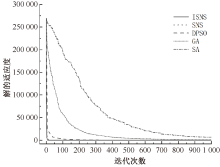
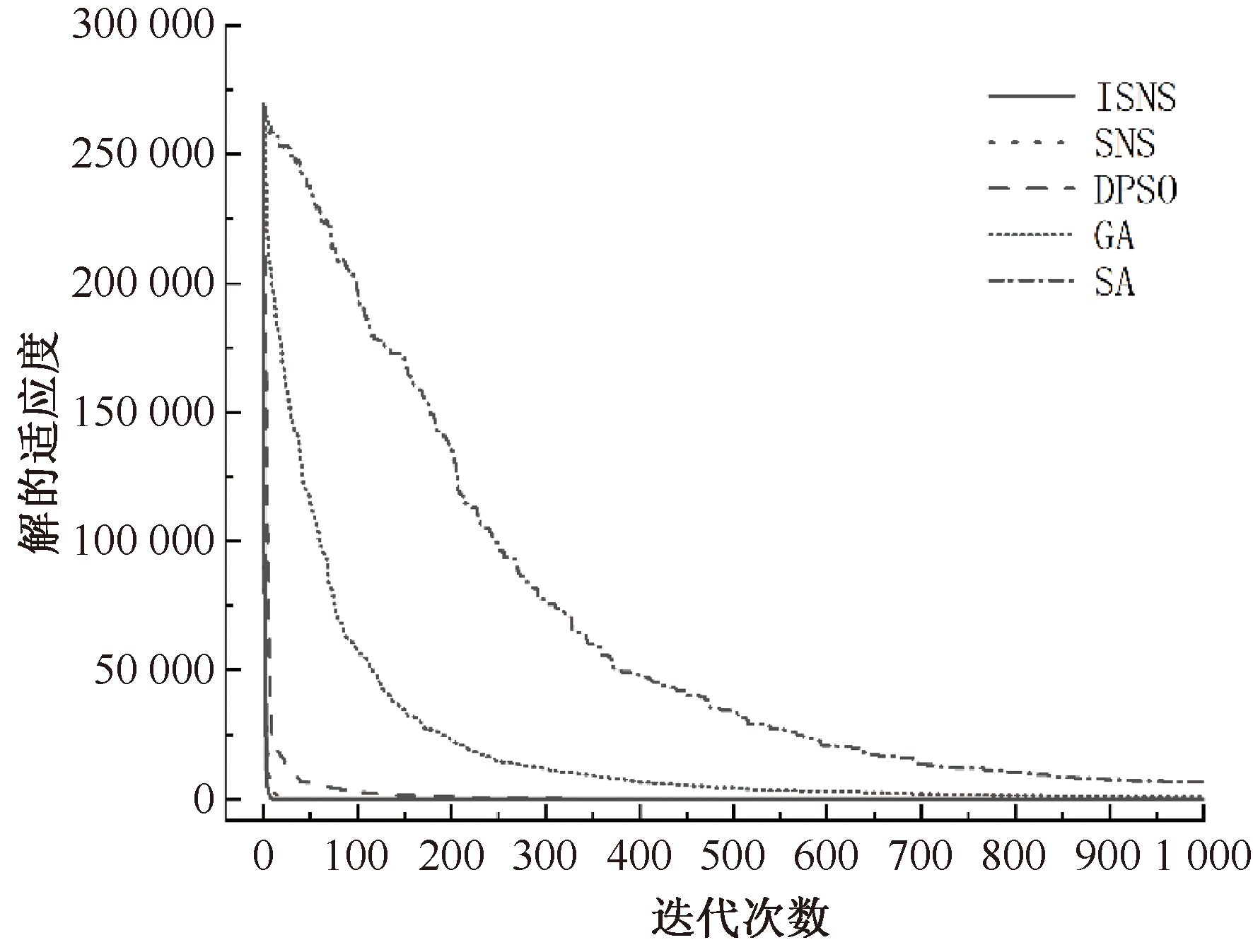
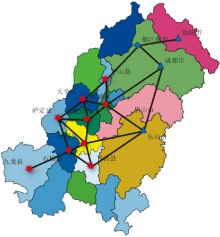
