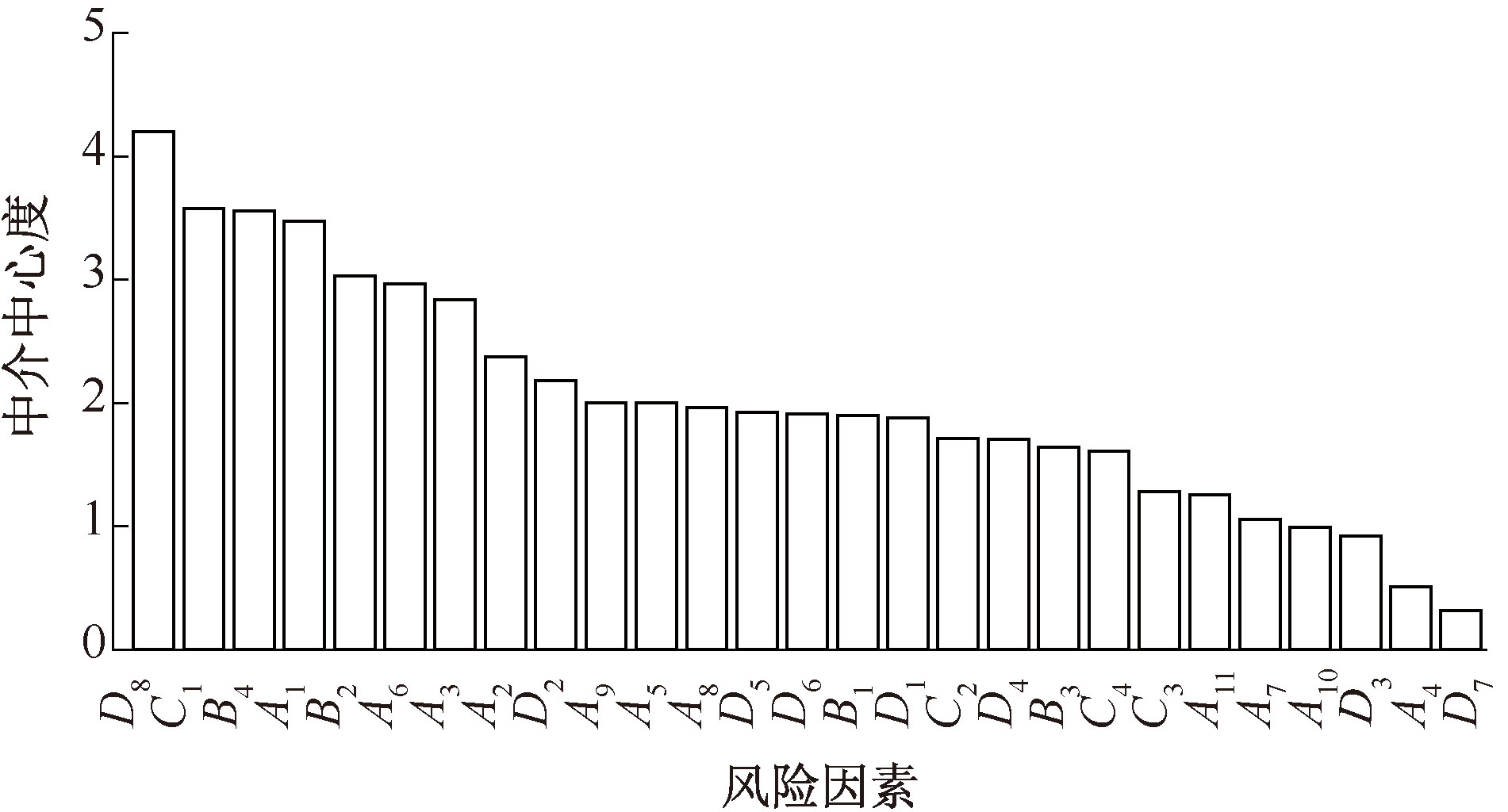
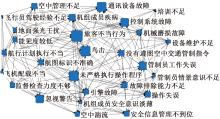
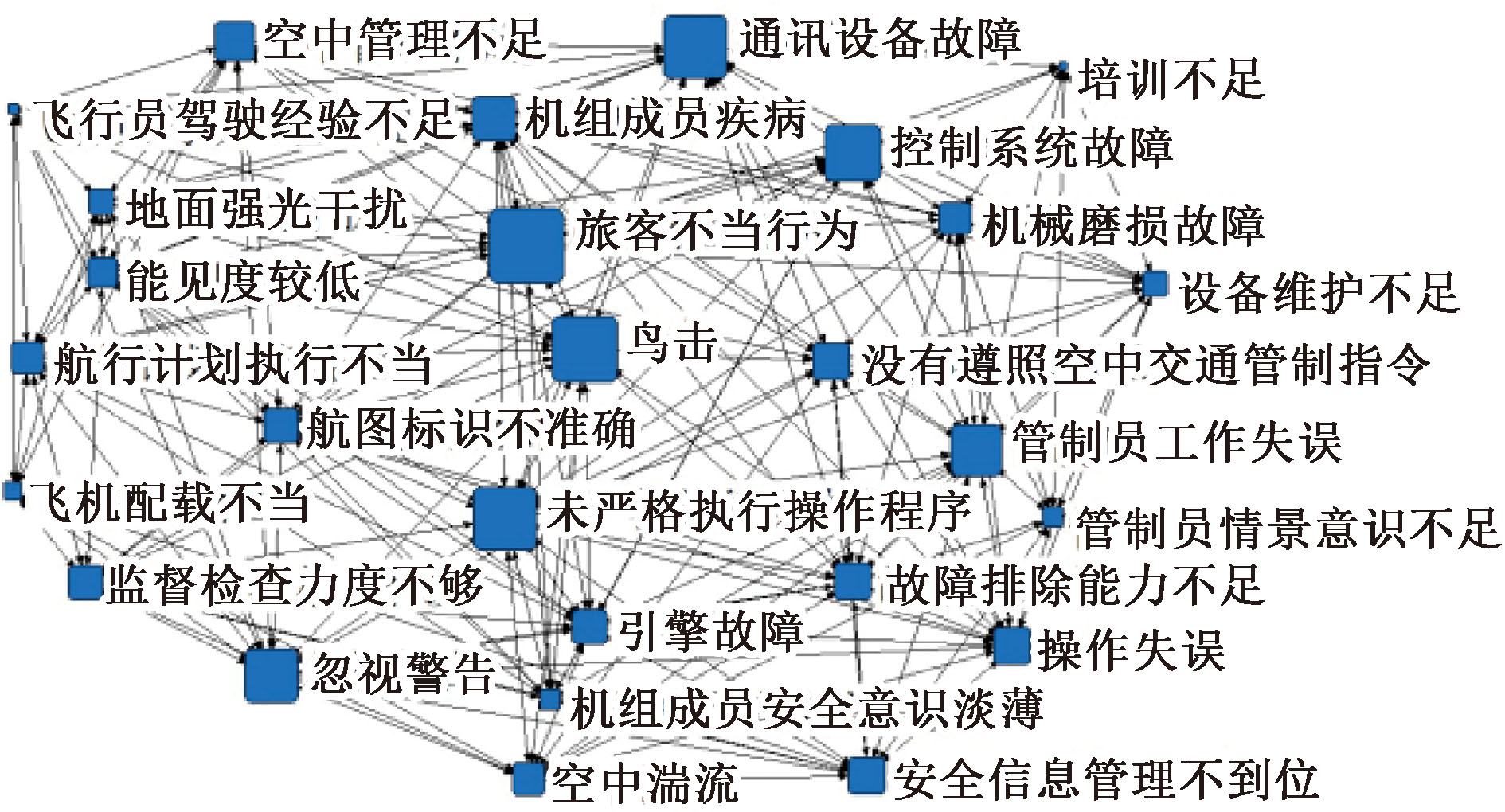
