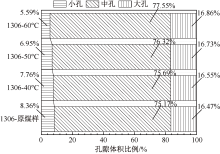
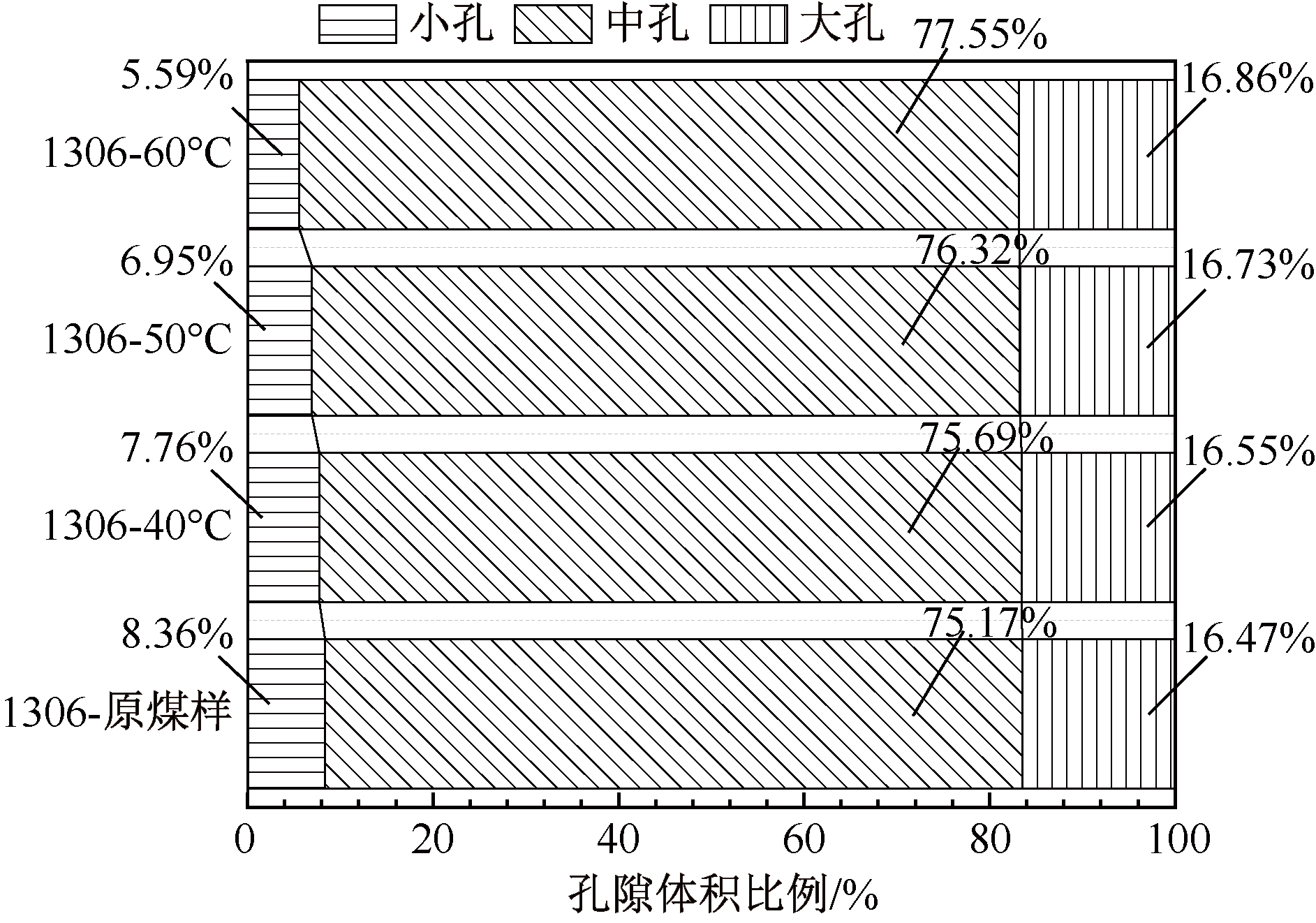
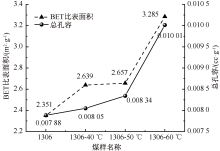
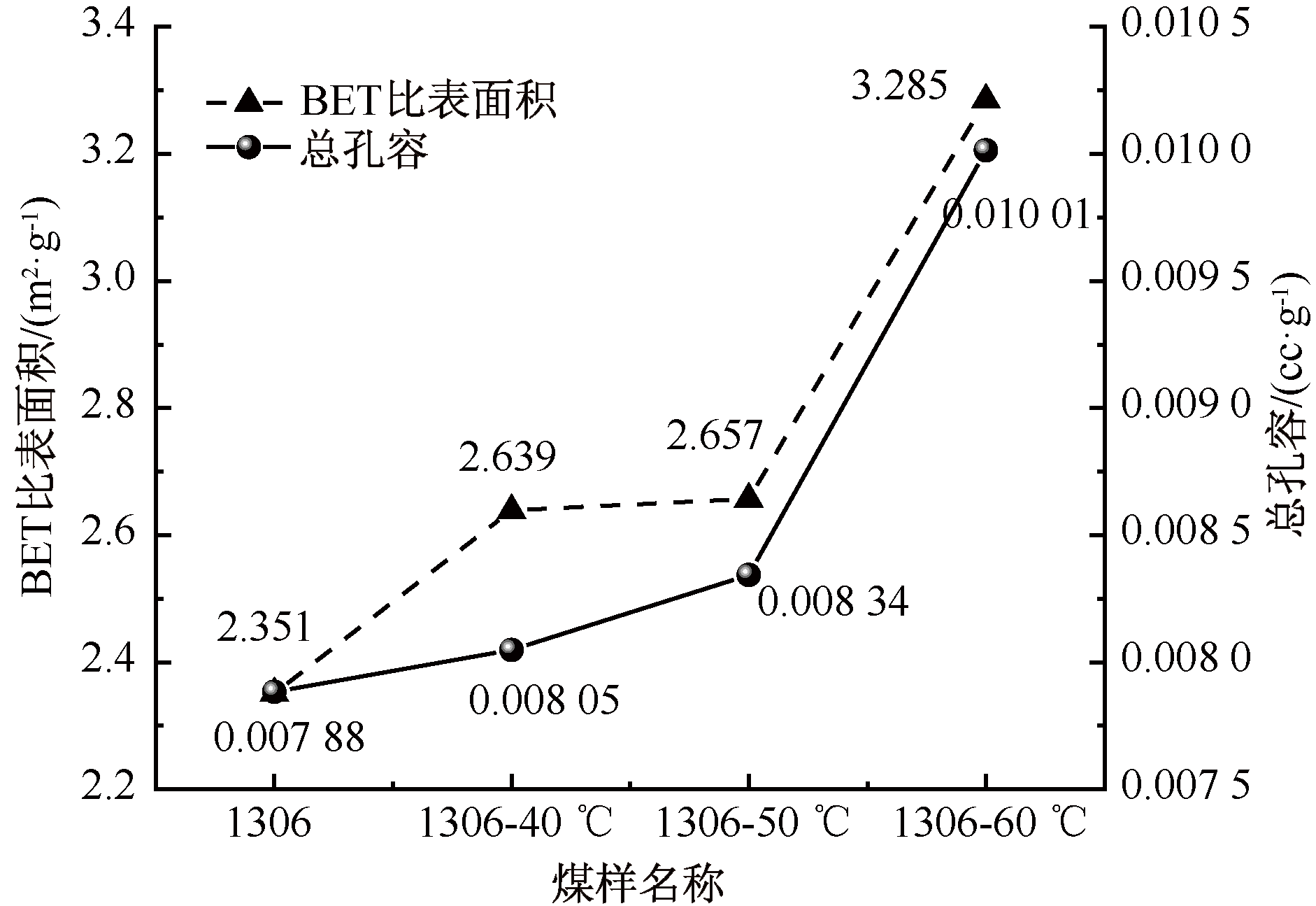
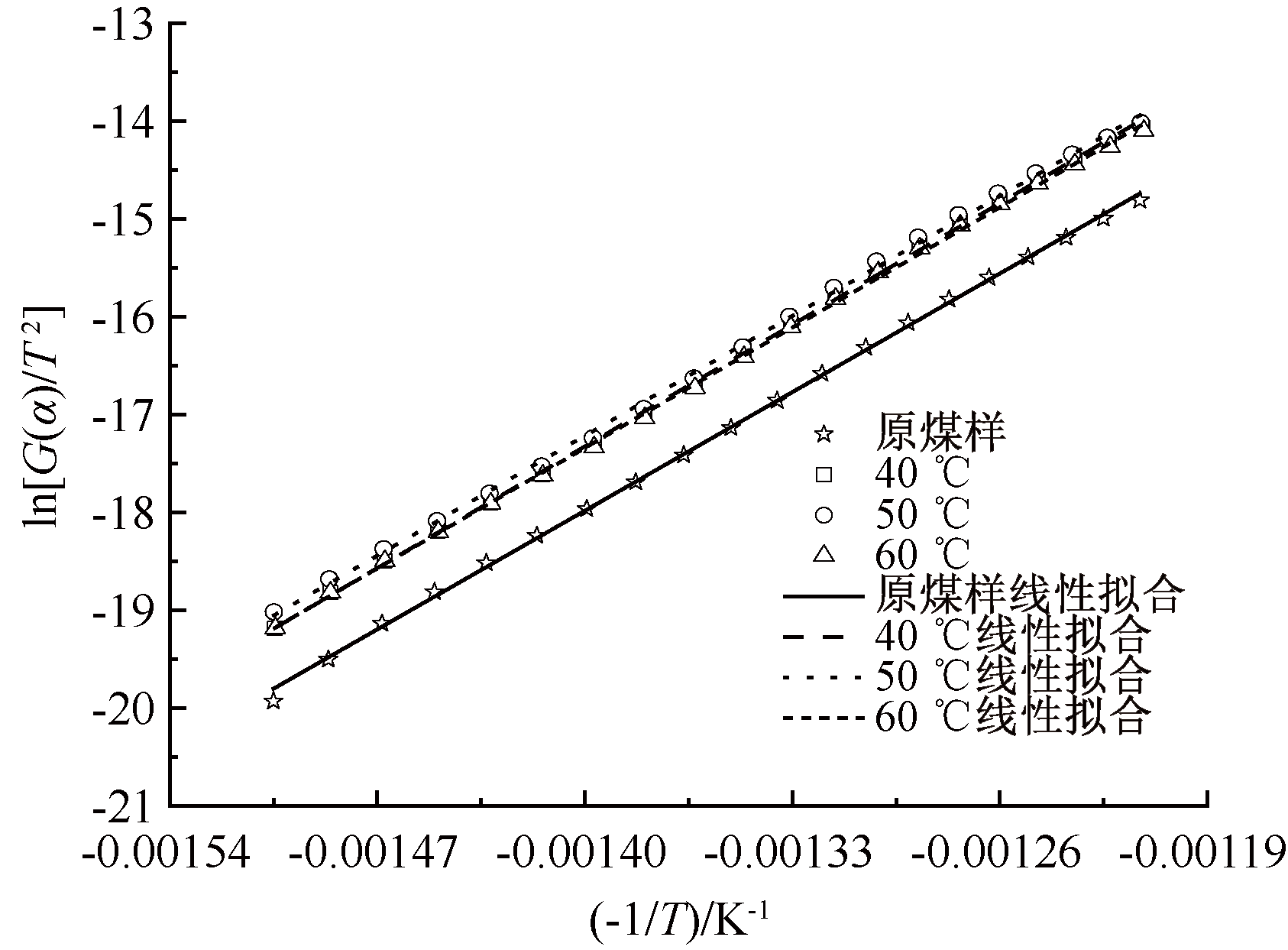
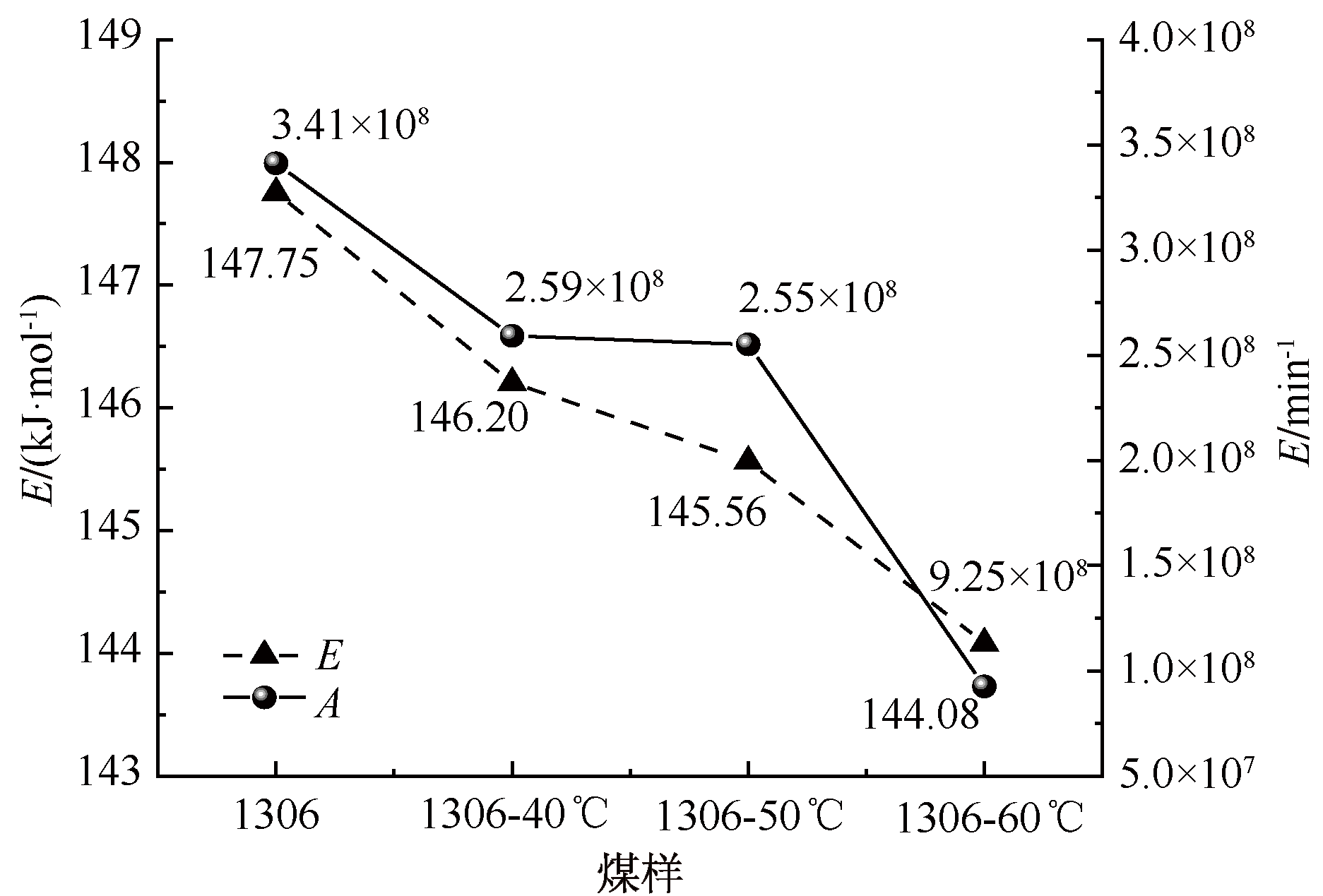
| [1] |
余学义, 穆驰, 王皓, 等. 孟加拉国Barapukuria 矿厚煤层分层协调减灾开采模式[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47 (6): 2 352-2 359.
|
|