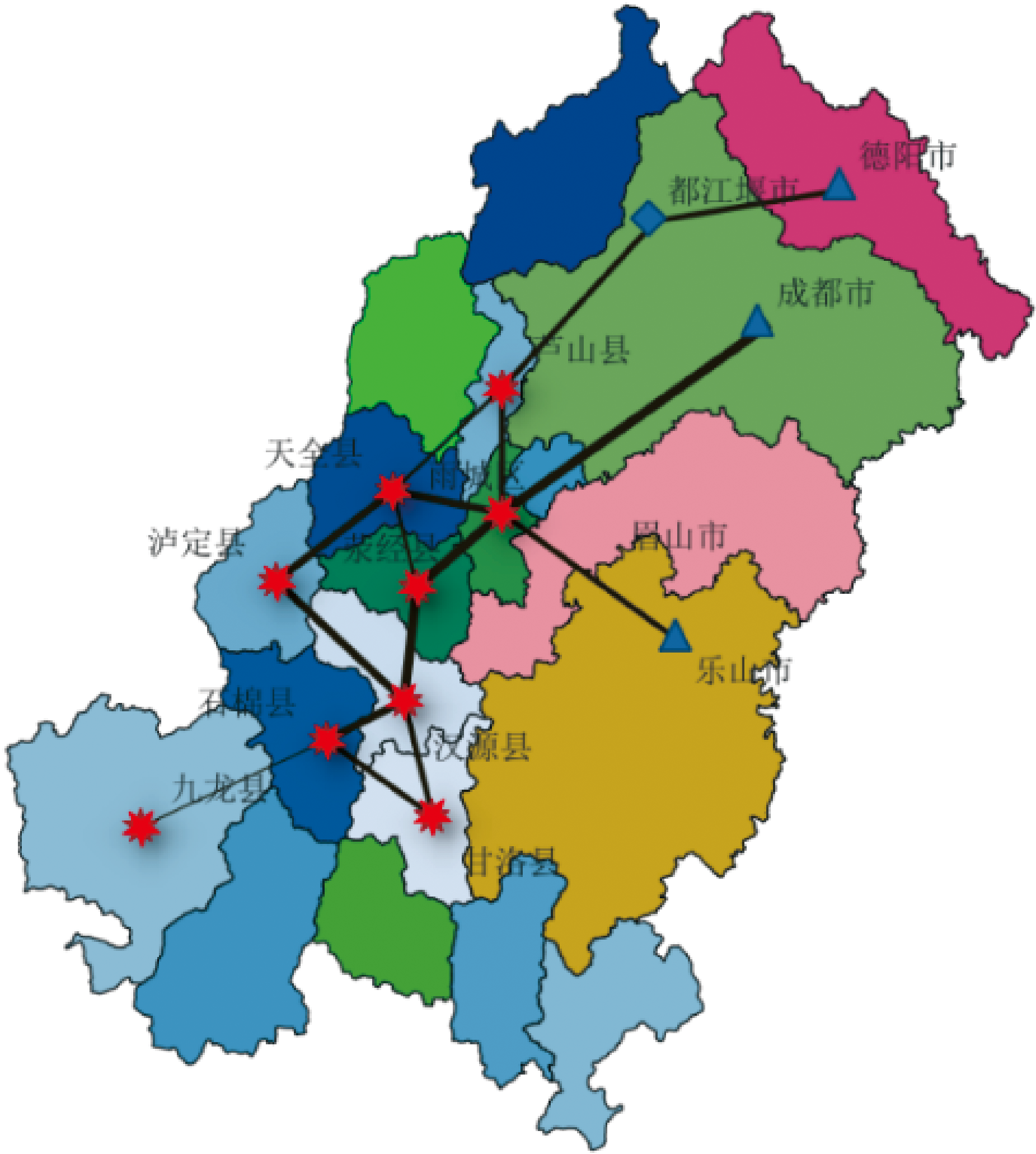
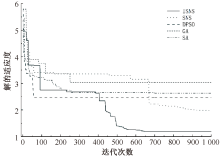
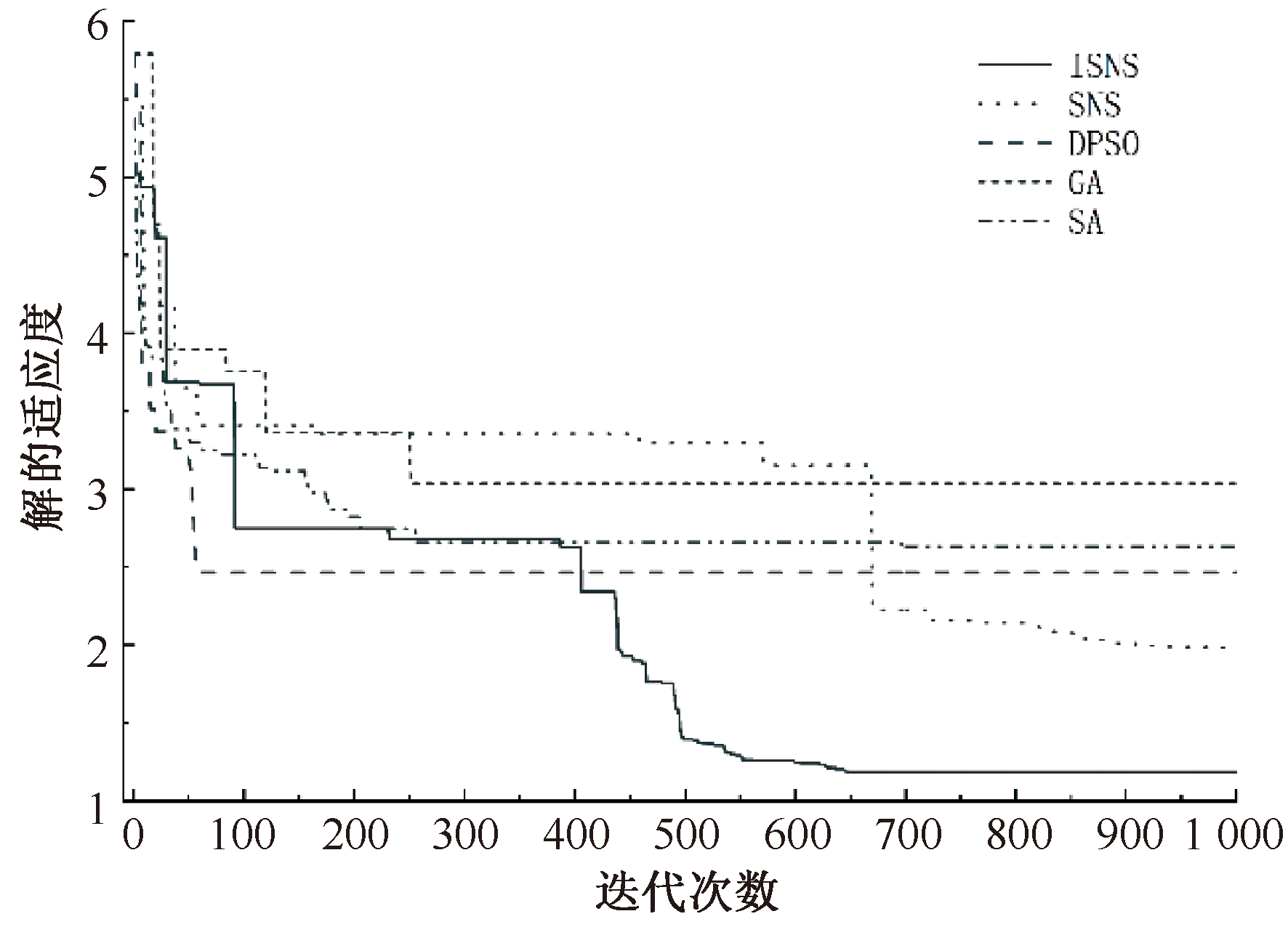
| [1] |
CHEN Rui, SHARMAN R, RAO H R, et al. Coordination in emergency response management[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2008, 51(5): 66-73.