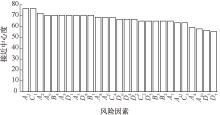
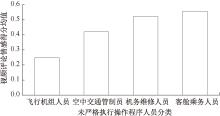
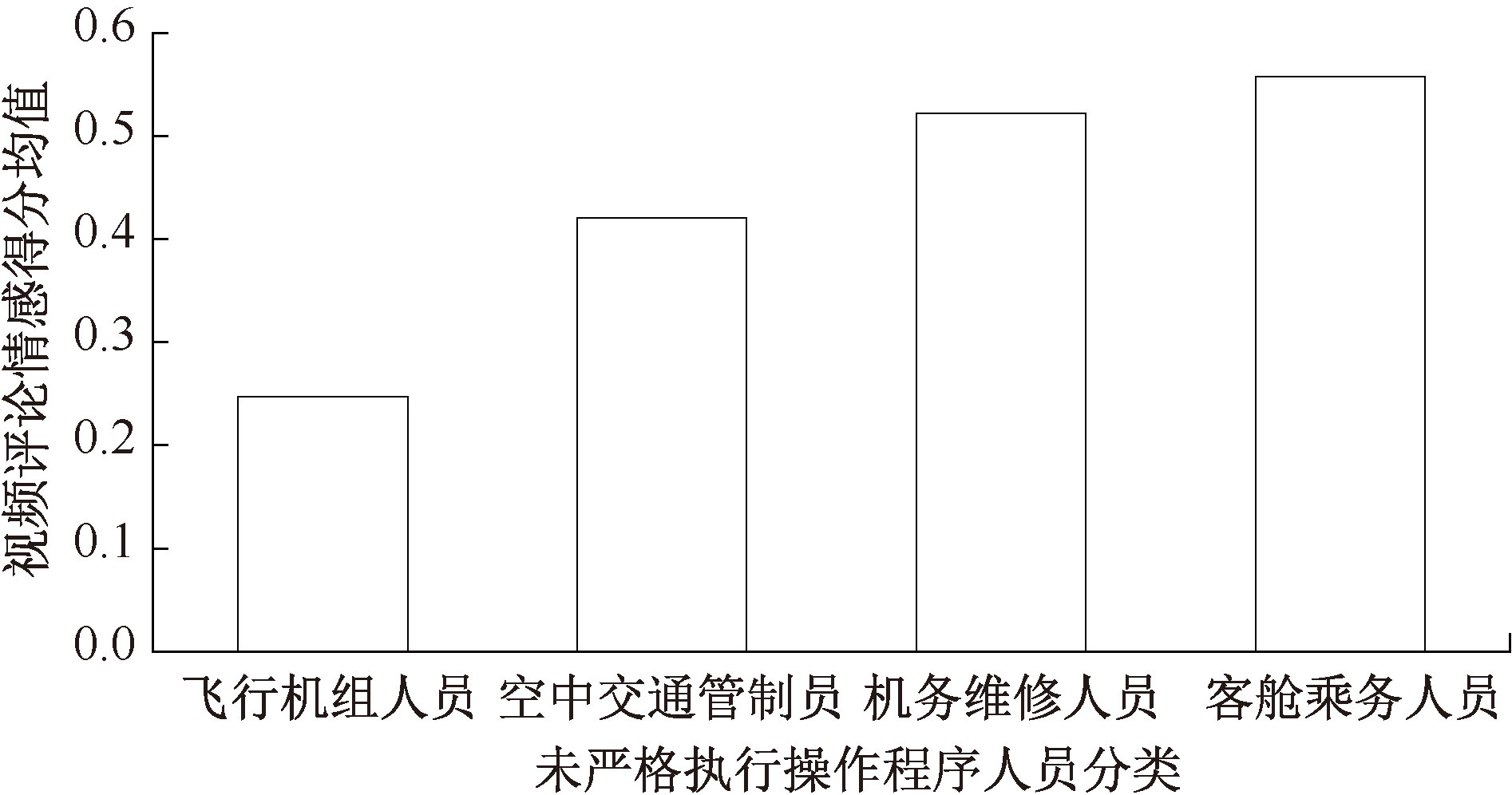
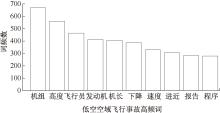
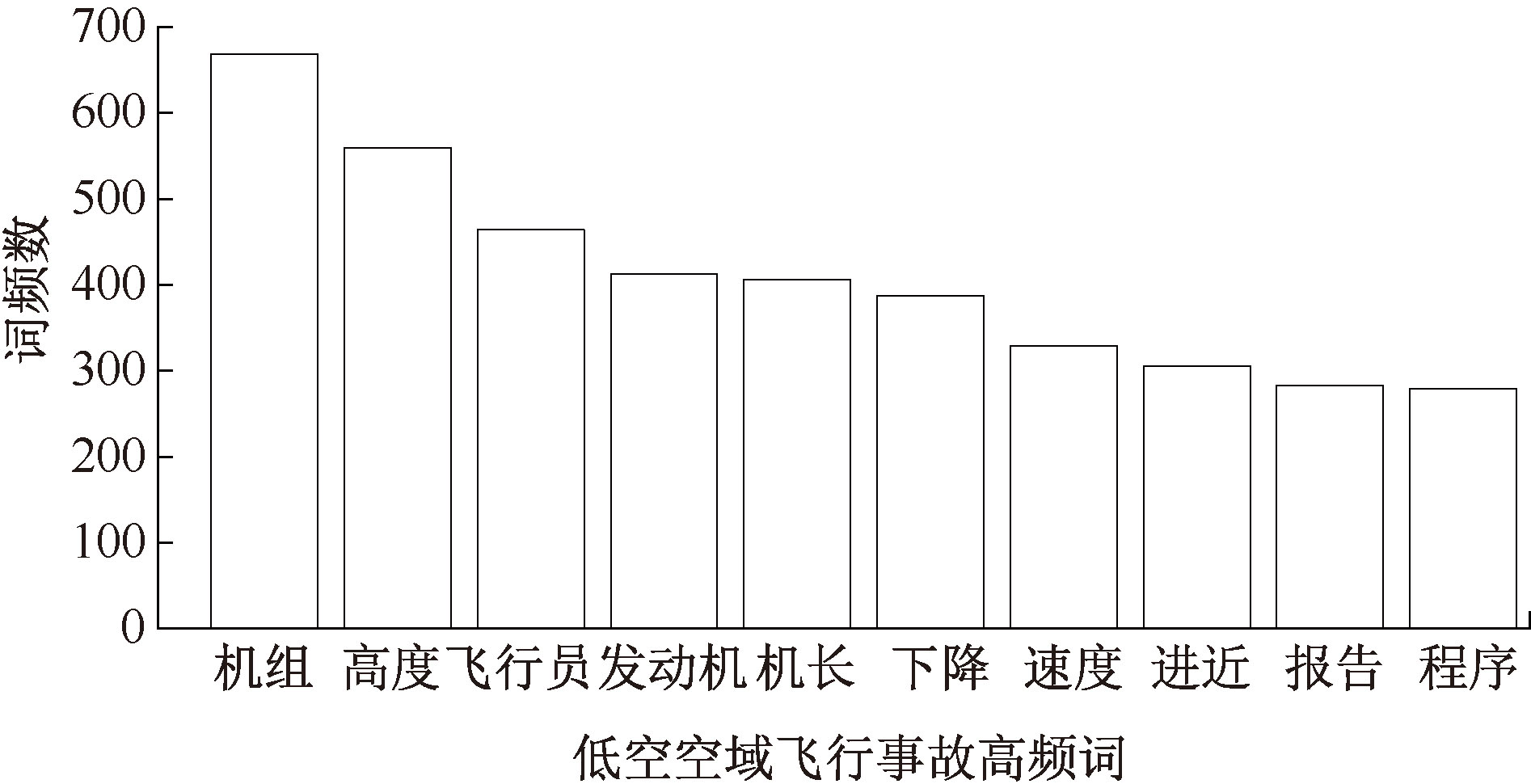
| [1] |
上观新闻. 济州航空事故中的致命因素[EB/OL]. (2024-12-30). https://www.jfdaily.com/wx/detail.do?id=835929.
