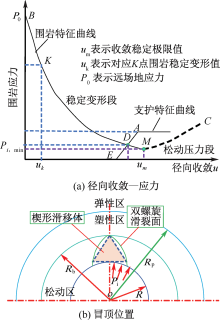
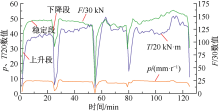
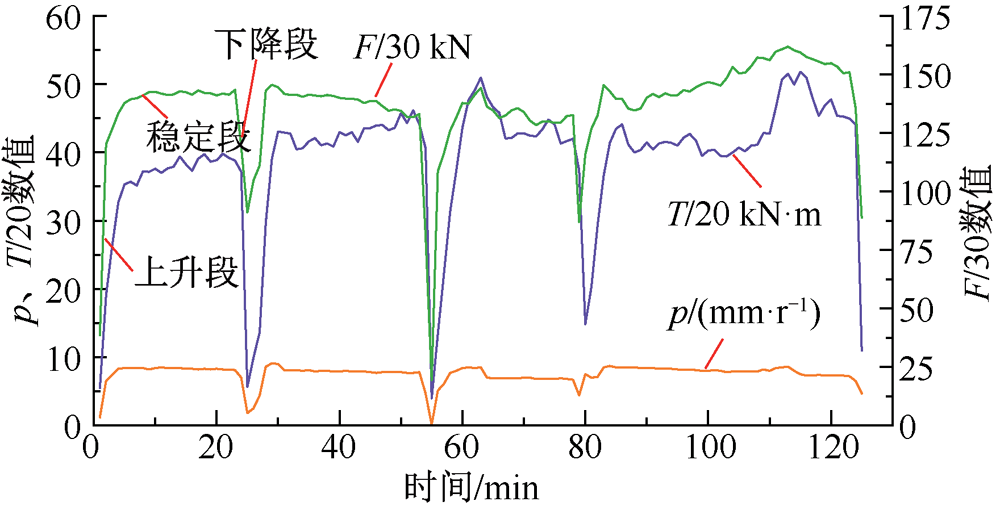
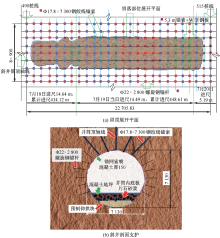
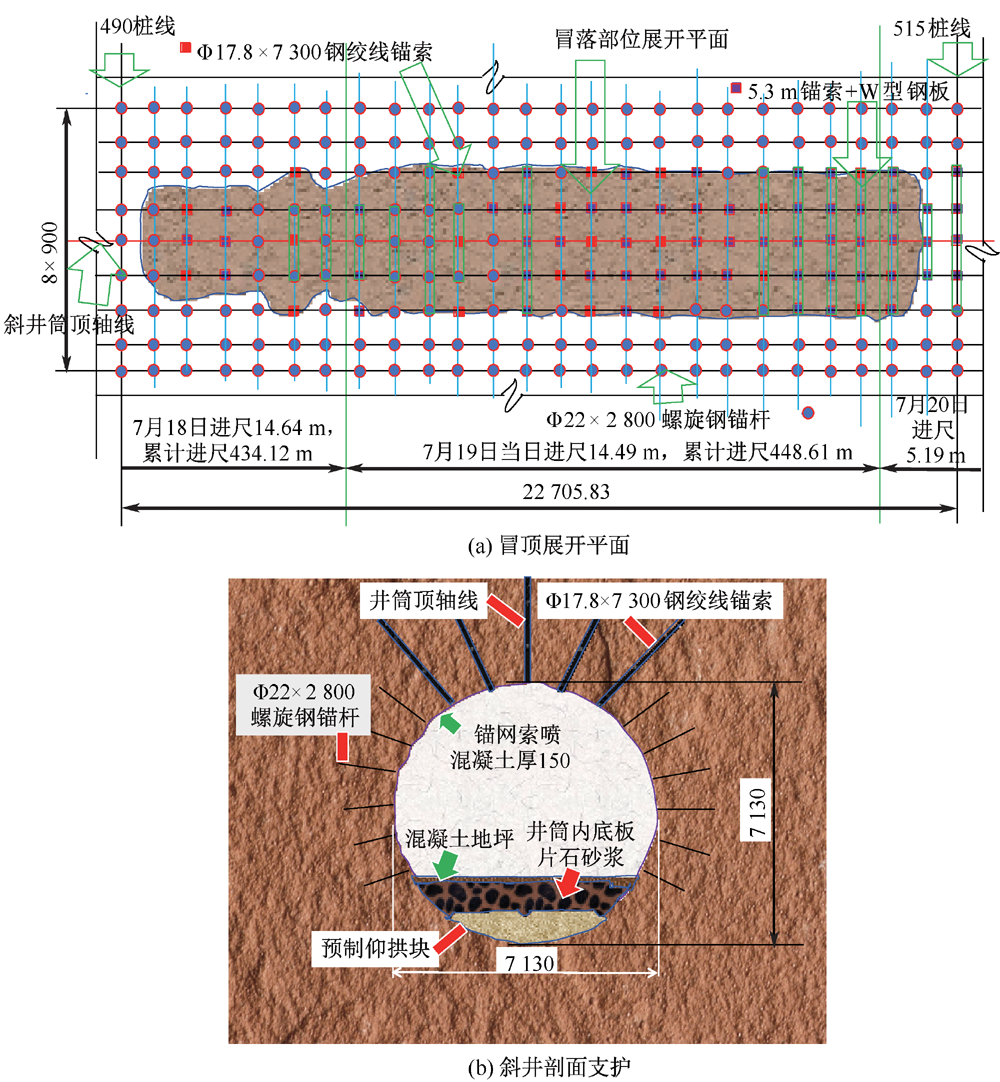
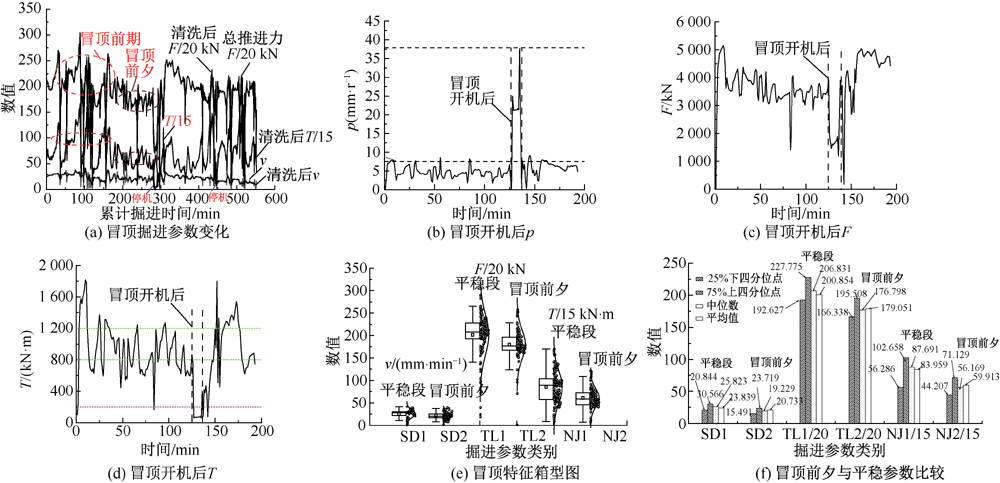
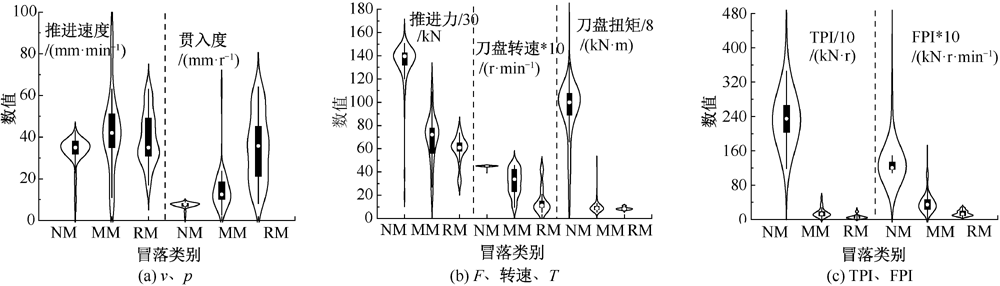
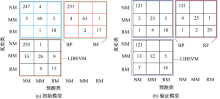
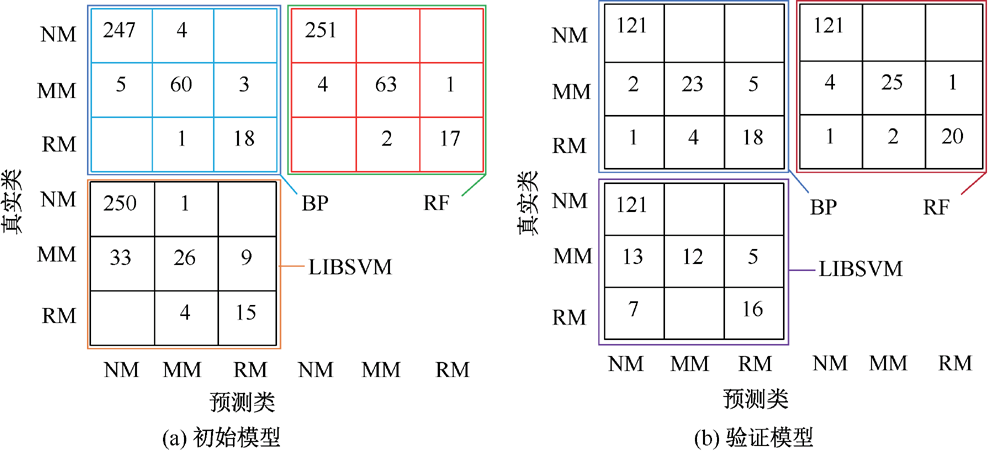
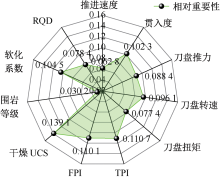
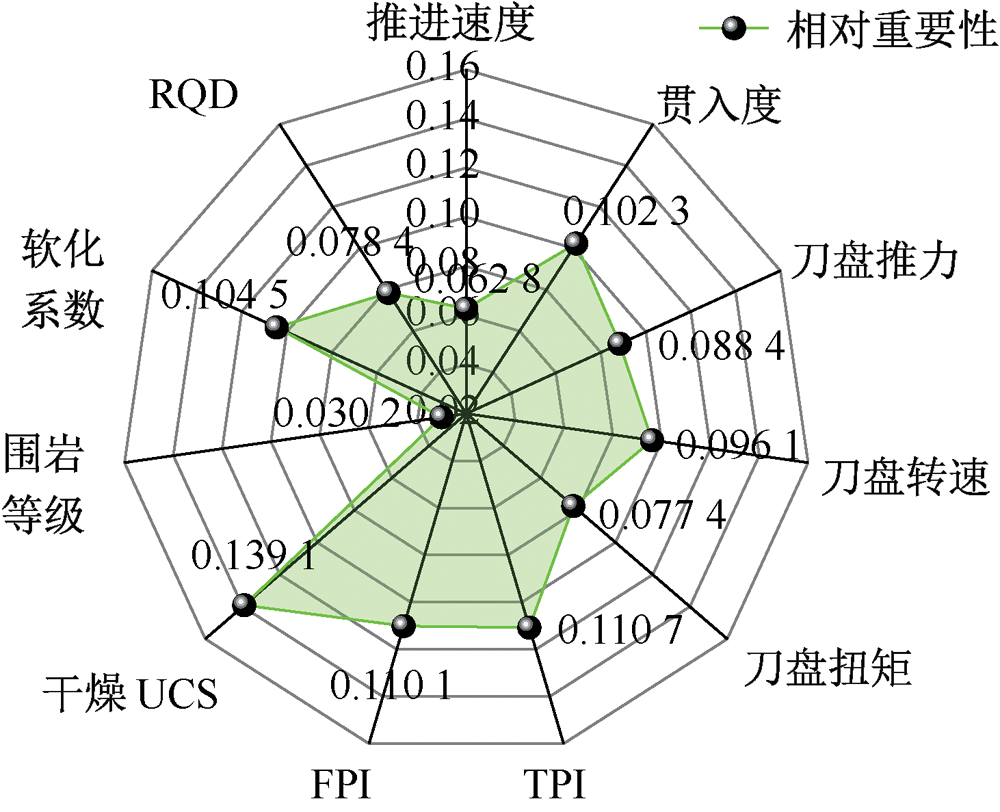
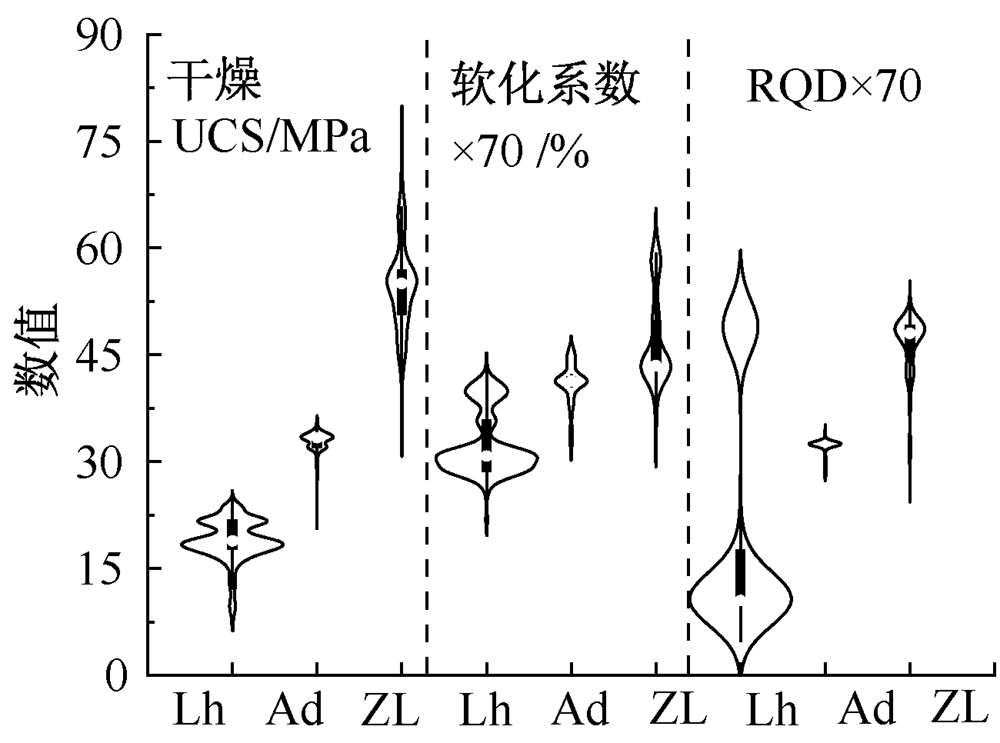
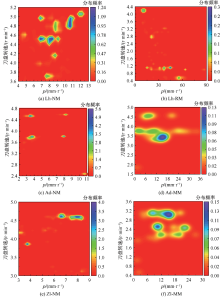
