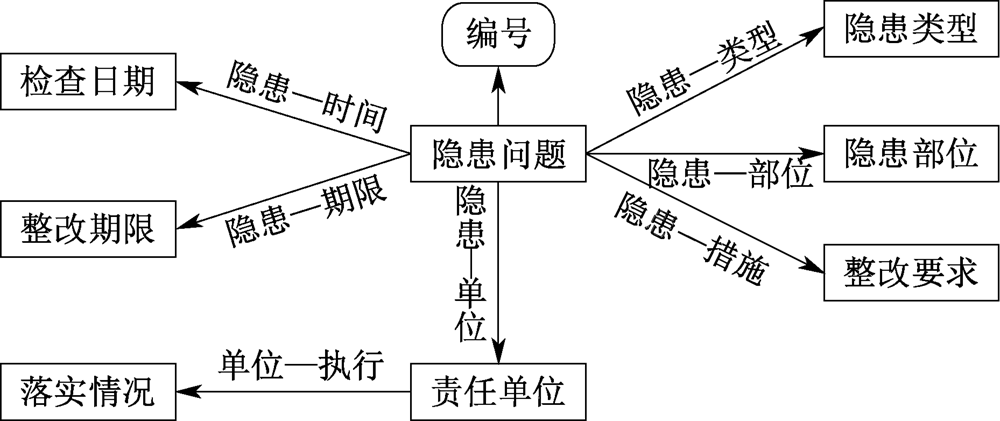
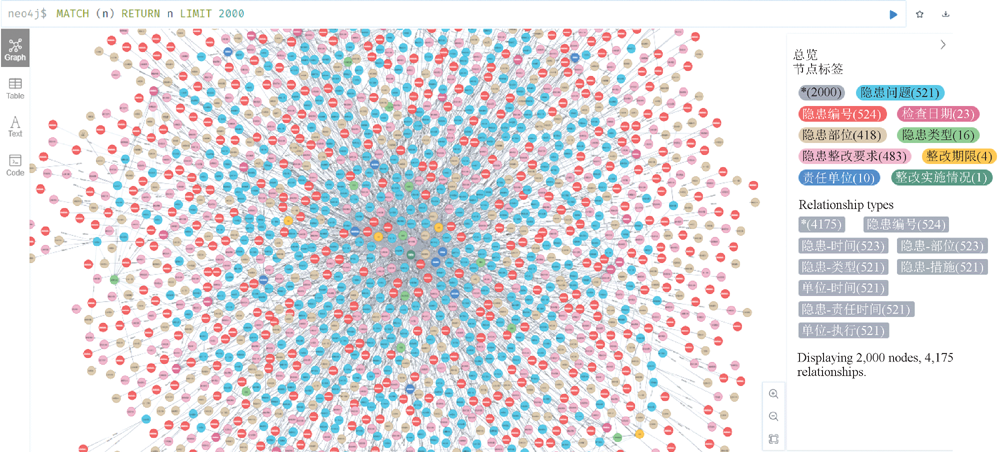
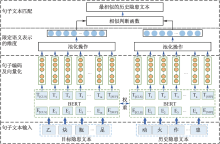
| [1] |
樊启祥, 林鹏, 魏鹏程, 等. 水电工程安全事故发生机制与管理对策[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(1):144-149.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.01.024
|
|
FAN Qixiang, LIN Peng, WEI Pengcheng, et al. Hydropower engineering safety accident occurrence mechanism and management strategies[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(1):144-149.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.01.024
|
| [2] |
王仁超, 张毅伟, 毛三军. 水电工程施工安全隐患文本智能分类与知识挖掘[J]. 水力发电学报, 2022, 41(11):96-106.
|
|
WANG Renchao, ZHANG Yiwei, MAO Sanjun. Intelligent text classification and knowledge mining of hidden safety hazards in hydropower engineering construction[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2022, 41(11):96-106.
|
| [3] |
靳嵩, 朱艳, 吴可嘉, 等. 基于BERT的海上船舶安全隐患分类[J]. 船舶工程, 2023, 45(增1):381-384.
