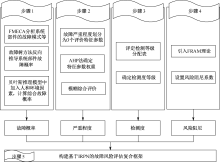
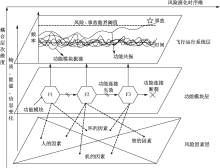
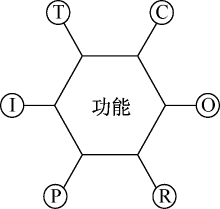
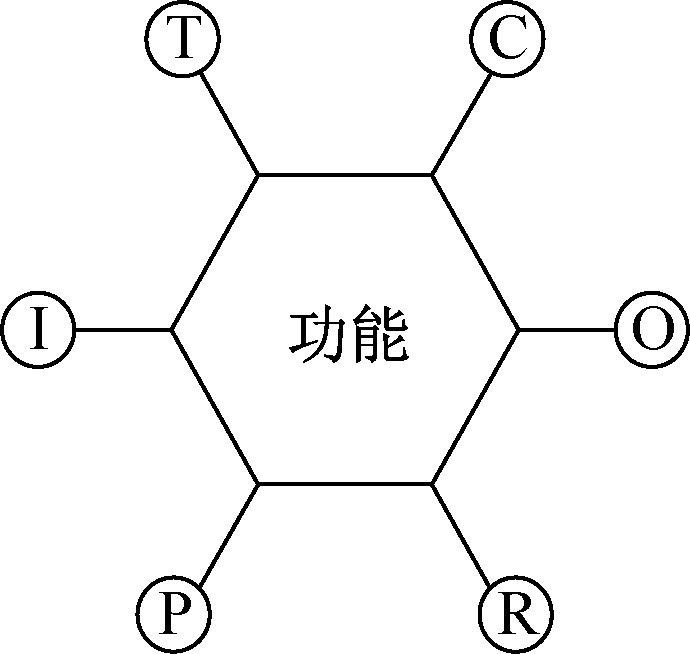
| [1] |
王岩韬, 陈冠铭. 基于时间序列模型的航班运行风险短期预测[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(5):33-38.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.05.006
|
|
WANG Yantao, CHEN Guanming. Short-time prediction of flight operation risk based on time series models[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(5): 33-38.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.05.006
|
| [2] |
王岩韬, 李景良, 谷润平. 基于多变量混沌时间序列的航班运行风险预测模型[J]. 工程科学学报, 2020, 42(12):1664-1673.
|
|
WANG Yantao, LI Jingliang, GU Runping. Flight operation risk prediction model based on the multivariate chaotic time series[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2020, 42(12): 1664-1673.
|
| [3] |
GUL M, YUCESAN M, CELIK E. A manufacturing failure mode and effect analysis based on fuzzy and probabilistic risk analysis[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 96: 1-12.
|
| [4] |
石旭东, 成博源, 黄琨, 等. 基于模糊TOPSIS-FMEA的飞机IDG风险评价[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(6): 2060-2064.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.06.35
|
|
SHI Xudong, CHENG Boyuan, HUANG Kun, et al. Risk assessment of aircraft IDG based on fuzzy TOPSIS FMEA[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(6): 2 060-2 064.
|
| [5] |
谢露强, 孙家臣, 王海燕. 基于改进FMECA-FBN和ER的铝矾土海运物流风险评估[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2022, 29(6): 10-21.
|
|
XIE Luqiang, SUN Jiachen, WANG Haiyan. Risk assessment of bauxite maritime logistics based on improved FMECA-FBN and ER[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(6): 10-21.
|
| [6] |
王岩韬, 赵昕颐. 空地数据实时传输下的飞机着陆风险预警方法[J]. 工程科学学报, 2023, 45(10): 1759-1770.
|
|
WANG Yantao, ZHAO Xinyi. Advanced warning method for aircraft landing risk under air-ground data real-time transmission conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2023, 45(10): 1759-1770.
|
| [7] |
郭媛媛, 孙有朝, 李龙彪. 基于蒙特卡罗方法的民用飞机故障风险评估方法[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(10): 155-163.
|
|
GUO Yuanyuan, SUN Youchao, LI Longbiao. Failure risk assessment method of civil aircraft based on Monte Garlo method[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2017, 38(10): 155-163.
|
| [8] |
徐一旻, 田梦莹, 李治, 等. FTA-BN在机场跑道入侵事故影响因素分析中的应用[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2023, 23(5): 1361-1367.
|
|
XU Yimin, TIAN Mengying, LI Zhi, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of airport runway incursion accident based on FTA-BN[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2023, 23(5): 1361-1367.
|
| [9] |
APPOH F, YUNUSA-KALTUNGO A. Composite hybrid framework for through-life multi-objective failure analysis and optimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 71 505-71 520.
|
| [10] |
LI Jun, XU Huibin. Reliability analysis of aircraft equipment based on FMECA method[J]. Physics Procedia, 2012, 25: 1816-1822.
|
| [11] |
CATELANI M, CIANI L, GALAR D, et al. FMECA assessment for railway safety-critical systems investigating a new risk threshold method[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 86 243-86 253.
|
| [12] |
陈颖, 康瑞. FMECA技术及其应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2014: 58-64.
|
| [13] |
HOLLNAGEL E. FRAM: the functional resonance analysis method: modelling complex socio-technical systems[M]. Aldershot: Town Publishing Ltd., 2012: 101-106.
|
| [14] |
CARVALHO P V R D. The use of functional resonance analysis method (FRAM) in a mid-air collision to understand some characteristics of the air traffic management system resilience[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2011, 96(11): 1482-1498.
|
| [15] |
王涵宇, 谭钦文. 基于FRAM的有限空间作业安全职责半定量分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(5): 88-95.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.05.1382
|
|
WANG Hanyu, TAN Qinwen. Semi quantitative analysis of safety duties in confined space operations based on FRAM[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(5): 88-95.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.05.1382
|
| [16] |
时统宇, 马煜森, 曹宇杰, 等. 基于改进功能共振分析法的 SPO 风险演化研究.[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(6):29-38.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.06.1428
|
|
SHI Tongyu, MA Yusen, CAO Yujie, et al. SPO risk evolution based on improved functional resonance analysis method[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(6): 29-38.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.06.1428
|