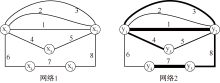
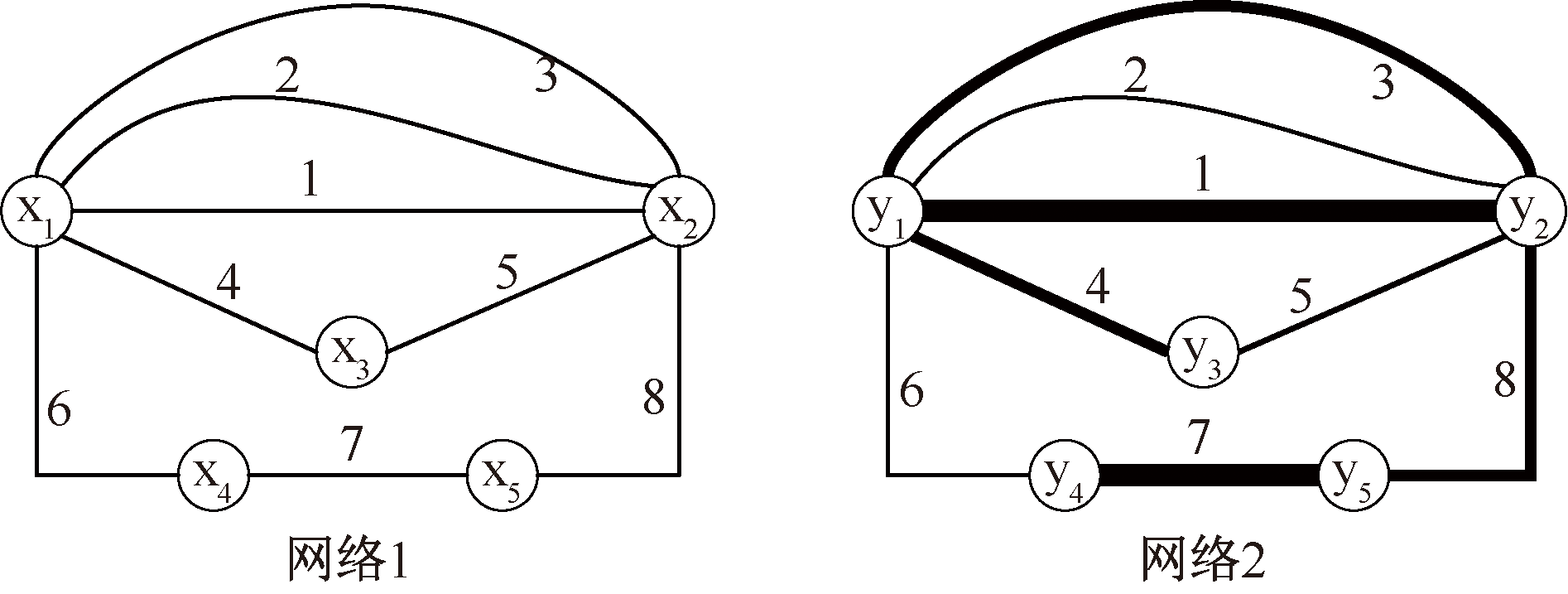
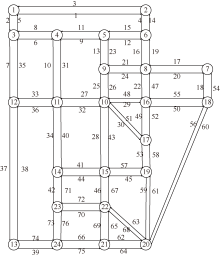
