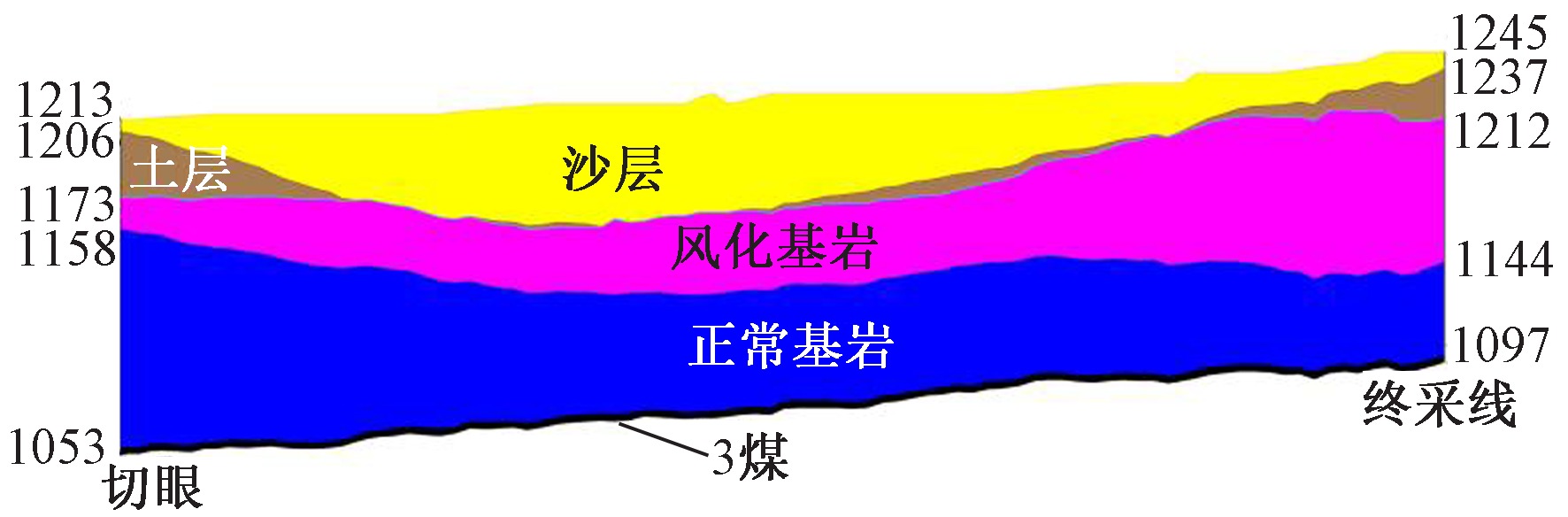
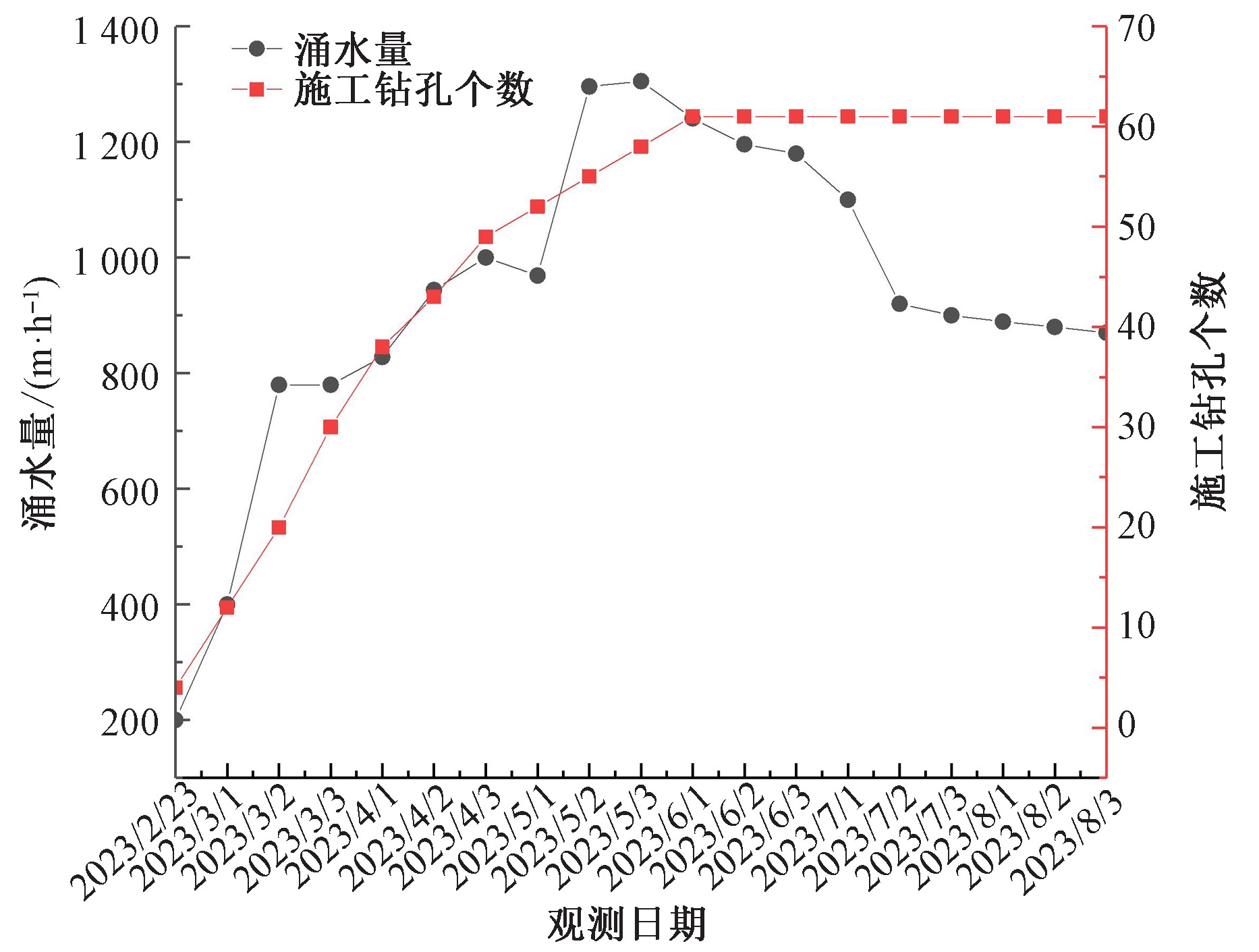
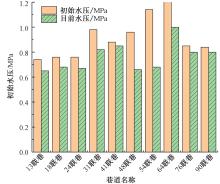