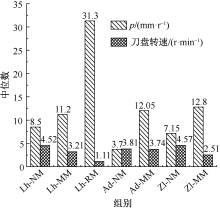
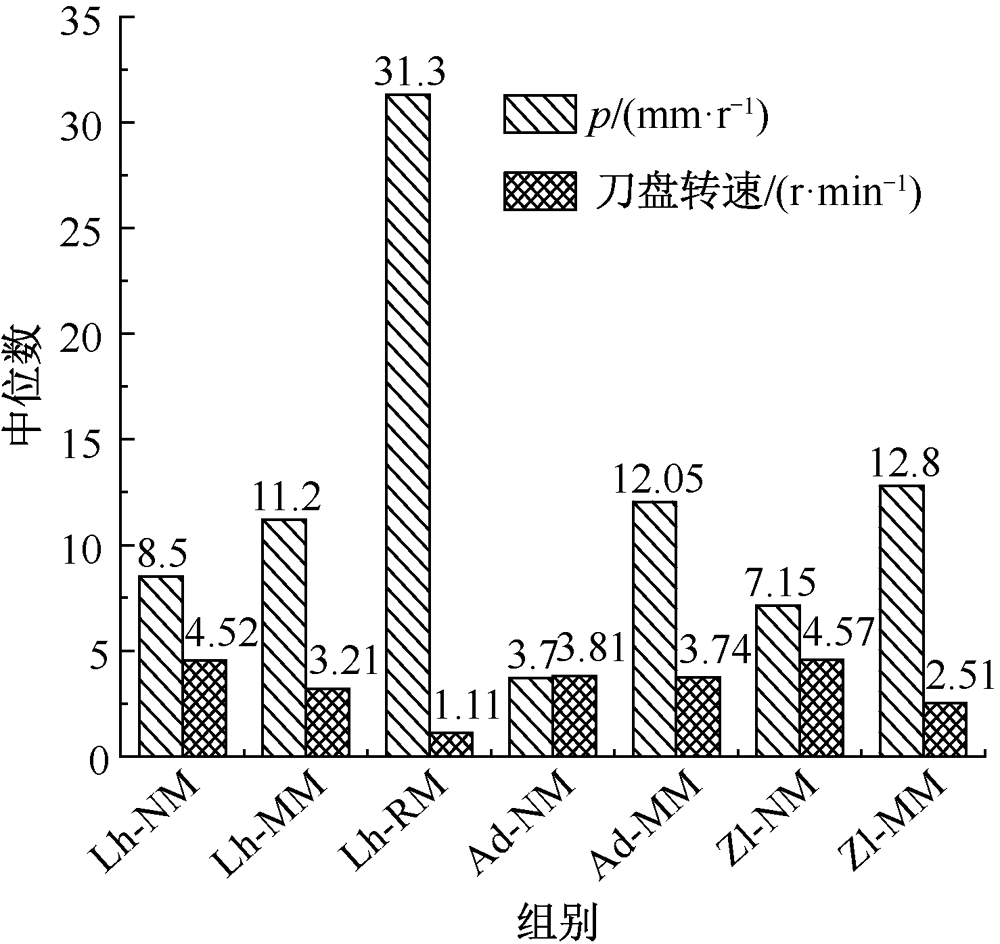
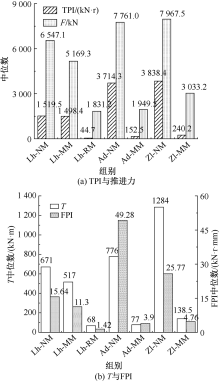
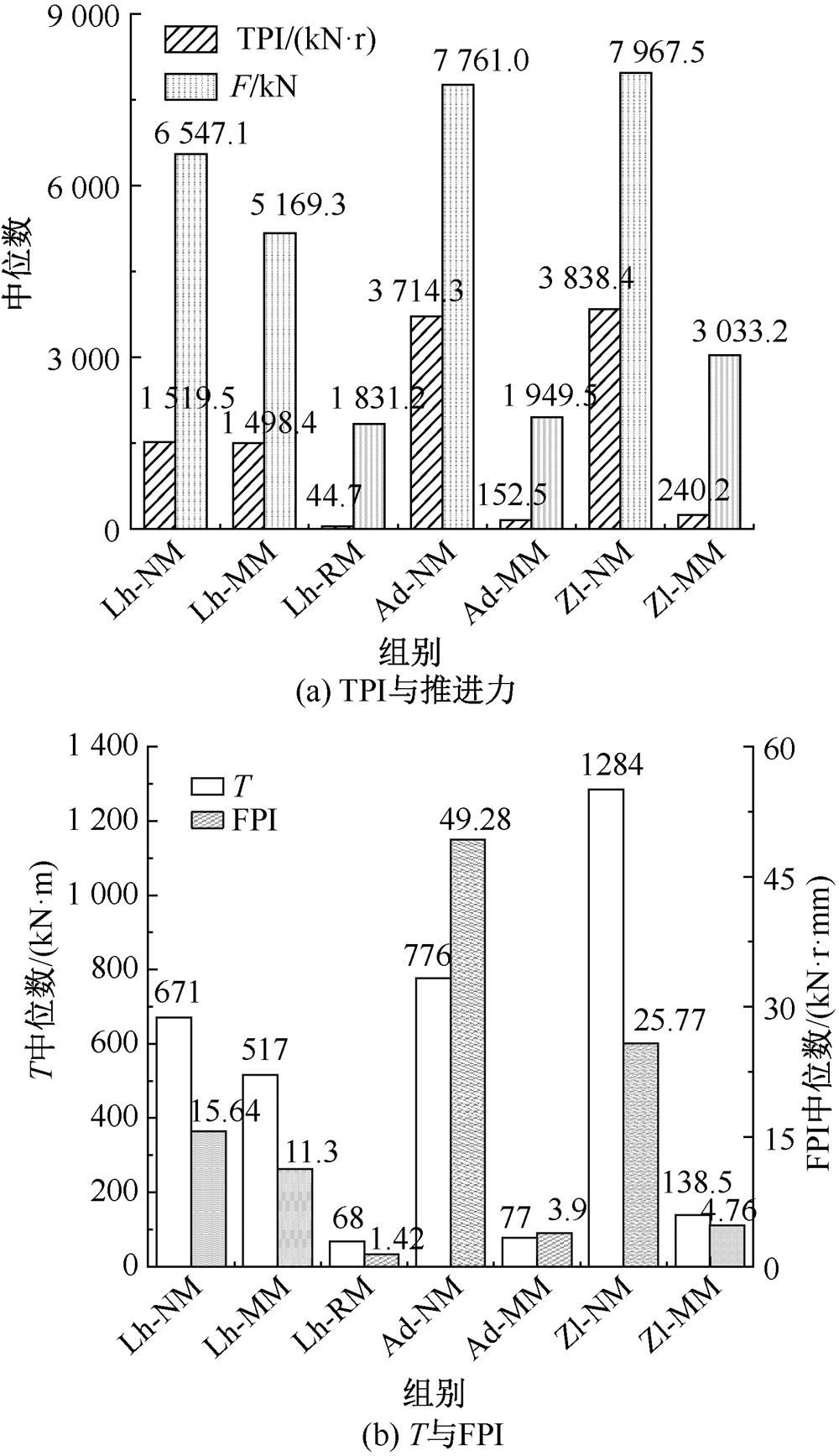
| [1] |
张民庆, 辛维克, 贾大鹏, 等. 顶部导洞法TBM卡机脱困技术研究与应用[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2023, 40(1): 68-75.
|
|
ZHANG Minqing, XIN Weike, JIA Dapeng, et al. Research and application of top pilot tunnel method rescue technology in TBM jamming[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2023, 40(1): 68-75.
|
| [2] |