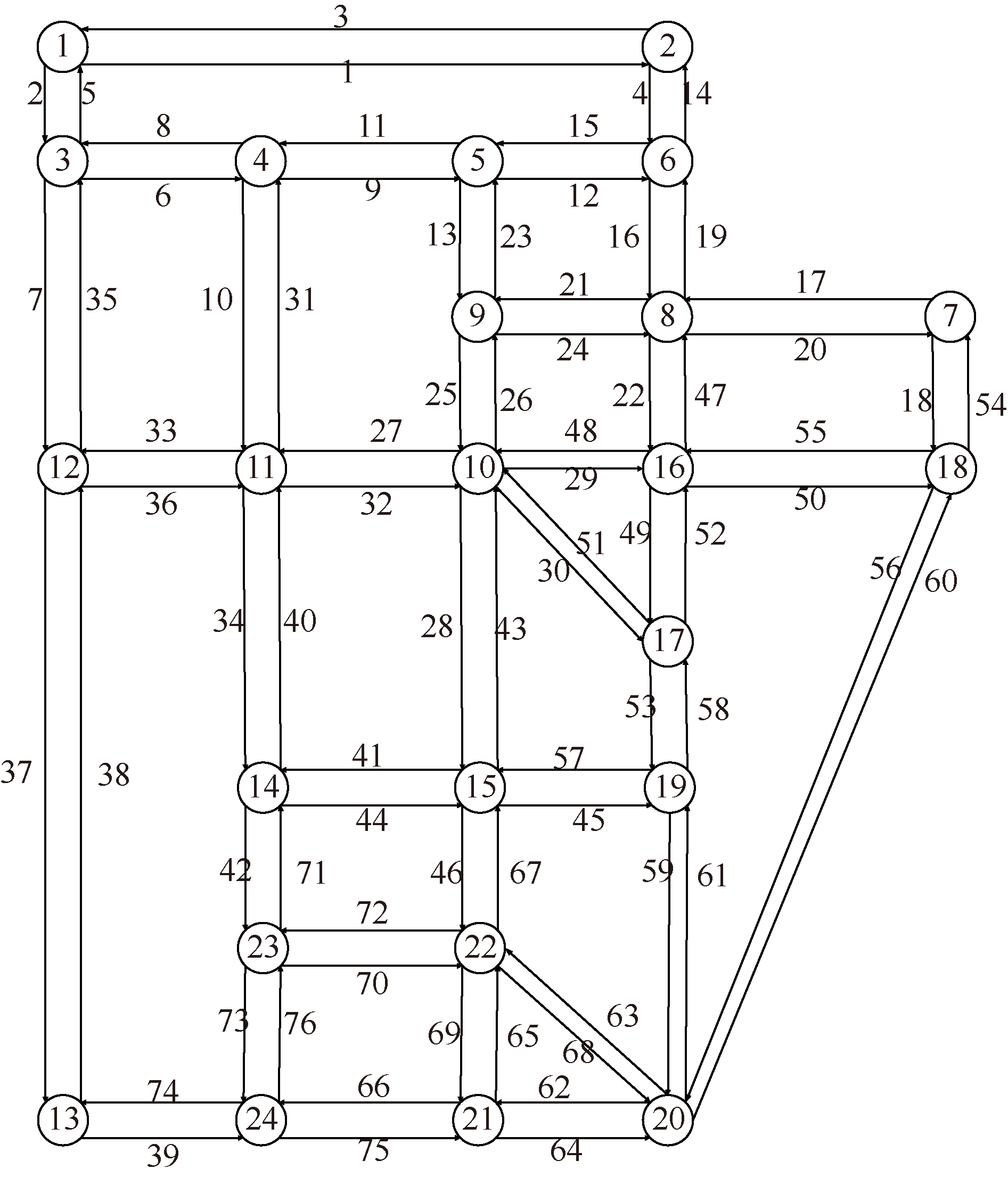
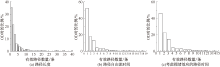
