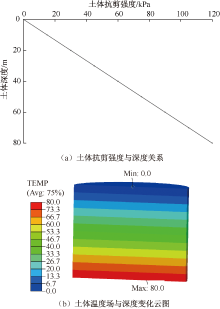
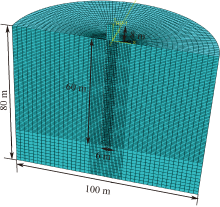
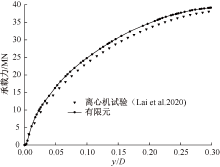
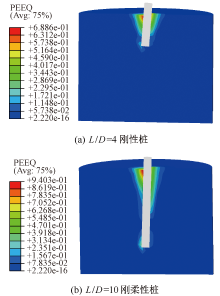
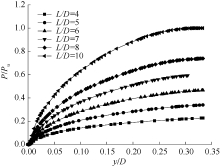
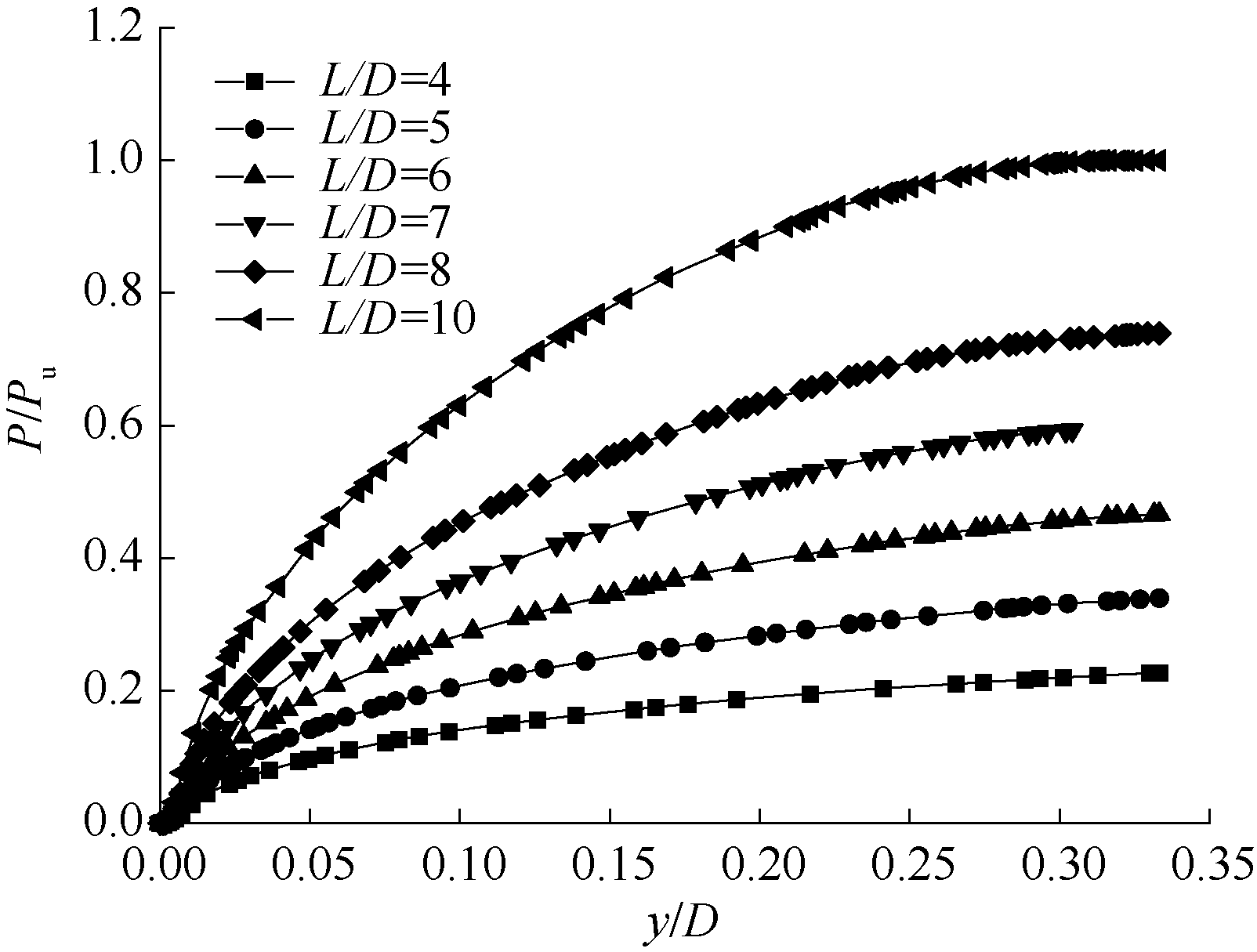
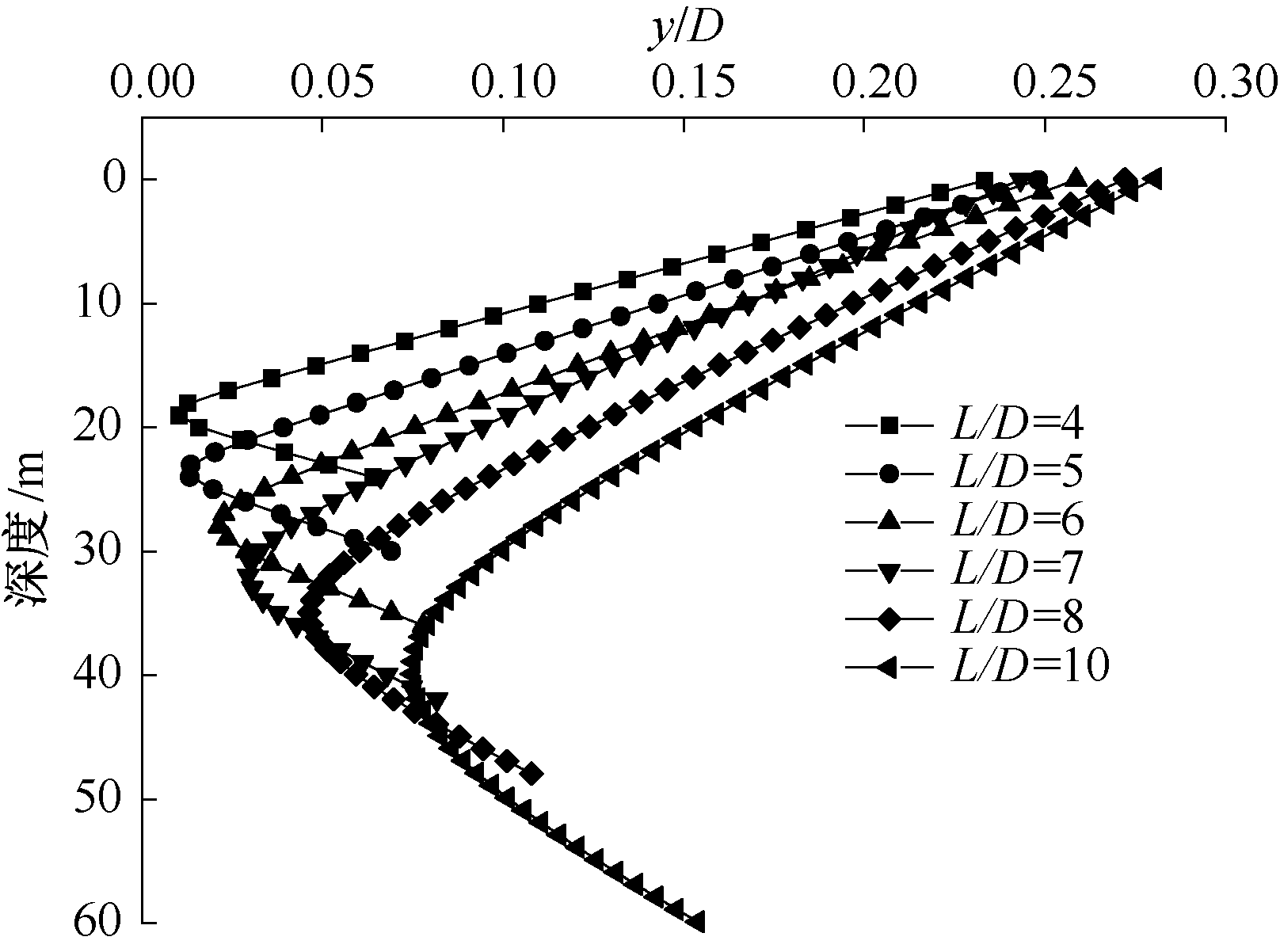
| [1] |
DÍAZ H, SOARES C G. Review of the current status, technology and future trends of offshore wind farms[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 209: DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107381.
|
| [2] |
孙艳国, 许成顺, 杜修力, 等. 海上风电复合基础承载性能对比研究[J]. 工程科学学报, 2022, 44(6):1098-1107.
|
|
SUN Yanguo, XU Chengshun, DU Xiuli, et al. Comparison of the bearing capacities of composite foundations for offshore wind turbines[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2022, 44(6): 1098-1107.
|
| [3] |
DNV G L. DNVGL-ST-0126-2016, Support structures for wind turbines[S].
|
| [4] |
朱照清, 龚维明, 戴国亮. 大直径钢管桩水平承载力现场试验研究[J]. 建筑科学, 2010, 26(9):36-39, 32.
|
|
ZHU Zhaoqing, GONG Weiming, DAI Guoliang. Field test research of horizontal bearing capacity of large diameter steel pipe pile[J]. Building Science, 2010, 26(9): 36-39, 32.
|
| [5] |
李超杰, 朱洪泽, 苏浩然, 等. 海上风电单桩基础轴向承载特性及软弱土层影响分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2023(2):185-191.
|
|
LI Chaojie, ZHU Hongze, SU Haoran, et al. Analysis of axial bearing characteristics of monopile foundation for offshore wind turbines and influence of soft soil layer[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2023(2): 185-191.
