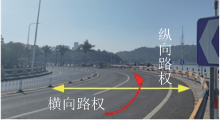
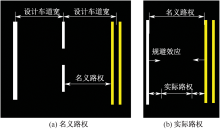
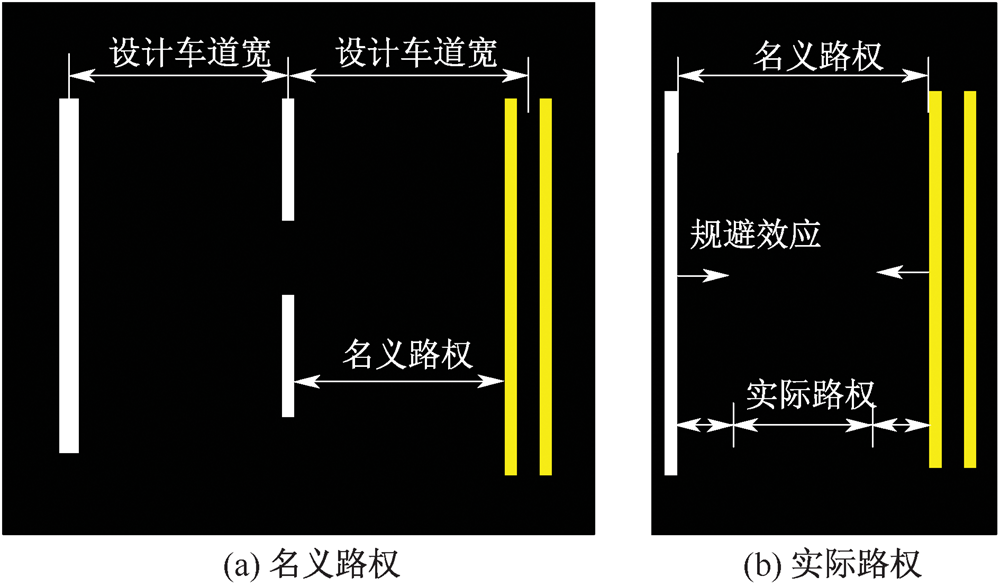
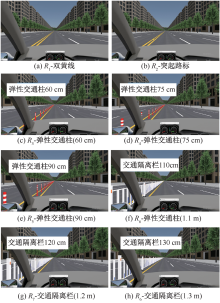
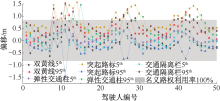
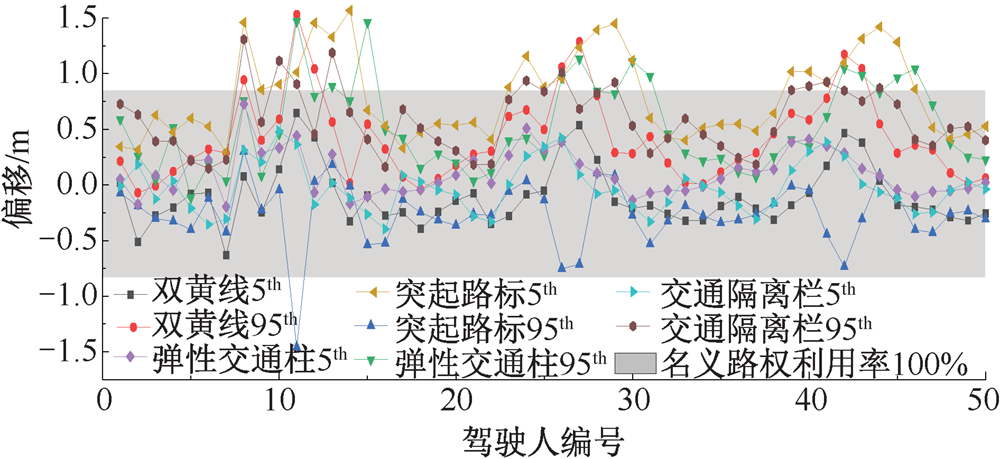
| [1] |
LIOI A, HAZOOR A, CASTRO M, et al. Impact on driver behaviour of guardrails of different height in horizontal-vertical coordinated road scenarios with a limited available sight distance[J]. Transportation Research Part F-Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2022, 84:287-300.
|
| [2] |
TAY R, CHURCHILL A. Effect of different median barriers on traffic speed[J]. Canadian Journal of Transportation, 2007, 1(1):56-66.
