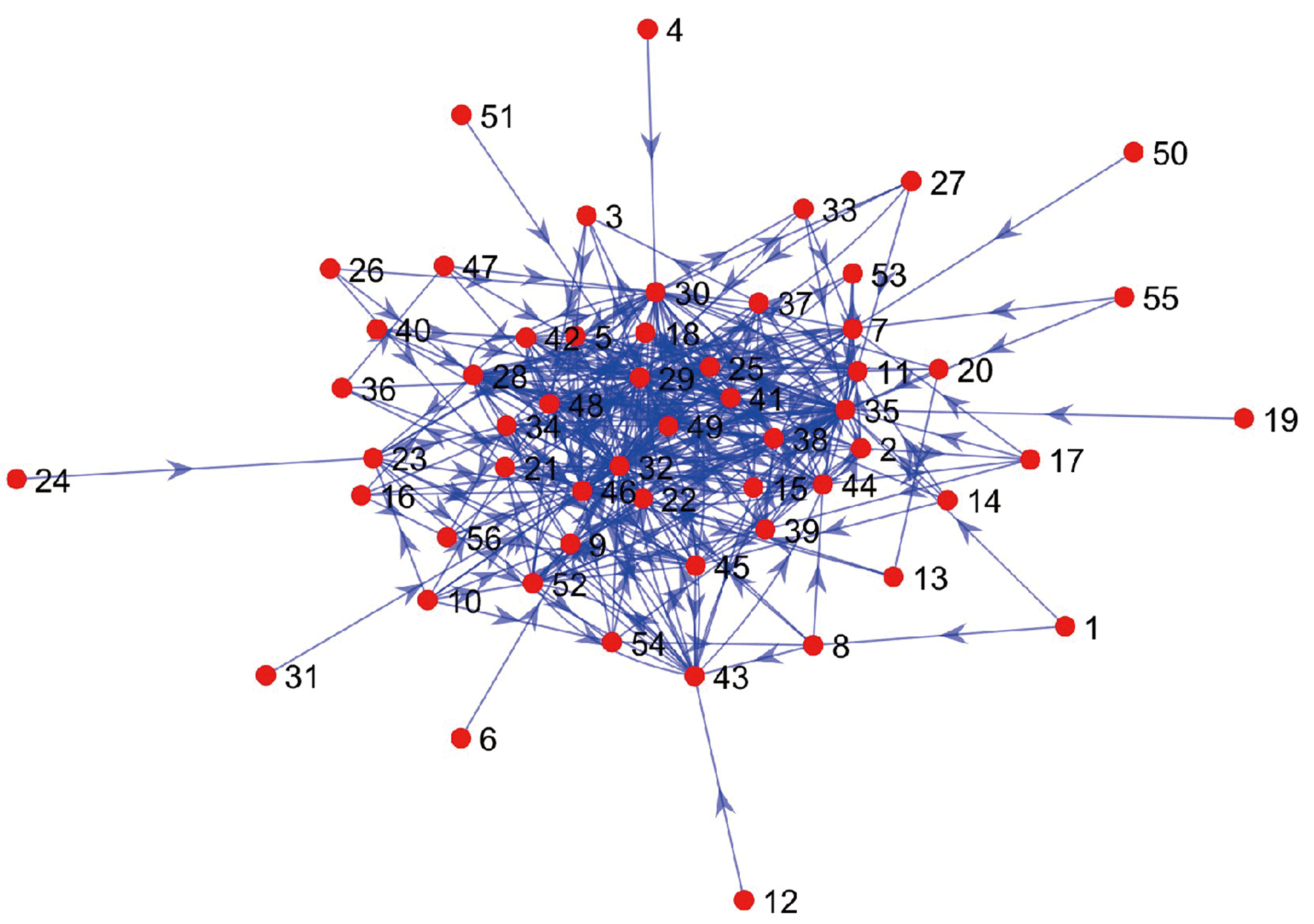
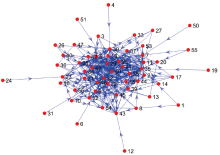
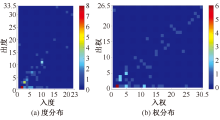
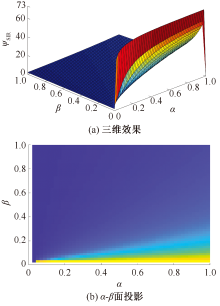
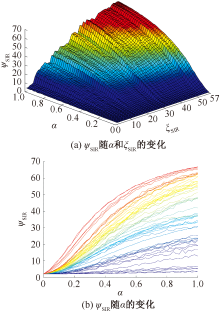
| [1] |
CHAI Tian, HAN Xue. A study on ship collision conflict prediction in the Taiwan strait using the EMD-based LSSVM method[J]. PloS One, 2021, 16(5): DOI: 0.1371/journal.pone.0250948.