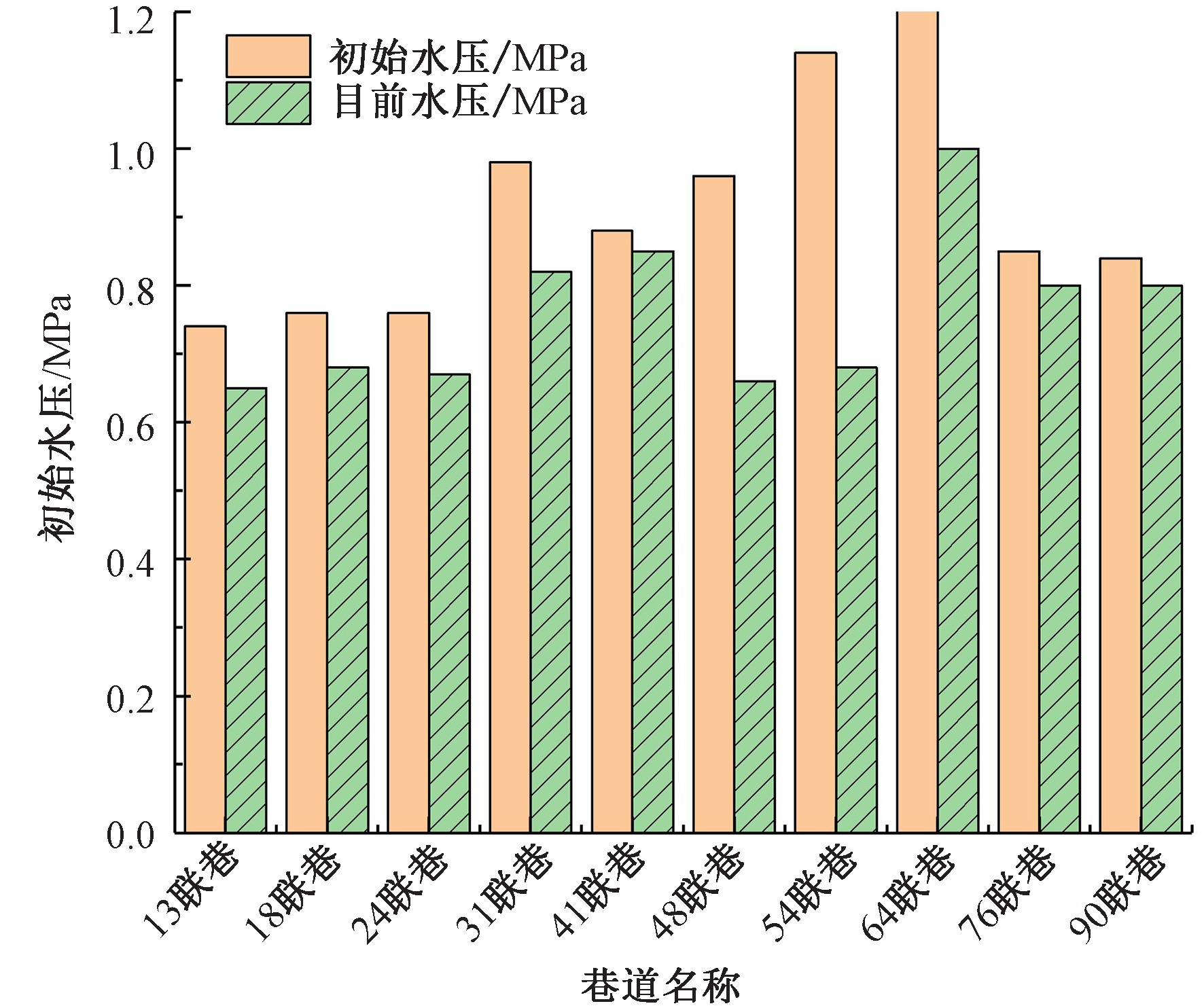
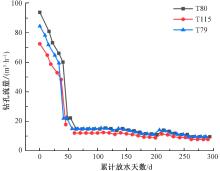