doi: 10.12396/znsd.222234
|
| [6] |
曹杨. 我国海洋石油安全事故分类与分级研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(3):18-24.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.03.003
|
|
CAO Yang. Research on classification and gradation of offshore oil accidents in China[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(3):18-24.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.03.003
|
| [7] |
常丁懿, 石娟, 瞿丽莉, 等. 智慧风电场应急管理体系及应用研究:5G技术赋能[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(9):57-67.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.09.0170
|
|
CHANG Dingyi, SHI Juan, QU Lili, et al. Smart emergency management system in wind farms and its application: 5G technology empowerment[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(9): 57-67.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.09.0170
|
| [8] |
刘惠. 复合荷载作用下的海上风机单桩基础承载特性研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2023.
|
|
LIU Hui. Study on bearing characteristics of monopile foundation of offshore wind turbine under composite loading[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2023.
|
| [9] |
WANG Xuefei, ZENG Xiangwu, LI Jiale. Assessment of bearing capacity of axially loaded monopiles based on centrifuge tests[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 167: 357-368.
doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.08.063
|
| [10] |
ZHANG Youhu, ANDERSEN K, TEDESCO G. Ultimate bearing capacity of laterally loaded piles in clay: some practical considerations[J]. Marine Structures, 2016, 50: 260-275.
doi: 10.1016/j.marstruc.2016.09.002
|
| [11] |
MURALI M, GRAJALES S, BEEMER R D, et al. Capacity of short piles and caissons in soft clay from geotechnical centrifuge tests[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2019, 145(10): DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.000209.
|
| [12] |
李容娜, 陈莉, 张欢, 等. 海上风机加翼单桩基础承载性能研究[J]. 河南科学, 2021, 39(6):948-953.
|
|
LI Rongna, CHEN Li, ZHANG Huan, et al. Bearing capacity of finned pile foundation for offshore wind turbine[J]. Henan Science, 2021, 39(6): 948-953.
|
| [13] |
郑川, 朱洪泽, 王皓, 等. 海上风机变径单桩基础竖向承载特性及变径参数影响研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2023(2):192-199.
|
|
ZHENG Chuan, ZHU Hongze, WANG Hao, et al. Research on vertical bearing characteristics and influence of correlation parameters of variable diameter monopile foundation for offshore wind turbine[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2023(2): 192-199.
doi: 10.12396/znsd.222382
|
| [14] |
张旭. 复合加载模式的单桩复合桶型基础极限承载特性和包络线分析[J]. 工业建筑, 2022, 52(5):187-193.
|
|
ZHANG Xu. Ultimate bearing characteristics and envelope analysis of the composite caisson foundation with a single pile in combined loading modes[J]. Industrial Construction, 2022, 52(5): 187-193.
|
| [15] |
黄周泉, 吴锋, 苏静波. 海上风电桩桶复合基础的竖向承载性能研究[J]. 水力发电, 2017, 43(12):83-86, 100.
|
|
HUANG Zhouquan, WU Feng, SU Jingbo. Vertical bearing capacity of pile-bucket composite foundation for offshore wind turbine[J]. Water Power, 2017, 43(12): 83-86, 100.
|
| [16] |
夏浩. 基于现场试验的单桩水平承载力分析[J]. 福建建设科技, 2021(2): 31-33.
|
|
XIA Hao. Analysis of lateral static load test on single pile in site[J]. Fujian Construction Science and Technology, 2021(2): 31-33.
|
| [17] |
BIENEN B, CASSIDY J M. Set up and resulting punch-through risk of jack-up spudcans during installation[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2013, 139(12): 2048-2059.
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000943
|
| [18] |
WANG Dong, BIENEN B. Numerical investigation of penetration of a large-diameter footing into normally consolidated kaolin clay with a consolidation phase[J]. GÉotechnique, 2016, 66(11): 947-952.
doi: 10.1680/jgeot.15.P.048
|
| [19] |
LAI Yongqing, WANG Lizhong, ZHANG Youhu, et al. Site-specific soil reaction model for monopiles in soft clay based on laboratory element stress-strain curves[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 220: DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.108437.
|
| [20] |
MARTIN C. Impact of centrifuge modelling on offshore foundation design[C]. International Symposium on Constitutive and Centrifuge Modelling, 2002: 135-153.
|
| [21] |
GAUDIN C, CASSIDY M J, BIENEN B, et al. Recent contributions of geotechnical centrifuge modelling to the understanding of jack-up spudcan behaviour[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2011, 38(7):900-914.
doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2010.12.001
|
| [22] |
赖踊卿. 软黏土地基海上风机大直径单桩水平受荷特性与分析模型[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2021.
|
|
LAI Yongqing. Modelling of lateral behaviour of large-diameter monopiles supporting offshore wind turbines in soft clay[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2021.
|
| [23] |
KLINKVORT R T, HEDEDAL O. Centrifuge modelling of offshore monopile foundation[C]. Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics II, 2010: 581-586.
|