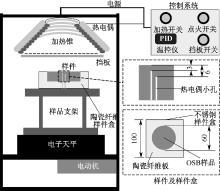
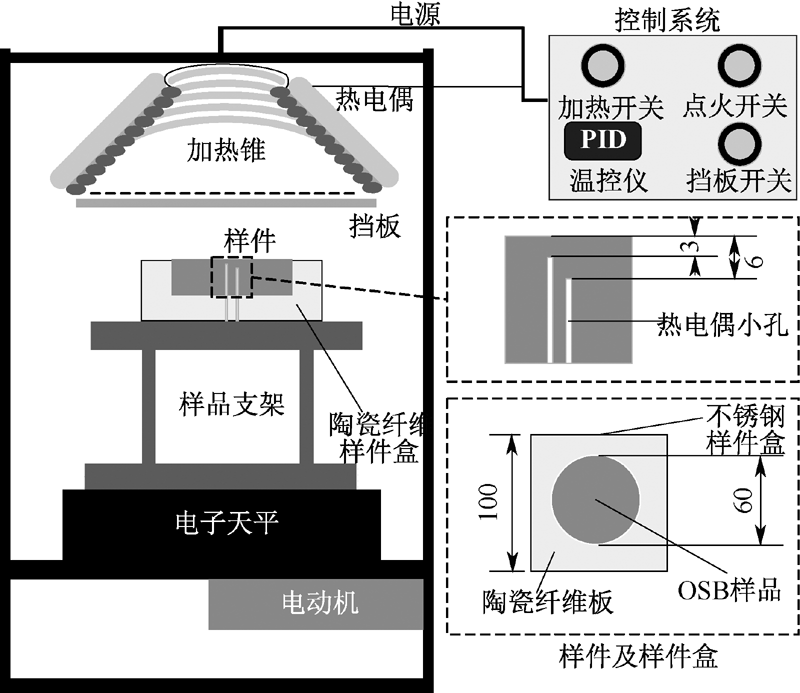
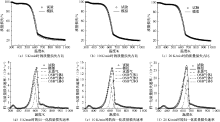
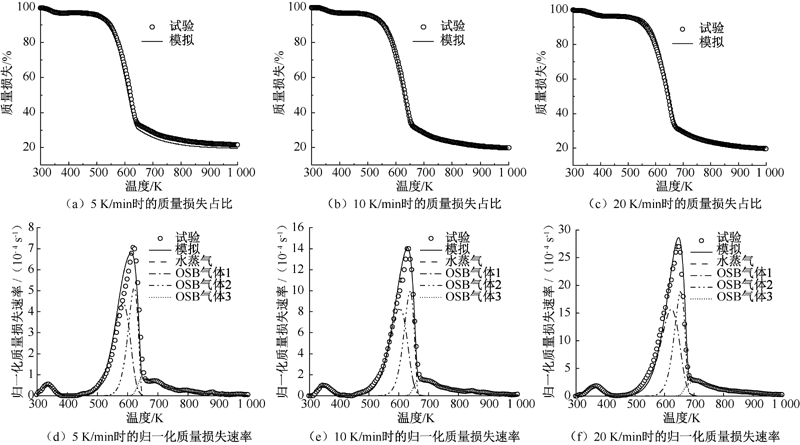
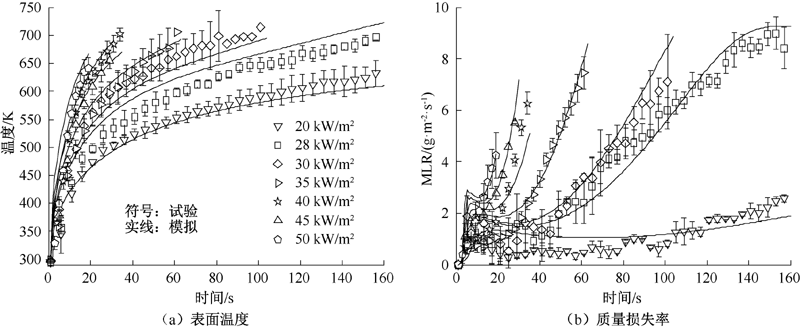
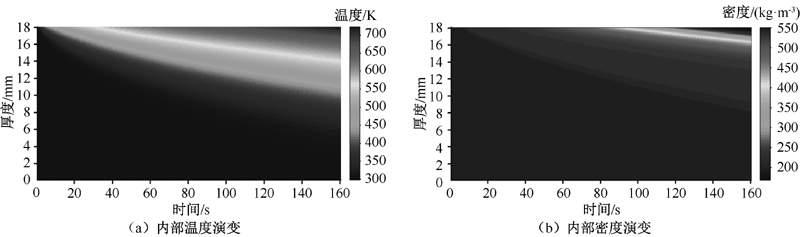
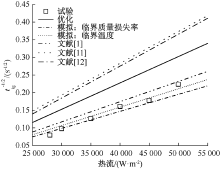
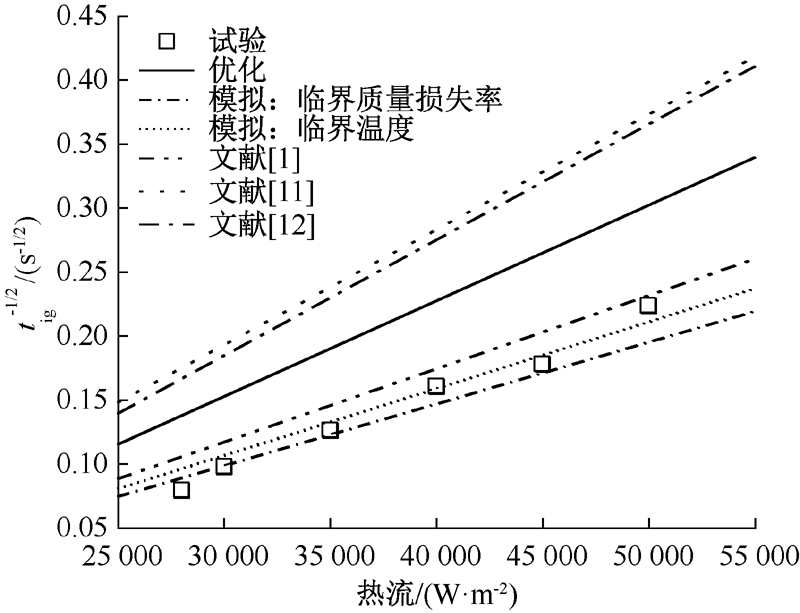
| [1] |
HABERLE I, SKREIBERG, ŁAZAR J, et al. Numerical models for thermochemical degradation of thermally thick woody biomass, and their application in domestic wood heating appliances and grate furnaces[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2017,63:204-252.
