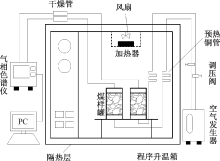
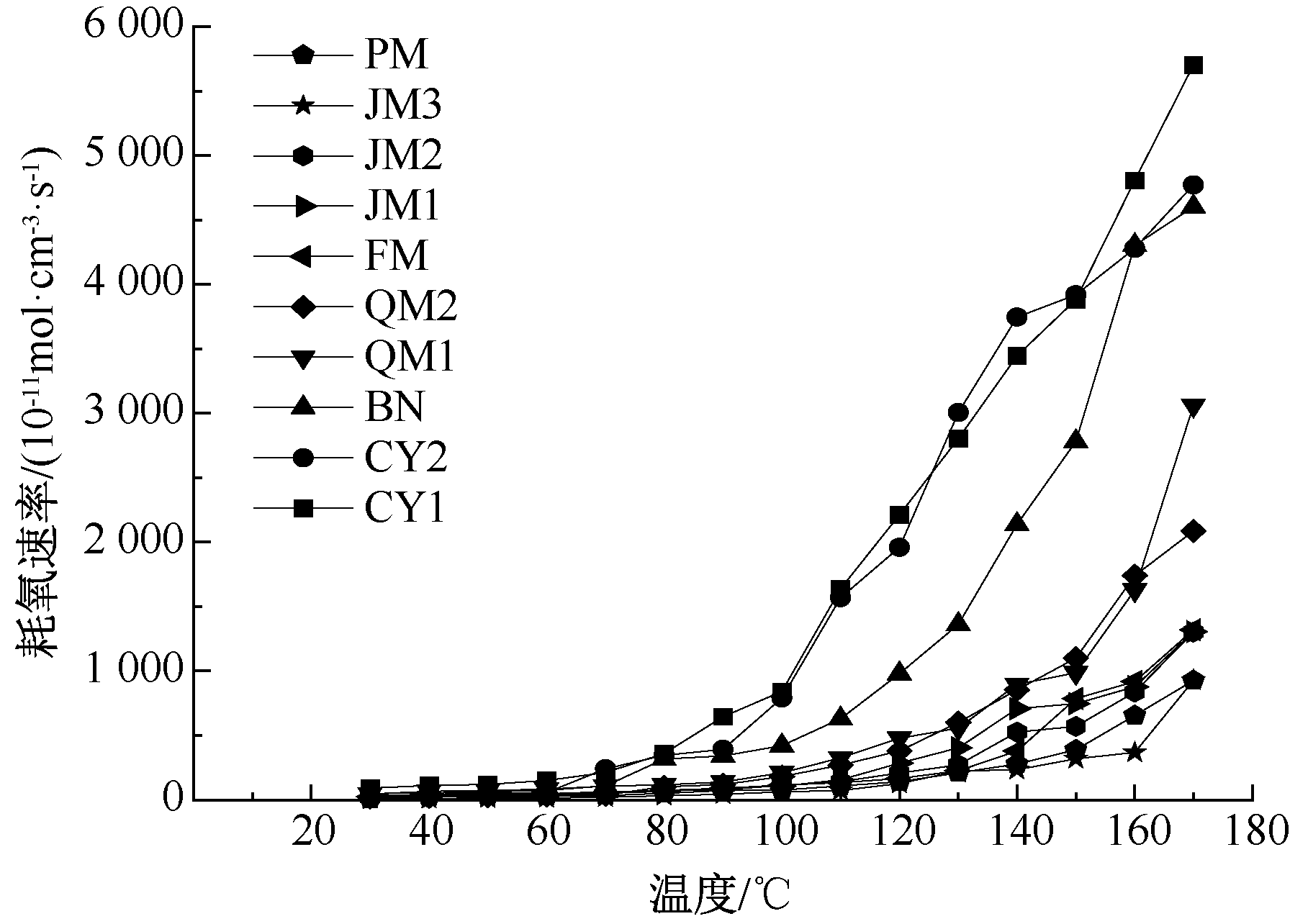
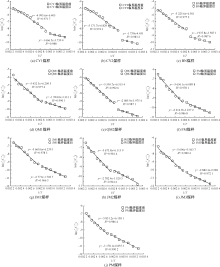
| [1] |
李敏, 林志军, 王德明, 等. 我国煤矿重特大火灾事故统计分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(1):115-121.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.01.0457
|
|
LI Min, LIN Zhijun, WANG Deming, et al. Statistical analysis of major coal mine fire accidents in China[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(1):115-121.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.01.0457
|
| [2] |
张江石, 李泳暾, 秦芳, 等. 煤矿事故因素的自组织映射分布研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(2):9-15.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.02.0949
|
|
ZHANG Jiangshi, LI Yongtun, QIN Fang, et al. Study on self-organizing mapping distribution of coal mine accident factors[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(2):9-15.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.02.0949
|
| [3] |
张玉涛, 李亚清, 邓军, 等. 煤炭自燃灾变过程突变特性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2015, 25(1):78-84.
|
|
ZHANG Yutao, LI Yaqing, DENG Jun, et al. Study on catastrophe characteristics of coal spontaneous combustion[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2015, 25(1):78-84.
|
| [4] |
ZHAO Jingyu, LU Shiping, SONG Jiajia, et al. Evaluation of oxygen concentration on low-temperature oxidation kinetics of long-flame coal[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2022, 79:DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2022.104841.
|
| [5] |
ONIFADE M, GENC B. Spontaneous combustion of coals and coal-shales[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2018, 28: DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2018.05.013.
|
| [6] |
YAN Hongwei, NIE Baisheng, KONG Fanbei, et al. Experimental investigation of coal particle size on the kinetic properties of coal oxidation and spontaneous combustion limit parameters[J]. Energy, 2023, 270: DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2023.126890.
|
| [7] |
贾廷贵, 强倩, 娄和壮, 等. 不同变质程度煤样氧化自燃热特性试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(10):62-67.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.009
|
|
JIA Tinggui, QIANG Qian, LOU Hezhuang, et al. Experimental study on thermal characteristics of coal samples with different metamorphism degree during spontaneous combustion[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(10):62-67.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.009
|
| [8] |
翟小伟, 成倬, 徐启飞, 等. 粒径对煤低温氧化阶段表观活化能影响试验研究[J]. 煤炭工程, 2020, 52(10):143-148.
|
|
ZHAI Xiaowei, CHENG Zhuo, XU Qifei, et al. Effect of particle size on apparent activation energy of coal in low temperature oxidation[J]. Coal Engineering, 2020, 52(10):143-148.
|
| [9] |
WANG Kai, HU Lihong, DENG Jun, et al. Multiscale thermal behavioral characterization of spontaneous combustion of pre-oxidized coal with different air exposure time[J]. Energy, 2023, 262: DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.125397.
|
| [10] |
张玉涛, 杨杰, 李亚清, 等. 煤自燃特征温度与微观结构变化及关联性分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2023, 51(4):80-87.
|
|
ZHANG Yutao, YANG Jie, LI Yaqing, et al. Correlation analysis between characteristic temperature and microstructure of coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(4):80-87.
|
| [11] |
邓军, 张宇轩, 赵婧昱, 等. 基于程序升温的不同粒径煤氧化活化能试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(1):214-219.
|
|
DENG Jun, ZHANG Yuxuan, ZHAO Jingyu, et al. Experiment study on oxidation and activated energy of different partical size coal based on programmed temperature rising[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(1):214-219.
|