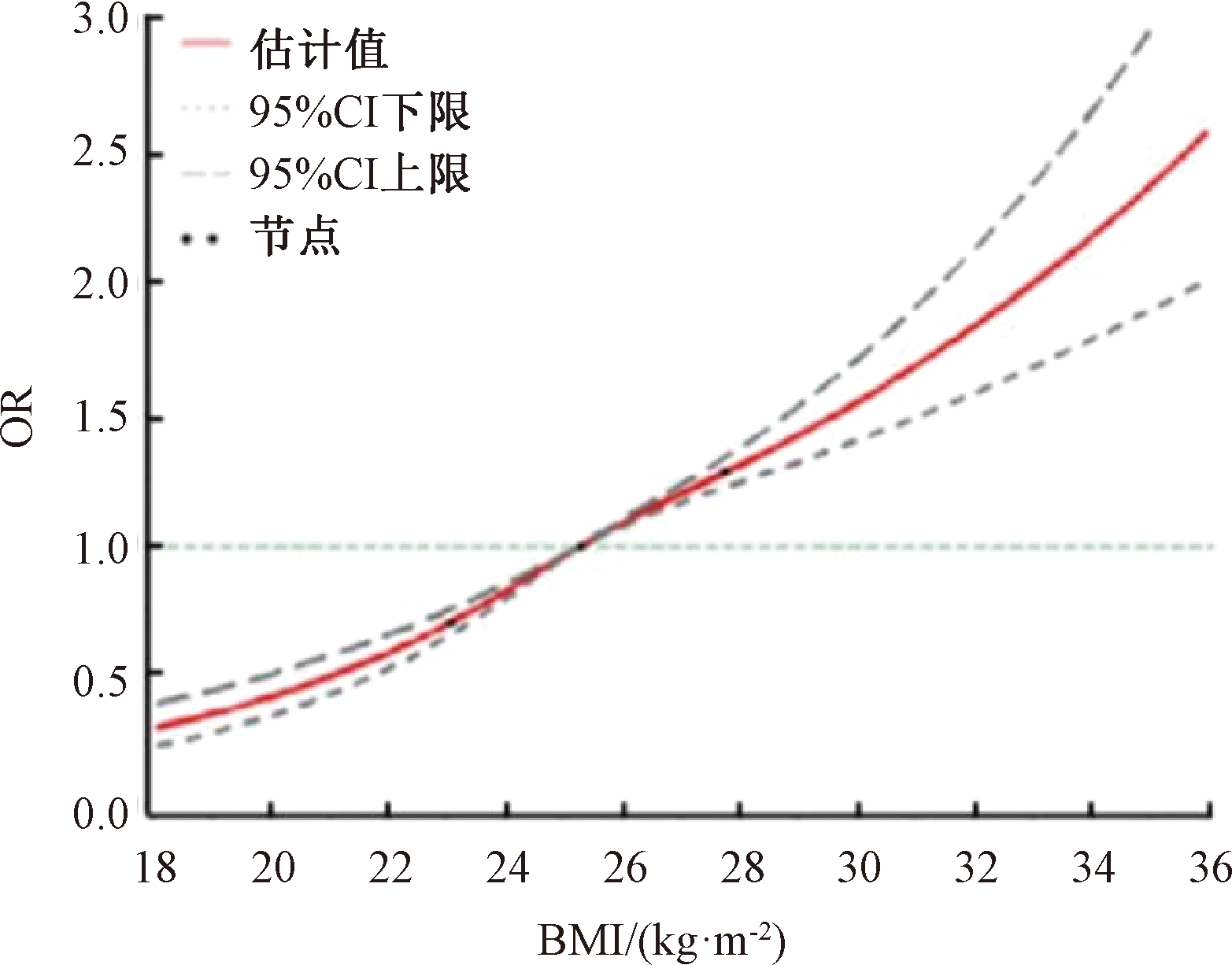
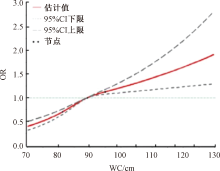
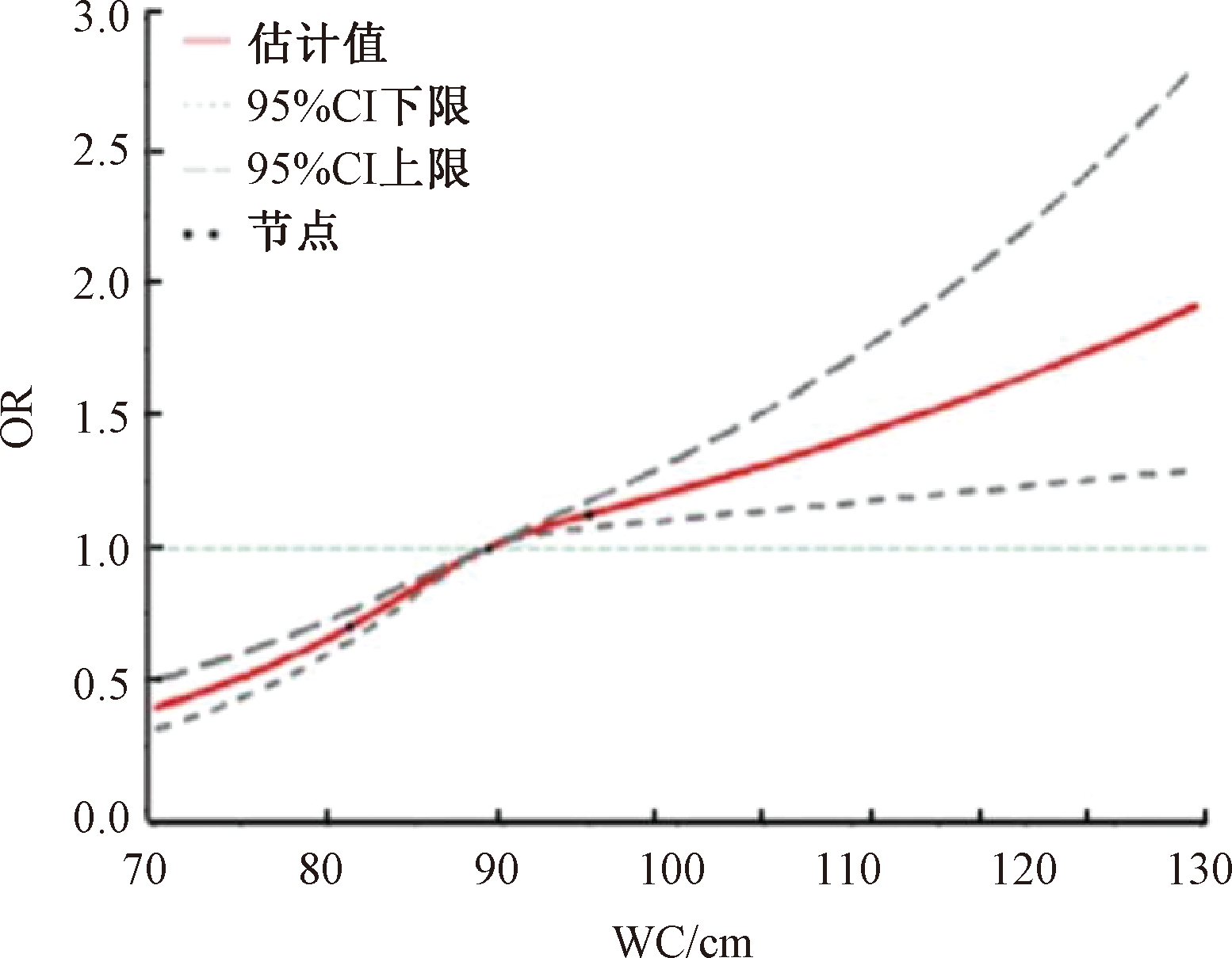
| [1] |
DALBETH N, MERRIMAN T R, STAMP L K. Gout[J]. The Lancet, 2016, 388(< W>10 055):2039-2052.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00346-9
|
| [2] |
VARGAS-SANTOS A B, NEOGI T. Management of gout and hyperuricemia in CKD[J]. American Journal of Kidney Diseases: the Official Journal of the National Kidney Foundation, 2017, 70(3):422-439.
