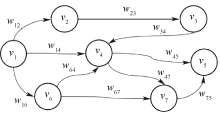
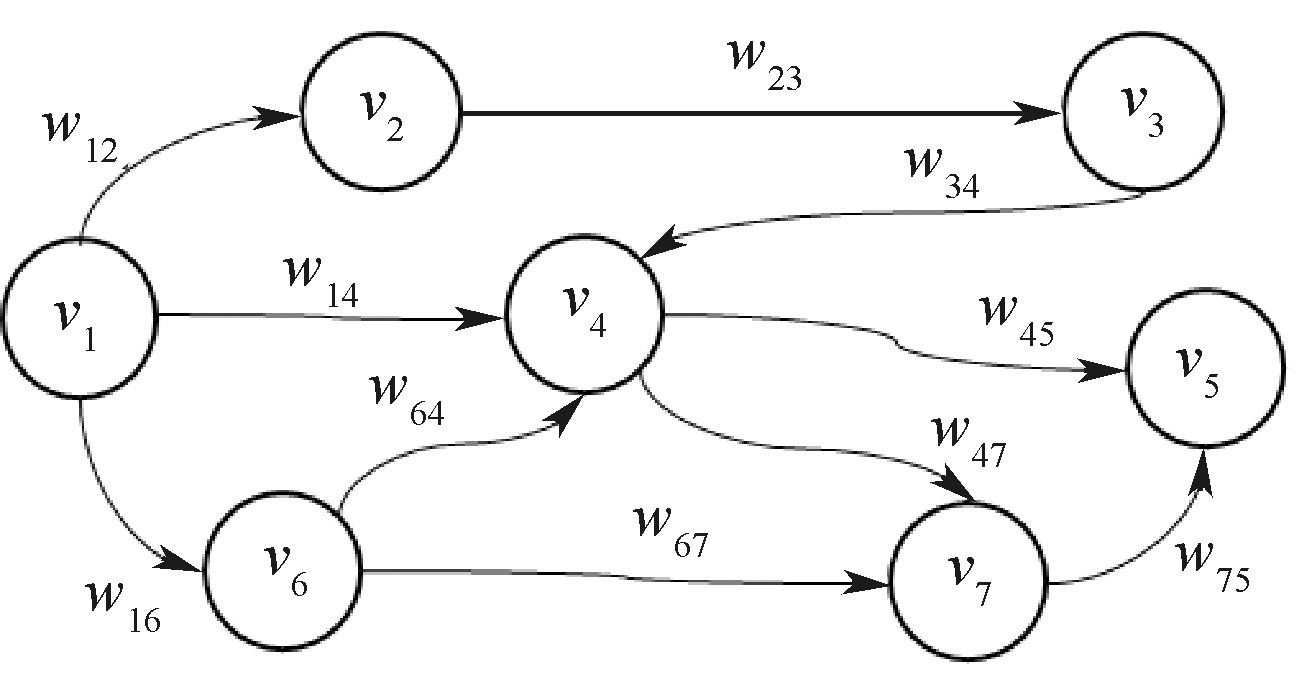
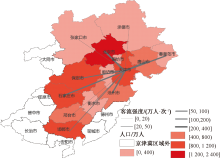
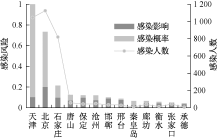
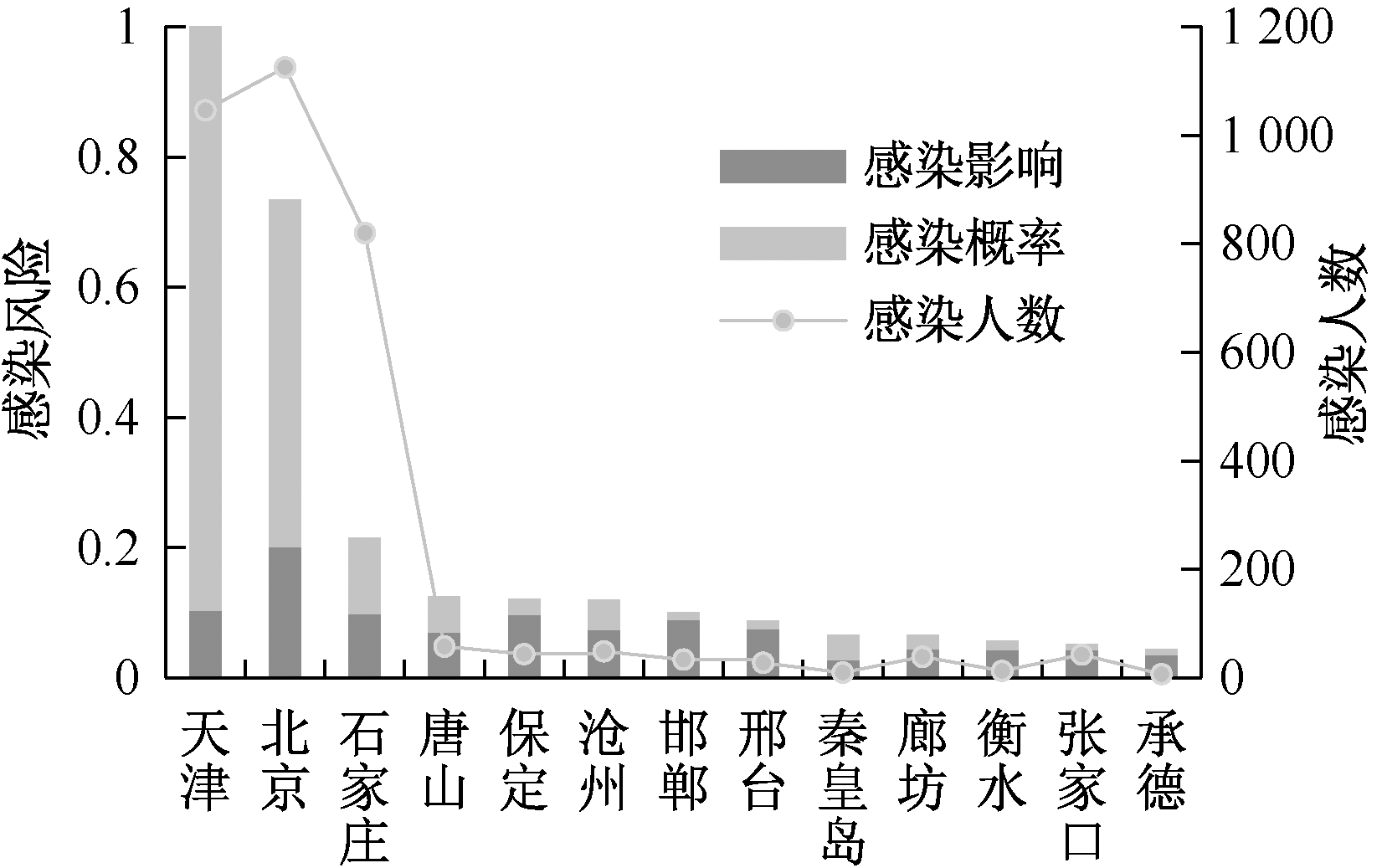
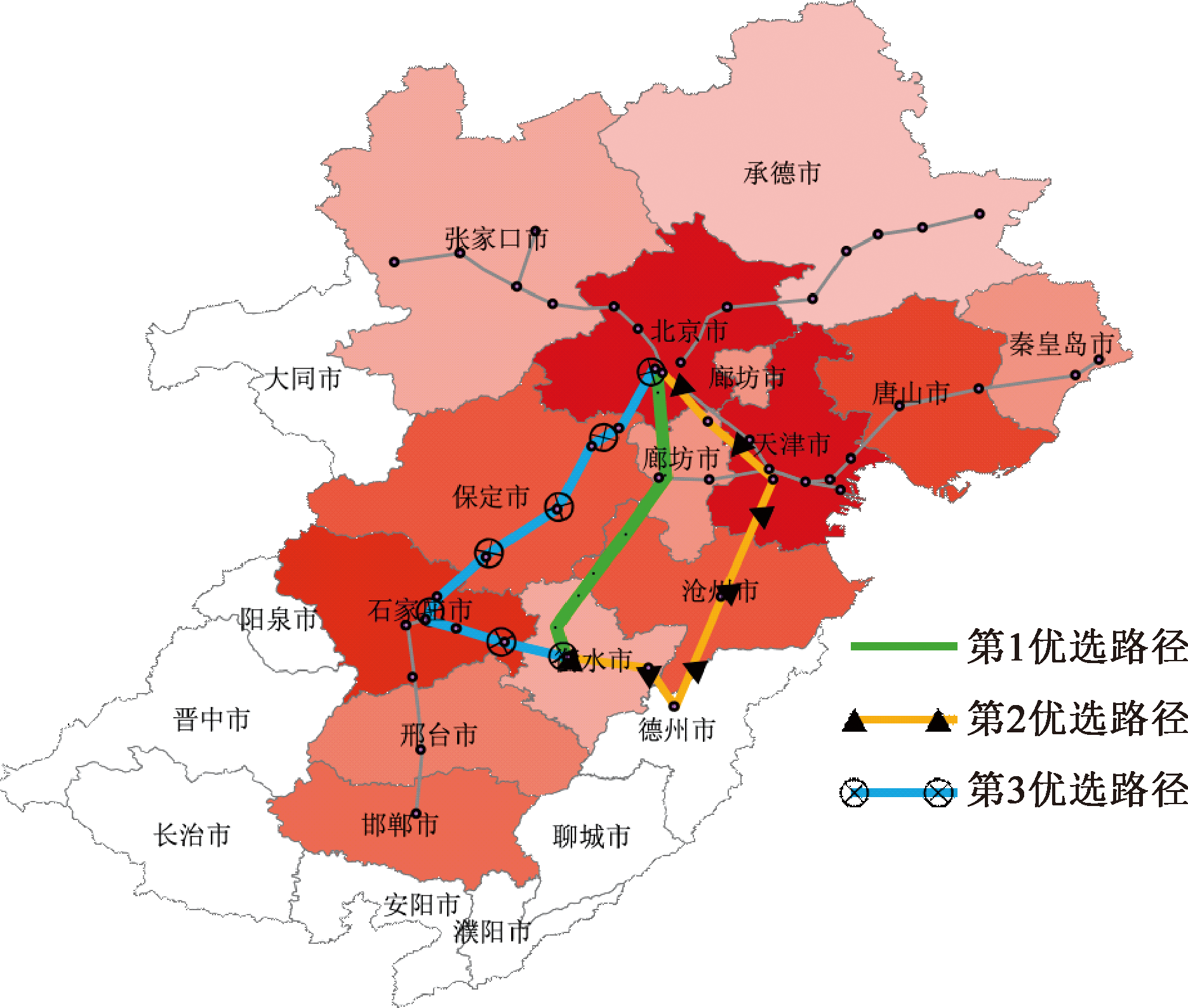
| [1] |
ELIAS W, ZATMEH-KANJ S. Extent to which COVID-19 will affect future use of the train in Israel[J]. Transport Policy, 2021, 110: 215-224.
doi: 10.1016/j.tranpol.2021.06.008
pmid: 34127894
|
| [2] |
ZHAO Pengjun, GAO Yukun. Public transit travel choice in the post COVID-19 pandemic era: an application of the extended theory of planned behavior[J]. Travel Behaviour and Society, 2022, 28: 181-195.
doi: 10.1016/j.tbs.2022.04.002
pmid: 35402163
|
| [3] |
BOGOCH I I, CREATORE M I, CETRON M S, et al. Assessment of the potential for international dissemination of Ebola virus via commercial air travel during the 2014 West African outbreak[J]. Lancet, 2015, 385(9962): 29-35.
doi: S0140-6736(14)61828-6
pmid: 25458732
|
| [4] |
JONES R M, MASAGO Y, BARTRAND T, et al. Characterizing the risk of infection from mycobacterium tuberculosis in commercial passenger aircraft using quantitative microbial risk assessment[J]. Risk Analysis, 2009, 29(3): 355-365.
