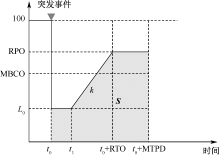
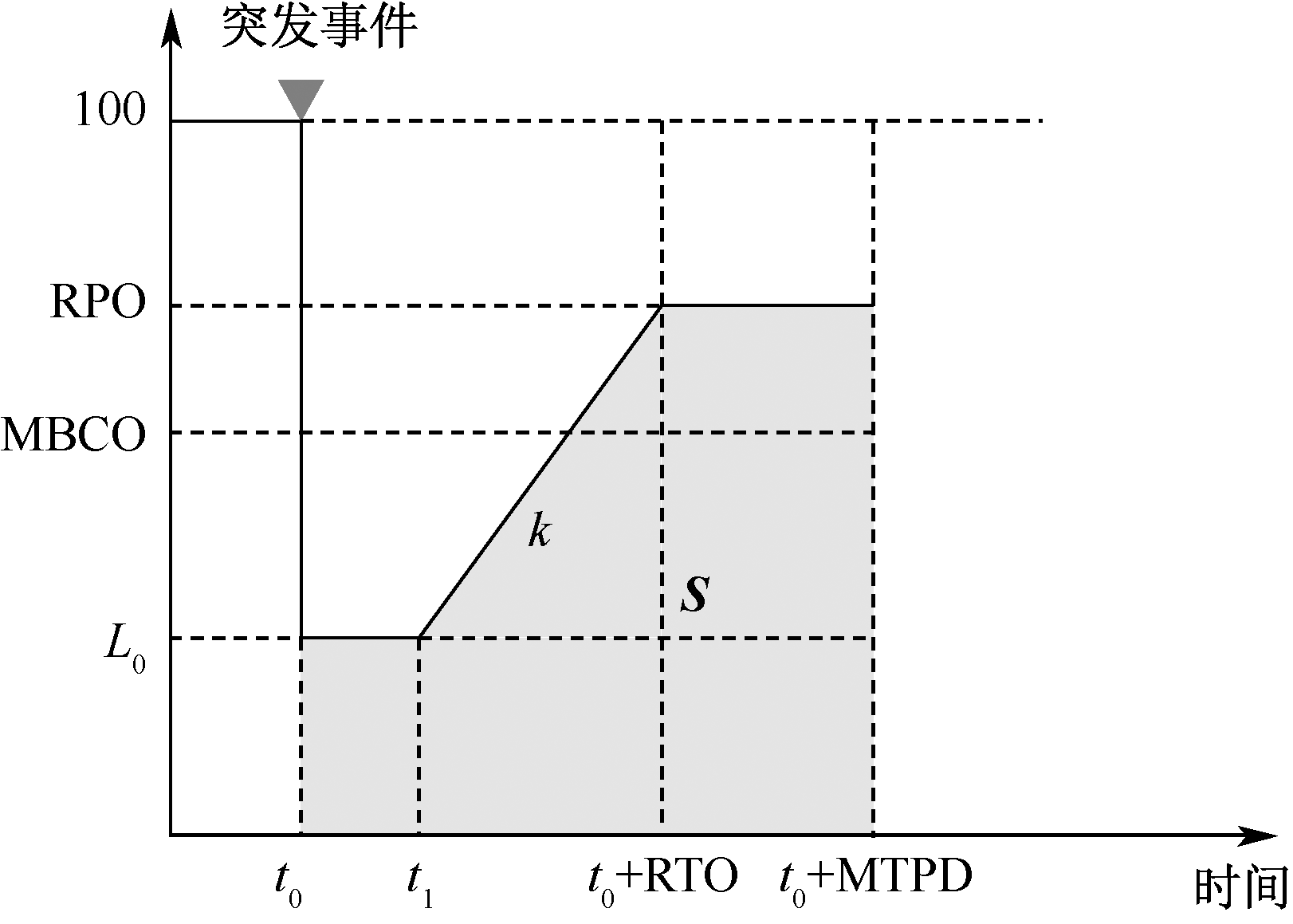
| [1] |
瞿英, 许生. 社区韧性的概念演进与中外前沿热点对比分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(11): 105-116.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.11.0791
|
|
QU Ying, XU Sheng. Conceptual evolution of community resilience and comparative analysis of frontier spots at home and abroad[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(11): 105-116.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.11.0791
|
| [2] |
国家减灾委员会. 国家减灾委员会关于印发《“十四五”国家综合防灾减灾规划》的通知[EB/OL]. [2025-03-06]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2022-07/22/content_5702154.htm.