|
| [2] |
刘正江, 吴兆麟, 邹开其, 等. 基于专家问卷调查的船舶碰撞事故中人的因素的识别[J]. 大连海事大学学报, 2003, 29(增 1):43-47.
|
|
LIU Zhengjiang, WU Zhaolin, ZOU Kaiqi, et al. Identifying the human factors in ship collisions based on the investigation by questionnaires[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2003, 29(S1): 43-47.
|
| [3] |
李娜. Logistic回归模型在船舶碰撞受损因素分析的应用[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2017, 39(22): 141-143.
|
|
LI Na. Application of Logistic regression model in damage analysis of ship collision[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2017, 39(22): 141-143.
|
| [4] |
刘俊峰, 胡志强. 船舶碰撞损伤风险分析方法及应用[J]. 船舶工程, 2017, 39(11): 23-29.
|
|
LIU Junfeng, HU Zhiqiang. A method for ship collision damage risk analysis and its application[J]. Ship Engineering, 2017, 39(11): 23-29.
|
| [5] |
AVLIJAŠ G, RADUNOVIĆ M. Application of event chain methodology in schedule risk analysis[J]. European Project Management Journal, 2019, 9(2): 26-34.
|
| [6] |
UĞURLU Ö, KÖSE E, YILDIRIM U, et al. Marine accident analysis for collision and grounding in oil tanker using FTA method[J]. Maritime Policy & Management, 2015, 42(2): 163-185.
|
| [7] |
RAIYAN A, DAS S, ISLAM M R. Event tree analysis of marine accidents in Bangladesh[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2017, 194: 276-283.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.10.006
|
| [8] |
MACRAE C. Human factors at sea: common patterns of error in groundings and collisions[J]. Maritime Policy & Management, 2009, 36(1): 21-38.
|
| [9] |
司东森, 张英俊, 郎坤, 等. 基于改进BN的集装箱船舶碰撞事故致因分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(10):31-37.
|
|
SI Dongsen, ZHANG Yingjun, LANG Kun. Causation analysis of container ship collision accidents based on improved BN[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(10): 31-37.
|
| [10] |
杨应柳, 晋良海, 邵波, 等. 基于复杂网络的煤矿火灾爆炸致因研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(1):145-151.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.01.0601
|
|
YANG Yingliu, JIN Lianghai, SHAO Bo, et al. Research on causes of coal mine fire and explosion based on complex network[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(1):145-151.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.01.0601
|
| [11] |
KITSAK M, GALLOS L K, HAVLIN S, et al. Identification of influential spreaders in complex networks[J]. Nature Physics, 2010, 6(11): 888-893.
|
| [12] |
MA Xiaoxue, DENG Wanyi, QIAO Weiliang, et al. A novel methodology concentrating on risk propagation to conduct a risk analysis based on a directed complex network[J]. Risk Analysis, 2022, 42(12): 2800-2822.
doi: 10.1111/risa.13870
pmid: 35028963
|
| [13] |
GARAS A, SCHWEITZER F, HAVLIN S. A k-shell decomposition method for weighted networks[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2012, 14(8): DOI: 10.1088/1367-2630/14/8/083030.
|
| [14] |
HOLLNAGEL E. Safety-II in practice: developing the resilience potentials[M]. London: Routledge, 2018:4-5.
|