|
|
JIN Song, ZHU Yan, WU Kejia, et al. Classification of ship safety hazards of marine vessel based on BERT[J]. Ship Engineering, 2023, 45(S1):381-384.
|
| [4] |
陈述, 习俊博, 王建平, 等. 水电工程施工安全隐患关联规则挖掘[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(8):75-82.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.011
|
|
CHEN Shu, XI Junbo, WANG Jianping, et al. Mining association rules of near-misses of hydropower projects construction[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(8):75-82.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.011
|
| [5] |
陈述, 刘文濯, 邵波, 等. 水电工程施工安全隐患时空分布特征研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(11):90-96.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.11.2227
|
|
CHEN Shu, LIU Wenzhuo, SHAO Bo, et al. Research on spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of safety nazards in hydropower projects[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(11):90-96.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.11.2227
|
| [6] |
肖琪耀, 贾宝山, 徐以诺, 等. 基于深度学习模型的煤矿安全隐患数据主题挖掘[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2024, 20(4):49-55.
|
|
XIAO Qiyao, JIA Baoshan, XU Yinuo, et al. Topics mining on potential safety hazard data of coal mine based on deep learning models[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2024, 20(4):49-55.
|
| [7] |
宁桂峰, 高龙, 刘利平. 基于遗传算法的采煤工作面隐患数据关联规则挖掘[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报, 2024, 6(2):136-145.
|
|
NING Guifeng, GAO Long, LIU Liping. Mining hidden danger data association rules of coal mining face based on genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering, 2024, 6(2):136-145.
|
| [8] |
陈述, 鲁世立, 王建平, 等. 缆机安全运行本体知识表示及复用方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(3):93-100.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.03.1321
|
|
CHEN Shu, LU Shili, WANG Jianping, et al. Representation and reuse of ontology knowledge for safe operation of cable crane[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(3):93-100.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.03.1321
|
| [9] |
臧洁, 周万林, 王妍. 融合多头注意力机制和孪生网络的语义匹配方法[J]. 计算机科学, 2023, 50(12):294-301.
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.221000083
|
|
ZANG Jie, ZHOU Wanlin, WANG Yan. Semantic Matching method integrating multi-head attention mechanism and siamese network[J]. Computer Science, 2023, 50(12):294-301.
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.221000083
|
| [10] |
阮光册, 钟静涵, 张祎笛. 基于深度学习的术语识别研究综述[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2024, 8(4):64-75.
doi: 10.11925/infotech.2096-3467.2023.0158
|
|
RUAN Guangce, ZHONG Jinghan, ZHANG Yidi. Review of term recognition studies based on deep learning[J]. Data Analysis and Knowledge Discovery, 2024, 8(4):64-75.
doi: 10.11925/infotech.2096-3467.2023.0158
|
| [11] |
管立本, 李实. 融合多粒度语义信息和知识图谱的中文医疗问答匹配模型[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(14):152-161.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2305-0453
|
|
GUAN Liben, LI Shi. A Chinese medical Q&A matching model based on multi-granularity semantic information and knowledge graph[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(14):152-161.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2305-0453
|
| [12] |
许童羽, 赵冬雪, 周云成, 等. 基于word2vec和Attention-Seq2Seq的水稻病虫害智能问答方法研究[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2019, 50(3):378-384.
|
|
XU Tongyu, ZHAO Dongxue, ZHOU Yuncheng, et al. Research on method of intelligent Q&A for rice pests and diseases based on word2vec and Attention-Seq2Seq[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2019, 50(3):378-384.
|
| [13] |
李琳, 段围, 周栋, 等. 基于深度语义匹配的法律条文推荐方法[J]. 软件学报, 2022, 33(7):2618-2632.
|
|
LI Lin, DUAN Wei, ZHOU Dong, et al. Law article recommendation approach based on deep semantic matching[J]. Journal of Software, 2022, 33(7):2618-2632.
