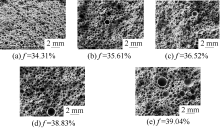
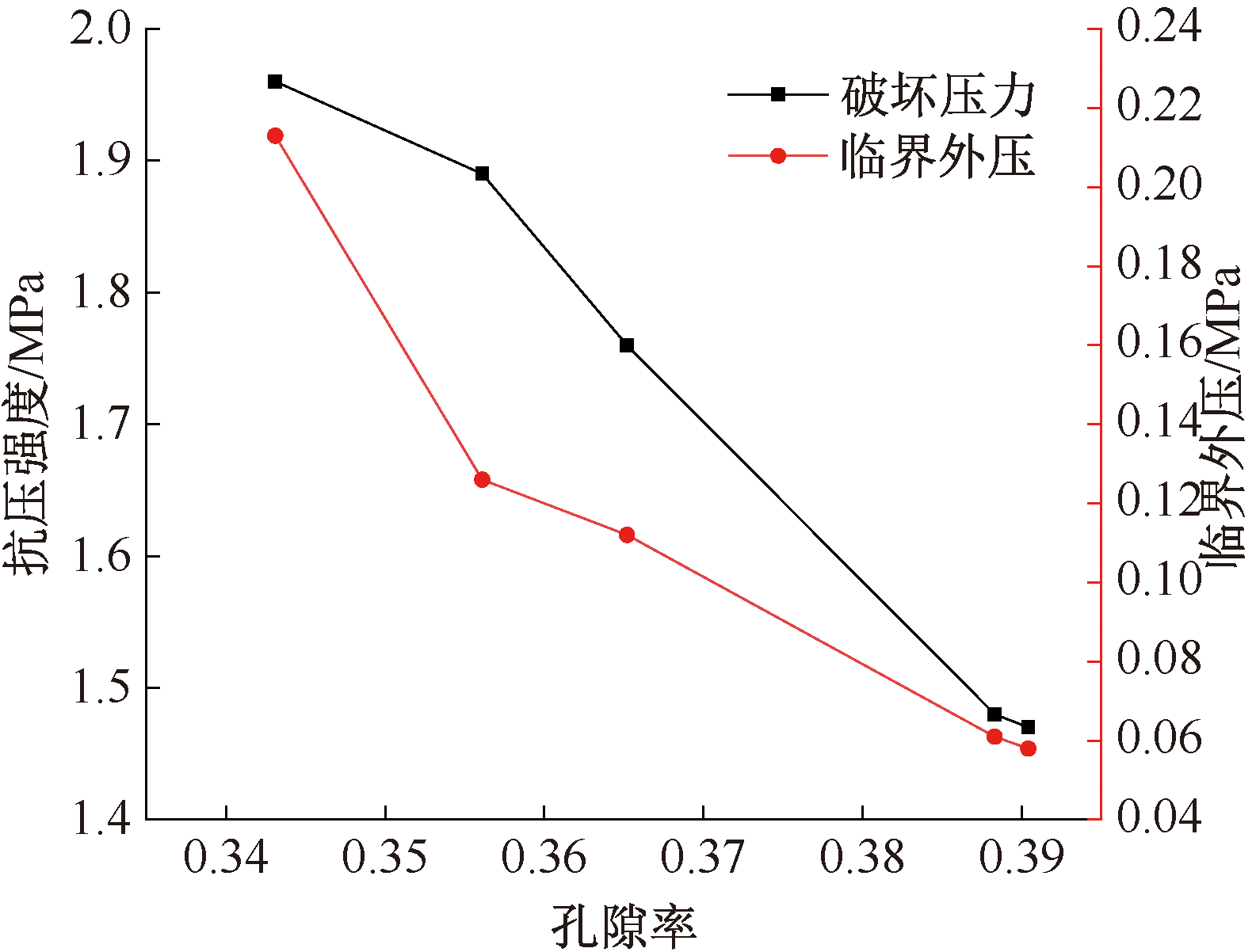
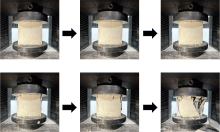