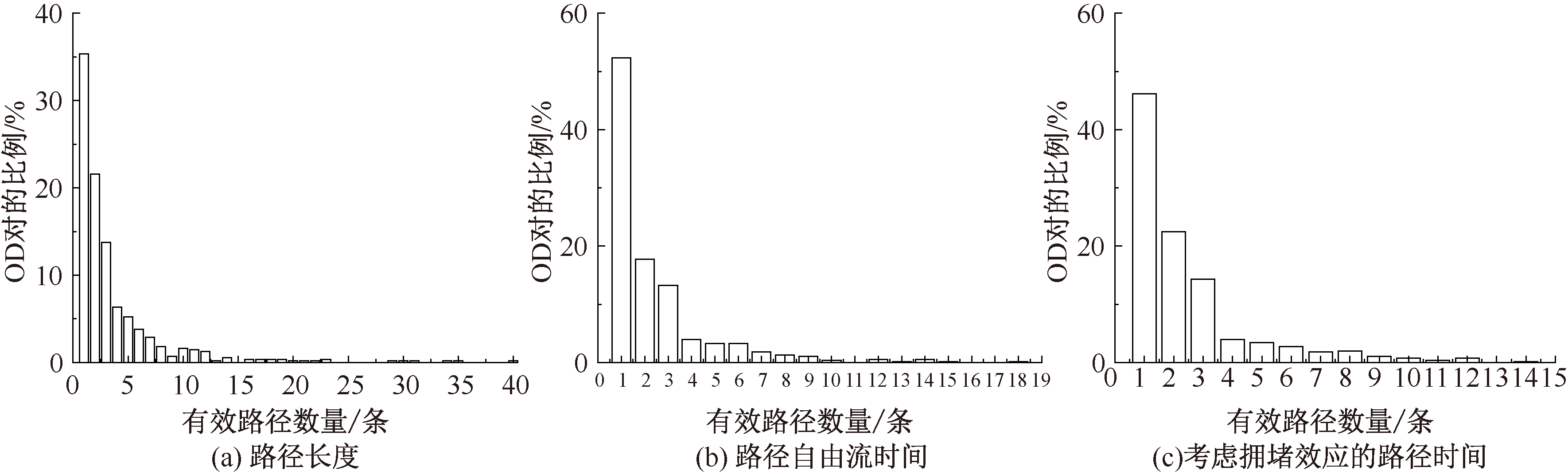
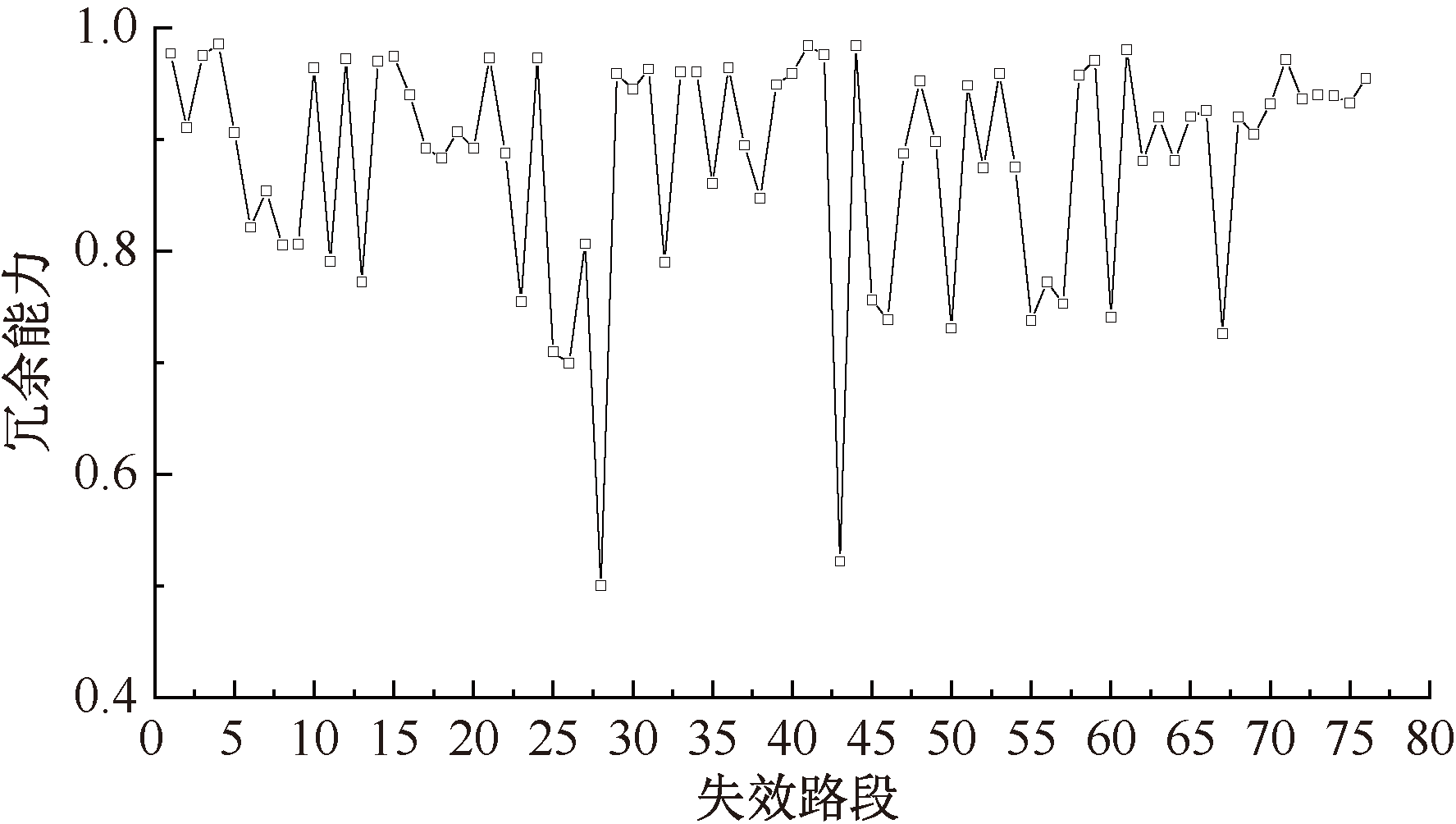
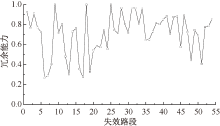