|
| [3] |
ISO22301, Societal security-business continuity management systems-requirements[S]. 2012.
|
| [4] |
SMITH R. Business continuity planning and service level agreements[J]. Information Management & Computer Security, 1995, 3(3): 17-19.
|
| [5] |
田敬秋, 王凯, 贾传圣, 等. 业务持续性管理在煤矿应急管理中的应用[J]. 煤矿安全, 2017, 48(1): 214-217.
|
|
TIAN Jingqiu, WANG Kai, JIA Chuansheng, et al. Application of business continuity management in emergency management of coal mine[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2017, 48(1): 214-217.
|
| [6] |
PARISE G, HESLA E, PARISE L, et al. Switching procedures and business continuity management: the flock logic of multiple source systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2016, 52(1): 60-66.
|
| [7] |
HASSEl H, CEDERGREN A. Integrating risk assessment and business impact assessment in the public crisis management sector[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2021, 56: DOI: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2021.102136.
|
| [8] |
TÓMASSON B. Using business continuity methodology for improving national disaster risk management[J]. Journal of Contingencies and Crisis Management, 2023, 31(1): 134-148.
|
| [9] |
李璎珂, 刘振翼, 李舒泓, 等. 基于Stackelberg博弈的应急物资政企协同储备决策模型[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2023, 19(6): 33-39.
|
|
LI Yingke, LIU Zhenyi, LI Shuhong, et al. Government-enterprise collaborative reserve decision-making model of emergency supplies based on Stackelberg game[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2023, 19(6): 33-39.
|
| [10] |
项寅. 社会环境视角下应急物资政企联合配置模型[J]. 运筹与管理, 2023, 32(10): 69-75.
doi: 10.12005/orms.2023.0321
|
|
XIANG Yin. Optimizing emergency material reserve considering supplier participation and social environment[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2023, 32(10): 69-75.
doi: 10.12005/orms.2023.0321
|
| [11] |
庞海云, 叶永. 基于实物期权契约的应急物资政企联合储备模型[J]. 系统管理学报, 2020, 29(4): 733-741.
|
|
PANG Haiyun, YE Yong. Government-enterprise joint reserve model of emergency materials based on real option contract[J]. Journal of Systems & Management, 2020, 29(4): 733-741.
|
| [12] |
王伟, 王芸清, 黄莉, 等. 基于损失定量的防汛应急物资配置优化研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(11): 189-195.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.11.2124
|
|
WANG Wei, WANG Yunqing, HUANG Li, et al. Research on optimization of flood control emergency material allocation based on loss quantification[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(11): 189-195.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.11.2124
|
| [13] |
|
|
LIU Yang, TIAN Jun, YU Ning, et al. Prepositioning model of emergency supplies and coordination mechanism considering human suffering perception via an option contract[J/OL]. Journal of Management Science: 1-18.[2024-04-17]. https://doi.org/10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2023.0109.
|
| [14] |
樊彧, 邵建芳, 王熹徽. 基于匮乏成本的应急物资政企合作储备与运输策略研究[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2024, 44(5): 1603-1614.
doi: 10.12011/SETP2023-0543
|
|
FAN Yu, SHAO Jianfang, WANG Xihui. A study of strategies on joint inventory and delivery of emergency supplies between the local authority and the suppliers based on deprivation cost[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2024, 44(5): 1603-1614.
|
| [15] |
DB 4403/T 345—2023, 救灾物资储备标准指引[S].
|
|
DB 4403/T 345-2023, Guidelines for disaster relief materials reserve[S].
|
| [16] |
李亚琴, 於家, 周泱, 等. 洪灾情景下食品类物资供需分配及配送路径优化:以上海市奉贤区为例[J]. 地理科学, 2024, 44(4): 573-585.
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.20230850
|
|
LI Yaqin, YU Jia, ZHOU Yang, et al. Optimization of the supply and demand allocation and distribution path of food supplies under flood scenarios: a case study in Fengxian district, Shanghai[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2024, 44(4): 573-585.
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.20230850
|
| [17] |
中国营养学会. 中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2023: 91-92.
|