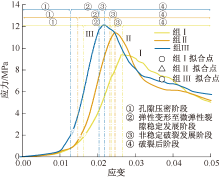
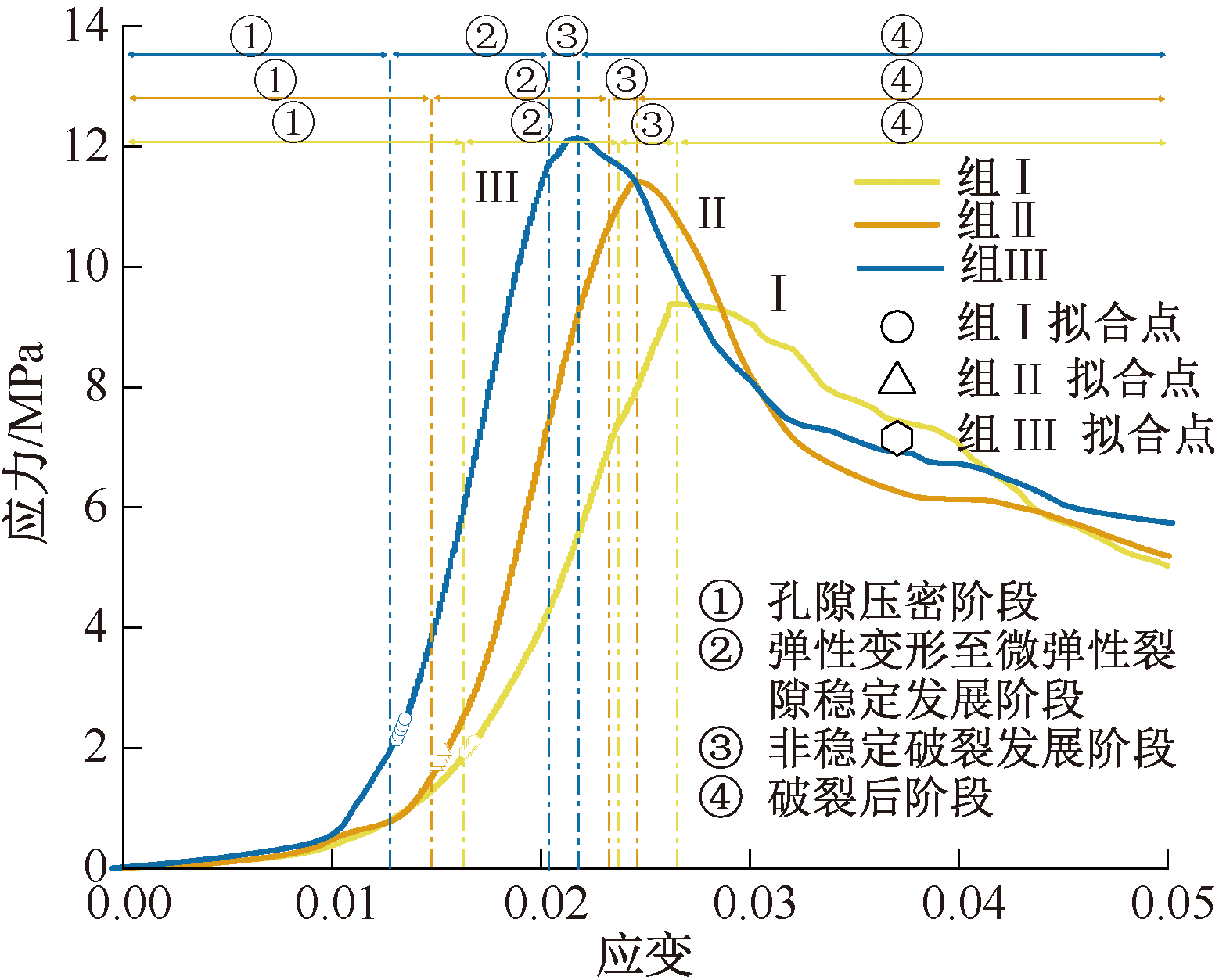
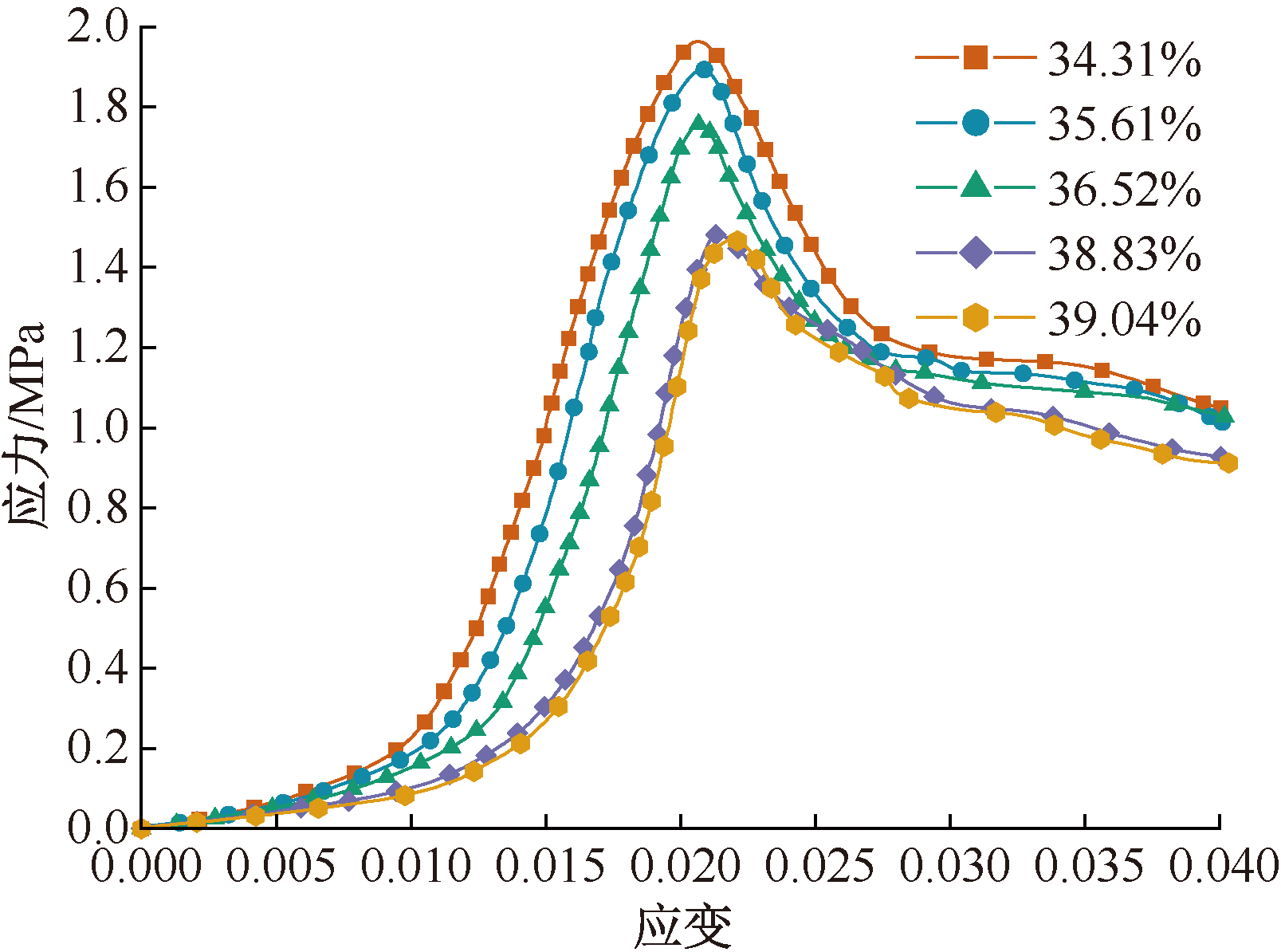