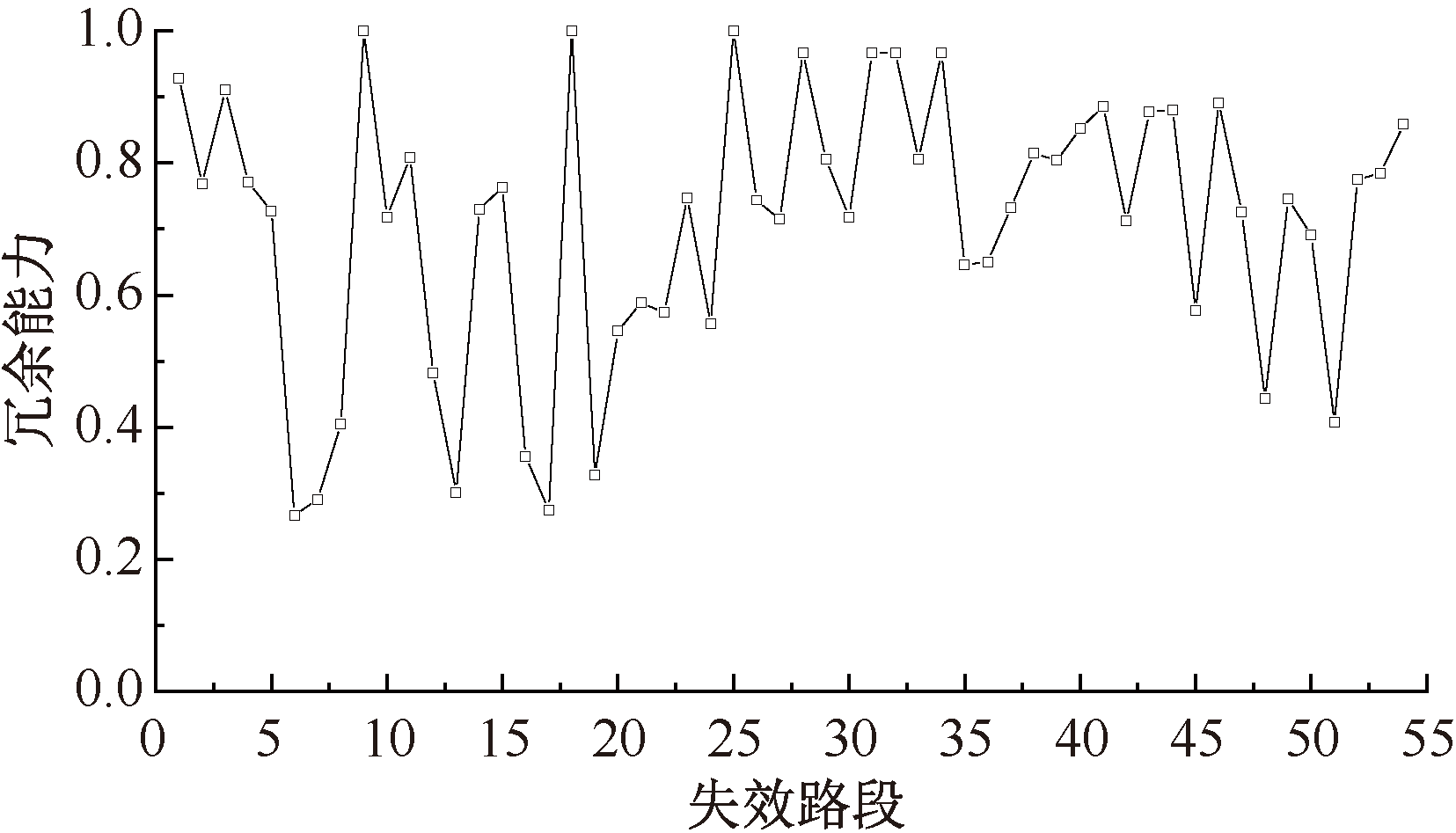
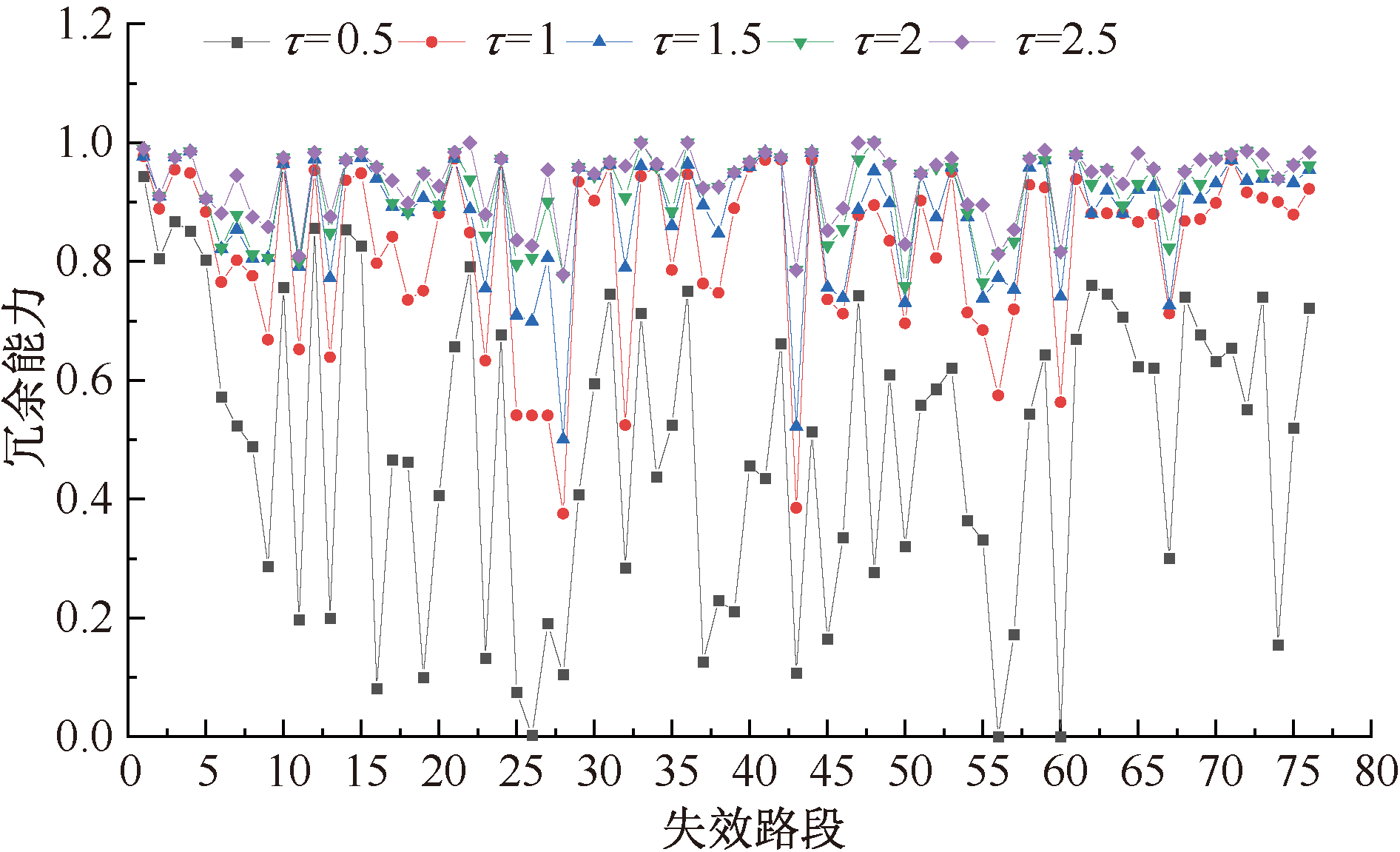
| [1] |
BERDICA K. An introduction to road vulnerability: what has been done, is done and should be done[J]. Transport Policy, 2002, 9(2): 117-127.