|
| [2] |
黄静洋, 潘璇, 付小蓉, 等. 中低空通用航空飞行计划安全风险评估[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33 (12):23-30.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.12.1873
|
|
HUANG Jingyang, PAN Xuan, FU Xiaorong, et al. Safety risk assessment for low and medium altitude general aviation fight plans[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023. 33(12):23-30.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.12.1873
|
| [3] |
许保光, 王蓓蓓, 池宏, 等. 基于贝叶斯网络的航空安全中不安全信息分析[J]. 中国管理科学, 2020, 28(12):118-129.
|
|
XU Baoguang, WANG Beibei, CHI Hong, et al. Insecurity information analysis in civil aviation safety based on Bayesian network[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2020, 28(12):118-129.
|
| [4] |
袁乐平, 张文东, 赵力梵, 等. 基于TEM模型的民航不安全事件关联规则挖掘与分析[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2022, 18(10):31-36.
|
|
YUAN Leping, ZHANG Wendong, ZHAO Lifan, et al. Mining and analysis of association rules in civil aviation unsafe incidents based on TEM model[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2022, 18(10):31-36.
|
| [5] |
王红, 祝寒, 林海舟. 航空安全事故因果关系抽取方法的研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2020, 56(11):265-270.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1902-0257
|
|
WANG Hong, ZHU Han, LIN Haizhou. Research on causality extraction of civil aviation accident[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2020, 56(11):265-270.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1902-0257
|
| [6] |
刘俊杰, 杜尹岚, 闫慧娟. Python环境下的航空安全报告信息分析方法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(10):4278-4283.
|
|
LIU Junjie, DU Yinlan, YAN Huijuan. The analysis method of aviation safety reporting information based on Python[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(10):4278-4283.
|
| [7] |
YUAN Leping, LIANG Man, XIE Yiran. Change-oriented risk management in civil aviation operation: a case study in China air navigation service provider[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2020: DOI: 10.1155/2020/4721437.
|
| [8] |
高凡, 徐思佳. 基于BERTopic模型的数字政府治理领域的主题识别与内容分析[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2024, 47(8): 95-106.
|
|
GAO Fan, XU Sijia. Topic identification and content analysis in the field of digital government governance based on BERTopic model[J]. Information Studies: Theory & Application, 2024, 47 (8): 95-106.
|
| [9] |
刘全龙, 张晓霖, 张悦倩, 等. 基于事故致因的标准化煤矿建筑规范库构建[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(5):128-133.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.05.1865
|
|
LIU Quanlong, ZHANG Xiaolin, ZHANG Yueqian, et al. Construction of a database of standardized coal mine building regulation based on accident causation[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(5):128-133.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.05.1865
|
| [10] |
SUNG Y Y, KIM S B. Topical keyphrase extraction with hierarchical semantic networks[J]. Decision Support Systems, 2020,128: DOI: 10.1016/j.dss.2019.113163.
|
| [11] |
YANG N, JO J, JEON M, et al. Semantic and explainable research related recommendation system based on semi-supervised methodology using BERT and LDA models[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022,190: DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.116209.
|
| [12] |
中国民用航空局. 航空器的运行文件[Z]. 2024-12-06.
|