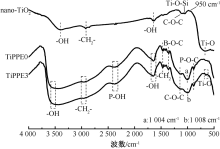
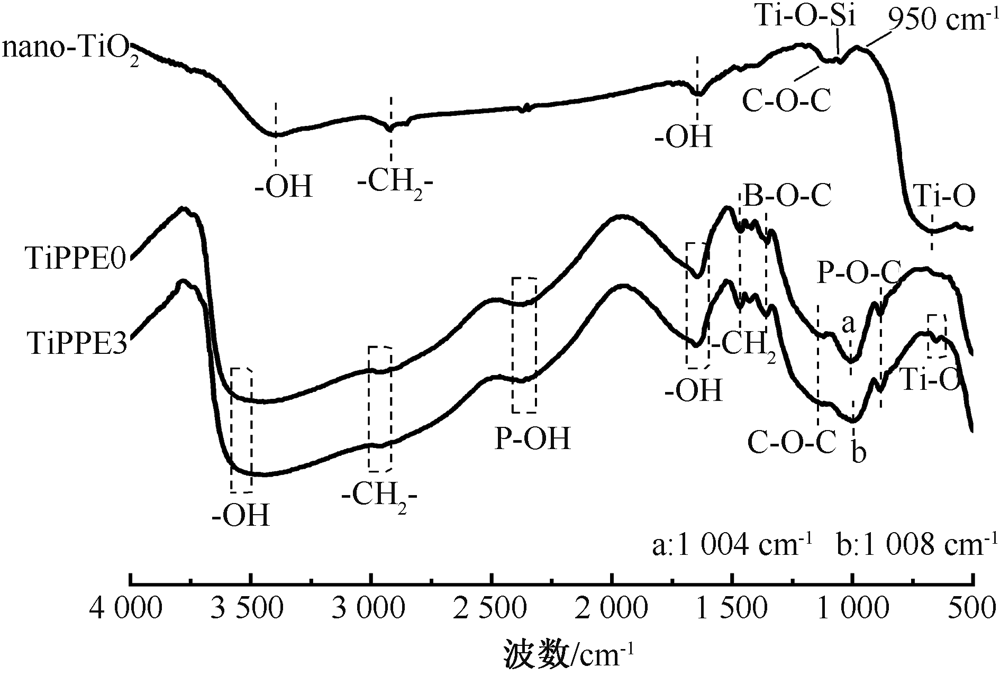
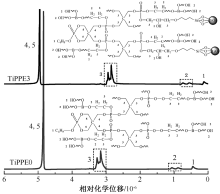
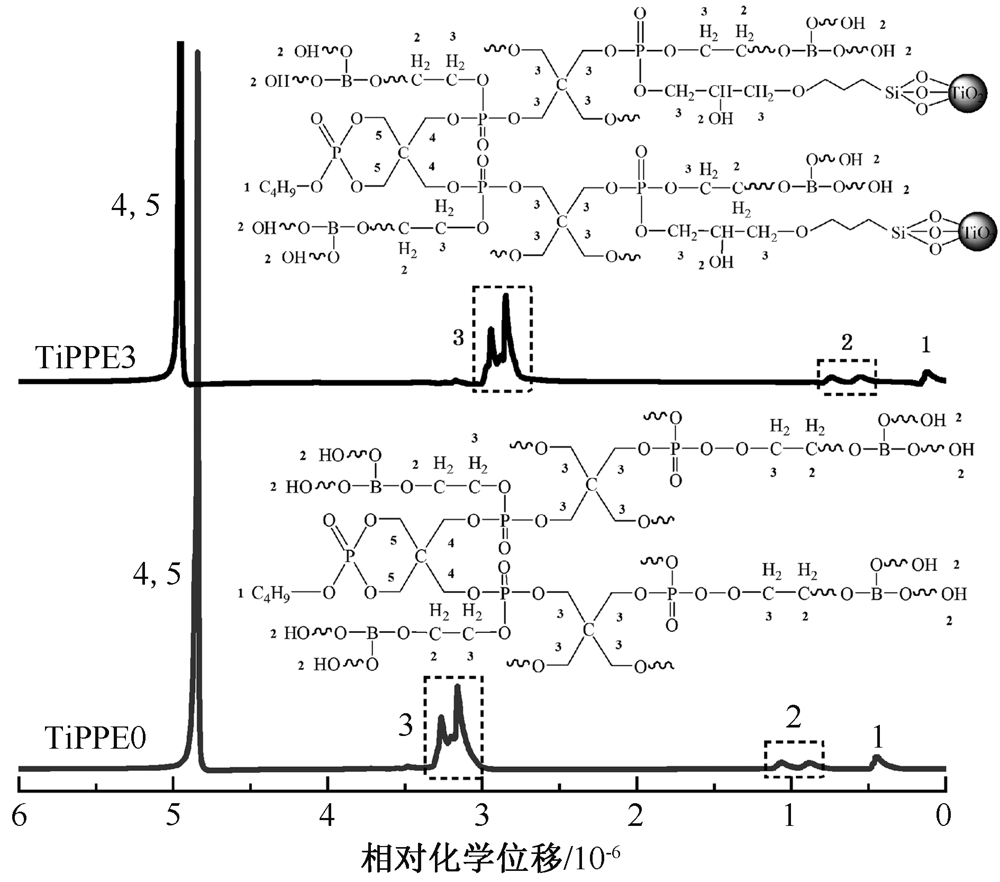
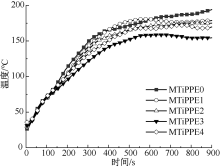
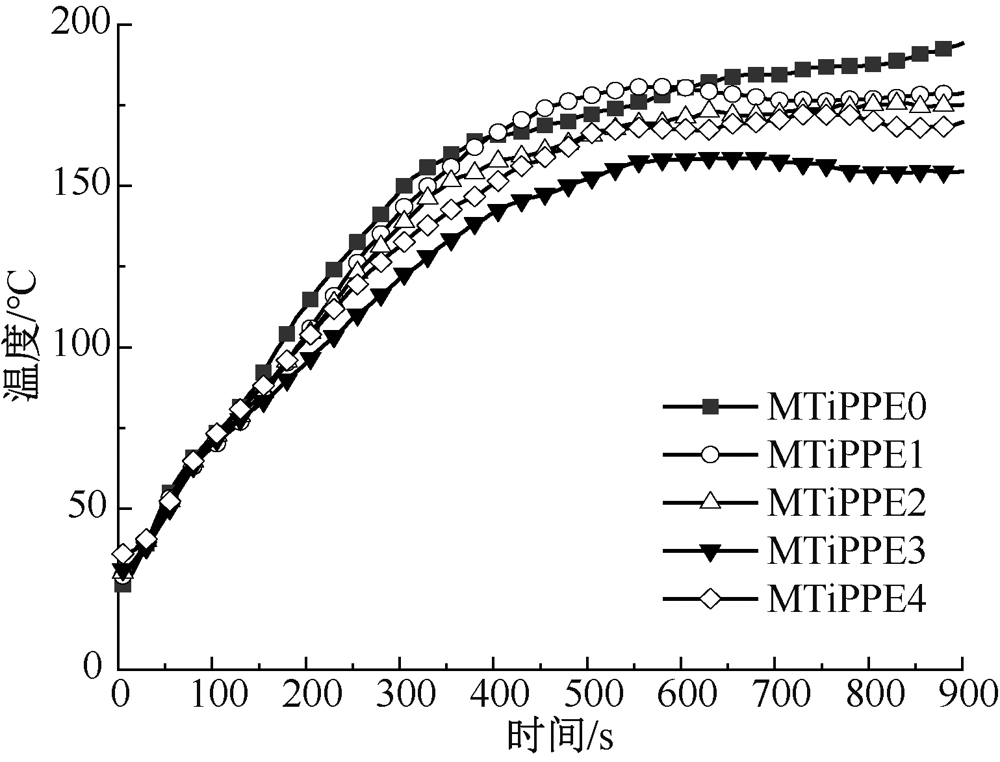