|
| [3] |
AASHO-2011, Roadside design guide[S].
|
| [4] |
魏文海. 多因素交互作用下缩减车道对驾驶行为的影响[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 40(4):117-126.
|
|
WEI Wenhai. Influence of lane reduction on driving behavior characteristics under multi-factor interaction[J]. Journal of Chang'an University: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 40(4):117-128.
|
| [5] |
吴文川. 城市道路增设中央隔离护栏相关问题及解决措施[J]. 福建建设科技, 2021(4):80-81, 117.
|
|
WU Wenchuan. The related problems and solutions of adding central isolation guardrail on urban roads[J]. Fujian Construction Science & Technology, 2021(4): 80-81, 117.
|
| [6] |
陶盼盼, 李元, 王益川. 北京市道路交通隔离设施精细化设置思路探讨[J]. 市政技术, 2022, 40(10):57-62.
|
|
TAO Panpan, LI Yuan, WANG Yichuan. Discussion on refined setting of traffic barricade in Beijing[J]. Journal of Municipal Technology, 2022, 40(10):57-62.
|
| [7] |
张宁, 陈恺, 何铁军, 等. 城市道路中间分隔带对比分析及设计[J]. 城市交通, 2007, 5(3):86-91.
|
|
ZHANG Ning, CHEN Kai, HE Tieijun, et al. Comparative study and design of urban street median[J]. Urban Transport of China, 2007, 5(3):86-91.
|
| [8] |
ROQUE C, LOURENÇO CARDOSO J, CONNELL T, et al. Topic analysis of road safety inspections using latent dirichlet allocation: a case study of roadside safety in Irish main roads[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2019, 131:336-349.
|
| [9] |
程瑞, 盘烨, 代军吉, 等. 公路路侧事故风险评估与路侧安全设计研究综述[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(9): 214-226.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.09.1864
|
|
CHENG Rui, PAN Ye, DAI Junji, et al. Research overview of roadside accident risk assessment and roadside safety design[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(9):214-226.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.09.1864
|
| [10] |
郑号染, 杜志刚, 王首硕, 等. 基于线性诱导的高速公路隧道交通安全优化设计[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33 (8): 134-141.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.08.1180
|
|
ZHENG Haoran, DU Zhigang, WANG Shoushuo, et al. Design of traffic safety optimization for expressway tunnel based on linear guidance[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(8):134-141.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.08.1180
|
| [11] |
王首硕. 高速公路隧道视线诱导信息组合理论及应用研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2023.
|
|
WANG Shoushuo. Study on theory and application of combining the visual guiding information in freeway tunnels[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2023.
|
| [12] |
CHEN Ying, DU Zhigang, JIANG Zehao, et al. Driver's shy away effect in urban extra-long underwater tunnel[J]. Promet-Traffic & Transportation, 2023, 35(4):552-566.
|
| [13] |
杨理波, 杜志刚, 徐弯弯, 等. 隧道内不同组合信息条件下驾驶员视错觉研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(1): 32-37.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.01.006
|
|
YANG Libo, DU Zhigang, XU Wanwan, et al. Research on drivers' visual illusion in tunnels under different combined visual information conditions[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(1):32-37.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.01.006
|
| [14] |
徐进, 张玉, 戴振华, 等. 人类自然驾驶状态下车辆轨迹摆动特性与车道宽度[J]. 汽车安全与节能学报, 2022, 13(4):718-728.
|
|
XU Jin, ZHANG Yu, DAI Zhenhua, et al. Vehicle trajectory oscillation characteristics and lane width control under human natural driving conditions[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2022, 13(4):718-728.
|
| [15] |
陈莹, 杜志刚, 许富强, 等. 基于规避行为的城市水下特长隧道驾驶负荷评价[J]. 公路, 2023, 68 (12): 206-214.
|
|
CHEN Ying, DU Zhigang, XU Fuqiang, et al. Driving load evaluation of urban underwater extra-long tunnel based on evasive behavior[J]. Highway, 2023, 68(12): 206-214.
|
| [16] |
CJJ37—2012, 城市道路工程设计规范(2016年版)[S].
|
|
CJJ37- 2012, Design specification for urban road engineering ( 2016 Edition)[S].
|
| [17] |
EL ESAWEY M, SAYED T. Evaluating safety risk of locating above ground utility structures in the highway right-of-way[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2012, 49:419-428.
|