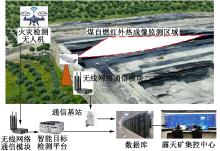
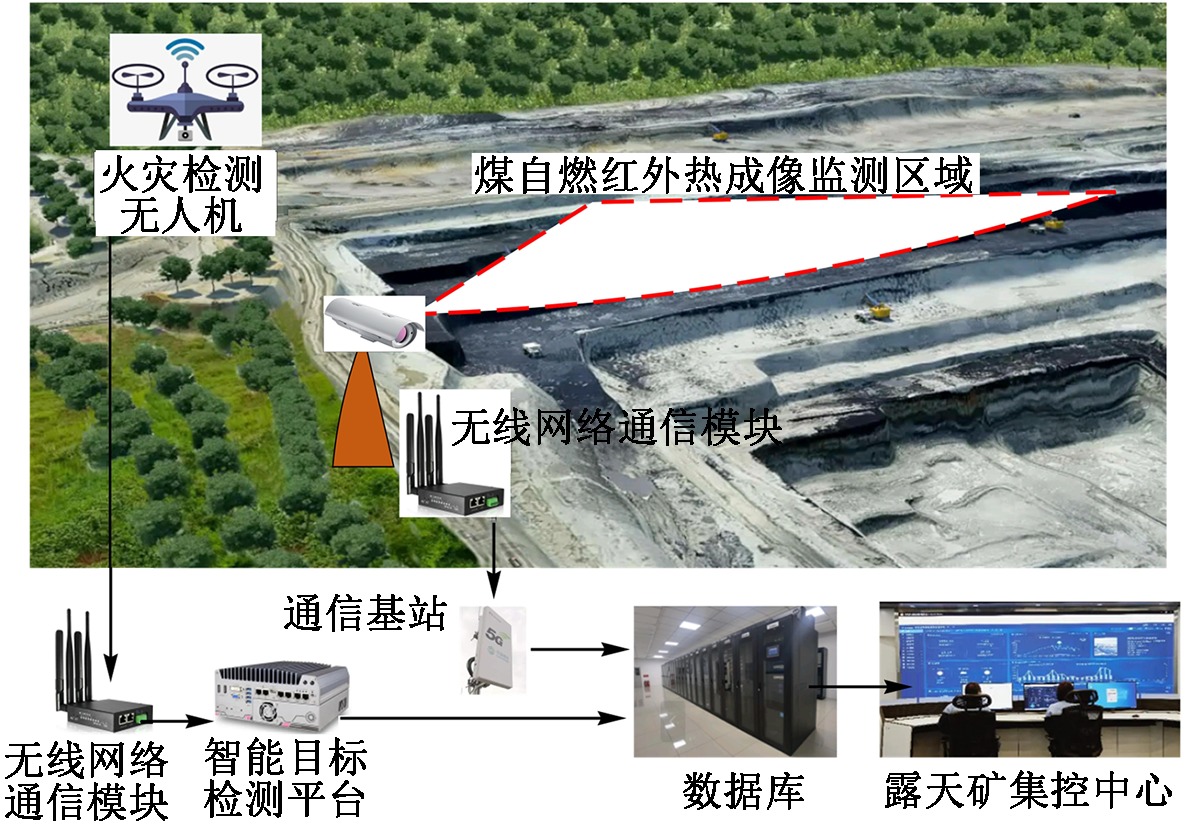
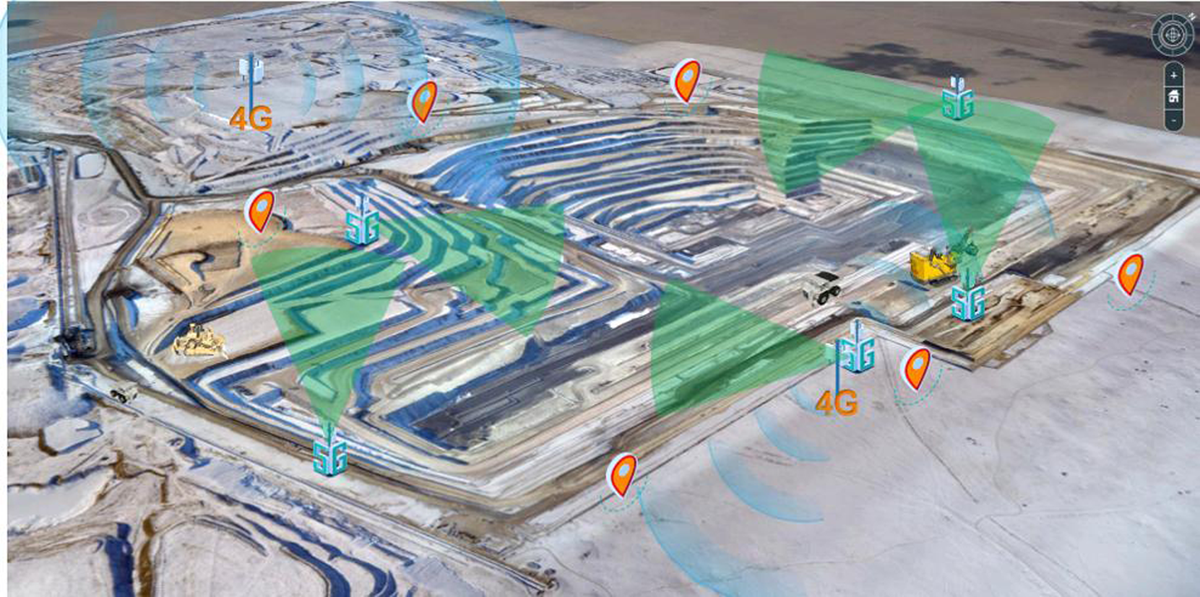
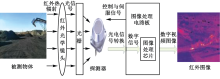
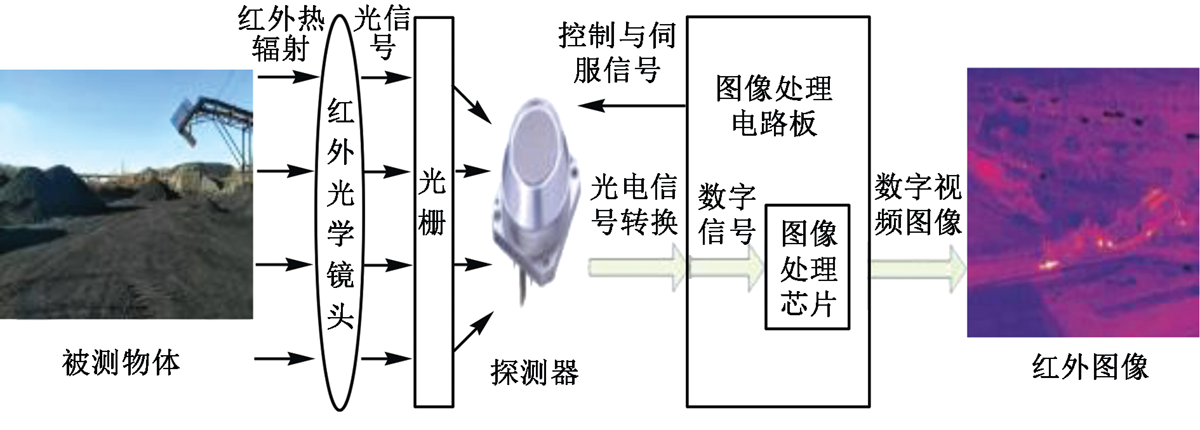
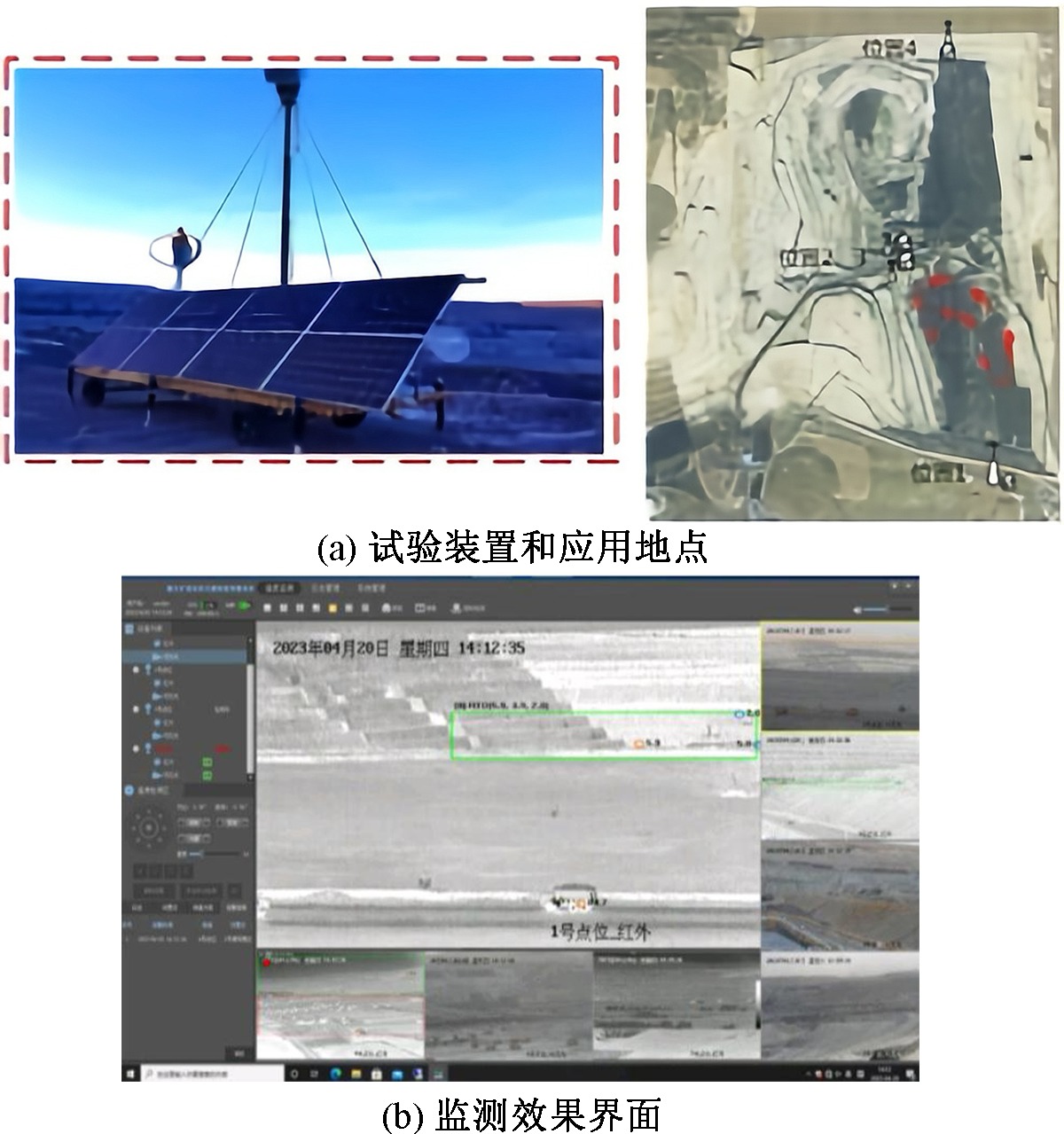
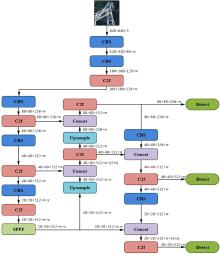
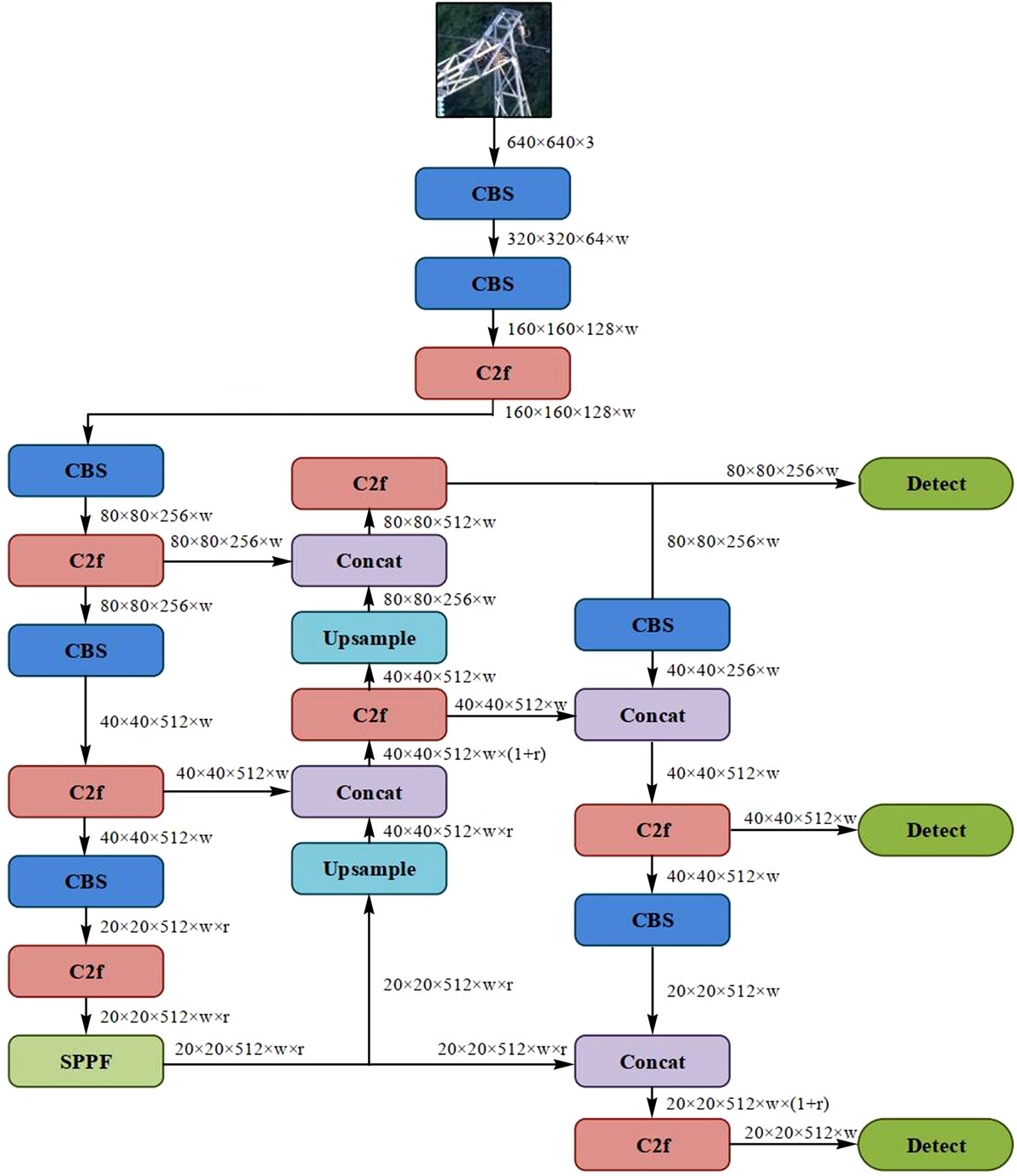
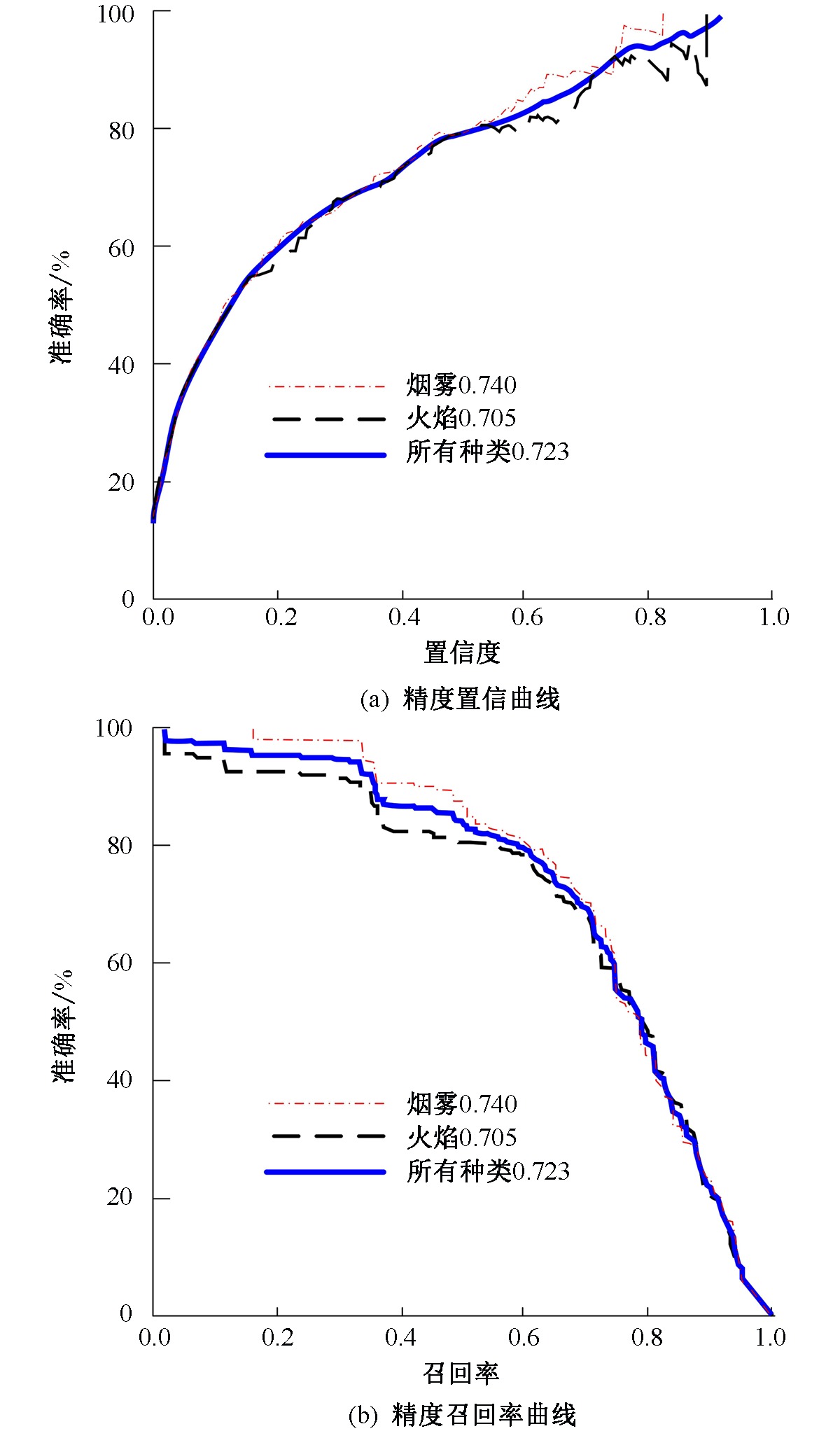
| [1] |
柯丽华, 陈魁香, 胡南燕, 等. 基于SNA的露天矿爆破安全风险评估[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(10):48-56.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.10.2045
