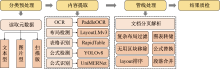
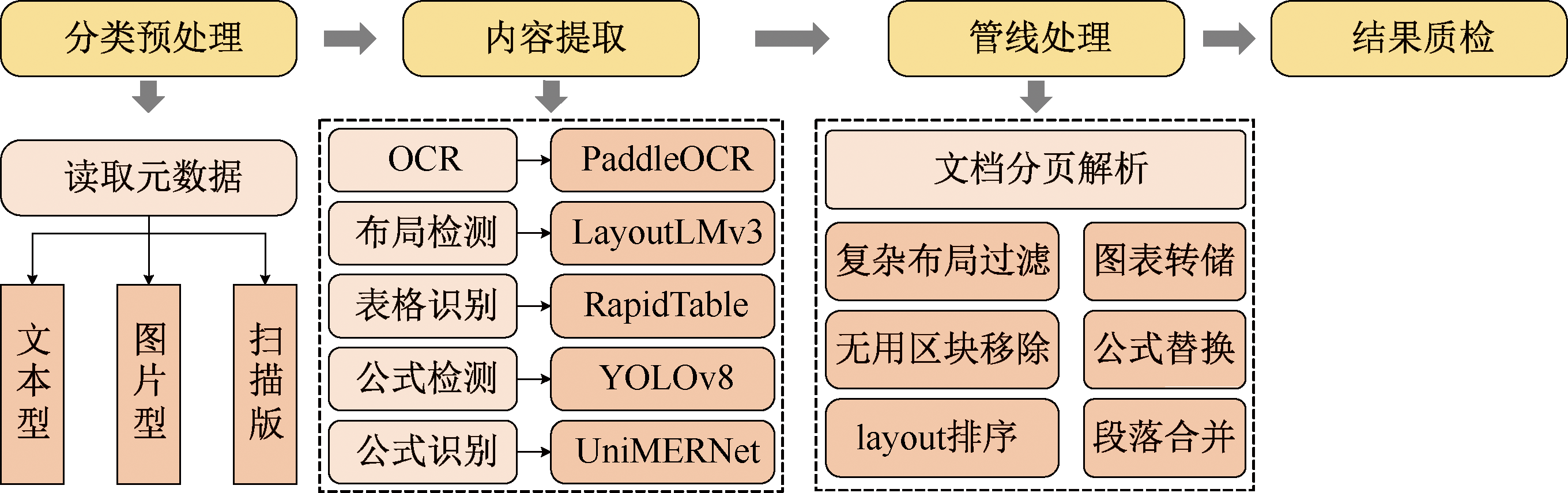
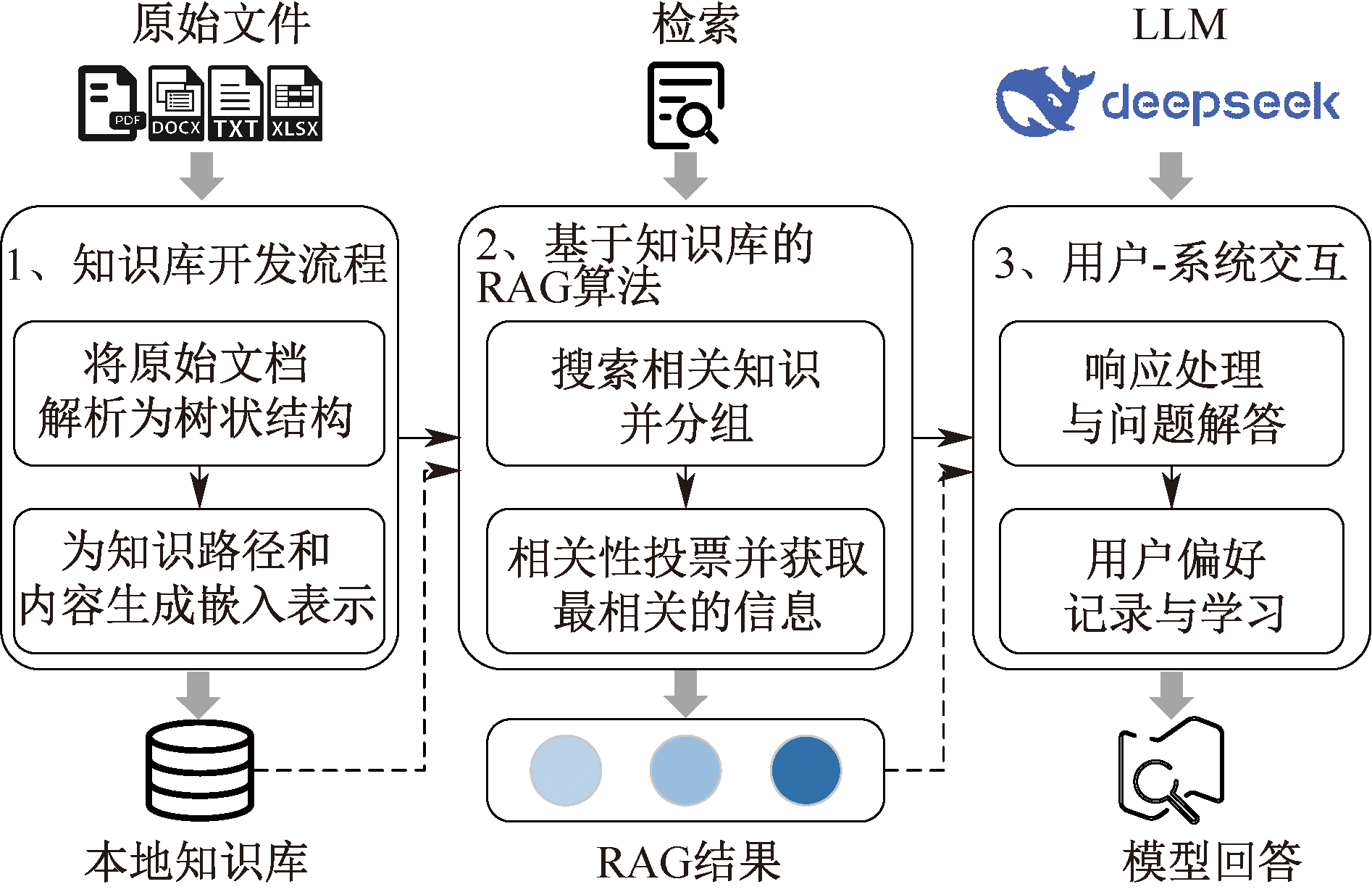
| [1] |
刘瑞祥, 柳先辉, 赵卫东, 等. 基于大语言模型的业务流程自动建模方法[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2025, 31(6):2001-2014.