YU Xueyi, MU Chi, WANG Hao, et al. Mining mode of layered and coordinated disaster reduction in thick coal seam of Barapukuria coal mine in Bangladeshi[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47 (6): 2 352-2 359.
|
| [2] |
邓军, 王凯, 翟小伟, 等. 复杂条件下孤岛综放面自燃防治技术研究[J]. 煤炭工程, 2015, 47 (9): 62-67.
|
|
DENG Jun, WANG Kai, ZHAI Xiaowei, et al. Spontaneous combustion control technology of fully mechanized island caving face under complex conditions[J]. Coal Engineering, 2015, 47(9): 62-67.
|
| [3] |
秦荣宏, 翟小伟. 孟巴矿高地温高湿环境采空区特厚遗煤自燃规律研究[J]. 煤矿开采, 2014, 19 (5): 100-102.
|
|
QIN Ronghong, ZHAI Xiaowei. Spontaneous combustion rule of extremely-thick residual coal in gob of Mengba Colliery under high temperature and high humidity environment[J]. Coal Ming Technology, 2014, 19 (5): 100-102.
|
| [4] |
庞卫东, 于保华, 马芝贺, 等. 特厚煤层复杂条件下火区启封方案优化及控制技术[J]. 煤炭工程, 2011, 43(2): 4-6.
|
|
PANG Weidong, YU Baohua, MA Zhihe, et al. Optimization and control technology of fire zone opening plan under complex conditions of extra thick coal seams[J]. Coal Engineering, 2011, 43(2): 4-6.
|
| [5] |
CHAO Jiangkun, GU Qiuyue, PAN Rongkun, et al. Influence of a high-temperature environment in deep mining on the characteristics of coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2022: DOI: 10.1080/00102202.2022.2093110.