|
| [2] |
JENELIUS E. Redundancy importance: links as rerouting alternatives during road network disruptions[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2010, 3: 129-137.
|
| [3] |
JENELIUS E, CATS O. The value of new public transport links for network robustness and redundancy[J]. Transportmetrica A: Transport Science, 2015, 11(9): 819-835.
|
| [4] |
EL-RASHIDY R A, GRANT-MULLER S. The evaluation of redundancy for road traffic networks[J]. Transport, 2016, 31(4): 427-439.
|
| [5] |
XU Xiangdong, CHEN A, JANSUWAN S, et al. Transportation network redundancy: complementary measures and computational methods[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2018, 114: 68-85.
|
| [6] |
SHRESTHA J K, PUDASAINI P, MUSSONE L. Rural road network performance and pre-disaster planning: an assessment methodology considering redundancy[J]. Transportation Planning and Technology, 2021, 44(7): 726-743.
|
| [7] |
WANG Zijian, XU Xiangdong. Assessing route redundancy of freeway networks in Mega-city regions[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2022, 106: DOI: 10.1016/j.trd.2022.103275.
|
| [8] |
XU Xiangdong, CHEN A, XU Guangming, et al. Enhancing network resilience by adding redundancy to road networks[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2021, 154: DOI: 10.1016/j.tre.2021.102448.
|
| [9] |
CHAN H Y, CHEN A, LI Guoyuan, et al. Evaluating the value of new metro lines using route diversity measures: the case of Hong Kong's mass transit railway system[J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 2021, 91: DOI: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2020.102945.
|
| [10] |
XU Xiangdong, PU Yichao. Route redundancy-based approach to identify the critical stations in metro networks: a mean-excess probability measure[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2020, 204: DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2020.107204.
|
| [11] |
崔欣, 路庆昌, 李建宇. 基于网络冗余性的城市轨道交通关键站点识别[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(12): 158-164.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.12.0274
|
|
CUI Xin, LU Qingchang, LI Jianyu. Key station identification of urban rail transit based on network redundancy[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(12): 158-164.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.12.0274
|
| [12] |
LU Qingchang, ZHANG Lei, XU Pengcheng, et al. Modeling network vulnerability of urban rail transit under cascading failures: a coupled map lattices approach[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2022, 221: DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2022.108320.
|
| [13] |
马敏, 胡大伟, 刘杰, 等. 基于客流加权的城市轨道交通网络抗毁性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(12): 141-149.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.12.0203
|
|
MA Min, HU Dawei, LIU Jie, et al. Invulnerability analysis of urban rail transit network based on weighted passenger flow[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(12): 141-149.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.12.0203
|
| [14] |
ZHAO Rong, XU Xiangdong, CHEN A. Alternative method of counting the number of efficient paths in a transportation network[J]. Transportmetrica A: Transport Science, 2022, 18(3): 1 207-1 233.
|
| [15] |
林思乡. 基于路段关键度的除雪车辆路径规划问题研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010.
|
|
LIN Sixiang. Research on snow-removal vehicle routing problem based on criticality of road segment[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010.
|