| [1] |
崔传峰, 王俊豪, 崔志超, 等. 基于灰色可拓模型的洮河下游泥石流易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2019, 30(6): 40-48.
|
|
CUI Chuanfeng, WANG Junhao, CUI Zhichao, et al. Evaluation of debris flow susceptibility in the lower reaches of Taohe River based on grey extension model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(6): 40-48.
|
| [2] |
史明远, 丁桂伶, 陈剑平, 等. 基于博弈论和K均值的北京山区小流域综合敏感性评价[J]. 工程地质学报, 2015, 23(4): 790-794.
|
|
SHI Mingyuan, DING Guiling, CHEN Jianping, et al. Game theory and K-means algorithm based comprehensive susceptibility analysis of catchments for debris flows in mountainous area of Beijing[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2015, 23(4): 790-794.
|
| [3] |
李晓婷, 刘文龙. 模糊综合评判法在甘肃陇南武都区石门乡泥石流危险性评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2020, 31(4): 71-76.
|
|
LI Xiaoting, LIU Wenlong. Application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method to debris flow risk evaluation in Shimen township in Wudu district of Longnan city, Gansu province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(4): 71-76.
|
| [4] |
曹洪洋, 王禹, 满兵. 基于改进灰色关联分析的泥石流危险性评价[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2015, 13(1): 91-94.
|
|
CAO Hongyang, WANG Yu, MAN Bing. Risk evaluation of potential debris flow based on the improved grey correlation method[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2015, 13(1): 91-94.
|
| [5] |
罗真富, 蒲达成, 谢洪斌, 等. 基于GIS和信息量法的泥石流流域滑坡危险性评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2011, 21(11): 144-150.
|
|
LUO Zhenfu, PU Dacheng, XIE Hongbin, et al. Landslide hazard evaluation in debris flow catchment area based on GIS and information method[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2011, 21(11): 144-150.
|
| [6] |
马彦彬, 李红蕊, 王林, 等. 机器学习方法在滑坡易发性评价中的应用:英文[J]. 土木与环境工程学报:中英文, 2022, 44(1): 53-67.
|
|
MA Yanbin, LI Hongrui, WANG Lin, et al. Machine learning algorithms and techniques for landslide susceptibility investigation: a literature review[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 44(1): 53-67.
|
| [7] |
刘汉龙, 马彦彬, 仉文岗. 大数据技术在地质灾害防治中的应用综述[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报, 2021, 41(4): 710-722.
|
|
LIU Hanlong, MA Yanbin, ZHANG Wengang. Application of big data techniques in geological disaster analysis and prevention: a systematic review[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2021, 41(4): 710-722.
|
| [8] |
仉文岗, 何昱苇, 王鲁琦, 等. 基于水系分区的滑坡易发性机器学习分析方法:以重庆市奉节县为例[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(5): 2 024-2 038.
|
|
ZHANG Wengang, HE Yuwei, WANG Luqi, et al. Machine learning solution for landslide susceptibility based on hydrographic division: case study of Fengjie county in Chongqing[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(5): 2 024-2 038.
|
| [9] |
LIU Songlin, WANG Luqi, ZHANG Wengang, et al. A physics-informed data-driven model for landslide susceptibility assessment in the three gorges reservoir area[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2023, 14(5): DOI: 10.1016/J.GSF.2023.101621.
|
| [10] |
宋英华, 吴昊, 刘丹, 等. 基于D-S证据理论的地震应急救援群决策[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(5): 163-168.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.05.025
|
|
SONG Yinghua, WU Hao, LIU Dan, et al. Group decision-making for earthquake emergency rescue plan based on D-S evidence theory[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(5): 163-168.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.05.025
|
| [11] |
曹文贵, 杨伟康, 翟友成. 基于D-S证据理论的岩体质量分级组合评价方法[J]. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 42(5): 86-91.