|
| [3] |
KUO C F, GRAINGE M J, MALLEN C, et al. Rising burden of gout in the UK but continuing suboptimal management: a nationwide population study[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 2015, 74(4):661-667.
|
| [4] |
ZHANG Mei, ZHU Xiaoxia, WU Jing, et al. Prevalence of hyperuricemia among Chinese adults: findings from two nationally representative cross-sectional surveys in 2015-16 and 2018-19[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2021, 12:DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.791983.
|
| [5] |
张生奎, 王镇德, 杨荔, 等. 倒班作业与高尿酸血症的剂量反应关系研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(11):1123-1127.
|
|
ZHANG Shengkui, WANG Zhende, YANG Li, et al. Dose-response relationship between shift work and hyperuricemia[J]. Chinese Journal of Disease Control and Prevention, 2018, 22(11):1123-1127.
|
| [6] |
陈红, 侯聪美. 职业安全与健康管理现状、挑战与合作管理模式应用前景[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(5):159-165.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.05.027
|
|
CHEN Hong, HOU Congmei. Current situation of occupational safety and health management and challenge it faces and application prospect of cooperative management mode[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(5):159-165.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.05.027
|
| [7] |
岳鹏超, 赵威. 员工健康对安全生产影响及意外事件防范[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(增1):192-196.
|
|
YUE Pengchao, ZHAO Wei. Influence of employees' health on work safety and accident prevention[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(S1):192-196.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.S1.034
|
| [8] |
TIAN Simiao, LIU Yaozhu, FENG Ao, et al. Sex-specific differences in the association of metabolically healthy obesity with hyperuricemia and a network perspective in analyzing factors related to hyperuricemia[J]. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2020, 11:DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.573452.
|
| [9] |
XIE Junhui, ZHANG Shujun, YU Xuefeng, et al. Association between liver enzymes with metabolically unhealthy obese phenotype[J]. Lipids in Health and Disease, 2018, 17(1):DOI:10.1186/s12944-018-0847-9.
|
| [10] |
HONG Lin, DAI Guoyou, HUANG Song, et al. Association between serum uric acid and liver enzymes in adults aged 20 years and older in the United States: NHANES 2005-2012[J]. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2023, 12(2):DOI:10.3390/jcm12020648.
|
| [11] |
JOSÉ I L P, GALILEO E, ANTONIO G-C. Relationship of hyperuricemia with low density lipoprotein, liver function tests and markers of systemic inflammation in patients with morbid obesity[J]. Gaceta Medica de Mexico, 2017, 153(2):S42-S50.
|
| [12] |
CONSULTATION W E. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies[J]. The Lancet, 2004, 363(9403):DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(3)15268-3.
|
| [13] |
ALBERTI KGMM, ZIMMET P, SHAW J, et al. The metabolic syndrome: a new worldwide definition[J]. The Lancet, 2005, 366(9 491):DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(5)67402-8.
|
| [14] |
ALBERTI K, ECKEL R H, GRUNDY S M, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention[J]. Circulation, 2009, 120(16):1640-1645.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192644
|
| [15] |
REY-LÓPEZ J P, REZENDE L F D, PASTOR-VALERO M, et al. The prevalence of metabolically healthy obesity: a systematic review and critical evaluation of the definitions used[J]. Obesity Reviews, 2014, 15(10):781-790.