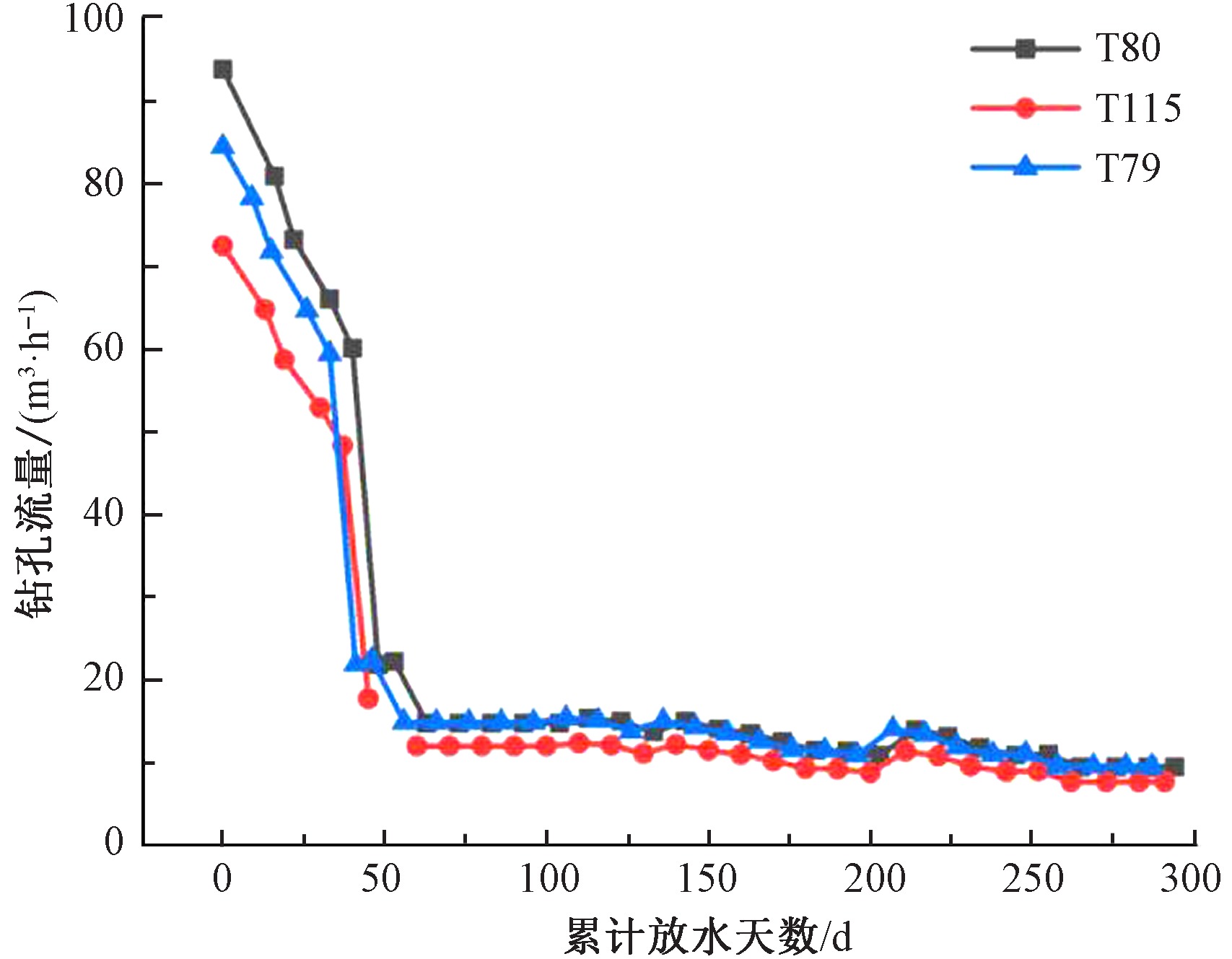
| [1] |
曾一凡, 朱慧聪, 武强, 等. 我国不同类别煤层顶板水害致灾机理与防控路径[J]. 煤炭学报, 2024, 49(3):1 539-1 555.