|
|
KE Lihua, CHEN Kuixiang, HU Nanyan, et al. Safety risk assessment of blasting in open-pit mine based on SNA[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(10):48-56.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.10.2045
|
| [2] |
尹一雄. 基于数量化理论的露天矿安全风险评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(增1):86-91.
|
|
YIN Yixiong. Safety risk assessment of open-pit mines based on quantitative theory[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(S1):86-91.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.S1.016
|
| [3] |
刘民强, 高小强, 陈钢. 露天矿山无人驾驶运输车辆轨迹防护方法[J]. 工矿自动化, 2022, 48(增1):80-82.
|
|
LIU Minqiang, GAO Xiaoqiang, CHEN Gang. Track protection method of unmanned transport vehicle in open-pit mine[J]. Journal of Mine Automation, 2022, 48(S1):80-82.
|
| [4] |
郭军, 刘华, 金彦, 等. 地下煤自燃隐蔽火源探测方法综述及新技术展望[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(8):111-119.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.08.0296
|
|
GUO Jun, LIU Hua, JIN Yan, et al. Summary of underground hidden coal spontaneous combustion fire source detection methods and prospect of new technologies[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(8):111-119.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.08.0296
|
| [5] |
汪云甲, 原刚, 王腾, 等. 煤田隐蔽火源多源遥感探测研究[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2022, 47(10):1651-1 661.
|
|
WANG Yunjia, YUAN Gang, WANG Teng, et al. Research on multi-source remote sensing detection of concealed fire sources in coal fields[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022, 47(10):1651-1 661.
|
| [6] |
费金彪, 文虎, 金永飞. 测氡法在浅埋煤层火区探测中的应用[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2018, 38(1):26-30.
|
|
FEI Jinbiao, WEN Hu, JIN Yongfei. Application of radon method in detection of fire area in shallow coal seam[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2018, 38(1):26-30.
|
| [7] |
李峰, 刘鸿福, 张新军, 等. 基于分形理论确定地下煤层自燃火区范围[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2013, 41(3):15-17.