WANG Zihui, ZHANG Shuo, FAN Deyuan, et al. A case study of displacement, stress condition and failure criterion of surrounding rock in deep super-large section double chambers in the Longgu coal mine, Shandong, China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 16 850-16 862.
|
| [3] |
李安云, 康鑫, 李森, 等. 富水弱胶结砂岩破坏特性与优化措施[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2024, 24(13): 5336-5343.
|
|
LI Anyun, KANG Xin, LI Sen, et al. Failure characteristics and optimization measures of weakly consolidated sandstone with rich water[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2024, 24(13): 5336-5343.
|
| [4] |
范京道, 魏东, 汪青仓, 等. 智能化建井理论技术研究与工程实践[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(1): 470-483.
|
|
FAN Jingdao, WEI Dong, WANG Qingcang, et al. Theory and practice of intelligent coal mine shaft excavation[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(1): 470-483.
|
| [5] |
丁秀丽, 张雨霆, 黄书岭, 等. 隧洞围岩大变形机制、挤压大变形预测及应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(3): 521-544.
|
|
DING Xiuli, ZHANG Yuting, HUANG Shuling, et al. Large deformation mechanism of surrounding rock masses of tunnels, prediction method of squeezing large deformation and its application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(3): 521-544.
|
| [6] |
李学华, 梁顺, 姚强岭, 等. 泥岩顶板巷道围岩裂隙演化规律与冒顶机理分析[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(6): 903-908.
|
|
LI Xuehua, LIANG Shun, YAO Qiangling, et al. Analysis on fissure-evolving law and roof-falling mechanism in roadway with mudstone roof[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(6): 903-908.
|
| [7] |
王新丰, 何毅, 陆明远, 等. 开挖卸荷扰动深部巷道围岩变形破坏特征研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(8): 83-90.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.012
|
|
WANG Xinfeng, HE Yi, LU Mingyuan, et al. Study on deformation and failure characteristics of deep roadway surrounding rock under excavation unloading disturbance[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(8): 83-90.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.012
|
| [8] |
李安云, 张凯, 徐金峰, 等. 破碎软岩斜井TBM开挖围岩稳定性及支护优化研究:以可可盖副斜井TBM掘进工程为例[J]. 隧道建设:中英文, 2023, 43(11): 1924-1934.