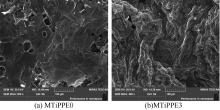
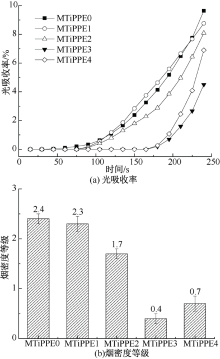
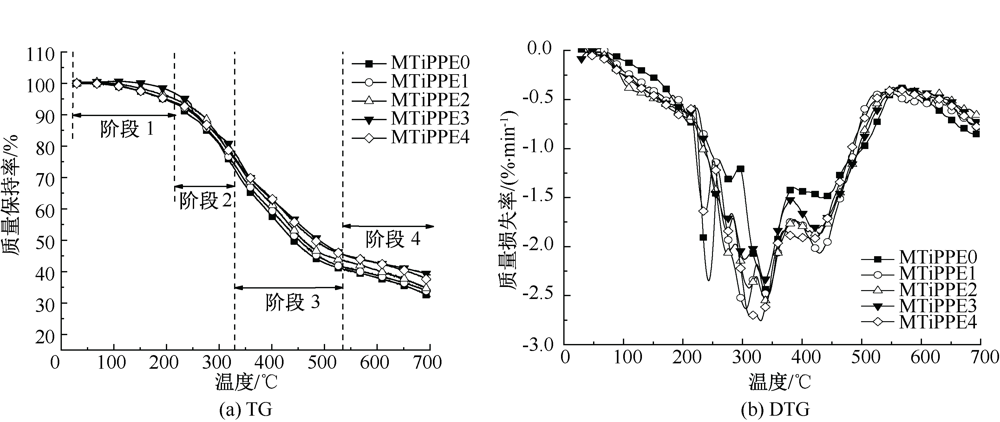
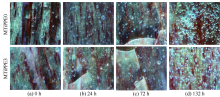
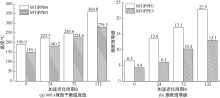
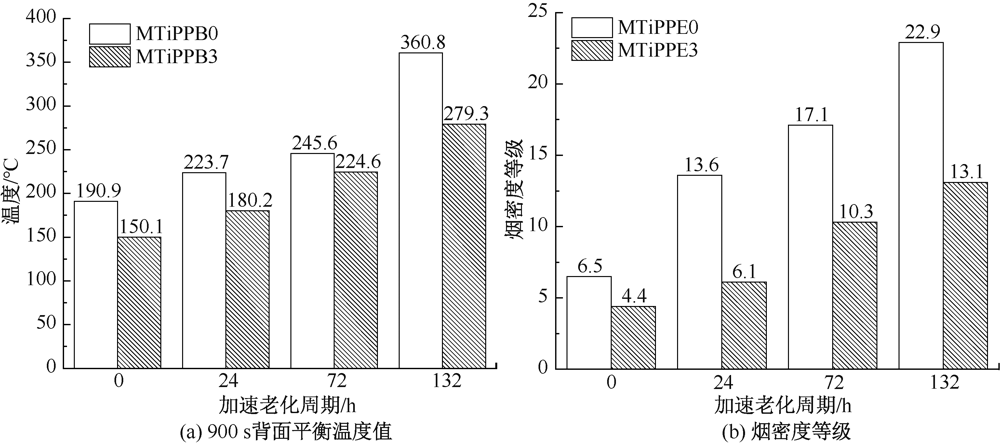
| [1] |
颜龙, 徐志胜, 刘顶立. 膨胀型透明防火涂料的设计制备、性能及阻燃抑烟机理[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2020:38-39.
|
| [2] |
方园, 赵华伟, 张冰洁, 等. 纳米TiO2改性环氧涂层对玻璃纤维/不饱和聚酯复合材料紫外-凝露老化特性的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(5):1407-1415.