|
|
ZENG Yifan, ZHU Huicong, WU Qiang, et al. Disaster-causing mechanism and prevention and control path of different types of coal seam roof water disasters in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2024, 49(3):1 539-1 555.
|
| [2] |
祁云, 薛凯隆, 汪伟, 等. 多策略改进SSA优化KELM的边坡稳定性预测模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2025, 35(3):92-98.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2025.03.0134
|
|
QI Yun, XUE Kailong, WANG Wei, et al. Multi-strategy improved SSA optimised KELM for slope stable state analysis model with applications[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2025, 35(3):92-98.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2025.03.0134
|
| [3] |
李雪涛, 王建国. 西部煤矿突水事故致灾因子分析与防控对策[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(6): 89-95.
|
|
LI Xuetao, WANG Jianguo. Disaster causation factors analysis and prevention measures of water inrush accidents in western coal mines[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(6): 89-95.
|
| [4] |
崔杰, 刘洋, 王振荣. 锦界煤矿水文地质条件分析及探查技术研究[J]. 煤炭工程, 2009, 9(3):72-74.
|
|
CUI Jie, LIU Yang, WANG Zhenrong. Hydrogeological condition analysis and exploration technique research of Jinjie Coal Mine[J]. Coal Engineering, 2009, 9(3): 72-74.
|
| [5] |
许峰, 靳德武, 杨茂林, 等. 神府-东胜矿区高强度开采顶板涌水特征及防治技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2022, 50(2):72-80.
|
|
XU Feng, JIN Dewu, YANG Maolin, et al. Characteristics of roof water inflow and control technology for high intensity mining in Dongsheng Mining Area Shenfu Coalfield[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2022, 50(2):72-80.
|
| [6] |
董书宁, 姬亚东, 王皓, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗纪煤田典型顶板水害防控技术与应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(7):2 367-2 375.
|
|
DONG Shuning, JI Yadong, WANG Hao, et al. Prevention and control technology and application of roof water disaster in Jurassic coal field of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(7):2 367-2 375.
|
| [7] |
郑磊. 薄基岩采动裂隙发育规律及应用研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2018.
|
|
ZHENG Lei. Study and application on the development law of thin bedrock mining fracture[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2018.
|
| [8] |
焦养泉, 王双明, 范立民, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗纪含煤岩系地下水系统关键要素与格架模型[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(7):2 411-2 422.
|
|
JIAO Yangquan, WANG Shuangming, FAN Limin, et al. Key elements and framework model of groundwater system in Jurassic coal measures of Ordos basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(7):2 411-2 422.
|
| [9] |
王毅, 孙常民. 浅埋薄基岩煤层顶板疏放水技术研究[J]. 煤炭工程, 2023, 55(增1):90-94.
|
|
WANG Yi, SUN Changmin. Time and space effect of water gushing from drainage boreholein coal mine and controlling drainage to prevent water disaster in coal seam[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 55(S1):90-94.
|
| [10] |
王庆, 刘卫卫, 崔岩波, 等. 定向钻进技术在煤层顶板软弱岩层疏放水中的应用[J]. 煤矿安全, 2017, 48(5):152-154.
|
|
WANG Qing, LIU Weiwei, CUI Yanbo, et al. Application of directional drilling technology in dredging and draining water of roof soft rock[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2017, 48(5):152-154.
|
| [11] |
马亚杰, 刘莉, 李悦, 等. 仰斜钻孔倾角对顶板含水层疏放水影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 山东科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 41(6):32-39.
|
|
MA Yajie, LIU Li, LI Yue, et al. Numerical simulation research on influence of inclined borehole angle on drainage of roof aquifer[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology:Natural Science, 2022, 41(6):32-39.
|
| [12] |
虎维岳, 姬亚东, 黄欢. 煤层顶板承压含水层涌水模式与疏放水钻孔优化设计[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(5):139-146.
|
|
HU Weiyue, JI Yadong, HUANG Huan. Mine water inflow modes and scientific design of drainage boreholes in roof confined aquifer of coal seam[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(5):139-146.
|