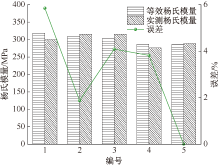
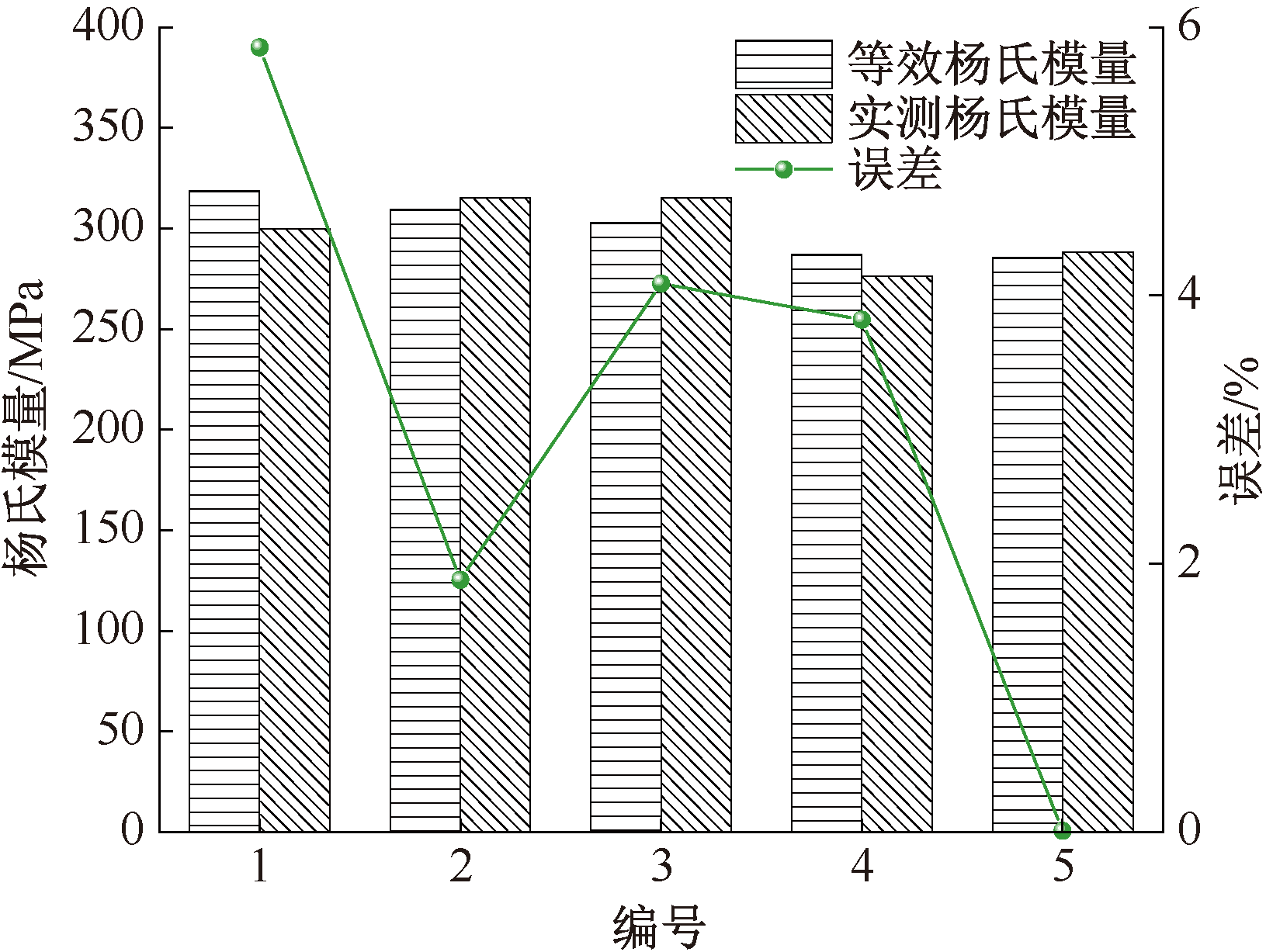
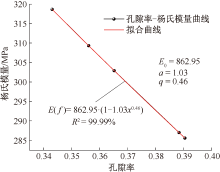
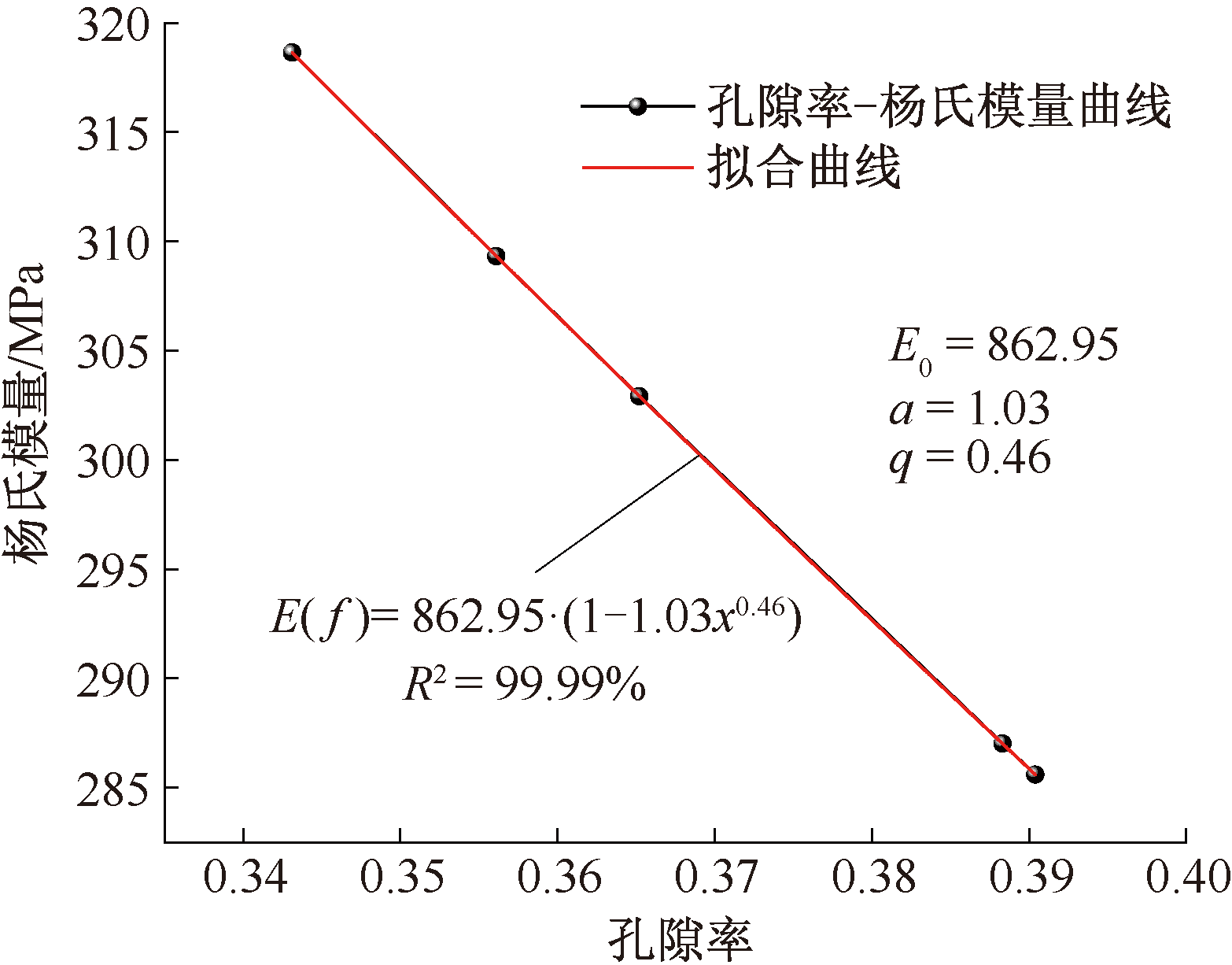
