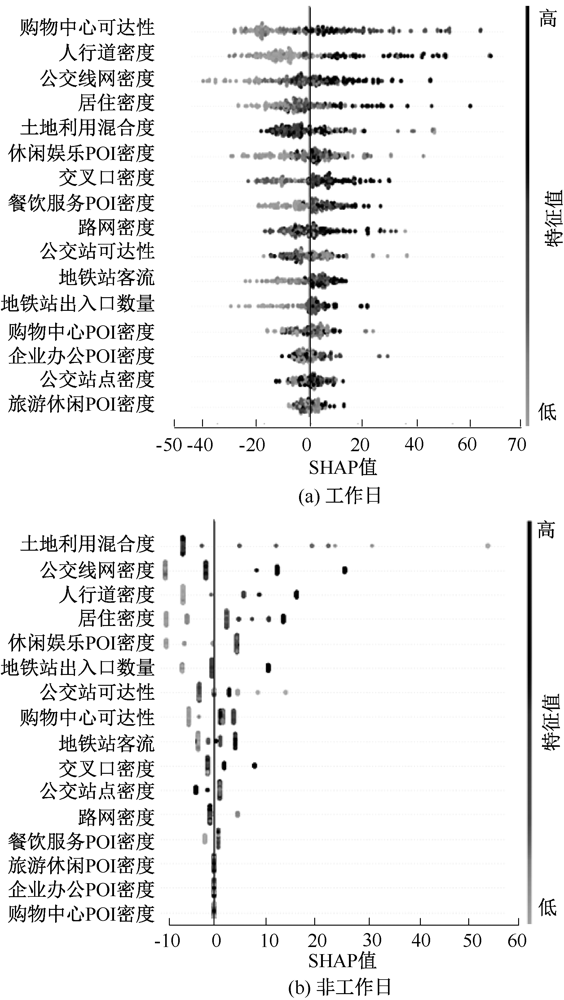
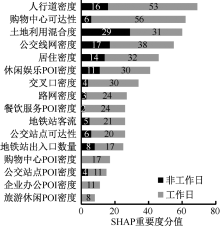
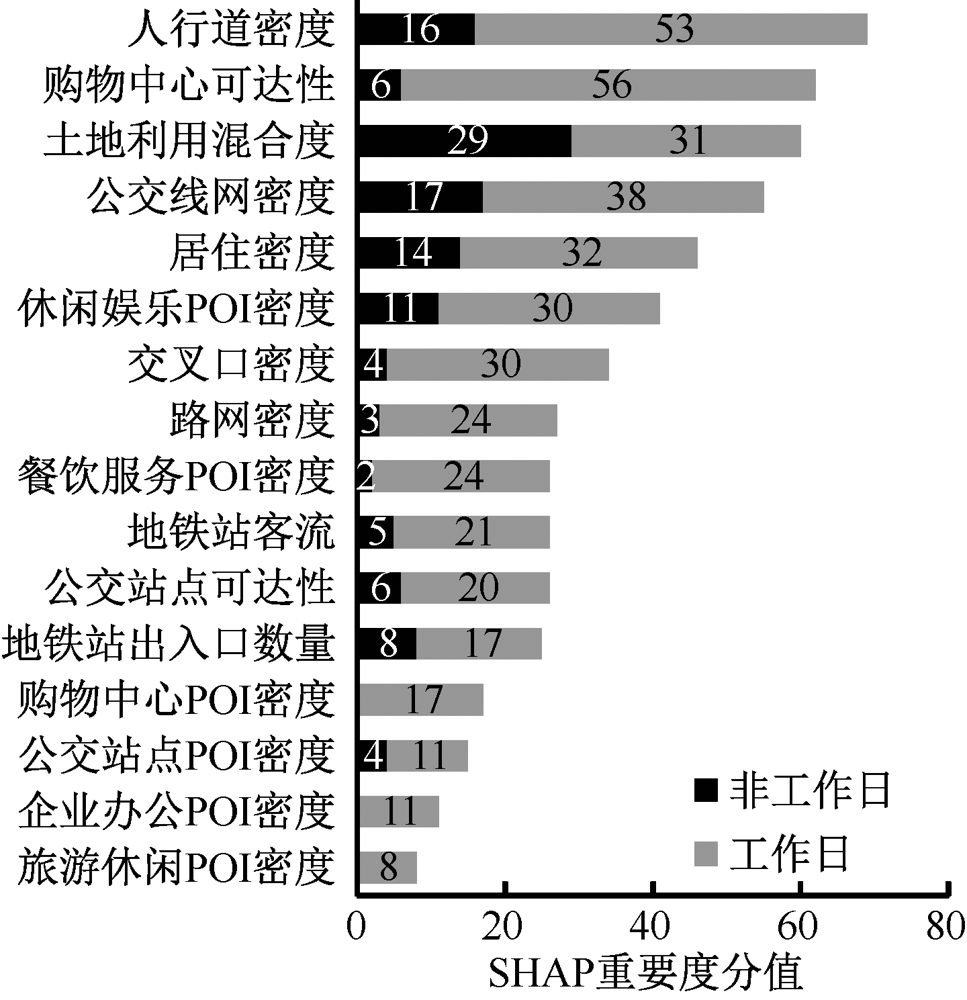
| [1] |
SALLIS J F, BULL F, BURDETT R, et al. Use of science to guide city planning policy and practice: how to achieve healthy and sustainable future cities[J]. Lancet, 2016, 388: 2 936- 2 947.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31522-7
pmid: 27598660
|
| [2] |
王成, 谢波. 土地利用视角下城市交通事故驱动机理的研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展, 2020, 39(9):1597-1606.
|
|
WANG Cheng, XIE Bo. Research progress on the driving mechanism of traffic accidents from the perspective of land use[J]. Progress in Geography, 2020, 39(9):1597-1606.
|
| [3] |
EWING R, DUMBAUGH E. The built environment and traffic safety: a review of empirical evidence[J]. Journal of Planning Literature, 2009, 23(4):347-367.
doi: 10.1177/0885412209335553
|
| [4] |
HUANG Yuan, WANG Xiaoguang, DAVID P. Examining spatial relationships between crashes and the built environment: a geographically weighted regression approach[J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 2018, 69(5): 221-233.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2018.04.027
|
| [5] |
XU Pengpeng, HUANG Helai. Modeling crash spatial heterogeneity: random parameter versus geographically weighting[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2015, 75(2):16-25.
doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2014.10.020
|
| [6] |
YANG Jiawen, JASON C, ZHOU Yufei. Elaborating non-linear associations and synergies of subway access and land uses with urban vitality in Shenzhen[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2021, 144(2):74-88.
doi: 10.1016/j.tra.2020.11.014
|
| [7] |
CHOI D, EWING R. Effect of street network design on traffic congestion and traffic safety[J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 2021, 96(10):1-9.
|
| [8] |
LIU Siyang, RONG Jian, ZHOU Chenjing, et al. Probability-based typology for description of built environments around urban rail stations[J]. Building and Environment, 2021, 205(11):1-12.
|
| [9] |
戢晓峰, 李德林, 杨文臣. 山区二级公路交通事故致因的时间演化机制[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(4):31-36.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.04.006
|
|
JI Xiaofeng, LI Delin, YANG Wenchen. Temporal evolution analysis on causes of traffic accidents occurring on secondary highways in mountain areas[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(4):31-36.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.04.006
|
| [10] |
戢晓峰, 张琪. 学区尺度下小学生通学事故风险评估及影响因素[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2021, 21(1):221-226.
|
|
JI Xiaofeng, ZHANG Qi. Risk assessment and influencing factors of pupils' school commuting accident risk in school district scale[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021, 21(1):221-226.
|