|
| [2] |
MONZÓN J, LIBERATORE F, VITORIANO B. A mathematical pre-disaster model with uncertainty and multiple criteria for facility location and network fortification[J]. Mathematics, 2020, 8(4):DOI: 10.3390/math8040529.
|
| [3] |
SUN Yougqiang, REN Yeqing, CAI Xingjuan. Biobjective emergency logistics scheduling model based on uncertain traffic conditions[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020, 2020: 1-15.
|
| [4] |
王庆荣, 王雪娜, 朱昌锋, 等. 需求不确定下的两阶段应急物流选址-路径研究[J/OL]. 灾害学: 1-12[2024-12-19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1097.P.20240920.1014.002.html.
|
|
WANG Qingrong, WANG Xuena, ZHU Changfeng, et al. Research on two-stage emergency logistics location-routing problem with uncertain demand[J/OL]. Journal of Catastrophology: 1-12[2024-12-19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1097.P.20240920.1014.002.html.
|
| [5] |
孙华丽, 曹文倩, 薛耀锋, 等. 考虑路径风险的需求不确定应急物流定位-路径问题[J]. 运筹与管理, 2018, 27(7): 37-42.
doi: 10.12005/orms.2018.0155
|
|
SUN Huali, CAO Wenqian, XUE Yaofeng, et al. Emergency logistics-rounting model with uncertain demand under p-ath risk[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2018, 27(7): 37-42.
doi: 10.12005/orms.2018.0155
|
| [6] |
AHMAD S, AZIKIN M, SUKRI A, et al. Aplikasi metode PCI (Pavement Condition Index) dalam mengukur tingkat kerusakan jalan dan pengaruhnya terhadap kecepatan kendaraan[J]. Rekonstruksi Tadulako: Civil Engineering Journal on Research and Development, 2020, 1(2): 17-22.
|
| [7] |
贾贵宾. 路面破损对道路通行能力的影响研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2015.
|
|
JIA Guibin. Research on road capacity resulting from pavement distress[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2015.
|
| [8] |
孙立军, 刘喜平. 路面使用性能的标准衰变方程[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 1995, 23(5): 512-518.
|
|
SUN Lijun, LIU Xiping. General deterioration equation for pavement performance[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 1995, 23(5): 512-518.
|
| [9] |
LIANG Tienfu. Distribution planning decisions using interactive fuzzy multi-objective linear programming[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2006, 157(10): 1303-1316.
|
| [10] |
于冬梅, 高雷阜, 赵世杰. 给定需求区域应急物资储备库选址模型及其解法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2015, 25(11): 170-176.
|
|
YU Dongmei, GAO Leifu, ZHAO Shijie. A location model with demand regious and algorithm for emergency supplies reposity[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2015, 25(11): 170-176.
|
| [11] |
周磊, 李前鹏, 李法朝. 考虑时间满意度的应急物资储备库选址模型与算法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(3): 188-194.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.03.1158
|
|
ZHOU Lei, LI Qianpeng, LI Fachao. Location model and algorithm for emergency material storage considering time satisfaction[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(3): 188-194.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.03.1158
|
| [12] |
TALATAHARI S, BAYZIDI H, SARAEE M. Social network search for global optimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 92 815-92 863.
|
| [13] |
王海军, 杜丽敬, 马士华. 震后应急物流系统中双目标开放式选址: 路径问题模型与算法研究[J]. 管理工程学报, 2016, 30(2): 108-115.
|
|
WANG Haijun, DU Lijing, MA Shihua. Model and algorithms for integrated open location and routing problem in emergency logistics under earthquake[J]. Journal of Industrial Engineering/Engineering Management, 2016, 30(2): 108-115.
|