|
| [2] |
张宇, 母军, 李思锦, 等. 阻燃剂硼酸-硼砂对杨木定向刨花板热解特性的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(1):127-133.
|
|
ZHANG Yu, MU Jun, LI Sijin, et al. The effect of boric acid-borax on the pyrolysis characteristics of poplar oriented strand board[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2015, 37(1):127-133.
|
| [3] |
岳海玲, 杨守生. 刨花板及其木质原材料燃烧热解特性对比试验[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2012, 22(1):46-52.
|
|
YUE Hailing, YANG Shousheng. Comparative experiments on pyrolysis and combustion properties between particle board and its wood raw materials[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2012, 22(1):46-52.
|
| [4] |
QUINTIERE J G, HARKLEROAD M, WALTON D. Measurement of material flame spread properties[J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 1983, 32(1/2/3/4):67-89.
doi: 10.1080/00102208308923653
|
| [5] |
WASAN S R, HEES P V, MERCI B. Study of pyrolysis and upward flame spread on charring materials—part I: experimental study[J]. Fire and Materials, 2011, 35(4):209-229.
doi: 10.1002/fam.1047
|
| [6] |
丁彦铭, 张雪婷, 杜文州, 等. 基于多组分热解气体的炭化可燃物燃烧模拟[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(9):155-163.
|
|
DING Yanming, ZHANG Xueting, DU Wenzhou, et al. Simulation of charring solid combustion based on multiple pyrolysis gases[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(9):155-163.
|
| [7] |
GONG Junhui, CHEN Yixuan, JIANG Juncheng, et al. A numerical study of thermal degradation of polymers: surface and in-depth absorption[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016,106:1366-1379.
|
| [8] |
GONG Junhui, GU Youmin, ZHAI Chunjie, et al. A hybrid pyrolysis mechanism of phenol formaldehyde and kinetics evaluation using isoconversional methods and genetic algorithm[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2020,690:DOI:10.1016/j.tca.2020.178708.
|
| [9] |
RICHTER F, REIN G. Heterogeneous kinetics of timber charring at the microscale[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2018, 138:1-9.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2018.11.019
|
| [10] |
BOONMEE N, QUINTIERE J G. Glowing and flaming autoignition of wood[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2002, 29(1): 289-296.
doi: 10.1016/S1540-7489(02)80039-6
|
| [11] |
BÁEZ S, VASCO D A, DÍAZ A, et al. Computational study of transient conjugate conductive heat transfer in light porous building walls[J]. Ingeniare, 2017, 25(4):654-661.
|
| [12] |
MEALY C, BOEHMER H, SCHEFFEY J L, et al. Characterization of the flammability and thermal decomposition properties of aircraft skin composite materials and combustible surrogates[R]. U.S. Department of Transportation Federal Aviation Administration, 2014.
|
| [13] |
YUEN R, CASEY R, DAVIS G D, et al. A three-dimensional mathematical model for the pyrolysis of wet wood[J]. Fire Safety Science, 1997,5:189-200.
|
| [14] |
ANCA-COUCE A, ZOBEL N, BERGER A, et al. Smouldering of pine wood: kinetics and reaction heats[J]. Combustion & Flame, 2012, 159(4):1708-1719.
|
| [15] |
LAUTENBERGER C, FERNANDEZ-PELLO C. A model for the oxidative pyrolysis of wood[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2009, 156(8):1503-1513.
doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2009.04.001
|
| [16] |
SAND U, SANDBERG J, LARFELDT J, et al. Numerical prediction of the transport and pyrolysis in the interior and surrounding of dry and wet wood log[J]. Applied Energy, 2008, 85(12):1208-1224.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2008.03.001
|
| [17] |
ZHAI Chunjie, GONG Junhui, ZHOU Xiaodong, et al. Pyrolysis and spontaneous ignition of wood under time-dependent heat flux[J]. Journal of Analytical & Applied Pyrolysis, 2017, 125(5):100-108.
|
| [18] |
DING Yanming, WANG Changjian, LU Shouxiang. Modeling the pyrolysis of wet wood using FireFOAM[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2015, 98(7):500-506.
doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2015.03.106
|
| [19] |
DELICHATSIOS M A. Ignition times for thermally thick and intermediate conditions in flat and cylindrical geometries[J]. Fire Safety Science, 2000,6:233-244.
|