|
|
CAO Wengui, YANG Weikang, ZHAI Youcheng. Combination evaluation method for the classification of rock mass quality based on D-S theory of evidence[J]. Journal of Hunan University: Natural Science, 2015, 42(5): 86-91.
|
| [12] |
张彪, 戴兴国. 基于指标距离与不确定度量的岩爆云模型预测研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2017, 38(增2): 257-265.
|
|
ZHANG Biao, DAI Xingguo. A cloud model for predicting rockburst intensity grade based on index distance and uncertainty measure[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(S2): 257-265.
|
| [13] |
苏永华. 岩土参数模糊隶属函数的构造方法及应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2007, 29(12): 1 772-1 779.
|
|
SU Yonghua. Constructing method of fuzzy membership function of geotechnical parameters and its application[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2007, 29(12): 1 772-1 779.
|
| [14] |
张友鹏, 李远远. 基于云模型和证据理论的铁路信号系统风险评估[J]. 铁道学报, 2016, 38(1): 75-80.
|
|
ZHANG Youpeng, LI Yuanyuan. Risk assessment of railway signal system based on cloud model and evidence theory[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2016, 38(1): 75-80.
|
| [15] |
FANG Ye, CHEN Jie, LI Yibing. Improvement of D-S evidence theory for multi-sensor conflicting information[J]. Symmetry, 2017, 9(5): 1-15.