|
|
LI Feng, LIU Hongfu, ZHANG Xinjun, et al. Determination of spontaneous combustion extent in coal seams on the basis of the fractal theory[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2013, 41(3):15-17.
|
| [8] |
李鑫, 杨桢, 代爽, 等. 受载复合煤岩破裂表面红外辐射温度变化规律[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(1):110-115.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.01.020
|
|
LI Xin, YANG Zhen, DAI Shuang, et al. Variation routine of surface infrared radiation temperature of composite coal rock in fracture under load[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(1):110-115.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.01.020
|
| [9] |
文虎, 马民, 费金彪. 基于红外成像技术的煤矿火灾治理[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2010, 38(1):28-30.
|
|
WEN Hu, MA Min, FEI Jinbiao. Mine fire disaster control based on infrared imaging technology[J]. Coal Science andTechnology, 2010, 38(1):28-30.
|
| [10] |
曹岂凯. 地质雷达探测技术在浅地表煤田火灾治理中的应用[J]. 能源技术与管理, 2016, 41(5):162-164.
|
|
CAO Qikai. Application of geological radar detection technology in fire control of shallow surface coal field[J]. Energy Technology and Management, 2016, 41(5):162-164.
|
| [11] |
孟峰, 徐煦, 薛国庆, 等. 5G+无人驾驶技术在国能宝日希勒露天煤矿智能化建设中的应用研究[J]. 中国煤炭, 2021, 47(增1):172-182.
|
|
MENG Feng, XU Xu, XUE Guoqiang, et al. Application research of 5G plus driveless technology in intelligent construction of China Energy Baorixile open-pit coal mine[J]. China Coal, 2021, 47(S1):172-182.
|
| [12] |
荣宝, 魏德志, 于海成, 等. 露天煤矿安全生产大数据存储与流式计算技术[J]. 工矿自动化, 2021, 47(增1):101-102.
|
|
RONG Bao, WEI Dezhi, YU Haicheng, et al. Open-pit coal mine safety production big datast orage and streaming computing technology[J]. Industryand Mine Automation, 2021, 47(S1):101-102.
|
| [13] |
付鑫, 郭阳. 基于电力大数据的变电主设备缺陷演化规律红外成像分析方法[J]. 计算技术与自动化, 2024, 43(1):123-128.
|
|
FU Xin, GUO Yang. Infrared imaging analysis method of defect evolution law of substation main equipment based on power big data[J]. Computing Technology and Automation, 2024, 43(1):123-128.
|
| [14] |
王海, 梁剑烽. 基于条件生成对抗网络的实验室红外监控系统[J]. 激光杂志, 2024, 45(3):193-198.
|
|
WANG Hai, LIANG Jianfeng. Laboratory infrared monitoring system based on conditionally generated countermeasure network[J]. Laser Journal, 2024, 45(3):193-198.
|
| [15] |
谢苗, 朱振, 卢进南. 基于红外图像处理技术的托辊卡阻检测方法[J]. 机械设计与研究, 2020, 36(5):152-157.
|
|
XIE Miao, ZHU Zhen, LU Jinnan. Research on detection method of roller jam based on infrared image processing technology[J]. Machine Design & Research, 2020, 36(5):152-157.
|
| [16] |
常捷, 张国维, 陈文江, 等. 基于YOLO-V3算法的加油站不安全行为检测[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(2):31-37.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.02.0298
|
|
CHANG Jie, ZHANG Guowei, CHEN Wenjiang, et al. Gas station unsafe behavior detection based on YOLO-V3 algorithm[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(2):31-37.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.02.0298
|
| [17] |
王海群, 王炳楠, 葛超. 重参数化YOLOv8路面病害检测算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(5):191-199.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2309-0354
|
|
WANG Haiqun, WANG Bingnan, GE Chao. Reparameterized YOLOv8 pavement disease detection algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(5):191-199.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2309-0354
|
| [18] |
王安静, 袁巨龙, 朱勇建, 等. 基于改进YOLOv8s的鼓形滚子表面缺陷检测算法[J]. 浙江大学学报:工学版, 2024, 58(2):370-380.
|
|
WANG Anjing, YUAN Julong, ZHU Yongjian, et al. Drum roller surface defect detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv8s[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Engineering Science, 2024, 58(2):370-380.
|