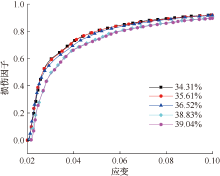
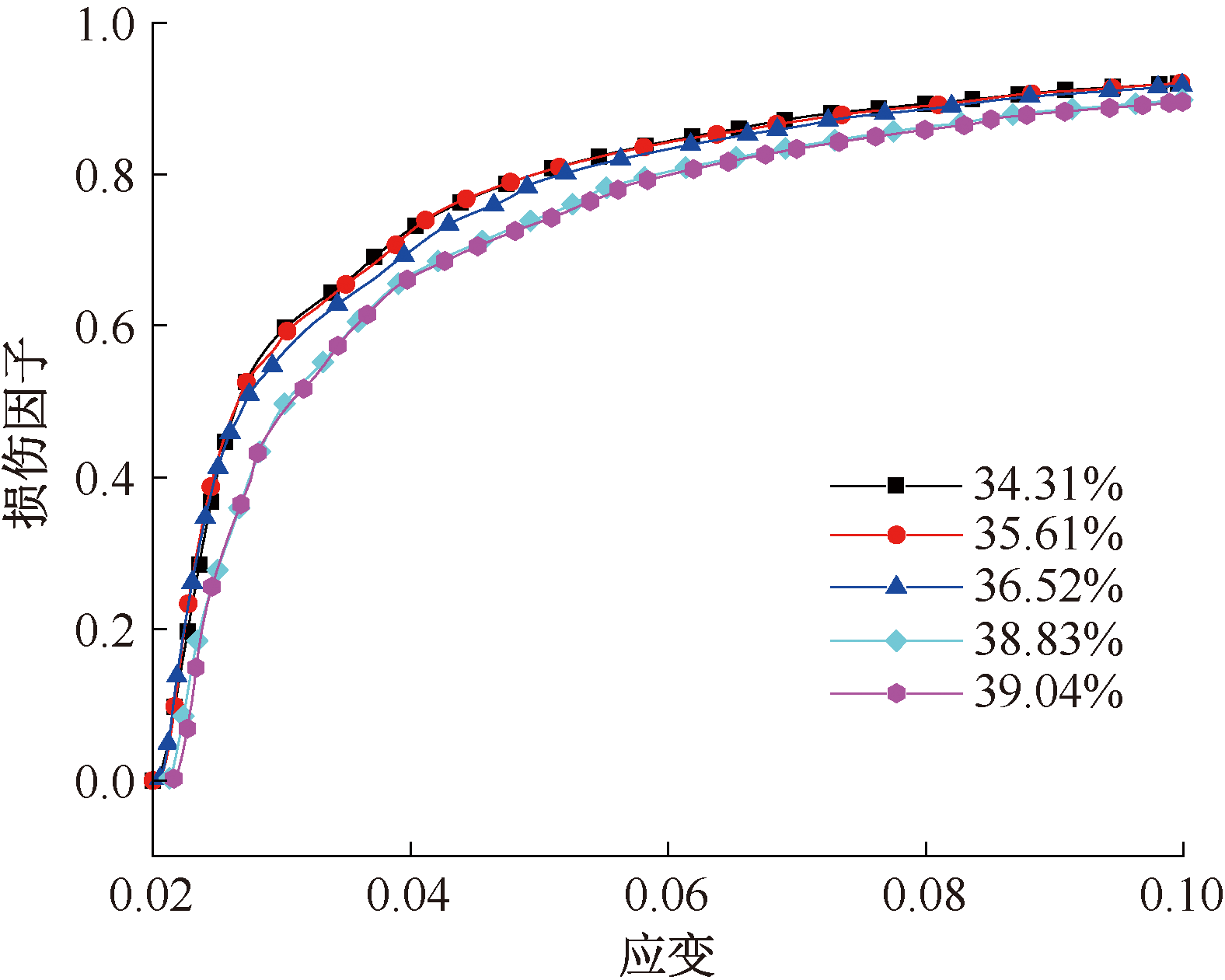
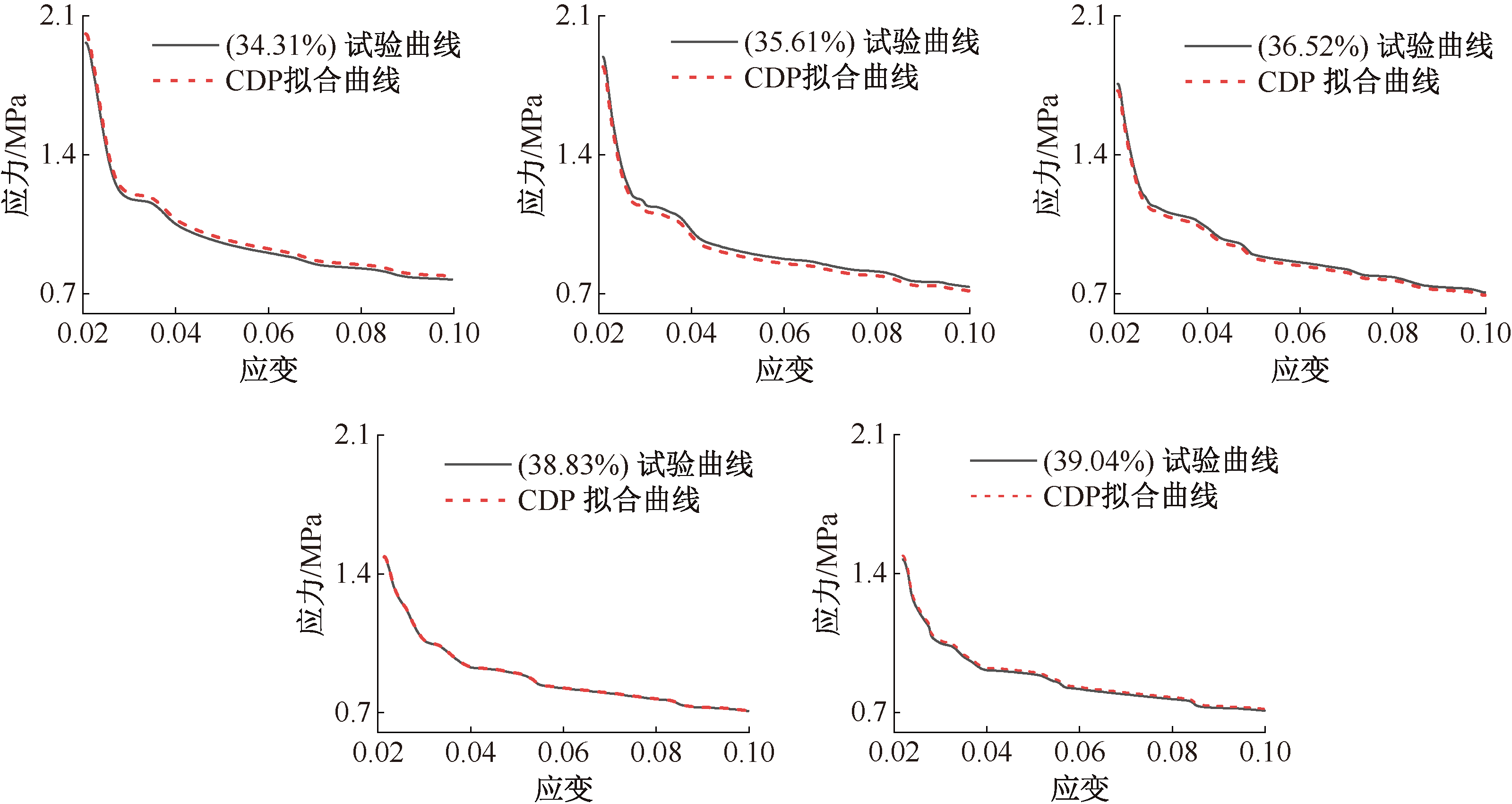
| [1] |
鲁义, 陈健, 邵淑珍, 等. 再生顶板煤自燃漏风裂隙控制机理[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(2):795-805.
|
|
LU Yi, CHEN Jian, SHAO Shuzhen, et al. Control mechanism of air leakage cracks at regenerated roof with coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(2):795-805.
|
| [2] |
吴芳华, 施式亮, 鲁义, 等. 磷石膏基自产气膨胀浆体防灭火性能研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(3):148-154.