|
| [6] |
JIA Huilin, YANG Yang, REN Wanxing, et al. Experimental study on the characteristics of the spontaneous combustion of coal at high ground temperatures[J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2022, 194(14): 2 880-2 893.
|
| [7] |
邓军, 王凯, 翟小伟, 等. 高地温环境对煤自燃特性影响的试验研究[J]. 煤矿安全, 2014, 45 (3): 13-15.
|
|
DENG Jun, WANG Kai, ZHAI Xiaowei, et al. Experimental study on the effect of high ground temperature environment on coal spontaneous combustion characteristics[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2014, 45 (3): 13-15.
|
| [8] |
马砺, 雷昌奎, 王凯, 等. 高地温环境对煤自燃危险性影响试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2016, 44 (1): 144-156.
|
|
MA Li, LEI Changkui, WANG Kai, et al. Experiment study on high geo-temperature environment affected to danger of coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2016, 44 (1): 144-156.
|
| [9] |
马砺, 雷昌奎, 王凯, 等. 高地温环境对煤自燃极限参数的影响研究[J]. 煤炭工程, 2015, 47 (12): 89-92.
|
|
MA Li, LEI Changkui, WANG Kai, et al. Impact of high ground temperature environment on limit parameters of coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Coal Engineering, 2015, 47 (12): 89-92.
|
| [10] |
NIU Huiyong, SUN Qingqing, BU Yunchuan, et al. Study of the microstructure and oxidation characteristics of residual coal in deep mines[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 373: DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133923.
|
| [11] |
NIU Huiyong, YU Xiaodong, SUN Qingqing, et al. Analysis of the thermal behavior characteristics and dynamics of coal under high primary temperature conditions in deep mines[J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2023: DOI: 10.1080/00102202.2023.2225210.
|
| [12] |
马冬娟, 唐一博. 高地温对不同变质程度煤自燃微观结构影响试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(12): 109-115.
|
|
MA Dongjuan, TANG Yibo. Experimental investigation on microstructure influence of high temperature on spontaneous combustion of coal with different ranks[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(12):109-115.
|
| [13] |
SARGEANT J, BEAMISH B, CHALMERS D. Times to ignition analysis of new south wales[C]. 9th Underground Coal Operators Conference, 2009:254-358.
|
| [14] |
张修峰, 杨胜强. 高地温环境对煤的自热危险性影响分析[J]. 中国矿业, 2016, 25 (9): 159-165.
|
|
ZHANG Xiufeng, YANG Shengqiang. The effect of high ground temperature environment on risk of coal self-heating[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2016, 25 (9): 159-165.
|
| [15] |
GB/T 21650.2—2008,压汞法和气体吸附法测定固体材料孔径分布和孔隙度.第2部分:气体吸附法分析介孔和大孔[S].
|
| [16] |
ZHANG Kaizhong, CHENG Yuanping, LI Wei, et al. Microcrystalline characterization and morphological structure of tectonic anthracite using XRD, liquid nitrogen adsorption, mercury porosimetry, and micro-CT[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33: 10 844-10 851.
|
| [17] |
THOMMES M, KANEKO K, NEIMARK A V, et al. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 2015, 87(9/10): 1 051-1 069.
|
| [18] |
XIN Haihui, TIAN Wenjiang, ZHOU Banghao, et al. Pore structure evolution and oxidation characteristic change of coal treated with liquid carbon dioxide and liquid nitrogen[J]. Energy, 2023, 268: DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2023.126674.
|
| [19] |
唐一博, 李云飞, 薛生, 等. 长期水浸对不同烟煤自燃参数与微观特性影响的实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(10): 2 642-2 648.
|
|
TANG Yibo, LI Yunfei, XUE Sheng, et al. Experimental investigation of long-term water immersion effect on spontaneous com-bustion parameters and microscopic characteristics of bituminous[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(10): 2 642-2 648.
|
| [20] |
贾廷贵, 强倩, 娄和壮, 等. 不同变质程度煤样氧化自燃热特性试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(10): 62-67.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.009
|
|
JIA Tinggui, QIANG Qian, LOU Hezhuang, et al. Experimental study on thermal characteristics of coal samples with different metamorphism degree during spontaneous combustion[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(10): 62-67.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.009
|
| [21] |
WANG Chenguang, WANG Deming, XIN Haihui, et al. Study on secondary oxidation characteristics of coal gangue at different pyrolysis rank[J]. Fuel, 2023,345:DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.12823.
|