|
|
LI Anyun, ZHANG Kai, XU Jinfeng, et al. Stability of surrounding rock and support optimization of a broken soft-rock-inclined shaft bored by tunnel boring machine: a case study of Kekegai sub-inclined shaft[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2023, 43(11): 1 924-1 934.
|
| [9] |
汪青仓, 刘全辉, 宋朝阳, 等. 煤矿超长斜井敞开式全断面掘进机施工可行性分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2023, 51(7): 310-320.
|
|
WANG Qingcang, LIU Quanhui, SONG Zhaoyang, et al. Feasibility analysis of excavation with open full section boring machine for ultra-long distance slant in coal mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(7): 310-320.
|
| [10] |
高召宁, 陈登国, 孙振川, 等. 考虑损伤和扩容影响的隧洞围岩稳定性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(7): 159-165.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.07.024
|
|
GAO Zhaoning, CHEN Dengguo, SUN Zhenchuan, et al. Stability analysis of tunnel surrounding rock considering influence of damage and dilatancy[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(7): 159-165.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.07.024
|
| [11] |
纪洪广, 孙利辉, 宋朝阳, 等. 西部矿区弱胶结地层工程围岩稳定性控制研究进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2023, 51(1): 117-127.
|
|
JI Hongguang, SUN Lihui, SONG Zhaoyang, et al. Research progress on stability control of surrounding rock in weakly cemented strata engineering in western China mining area[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(1): 117-127.
|
| [12] |
HE Manchao, SUI Qiru, TAO Zhigang. Excavation compensation theory and supplementary technology system for large deformation disasters[J]. Deep Underground Science and Engineering, 2023, 2(2): 105-128.
|
| [13] |
俞茂宏, 武霞霞, 史俊, 等. 确定土体破坏准则的一个新方法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2020, 54(8): 1-10.
|
|
YU Maohong, WU Xiaxia, SHI Jun, et al. A new strategy for determining failure criteria of soil[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2020, 54(8): 1-10.
|
| [14] |
刘阳阳, 苏永华, 罗彪, 等. 基于极限状态的隧道围岩稳定性分析原理与方法[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2024, 21(10):4175-4 186.
|
|
LIU Yangyang, SU Yonghua, LUO Biao, et al. Principle and method of stability analysis of tunnel surrounding rock based on limit state[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2024, 21(10):4175-4 186.
|
| [15] |
RABCEWICZ L. The new Austrian tunnelling method[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1964: 173-175.
|
| [16] |
CHEN Zuyu, ZHANG Yunpei, LI Jianbin, et al. Diagnosing tunnel collapse sections based on TBM tunneling big data and deep learning: a case study on the Yinsong project, China[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2020, 108(3): 103 700-103 709.
|
| [17] |
仉文岗, 唐理斌, 陈福勇, 等. 基于4种超参数优化算法及随机森林模型预测TBM掘进速度[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2021, 29(5): 1186-1200.
|
|
ZHANG Wen'gang, TANG Libin, CHEN Fuyong, et al. Prediction for TBM penetration rate using four hyperparameter optimization methods and random forest model[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2021, 29(5): 1186-1200.
|
| [18] |
ROSTAMI J. Performance prediction of hard rock tunnel boring machines (TBMs) in difficult ground[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2016, 57: 173-182.
|
| [19] |
张茹, 吕游, 张泽天, 等. 深地工程多维信息感知与智能建造的发展与展望[J]. 煤炭学报, 2024, 49(3): 1259-1290.
|
|
ZHANG Ru, LYU You, ZHANG Zetian, et al. Development and prospect of multidimensional information perception and intelligent construction in deep earth engineering[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2024, 49(3): 1259-1290.
|
| [20] |
黄曾华. 综采装备单机智能化向智能协同模式转型的探索研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(4): 169-175.
|
|
HUANG Zenghua. Exploration and research on transformation from intelligent single machine equipment to intelligent synergy in coal mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(4): 169-175.
|