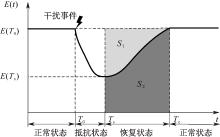
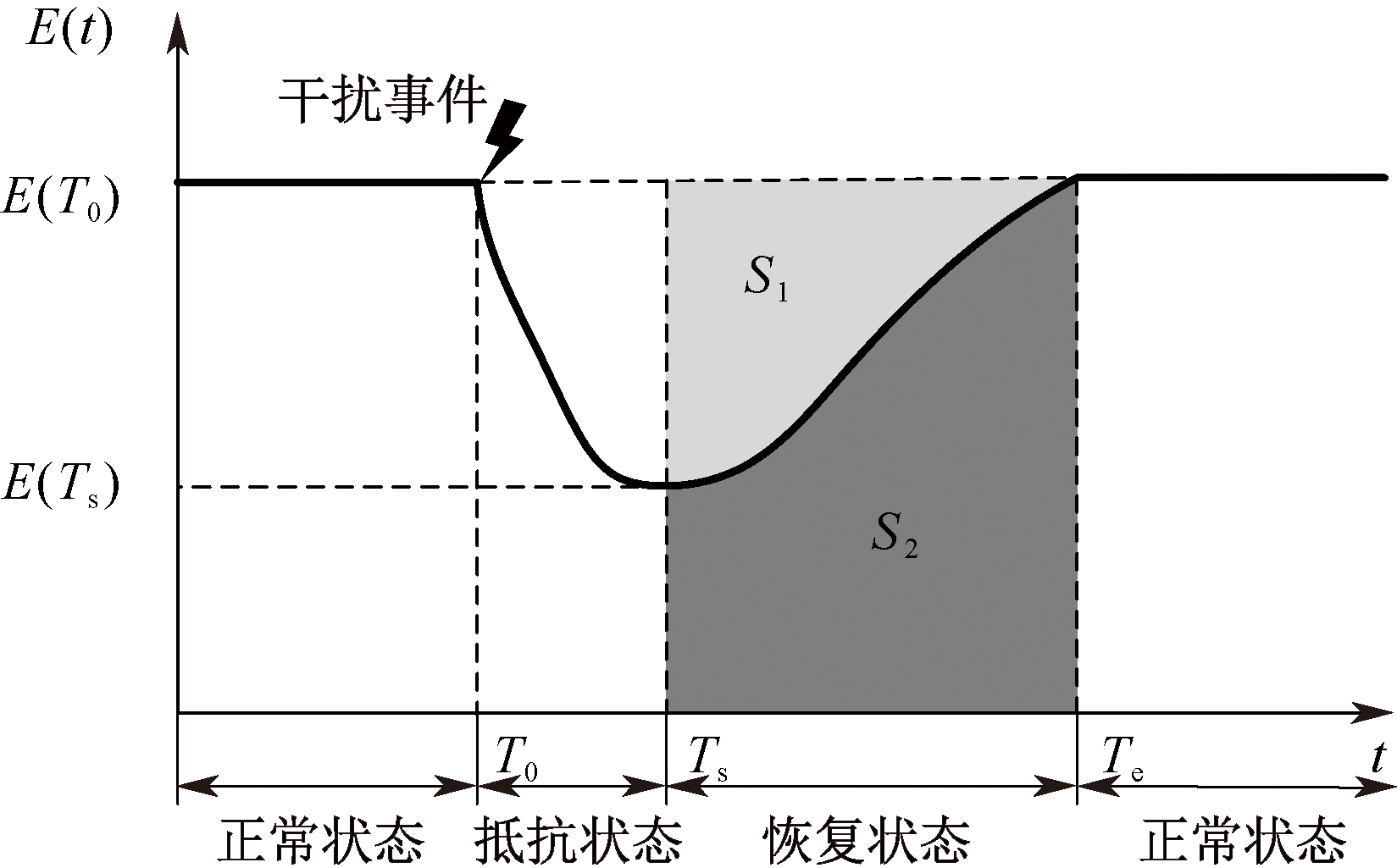
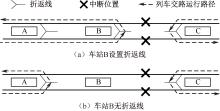
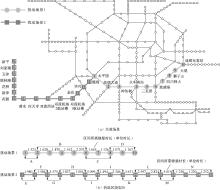
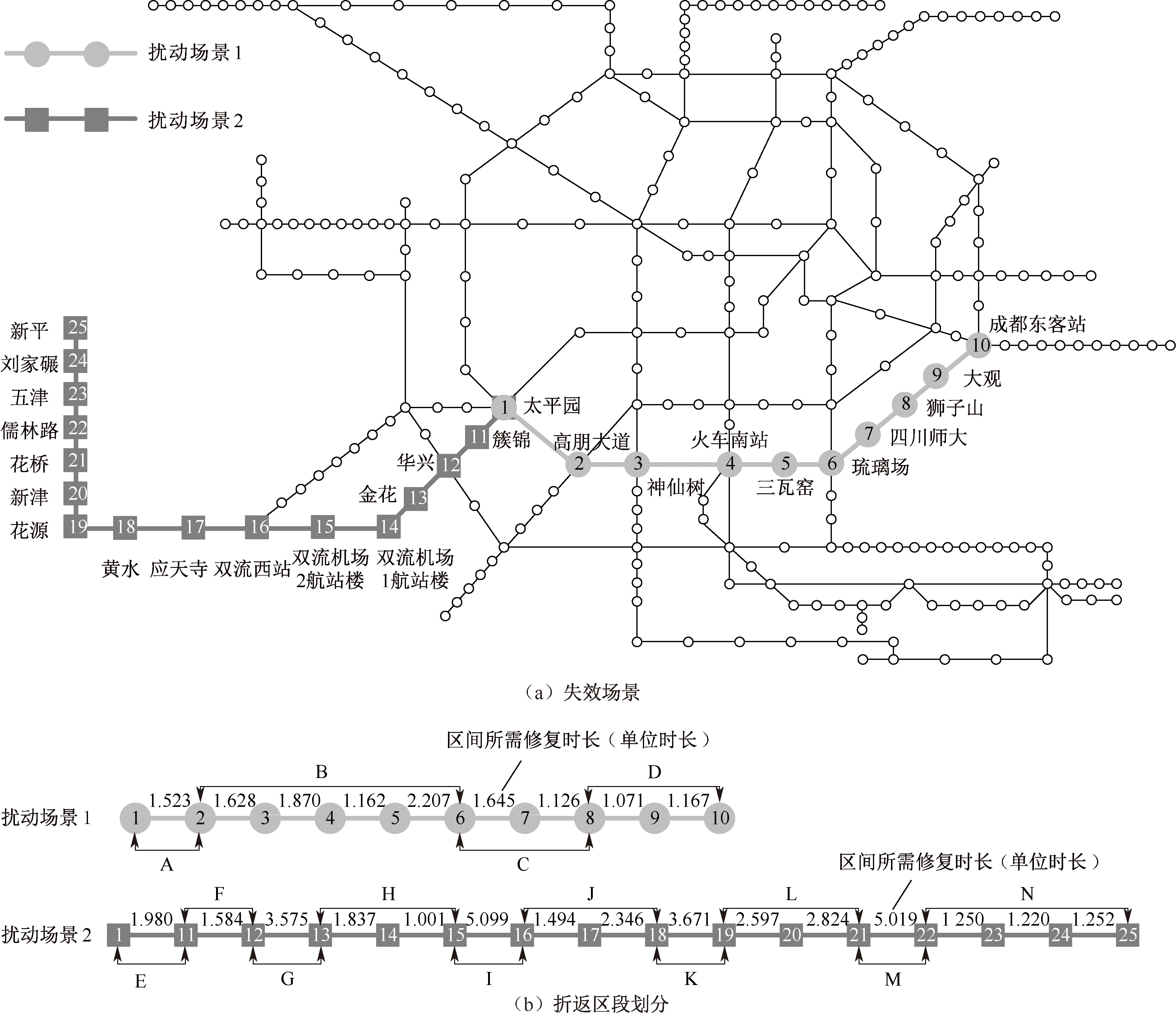
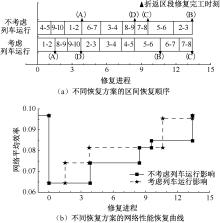
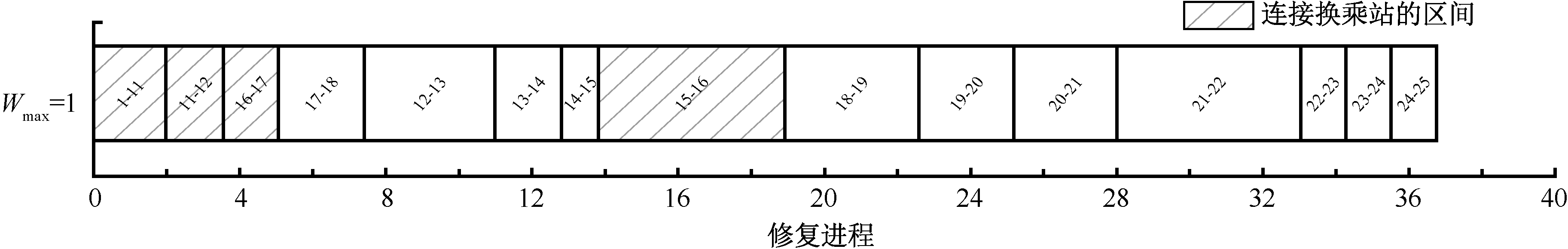
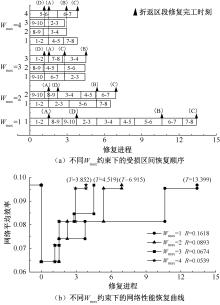
| [1] |
鞠艳妮, 李宗平, 陈宇帆, 等. 区域轨道交通系统节点重要度及故障恢复研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(2): 112-119.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.02.016
|
|
JU Yanni, LI Zongping, CHEN Yufan, et al. Study on node importance and failure recovery of regional rail transit system[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(2): 112-119.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.02.016
|
| [2] |
ZHANG Dongming, DU Fei, HANG Hongwei, et al. Resiliency assessment of urban rail transit networks: Shanghai metro as an example[J]. Safety Science, 2018, 106: 230-243.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2018.03.023
|
| [3] |
殷勇, 陈锦渠, 朱蔓, 等. 城市轨道交通站点失效修复策略[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2020, 55(4): 865-872.