doi: 10.1111/obr.2014.15.issue-10
|
| [16] |
FEIG D I, KANG D-H, JOHNSON R J. Uric acid and cardiovascular risk[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2008, 359(17):1811-1821.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0800885
pmid: 18946066
|
| [17] |
KWO P Y, COHEN S M, LIM J K. ACG clinical guideline: evaluation of abnormal liver chemistries[J]. The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 2017, 112(1):18-35.
doi: 10.1038/ajg.2016.517
|
| [18] |
STADLER M, BOLLOW E, FRITSCH M, et al. Prevalence of elevated liver enzymes in adults with type 1 diabetes: a multicentre analysis of the German/Austrian DPV database[J]. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism, 2017, 19(8):1171-1178.
|
| [19] |
YOUNOSSI Z M, WONG G, ANSTEE Q M, et al. The global burden of liver disease[J]. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2023, 21(8):1978-1991.
doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.015
|
| [20] |
YU Jia, SUN Hongyan, ZHU Jinhua, et al. Asymptomatic hyperuricemia and metabolically unhealthy obesity: a cross-sectional analysis in the Tianning cohort[J]. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity, 2021, 14:1367-1374.
doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S301363
|
| [21] |
GUERRERO-ROMERO F, SIMENTAL-MENDÍA L E. Hyperuricemia is associated with the presence of metabolically obese normal-weight and metabolically healthy obese phenotypes[J]. Endocrine Research, 2022, 47(3/4):124-129.
doi: 10.1080/07435800.2022.2108049
|
| [22] |
MOLLA N H, KATHAK R R, SUMON A H, et al. Assessment of the relationship between serum uric acid levels and liver enzymes activity in Bangladeshi adults[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1):DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-99623-z.
|
| [23] |
LI Changgui, HSIEH Mingchia, CHANG Shunjen. Metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and hyperuricemia[J]. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 2013, 25(2):210-216.
doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32835d951e
pmid: 23370374
|
| [24] |
MCCORMICK N, O'CONNOR M J, YOKOSE C, et al. Assessing the causal relationships between insulin resistance and hyperuricemia and gout using bidirectional mendelian randomization[J]. Arthritis & Rheumatology, 2021, 73(11):2096-2104.
|
| [25] |
LIU Chenbing, SHAO Min, LU Ling, et al. Obesity, insulin resistance and their interaction on liver enzymes[J]. PloS One, 2021, 16(4):DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249299.
|
| [26] |
SMITH G I, MITTENDORFER B, KLEIN S. Metabolically healthy obesity: facts and fantasies[J]. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2019, 129(10):3978-3989.
doi: 10.1172/JCI129186
|
| [27] |
BARAZZONI R, CAPPELLARI G G, RAGNI M, et al. An overview of fundamental alterations[J]. Eating and Weight Disorders, 2018, 23(2):149-157.
doi: 10.1007/s40519-018-0481-6
|
| [28] |
UETANI E, TABARA Y, IGASE M, et al. Liver enzyme and adipocytokine profiles are synergistically associated with insulin resistance: the J-SHIPP study[J]. Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis, 2012, 19(6):577-584.
doi: 10.5551/jat.11924
pmid: 22653114
|
| [29] |
KAMADA Y, NAKAMURA T, FUNAHASHI T, et al. Visceral obesity and hypoadiponectinemia are significant determinants of hepatic dysfunction: an epidemiologic study of 3 827 Japanese subjects[J]. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, 2009, 43(10):995-1000.
doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181962de8
|
| [30] |
APPLETON S L, SEABORN C J, VISVANATHAN R, et al. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease outcomes in the metabolically healthy obese phenotype: a cohort study[J]. Diabetes Care, 2013, 36(8):2388-2394.
doi: 10.2337/dc12-1971
pmid: 23491523
|
| [31] |
DONG Xiaokang, LI Yuqian, ZHANG Lulu, et al. Independent and interactive effect of sitting time and physical activity on prevalence of hyperuricemia: the Henan rural cohort study[J]. Arthritis Research & Therapy, 2021, 23(1):DOI:10.1186/s13075-020-02385-8.
|