|
|
FANG Yuan, ZHAO Huawei, ZHANG Bingjie, et al. Effect of nano TiO2 modified epoxy coating on UV-condensation aging characteristics of glass fiber/unsaturated polyester composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(5):1407-1415.
|
| [3] |
胡肖, 颜龙, 黄傲, 等. 磷系阻燃剂在透明防火涂料中的应用研究进展[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2021, 40(7):1061-1064.
|
|
HU Xiao, YAN Long, HUANG Ao, et al. Progress in research and application of phosphorous flame retardants in transparent fire-retardant coatings[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2021, 40(7):1061-1064.
|
| [4] |
YAN Long, XU Zhisheng, DENG Nan. Effects of polyethylene glycol borate on the flame retardancy and smoke suppression properties of transparent fire-retardant coatings applied on wood substrates[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2019, 135:123-134.
doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.05.043
|
| [5] |
ZHOU Jianping, TAN Zhongyuan, LIU Zhilei, et al. Preparation of transparent fluorocarbon/TiO2-SiO2 composite coating with improved self-cleaning performance and anti-aging property[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 396:161-168.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.11.014
|
| [6] |
BEHESHTI A, HERIS S Z. Experimental investigation and characterization of an efficient nanopowder-based flame retardant coating for atmospheric-metallic substrates[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 269:22-29.
doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.08.048
|
| [7] |
DI Jianfeng, XU Jia, DU Wenqin. Study on flame retardant and anti-UV finishing technology of cotton knitted fabric[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2011, 694:820-823.
doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.694.820
|
| [8] |
张安振, 张建春, 孔祥荣, 等. 超薄型钢结构防火卷材的研制及性能测试[J]. 涂料工业, 2016, 46(8):19-22.
|
|
ZHANG Anzhen, ZHANG Jianchun, KONG Xiangrong, et al. Preparation and property of ultrathin fire resistant steel structure[J]. Paint & Coatings Industry, 2016, 46(8):19-22.
|
| [9] |
JULIEN Loste, JOSE-MARIE Lopez-Cuesta, LAURENT Billon, et al. Transparent polymer nanocomposites: an overview on their synthesis and advanced properties[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2019, 89:133-158.
doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2018.10.003
|
| [10] |
GB 12441—2018,饰面型防火涂料[S].
|
|
GB 12441-2018, Finishing fire retardant paint[S].
|
| [11] |
ASTM E84-12b, Standard test method for surface burning characteristics of building materials[S]. 2012.
|
| [12] |
GB/T 8627—2007,建筑材料燃烧或分解的烟密度试验方法[S].
|
|
GB/T 8627-2007,Smoke density test method for burning or decomposition of building materials[S].
|
| [13] |
ASTM G154—2006,非金属材料荧光紫外曝露设备的操作标准[S].
|
|
ASTM G154-2006, Standard practice for operating xenon arc light apparatus for exposure of non-metallic materials[S].
|
| [14] |
ZHU Peng, LIU Bing, BAO Limin. Preparation of double-coated TiO2 nanoparticles using an anchoring grafting method and investigation of the UV resistance of its reinforced PEI film[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2017, 104:81-90.
doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2016.12.009
|
| [15] |
徐志胜, 周寰, 颜龙, 等. 硼酸三聚氰胺在膨胀型防火涂料中的协同作用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(12):40-45.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.12.007
|
|
XU Zhisheng, ZHOU Huan, YAN Long, et al. Synergistic effect of melamine borate in intumescent fire-retardant coatings[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(12):40-45.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.12.007
|
| [16] |
李耀庄, 冯钰微, 徐志胜, 等. 蛤蜊壳在膨胀型防火涂料中的阻燃和抑烟作用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(7):41-47.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.07.007
|
|
LI Yaozhuang, FENG Yuwei, XU Zhisheng, et al. Effect of clam shell bio-filler on flame retardancy and smoke suppression properties of intumescent fire retardant coatings[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(7):41-47.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.07.007
|