|
|
YIN Yong, CHEN Jinqu, ZHU Man. Repair strategies for failure of urban rail transit stations[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(4): 865-872.
|
| [4] |
陈锦渠, 殷勇, 朱蔓. 城市轨道交通区间失效修复策略仿真研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2021, 38(8): 139-143.
|
|
CHEN Jinqu, YIN Yong, ZHU Man. Simulation of repairs strategy of urban rail transit link's failure[J]. Computer Simulation, 2021, 38(8): 139-143.
|
| [5] |
黄莺, 刘梦茹, 魏晋果, 等. 基于韧性曲线的城市地铁网络恢复策略研究[J]. 灾害学, 2021, 36(1): 32-36.
|
|
HUANG Ying, LIU Mengru, WEI Jinguo, et al. Research on urban metro network recovery strategy based on resilience curve[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2021, 36(1): 32-36.
|
| [6] |
张洁斐, 任刚, 马景峰, 等. 基于韧性评估的地铁网络修复时序决策方法[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 20(4):14-20.
|
|
ZHANG Jiefei, REN Gang, MA Jingfeng, et al. Resilience evaluation and failure recovery strategy of metro network considering bus connection scenario[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(4): 14-20.
|
| [7] |
吕彪, 管心怡, 高自强. 地铁网络服务韧性评估与最优恢复策略[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2021, 21(5): 198-205.
|
|
LYU Biao, GUAN Xinyi, GAO Ziqiang. Evaluation and optimal recovery strategy of metro network service resilience[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021, 21(5): 198-205.
|
| [8] |
SAADA Y, AYYUB B M, ZHANG Yanjie, et al. Resilience-Based strategies for topology enhancement and recovery of metrorail transit networks[J]. Asce-Asme Journal of Risk and Uncertainty in Engineering Systems, Part a: Civil Engineering, 2020, 6(2):DOI: 10.1061/AJRUA6.0001057.
doi: 10.1061/AJRUA6.0001057
|
| [9] |
ZHANG Jiefei, REN Gang, SONG Jianhua. Resilience-based restoration sequence optimization for metro networks: a case study in China[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2022, 2022: 1-22.
|
| [10] |
陈锦渠, 左彤, 朱蔓, 等. 城市轨道交通网络失效修复策略[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(1): 316-323.
|
|
CHEN Jinqu, ZUO Tong, ZHU Man, et al. Repair strategies for a damaged urban rail transit network[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(1): 316-323.
|
| [11] |
HIROKI N, MASAAKI F. Rethinking critical node problem for railway networks from the perspective of turn-back operation[J]. Physica a-Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2020, 558(1):DOI: 10.1016/j.physa.2020.124950.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2020.124950
|
| [12] |
LIU Jie, SCHONFELD P M, ZHAN Shuguang, et al. Reducing an urban rail transit network passenger-oriented vulnerability by adding turn-back tracks[J]. Transportmetrica B: Transport Dynamics, 2022, 10(1): 667-692.
doi: 10.1080/21680566.2022.2025953
|
| [13] |
杨景峰, 朱大鹏, 赵瑞琳. 城轨网络站点重要度评估与级联失效抗毁性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(8): 161-167.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.08.1148
|
|
YANG Jingfeng, ZHU Dapeng, ZHAO Ruilin. Evaluation of station importance and cascading failure resistance analysis of urban rail transit network[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(8): 161-167.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.08.1148
|
| [14] |
毕玮, 汤育春, 冒婷婷, 等. 城市基础设施系统韧性管理综述[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(6):14-28.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.06.003
|
|
BI Wei, TANG Yuchun, MAO Tingting, et al. Review on resilience management of urban infrastructure system[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(6):14-28.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.06.003
|
| [15] |
BRUNEAU M, CHANG S E, EGUCHI R T, et al. A framework to quantitatively assess and enhance the seismic resilience of communities[J]. Earthquake Spectra, 2003, 19(4): 733-752.
doi: 10.1193/1.1623497
|