doi: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.2008.01161.x
pmid: 19076326
|
| [5] |
ZHAO Shi, ZHUANG Zian, RAN Jinjun, et al. The association between domestic train transportation and novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak in China from 2019 to 2020: a data-driven correlational report[J]. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease, 2020, 33: DOI: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101568.
doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101568
|
| [6] |
WEI Ye, WANG Jiaoe, SONG Wei, et al. Spread of COVID-19 in China: analysis from a city-based epidemic and mobility model[J]. Cities, 2021, 110: DOI: 10.1016/j.cities.2020.103010.
doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2020.103010
|
| [7] |
ZHANG Linfeng, YANG Hangjun, WANG Kun, et al. Measuring imported case risk of COVID-19 from inbound international flights:a case study on China[J]. Journal of Air Transport Management, 2020, 89: DOI: 10.1016/j.jairtraman.2020.101918.
doi: 10.1016/j.jairtraman.2020.101918
|
| [8] |
林家泉, 孙凤山, 李亚冲. 客舱内呼吸道病原体传播机制与感染风险评估[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(2): 146-151.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.02.023
|
|
LIN Jiaquan, SUN Fengshan, LI Yachong. Transmission mechanism of respiratory pathogens in aircraft cabin and infection risk assessment[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(2): 146-151.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.02.023
|
| [9] |
RAVEAU S, GUO Zhan, MUNOZ J C, et al. A behavioural comparison of route choice on metro networks: time, transfers, crowding, topology and socio-demographics[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2014, 66: 185-195.
doi: 10.1016/j.tra.2014.05.010
|
| [10] |
JIANG Yu, CEDER A. Incorporating personalization and bounded rationality into stochastic transit assignment model[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2021, 127: DOI: 10.1016/j.trc.2021.103127.
doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2021.103127
|
| [11] |
ZHANG Yongsheng, YAO Enjian, ZHANG Junyi, et al. Estimating metro passengers' path choices by combining self-reported revealed preference and smart card data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 92: 76-89.
doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2018.04.019
|
| [12] |
ZENG Jin, JIN Xiaonan, DONG Chunjiao, et al. A transfer route choice model of railway passengers based on the maximum utility[C]. Proceeding in International Conference on Transportation and Development 2016:Projects and Practices for Prosperity, 2016: 422-433.
|
| [13] |
TIAN Zhiqiang, SUN Guofeng, CHEN Dingjun, et al. Method for determining the valid travel route of railways based on generalised cost under the syncretic railway network[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2020, 2020: DOI: 10.1155/2020/8287648.
doi: 10.1155/2020/8287648
|
| [14] |
赵宇刚, 洪雁, 杨华峰. 基于路网规划的铁路旅客出行路径选择研究[J]. 铁道经济研究, 2014 (1): 39-43.
|
|
ZHAO Yugang, HONG Yan, YANG Huafeng. Study on railway passenger travel route choice based on road network planning[J]. Railway Economics Research, 2014 (1): 39-43.
|
| [15] |
常志朋. 遵循底线思维的重大公共卫生风险评估模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(9): 171-178.
|
|
CHANG Zhipeng. Evaluation model of major public health risk based on bottom-line thinking[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(9): 171-178.
|
| [16] |
ISO31000:2009, Risk management-principles and guidelines[S].
|
| [17] |
LI Tao, RONG Lili, ZHANG Anming. Assessing regional risk of COVID-19 infection from Wuhan via high-speed rail[J]. Transport Policy, 2021, 106: 226-238.
doi: 10.1016/j.tranpol.2021.04.009
pmid: 33867701
|
| [18] |
夏晓梅, 范炳全. 基于广义费用的多用户公路网平衡配流模型[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2009, 9(3): 76-80.
|
|
XIA Xiaomei, FAN Bingquan. Multi-user highway network equilibrium model based on generalized cost[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2009, 9(3): 76-80.
|