|
|
WU Fanghua, SHI Shiliang, LU Yi, et al. Fire prevention and extinguishing performance of phosphogypsum based self-produced gas expansion slurry[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(3):148-154.
|
| [3] |
丁仰卫, 杨海龙, 鲁义, 等. 磷石膏自产气膨胀浆体自膨胀扩散特性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2025, 35(7):82-90.
|
|
DING Yangwei, YANG Hailong, LU Yi, et al. Study on spontaneous expansion and diffusion characteristics of phosphogypsum based self-produced gas expansion slurry[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2025, 35(7):82-90.
|
| [4] |
温小韵, 童雄, 尚江涛, 等. 磷石膏基胶凝材料的力学性能及应用研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2025, 44(3):953-969.
|
|
WEN Xiaoyun, TONG Xiong, SHANG Jiangtao, et al. Progress on application and mechanical properties of phosphogypsum cementitious materials[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2025, 44(3):953-969.
|
| [5] |
周程涛, 陈波, 高志涵, 等. 考虑异形孔的泡沫混凝土单轴压缩离散元模拟[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(7):3726-3736.
|
|
ZHOU Chengtao, CHEN Bo, GAO Zhihan, et al. Discrete element simulation of foam concrete under uniaxial compression considering nonspherical pores[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(7):3726-3736.
|
| [6] |
李方贤, 余其俊, 罗云峰, 等. 泡沫混凝土气孔结构数学表征及其分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2018, 53(6):1205-1210.
|
|
LI Fangxian, YU Qijun, LUO Yunfeng, et al. Mathematical description and analysis on characteristics of pore structure for foam concrete[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(6):1205-1210.
|
| [7] |
|
|
LIU Ziqi, CHEN Gang, SU Zhoucheng, et al. Thermo-mechanical multiphysical properties prediction of fiber-reinforced composites based on micromechanics and machine learning[J/OL]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica:1-17. [2025-03-12]. https://doi.org/10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20250312.001.
|
| [8] |
MORI T, TANAKA K. Average stress in matrix and average elastic energy of materials with misfitting inclusions[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1973, 21(5):571-574.
|
| [9] |
彭鹏, 彭峰, 孙振宇, 等. 基于分形理论和Mori-Tanaka方法的颗粒土渗透注浆加固体性能预测方法及应用[J]. 力学学报, 2022, 54(11):3099-3112.
|
|
PENG Peng, PENG Feng, SUN Zhenyu, et al. Property prediction methods of granular soil penetration grouting reinforced body based on fractal theory and Mori-Tanaka method[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2022, 54(11):3099-3112.
|
| [10] |
GAO Yuan, CHENG Yin, CHEN Jianzhuang. Experimental study and 3-D meso-scale discrete element modeling on the compressive behavior of foamed concrete[J]. Buildings, 2023, 13(3):DOI: 10.3390/buildings13030674.
|
| [11] |
JING Mao, NI Guanhua, XU Yuhang, et al. Modeling and optimization of mechanical properties of drilling sealing materials based on response surface method[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 377:DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134452.
|
| [12] |
DONG Kai, NI Guanhua, XU Yuhang, et al. Effect of optimized pore structure on sealing performance of drilling sealing materials in coal mine[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 274:DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121765.
|
| [13] |
杨澜, 蹇开林, 张亮. 凹凸边界形状热弹性问题的自适应无网格法[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2022, 45(12):36-47.
|
|
YANG Lan, JIAN Kailin, ZHANG Liang, Adaptive meshless method for thermoelastic problems with concave convex boundary[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2022, 45(12):36-47.
|
| [14] |
XIE Jun, SHI Pengpeng, LI Fengjun. Exact solutions for the symmetric elastoplastic response of functionally graded pressure vessels[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 192:DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2023.111165.
|
| [15] |
QU Jianmin, CHERKAOUI M. Fundamentals of Micromechanics of Solids[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2006: 154-195.
|
| [16] |
苏杰. 原位自生颗粒增强铝基复合材料细观力学行为研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2022.
|
|
SU Jie. Research on micromechanics behavior of in-situ particle reinforced aluminum matrix composites[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2022.
|