|
| [14] |
张晓健, 张栋梁, 李明超, 等. 面向质量检测的混凝土坝施工规范智能检索[J]. 水力发电学报, 2023, 42(4):114-125.
|
|
ZHANG Xiaojian, ZHANG Dongliang, LI Mingchao, et al. Intelligent retrieval of concrete dam construction specification for quality inspection[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2023, 42(4):114-125.
|
| [15] |
罗香玉, 杜浩, 华颖, 等. 一种煤矿顶板灾害防治知识图谱构建方法[J]. 工矿自动化, 2024, 50(6):54-60.
|
|
LUO Xiangyu, DU Hao, HUA Ying, et al. A method for constructing a knowledge graph of coal mine roof disaster prevention and control[J]. Journal of Mine Automation, 2024, 50(6):54-60.
|
| [16] |
张吉祥, 张祥森, 武长旭, 等. 知识图谱构建技术综述[J]. 计算机工程, 2022, 48(3):23-37.
doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0061803
|
|
ZHANG Jixiang, ZHANG Xiangsen, WU Changxu, et al. Survey of knowledge graph construction techniques[J]. Computer Engineering, 2022, 48(3):23-37.
doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0061803
|
| [17] |
王莉, 王建平, 许娜, 等. 基于知识图谱的地铁工程事故知识建模与分析[J]. 土木工程与管理学报, 2019, 36(5):109-114,122.
|
|
WANG Li, WANG Jianping, XU Na, et al. Knowledge graph-based metro engineering accidents knowledge modeling and analysis[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management, 2019, 36(5):109-114,122.
|
| [18] |
郭天颖, 茆晓阳, 段齐骏, 等. 基于知识图谱的地震救援装备智能管理方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(7):239-245.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.07.2014
|
|
GUO Tianying, MAO Xiaoyang, DUAN Qijun, et al. Intelligent management and scheduling approach for earthquake rescue equipment based on knowledge graph[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(7):239-245.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.07.2014
|
| [19] |
HU Caiping, SNU Xuekui, DAI Hua, et al. Research on log anomaly detection based on sentence-BERT[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(17):DOI: 10.3390/ELECTRONICS12173580.
|
| [20] |
叶文豪, 王东波, 沈思, 等. 基于孪生网络的基金与受资助论文相关性判别模型构建研究[J]. 情报学报, 2020, 39(6):609-618.
|
|
YE Wenhao, WANG Dongbo, SHEN Si, et al. Research on constructing a model of correlation discrimination between funds and funded papers based on siamese network[J]. Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information, 2020, 39(6):609-618.
|
| [21] |
苏锦钿, 洪晓斌, 余珊珊. 基于多模型集成的语义文本相似性判断[J]. 华南理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 50(4):1-9.
|
|
SU Jindian, HONG Xiaobin, YU Shanshan. Semantic textual similarity justification based on multi-model ensemble[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology:Natural Science Edition, 2022, 50(4):1-9.
|
| [22] |
CAO Kunyu, CHEN Shu, ZHANG Xinkai, et al. Identification of causative factors for fatal accidents in the electric power industry using text categorization and catastrophe association analysis techniques[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2024,102:290-308.
|
| [23] |
夏占杰, 张贝克, 高东. 基于数据增强的HSE检查纪要命名实体识别[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(12):53-62.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.12.2727
|
|
XIA Zhanjie, ZHANG Beike, GAO Dong. Named entity recognition of HSE inspection minutes based on data enhancement[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(12):53-62.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.12.2727
|
| [24] |
钱杨舸, 秦小林, 张思齐, 等. 基于深度学习的文本语义匹配综述[J]. 软件导刊, 2022, 21(12):252-261.
|
|
QIAN Yangge, QIN Xiaolin, ZHANG Siqi, et al. Survey of texts semantic matching based on deep learning[J]. Software Guide, 2022, 21(12):252-261.
|
| [25] |
JADHAV S S, THEPADE S. Fake news identification and classification using dssm and improved recurrent neural network classifier[J]. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(12):1058-1068.
|