|
|
LIU Ruixiang, LIU Xianhui, ZHAO Weidong, et al. Automatic business process modeling method based on large language models[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2025, 31(6):2001-2014.
|
| [2] |
朱俊仪, 朱尚明. 利用检索增强生成技术开发本地知识库应用[J]. 通信学报, 2024, 45(增2): 242-247.
|
|
ZHU Junyi, ZHU Shangming. Development of local knowledge base application using retrieval augmented generation technology[J]. Journal on Communications, 2024, 45(S2): 242-247.
|
| [3] |
祝哲, 周文倩, 林婕, 等. 大语言模型技术赋能的应急管理框架[J]. 指挥与控制学报, 2024, 10(6): 677-688.
|
|
ZHU Zhe, ZHOU Wenqian, LIN Jie, et al. Emergency management framework enabled by large language model technology[J]. Journal of Command and Control, 2024, 10(6): 677-688.
|
| [4] |
林鹏, 向云飞, 樊启祥, 等. 基础设施工程安全智能化管控变革、挑战与思考[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(7): 8-19.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.07.0187
|
|
LIN Peng, XIANG Yunfei, FAN Qixiang, et al. Evolution, challenges, and thoughts on intelligent management and control for infrastructure engineering safety[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(7): 8-19.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.07.0187
|
| [5] |
唐海洋, 刘振翼, 陈东平, 等. ChatSOS:基于大语言模型的安全工程知识问答模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(8): 178-185.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.08.1901
|
|
TANG Haiyang, LIU Zhenyi, CHEN Dongping, et al. ChatSOS: large language model-based knowledge Q & A system for safety engineering[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(8): 178-185.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.08.1901
|
| [6] |
王明达, 赵宝熙, 吴志生, 等. 基于大语言模型的燃气事故调查报告实体识别[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2025, 21(2): 139-145.
|
|
WANG Mingda, ZHAO Baoxi, WU Zhisheng, et al. Entity recognition of gas accident investigation reports based on large language model[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2025, 21(2): 139-145.
|
| [7] |
WAN Yuwei, CHEN Zheyuan, LIU Ying, et al. Empowering LLMs by hybrid retrieval-augmented generation for domain-centric Q&A in smart manufacturing[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2025, 65: DOI: 10.1016/j.aei.2025.103212.
|
| [8] |
WU Chengke, DING Wenjun, JIN Qisen, et al. Retrieval augmented generation-driven information retrieval and question answering in construction management[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2025, 65: DOI: 10.1016/j.aei.2025.103158.
|
| [9] |
WONG Saika, ZHENG Chunmo, SU Xing, et al. Construction contract risk identification based on knowledge-augmented language models[J]. Computers in Industry, 2024, 157/158:DOI: 10.1016/j.compind.2024.104082.
|
| [10] |
SUN Jianwen, SHI Wangzi, SHEN Xiaoxuan, et al. Multi-objective math problem generation using large language model through an adaptive multi-level retrieval augmentation framework[J]. Information Fusion, 2025, 119: DOI: 10.1016/j.inffus.2025.103037.
|
| [11] |
REN Tengfei, ZHANG Zhipeng, JIA Bo, et al. Retrieval-augmented generation-aided causal identification of aviation accidents: a large language model methodology[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2025, 278: DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2025.127306.
|
| [12] |
SILVA L, BARBOSA L. Improving dense retrieval models with LLM augmented data for dataset search[J]. Knowledge-based Systems, 2024, 294: DOI: 10.1016/j.knosys.2024.111740.
|
| [13] |
LEE J, AHN S, KIM D, et al. Performance comparison of retrieval-augmented generation and fine-tuned large language models for construction safety management knowledge retrieval[J]. Automation in Construction, 2024, 168:DOI: 10.1016/j.autcon.2024.105846.
|
| [14] |
ZHANG Haiyang, YAN Wei, HU Huicong, et al. An LLM-based knowledge and function-augmented approach for optimal design of remanufacturing process[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2025, 65: DOI: 10.1016/j.aei.2025.103206.
|
| [15] |
JEON J, SIM Y, LEE H, et al. ChatCNC: conversational machine monitoring via large language model and real-time data retrieval augmented generation[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2025, 79: 504-514.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2025.01.018
|
| [16] |
VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 30: DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1706.03762.
|
| [17] |
王文湖, 韦昌法. 基于大语言模型和知识库的阿尔茨海默病智能问答系统构建研究[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2025, 27 (3): 856-866.
|
|
WANG Wenhu, WEI Changfa. Research on the construction of an intelligent question-answering system for alzheimer's disease based on large language models and knowledge bases[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 856-866.
|