|
| [16] |
邓勇, 施文康, 朱振福. 一种有效处理冲突证据的组合方法[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2004, 23(1): 27-32.
|
|
DENG Yong, SHI Wenkang, ZHU Zhenfu. Efficient combination approach of conflict evidence[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2004, 23(1): 27-32.
|
| [17] |
李德毅, 孟海军, 史雪梅. 隶属云和隶属云发生器[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 1995, 32(6): 15-20.
|
|
LI Deyi, MENG Haijun, SHI Xuemei. Membership cloud and membership generators[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 1995, 32(6): 15-20.
|
| [18] |
汪明武, 金菊良. 联系数理论与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017. 55-75.
|
|
WANG Mingwu, JIN Juliang. The theory and applications of connection numbers[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017: 55-75.
|
| [19] |
毛艺帆, 张多林, 王路. 基于重合度的证据冲突度量方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2017, 32(2): 293-298.
|
|
MAO Yifan, ZHANG Duolin, WANG Lu. Measurement of evidence conflict based on overlapping degree[J]. Control and Decision, 2017, 32(2): 293-298.
|
| [20] |
DENG Yong. Deng entropy[J]. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals: the Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, and Nonequilibrium and Complex Phenomena, 2016, 91:549-553.
|
| [21] |
薛喜成. 西秦岭矿山泥石流发育规律与环境效应[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 2008: 77-155.
|
| [22] |
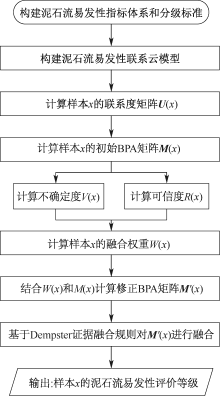
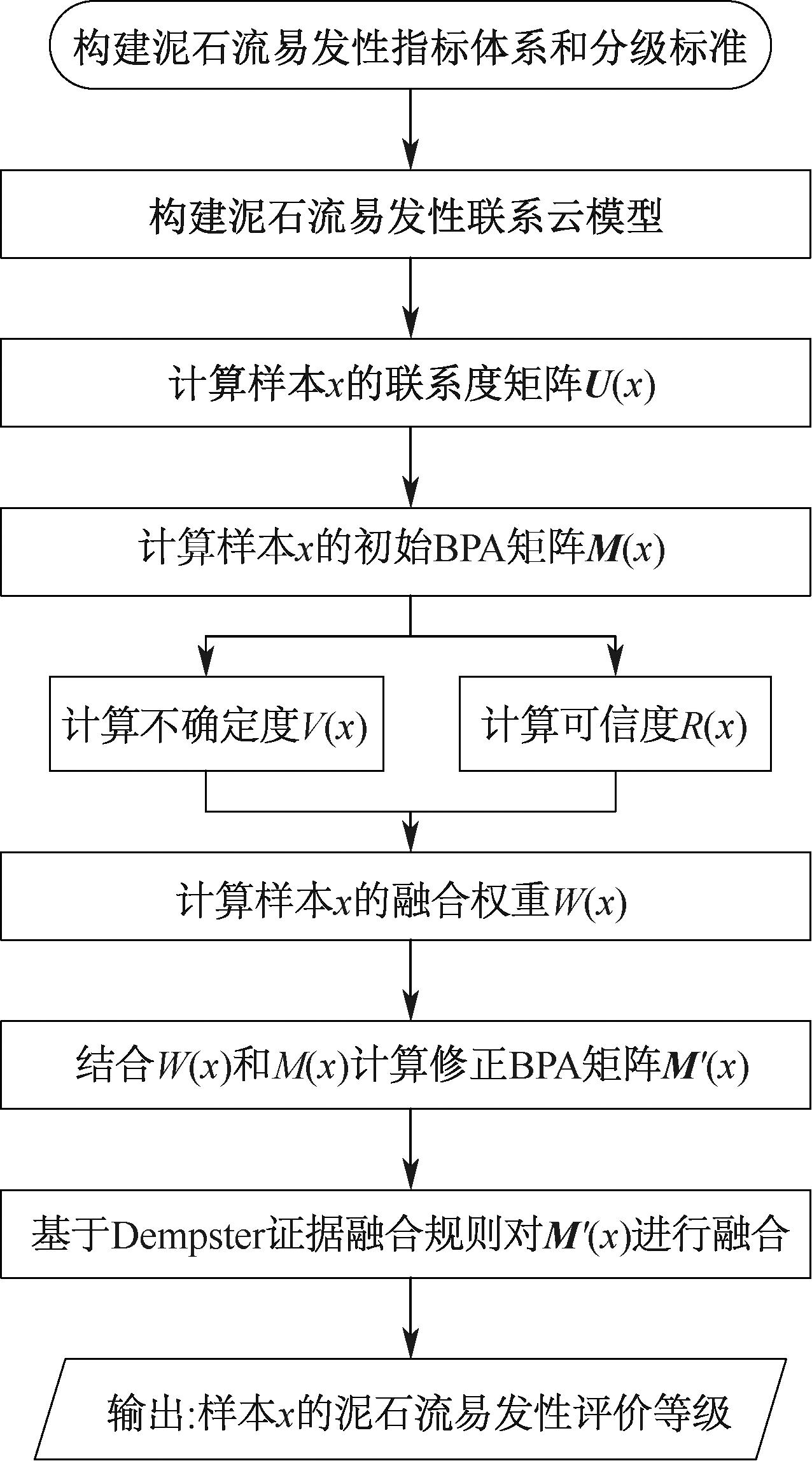
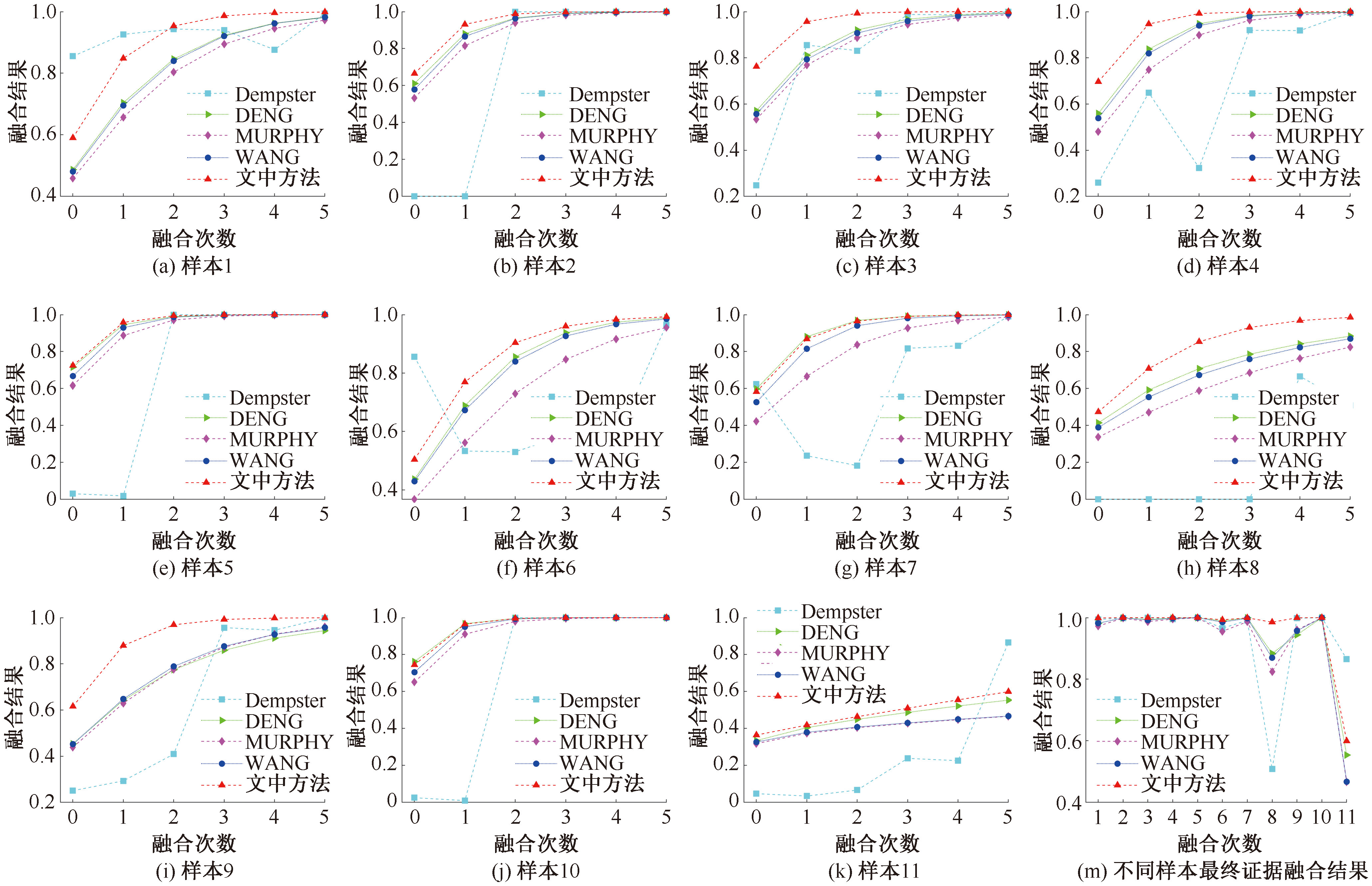
孙祥, 汪明武, 李杰, 等. 基于博弈论的泥石流灾害易发性联系云评价模型[J]. 合肥工业大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 43(10): 1 357-1 361.
|
|
SUN Xiang, WANG Mingwu, LI Jie, et al. Vulnerability evaluation of debris flow disaster based on game theory and connection cloud model[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology:Natural Science, 2020, 43(10): 1 357-1 361.
|
| [23] |
MURPHY C K. Combining belief functions when evidence conflicts[J]. Decision Support Systems, 2000, 29(1): 1-9.
|
| [24] |
汪明武, 董昊, 叶晖, 等. 基于联系云-证据理论的岩爆烈度预测模型[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2018, 39(9): 1 021-1 029.
|
|
WANG Mingwu, DONG Hao, YE Hui, et al. A connection cloud-evidence theory coupling model for prediction of rockburst intensity[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2018, 39(9): 1 021-1 029.
|